Abstract
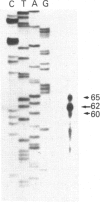
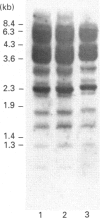
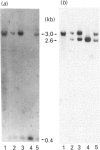
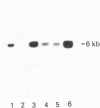
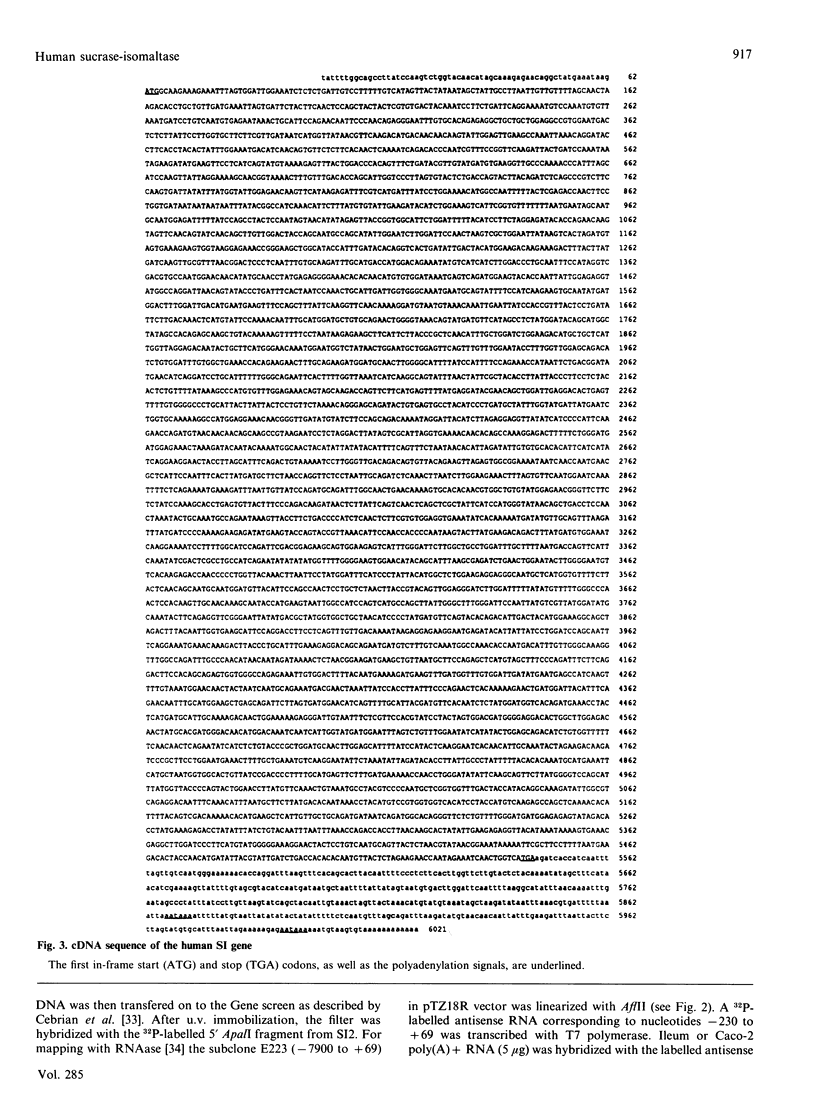
The complete sequence of the 6 kb cDNA and the 5' genomic structure are reported for the gene coding for the human intestinal brush border hydrolase sucrase-isomaltase. The human sucrase-isomaltase cDNA shows a high level of identity (83%) with that of the rabbit enzyme, indicating that the protein shares the same structural domains in both species. In addition to the previously reported homology with lysosomal alpha-glucosidase, the sucrase and isomaltase subunits also appear to be homologous to a yeast glucoamylase. A 14 kb human genomic clone has been isolated which includes the first three exons and the first two introns of the gene, as well as 9.5 kb 5' to the major start site of transcription. The first exon comprises 62 bp of untranslated sequence and the second starts exactly at the initiation ATG codon. Typical CAAT and TATA boxes are seen upstream of the first exon. A genetic polymorphism is described which involves a PstI site in the second intron. Southern blotting, sequencing and mRNA studies indicate that the structures of the sucrase-isomaltase gene and its mRNA are unaltered in the two human colon cancer cell lines Caco-2 and HT-29 in comparison with normal human small intestine.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M. Regulation of sugar utilization in Saccharomyces species. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):4873–4877. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.4873-4877.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebrian J., Berthelot N., Laithier M. Genome structure of cottontail rabbit herpesvirus. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):523–531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.523-531.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. C., Erwin A. E., Lee A. S. Glucose-regulated protein (GRP94 and GRP78) genes share common regulatory domains and are coordinately regulated by common trans-acting factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2153–2162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantret I., Trugnan G., Dussaulx E., Zweibaum A., Rousset M. Monensin inhibits the expression of sucrase-isomaltase in Caco-2 cells at the mRNA level. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 1;235(1-2):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81246-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. H., Chen Z. Y., Chow T. Y., Chen J. C., Tan S. T., Hsu W. H. Nucleotide sequence and expression of the isoamylase gene from an isoamylase-hyperproducing mutant, Pseudomonas amyloderamosa JD210. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Nov 30;1087(3):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90004-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demmer L. A., Birkenmeier E. H., Sweetser D. A., Levin M. S., Zollman S., Sparkes R. S., Mohandas T., Lusis A. J., Gordon J. I. The cellular retinol binding protein II gene. Sequence analysis of the rat gene, chromosomal localization in mice and humans, and documentation of its close linkage to the cellular retinol binding protein gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2458–2467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis C. L., Ciriacy M., Young E. T. A positive regulatory gene is required for accumulation of the functional messenger RNA for the glucose-repressible alcohol dehydrogenase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 5;148(4):355–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90181-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessen P., Fondrat C., Valencien C., Mugnier C. BISANCE: a French service for access to biomolecular sequence databases. Comput Appl Biosci. 1990 Oct;6(4):355–356. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/6.4.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohmen R. J., Strasser A. W., Dahlems U. M., Hollenberg C. P. Cloning of the Schwanniomyces occidentalis glucoamylase gene (GAM1) and its expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1990 Oct 30;95(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90421-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouy M., Gautier C., Attimonelli M., Lanave C., di Paola G. ACNUC--a portable retrieval system for nucleic acid sequence databases: logical and physical designs and usage. Comput Appl Biosci. 1985 Sep;1(3):167–172. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/1.3.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Homologous recognition of a promoter domain common to the MSV LTR and the HSV tk gene. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green F., Edwards Y., Hauri H. P., Povey S., Ho M. W., Pinto M., Swallow D. Isolation of a cDNA probe for a human jejunal brush-border hydrolase, sucrase-isomaltase, and assignment of the gene locus to chromosome 3. Gene. 1987;57(1):101–110. