Abstract
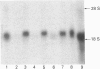
mRNAs encoding cytochrome P-450s CYP1A2 and CYP2B1/2 have been quantified in rat hepatocytes cultured for periods up to 72 h under several different culture conditions that maintain total cytochrome P-450 content. When hepatocytes were cultured at either 37 or 30 degrees C in Williams E media, both CYP1A2 and CYP2B1/2 mRNAs declined dramatically. However, when cultured at 30 degrees C for 24 h, the decline in these mRNAs was not as great as that observed in cells grown at 37 degrees C. The addition of dimethyl sulphoxide to cells grown at 37 degrees C did not affect the rate of disappearance of the CYP1A2 or CYP2B1/2 mRNAs. These mRNAs also declined rapidly in cells grown in 'P-450 medium' i.e. RPMI 1640 medium without cyst(e)ine but supplemented with 0.1 mM-delta-aminolaevulinic acid. However, the levels of CYP2B1/2 mRNAs were maintained when hepatocytes were cultured in Williams E medium supplemented with 0.5 mM-metyrapone. These conditions did not, however, maintain the levels of CYP1A2 mRNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blankson E. A., Chenery R. J., Paine A. J. Cytochrome P450 maintenance and diazepam metabolism in cultured rat hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Aug 22;42(6):1241–1245. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90260-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giachelli C. M., Omiecinski C. J. Developmental regulation of cytochrome P-450 genes in the rat. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 May;31(5):477–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J. The molecular biology of cytochrome P450s. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Dec;40(4):243–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B. Hybridization of oligo(dT) to RNA on nitrocellulose. Gene Anal Tech. 1987 Mar-Apr;4(2):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(87)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota K., Kawanishi T., Sunouchi M., Ohno Y., Takanaka A., Yamazoe Y., Kato R., Murakoshi Y. Induction of cytochrome P-450c and P-450d by metyrapone in the primary culture of rat hepatocytes. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;51(1):136–139. doi: 10.1254/jjp.51.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake B. G., Paine A. J. Induction of hepatic cytochrome P-450 and drug metabolism by metyrapone in the rat: relevance to its effects in rat-liver cell culture. Xenobiotica. 1983 Dec;13(12):725–730. doi: 10.3109/00498258309052234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake B. G., Paine A. J. The effect of hepatocyte culture conditions on cytochrome P-450 linked drug metabolising enzymes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Jun 1;31(11):2141–2144. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90438-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muakkassah-Kelly S. F., Bieri F., Waechter F., Bentley P., Stäubli W. Long-term maintenance of hepatocytes in primary culture in the presence of DMSO: further characterization and effect of nafenopin, a peroxisome proliferator. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Jul;171(1):37–51. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90249-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Nelson D. R., Coon M. J., Estabrook R. W., Feyereisen R., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Gonzalez F. J., Guengerich F. P., Gunsalus I. C., Johnson E. F. The P450 superfamily: update on new sequences, gene mapping, and recommended nomenclature. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Jan-Feb;10(1):1–14. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine A. J., Hockin L. J., Legg R. F. Relationship between the ability of nicotinamide to maintain nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide in rat liver cell culture and its effect on cytochrome P-450. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 15;184(2):461–463. doi: 10.1042/bj1840461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine A. J., Hockin L. J. Nutrient imbalance causes the loss of cytochrome P-450 in liver cell culture: formulation of culture media which maintain cytochrome P-450 at in vivo concentrations. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Dec 1;29(23):3215–3218. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90590-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine A. J. The cytochrome P450 gene superfamily. Int J Exp Pathol. 1991 Jun;72(3):349–363. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine A. J. The maintenance of cytochrome P-450 in rat hepatocyte culture: some applications of liver cell cultures to the study of drug metabolism, toxicity and the induction of the P-450 system. Chem Biol Interact. 1990;74(1-2):1–31. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(90)90055-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine A. J., Villa P., Hockin L. J. Evidence that ligand formation is a mechanism underlying the maintenance of cytochrome P-450 in rat liver cell culture. Potent maintenance by metyrapone. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 15;188(3):937–939. doi: 10.1042/bj1880937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine A. J., Villa P. Ligands maintain cytochrome P-450 in liver cell culture by affecting its synthesis and degradation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Nov 28;97(2):744–750. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90327-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I. R., Shephard E. A., Ashworth A., Rabin B. R. Cloning and sequence analysis of a rat liver cDNA coding for a phenobarbital-inducible microheterogenous cytochrome P-450 variant: regulation of its messenger level by xenobiotics. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):41–52. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike S. F., Shephard E. A., Rabin B. R., Phillips I. R. Induction of cytochrome P-450 by phenobarbital is mediated at the level of transcription. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Jul 15;34(14):2489–2494. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90531-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raval P., Iversen P. L., Bresnick E. Induction of cytochromes P450IA1 and P450IA2 as determined by solution hybridization. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jun 1;41(11):1719–1723. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90175-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shean K., Paine A. J. Immunochemical quantification of cytochrome P450IA and IIB subfamilies in the livers of metyrapone-treated rats. Relevance to the ability of metyrapone to prevent the loss of cytochrome P-450 in rat hepatocyte culture. Biochem J. 1990 May 1;267(3):715–719. doi: 10.1042/bj2670715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward A. R., Dannan G. A., Guzelian P. S., Guengerich F. P. Changes in the concentration of seven forms of cytochrome P-450 in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Jan;27(1):125–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]