Abstract
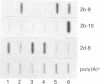
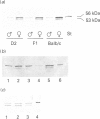
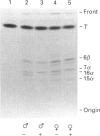
The sex-dependent expression and inducibility of the cytochrome P450 2B subfamily was studied in DBA/2 and Balb/c mice, and their F1 recombinants, at the mRNA, protein and activity levels. Analysis of poly(A)+ RNA with specific oligonucleotide probes directed to known mRNAs within the mouse 2B subfamily revealed that the levels of P450 2b-10 and 2b-9 mRNAs were co-regulated with two proteins (56 and 53 kDa) detected by a 2B-specific polyclonal antibody. Other mRNAs related to the 2B subfamily were barely or not at all detectable, and did not coincide with protein expression, suggesting that P450s 2b-9 and 2b-10 are the major 2B isoenzymes present in mouse liver. Specifically, castration of males increased the expression of 2b-9 and 2b-10 mRNAs and protein up to female levels, and testosterone administration to castrated mice reversed these changes. Ovariectomy of females appears to increase the expression of these P450s slightly. 2b-10, but not 2b-9, mRNA and protein were induced by phenobarbital. Based on immunoinhibition studies and the levels of these isoenzymes, P4502b-10 appears to be the major catalyst of 7-pentoxyresorufin O-dealkylation. Both P4502b-9 and P4502b-10 contribute up to 30% of the testosterone 16 alpha-hydroxylation, the balance being catalysed by P450s within the 2D subfamily. These experiments show that the female-predominant expression of the two mouse liver isoenzymes P4502b-9 and P4502b-10 is dependent on sex hormones. The fact that P4502b-9 does not respond to phenobarbital, while P4502b-10 is regulated by both phenobarbital and sex hormones, demonstrates the complexity of P450 expression even within one subfamily.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dannan G. A., Guengerich F. P., Waxman D. J. Hormonal regulation of rat liver microsomal enzymes. Role of gonadal steroids in programming, maintenance, and suppression of delta 4-steroid 5 alpha-reductase, flavin-containing monooxygenase, and sex-specific cytochromes P-450. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10728–10735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devore K., Harada N., Negishi M. Characterization of testosterone 16 alpha-hydroxylase (I-P-450(16) alpha) induced by phenobarbital in mice. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5632–5637. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada N., Negishi M. Mouse liver testosterone 15 alpha-hydroxylase (cytochrome P-450(15) alpha). Purification, regioselectivity, stereospecificity, and sex-dependent expression. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1265–1271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada N., Negishi M. Mouse liver testosterone 16 alpha-hydroxylase (cytochrome P-450(16) alpha). Purification, regioselectivity, stereospecificity, and immunochemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12285–12290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honkakoski P., Lang M. A. Mouse liver phenobarbital-inducible P450 system: purification, characterization, and differential inducibility of four cytochrome P450 isozymes from D2 mouse. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Aug 15;273(1):42–57. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90160-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakso M., Masaki R., Noshiro M., Negishi M. Structures and characterization of sex-specific mouse cytochrome P-450 genes as members within a large family. Duplication boundary and evolution. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jan 30;195(2):477–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang M. A., Gielen J. E., Nebert D. W. Genetic evidence for many unique liver microsomal P-450-mediated monooxygenase activities in heterogeneic stock mice. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12068–12075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemoine A., Marie S., Cresteil T. Expression of cytochrome P-450 isozymes in the liver of hypophysectomized rats. Evidence for different regulation mechanisms concerning P450IIB and P450IIIA subfamilies. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Nov 15;177(3):597–604. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Nelson D. R., Coon M. J., Estabrook R. W., Feyereisen R., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Gonzalez F. J., Guengerich F. P., Gunsalus I. C., Johnson E. F. The P450 superfamily: update on new sequences, gene mapping, and recommended nomenclature. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Jan-Feb;10(1):1–14. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noshiro M., Lakso M., Kawajiri K., Negishi M. Rip locus: regulation of female-specific isozyme (I-P-450(16 alpha) of testosterone 16 alpha-hydroxylase in mouse liver, chromosome localization, and cloning of P-450 cDNA. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 23;27(17):6434–6443. doi: 10.1021/bi00417a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Mak I., Glover E., Boatman R. J., Ebetino F. H., Kende A. S. 1,4-Bis[2-(3,5-dichloropyridyloxy)]benzene, a potent phenobarbital-like inducer of microsomal monooxygenase activity. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;18(3):571–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronis M. J., Johansson I., Hultenby K., Lagercrantz J., Glaumann H., Ingelman-Sundberg M. Acetone-regulated synthesis and degradation of cytochrome P450E1 and cytochrome P4502B1 in rat liver [corrected]. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jun 1;198(2):383–389. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16026.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraki H., Guengerich F. P. Turnover of membrane proteins: kinetics of induction and degradation of seven forms of rat liver microsomal cytochrome P-450, NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase, and epoxide hydrolase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Nov 15;235(1):86–96. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90257-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Ko A., Walsh C. Regioselectivity and stereoselectivity of androgen hydroxylations catalyzed by cytochrome P-450 isozymes purified from phenobarbital-induced rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11937–11947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Morrissey J. J., LeBlanc G. A. Female-predominant rat hepatic P-450 forms j (IIE1) and 3 (IIA1) are under hormonal regulatory controls distinct from those of the sex-specific P-450 forms. Endocrinology. 1989 Jun;124(6):2954–2966. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-6-2954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr The regulation of cytochrome P-450 gene expression. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1986;26:333–369. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.26.040186.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G., Itakura T., Kawajiri K., Skow L., Negishi M. Gene family of male-specific testosterone 16 alpha-hydroxylase (C-P-450(16 alpha)) in mice. Organization, differential regulation, and chromosome localization. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2920–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazoe Y., Shimada M., Murayama N., Kato R. Suppression of levels of phenobarbital-inducible rat liver cytochrome P-450 by pituitary hormone. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7423–7428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaphiropoulos P. G., Mode A., Norstedt G., Gustafsson J. A. Regulation of sexual differentiation in drug and steroid metabolism. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Apr;10(4):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90167-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]