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauri H. P. Biogenesis and intracellular transport of intestinal brush border membrane hydrolases. Use of antibody probes and tissue culture. Subcell Biochem. 1988;12:155–219. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-1681-5_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignment on a microcomputer. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoefsloot L. H., Hoogeveen-Westerveld M., Kroos M. A., van Beeumen J., Reuser A. J., Oostra B. A. Primary structure and processing of lysosomal alpha-glucosidase; homology with the intestinal sucrase-isomaltase complex. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1697–1704. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02998.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoefsloot L. H., Hoogeveen-Westerveld M., Reuser A. J., Oostra B. A. Characterization of the human lysosomal alpha-glucosidase gene. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 1;272(2):493–497. doi: 10.1042/bj2720493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunziker W., Spiess M., Semenza G., Lodish H. F. The sucrase-isomaltase complex: primary structure, membrane-orientation, and evolution of a stalked, intrinsic brush border protein. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):227–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90739-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroix B., Kedinger M., Simon-Assmann P., Rousset M., Zweibaum A., Haffen K. Developmental pattern of brush border enzymes in the human fetal colon. Correlation with some morphogenetic events. Early Hum Dev. 1984 Feb;9(2):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(84)90089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantei N., Villa M., Enzler T., Wacker H., Boll W., James P., Hunziker W., Semenza G. Complete primary structure of human and rabbit lactase-phlorizin hydrolase: implications for biosynthesis, membrane anchoring and evolution of the enzyme. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2705–2713. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03124.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martiniuk F., Mehler M., Tzall S., Meredith G., Hirschhorn R. Sequence of the cDNA and 5'-flanking region for human acid alpha-glucosidase, detection of an intron in the 5' untranslated leader sequence, definition of 18-bp polymorphisms, and differences with previous cDNA and amino acid sequences. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;9(2):85–94. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Gaffney D., Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. The consensus sequence YGTGTTYY located downstream from the AATAAA signal is required for efficient formation of mRNA 3' termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1347–1368. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muleris M., Salmon R. J., Dutrillaux B. Cytogenetics of colorectal adenocarcinomas. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1990 Jun;46(2):143–156. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(90)90100-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Najjar S. M., Hampp L. T., Rabkin R., Gray G. M. Sucrase-alpha-dextrinase in diabetic BioBreed rats: reversible alteration of subunit structure. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 1):G275–G283. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.260.2.G275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehlin J. O., Ronne H. Yeast MIG1 repressor is related to the mammalian early growth response and Wilms' tumour finger proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2891–2898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07479.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordström C., Dahlqvist A. Quantitative distribution of some enzymes along the villi and crypts of human small intestine. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1973;8(5):406–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O. Distinct repressible mRNAs for cytoplasmic and secreted yeast invertase are encoded by a single gene. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):525–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset M., Chantret I., Darmoul D., Trugnan G., Sapin C., Green F., Swallow D., Zweibaum A. Reversible forskolin-induced impairment of sucrase-isomaltase mRNA levels, biosynthesis, and transport to the brush border membrane in Caco-2 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Dec;141(3):627–635. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041410322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset M., Laburthe M., Pinto M., Chevalier G., Rouyer-Fessard C., Dussaulx E., Trugnan G., Boige N., Brun J. L., Zweibaum A. Enterocytic differentiation and glucose utilization in the human colon tumor cell line Caco-2: modulation by forskolin. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Jun;123(3):377–385. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041230313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset M., Trugnan G., Brun J. L., Zweibaum A. Inhibition of the post-translational processing of microvillar hydrolases is associated with a specific decreased expression of sucrase-isomaltase and an increased turnover of glucose in Caco-2 cells treated with monensin. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 10;208(1):34–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81526-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebastio G., Hunziker W., O'Neill B., Malo C., Ménard D., Auricchio S., Semenza G. The biosynthesis of intestinal sucrase-isomaltase in human embryo is most likely controlled at the level of transcription. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):830–839. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90442-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenza G. The J.E. Purkyne lecture: the insertion of stalked proteins of the brush border membranes: the state of the art in 1988. Biochem Int. 1989 Jan;18(1):15–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiu R. P., Pouyssegur J., Pastan I. Glucose depletion accounts for the induction of two transformation-sensitive membrane proteinsin Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chick embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3840–3844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skovbjerg H. Immunoelectrophoretic studies on human small-intestinal brush-border proteins. Biochem J. 1981 Mar 1;193(3):887–890. doi: 10.1042/bj1930887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suggs S. V., Wallace R. B., Hirose T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. Use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes: isolation of cloned cDNA sequences for human beta 2-microglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6613–6617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetser D. A., Birkenmeier E. H., Klisak I. J., Zollman S., Sparkes R. S., Mohandas T., Lusis A. J., Gordon J. I. The human and rodent intestinal fatty acid binding protein genes. A comparative analysis of their structure, expression, and linkage relationships. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16060–16071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetser D. A., Hauft S. M., Hoppe P. C., Birkenmeier E. H., Gordon J. I. Transgenic mice containing intestinal fatty acid-binding protein-human growth hormone fusion genes exhibit correct regional and cell-specific expression of the reporter gene in their small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9611–9615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taya Y., Devos R., Tavernier J., Cheroutre H., Engler G., Fiers W. Cloning and structure of the human immune interferon-gamma chromosomal gene. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):953–958. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01277.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thukral S. K., Eisen A., Young E. T. Two monomers of yeast transcription factor ADR1 bind a palindromic sequence symmetrically to activate ADH2 expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1566–1577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber P. G. Regulation of sucrase-isomaltase gene expression along the crypt-villus axis of rat small intestine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 31;173(3):765–773. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80853-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umek R. M., Friedman A. D., McKnight S. L. CCAAT-enhancer binding protein: a component of a differentiation switch. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):288–292. doi: 10.1126/science.1987644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Kern S. E., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Nakamura Y., White R. Allelotype of colorectal carcinomas. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):207–211. doi: 10.1126/science.2565047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertheimer E., Sasson S., Cerasi E., Ben-Neriah Y. The ubiquitous glucose transporter GLUT-1 belongs to the glucose-regulated protein family of stress-inducible proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2525–2529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweibaum A., Pinto M., Chevalier G., Dussaulx E., Triadou N., Lacroix B., Haffen K., Brun J. L., Rousset M. Enterocytic differentiation of a subpopulation of the human colon tumor cell line HT-29 selected for growth in sugar-free medium and its inhibition by glucose. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Jan;122(1):21–29. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041220105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweibaum A., Triadou N., Kedinger M., Augeron C., Robine-Léon S., Pinto M., Rousset M., Haffen K. Sucrase-isomaltase: a marker of foetal and malignant epithelial cells of the human colon. Int J Cancer. 1983 Oct 15;32(4):407–412. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910320403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]