Abstract
Eight dimeric isoenzymes of glutathione S-transferase (GST) were purified from liver, kidney and testis of the Syrian golden hamster, using S-hexylglutathione affinity chromatography and chromatofocusing. The isoenzymes were characterized according to their substrate selectivity, physical properties and amino acid sequence analysis. Thus a classification into Alpha, Mu and Pi classes was made in analogy with GSTs of other species. Two Alpha-class GSTs were purified, termed A1A1 (pI 8.9) and A1A2 (pI 8.6). Four Mu-class subunits were detected (M1-M4), all forming homodimers, with M2 and M3 also forming a heterodimer. The isoelectric points ranged from 5.9 to 8.6. One Pi-class isoenzyme was purified and termed P1P1 (pI 6.8). Using h.p.l.c. analysis, the subunit composition was determined in a number of organs. The major subunits in liver were A1 and M1. Subunit A1 was also the major subunit in the kidney. Subunit M1 was not detected in kidney, while subunit P1 was not found in the liver. Pancreas and trachea contained predominantly the Pi-class subunit, P1. GST in the testis was mostly of the Mu class. The major subunit was M4, and subunits M2 and M3 were exclusively detected in the testis.
Full text
PDF
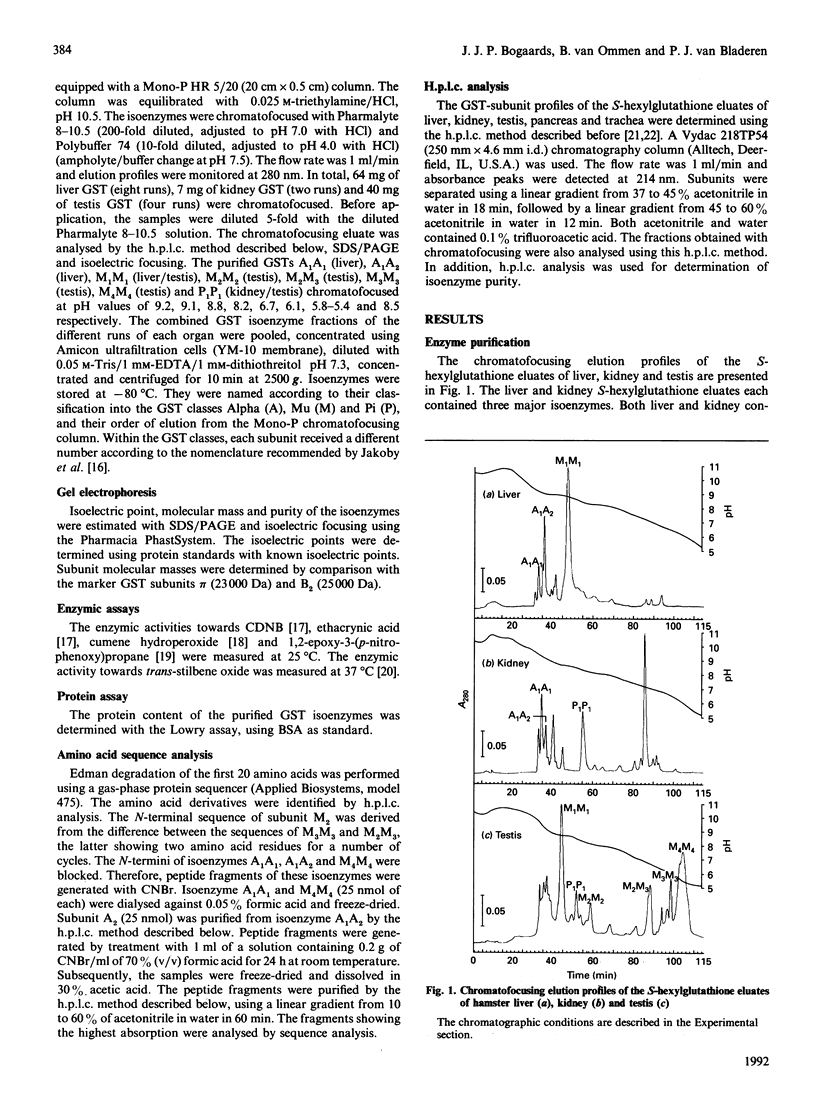
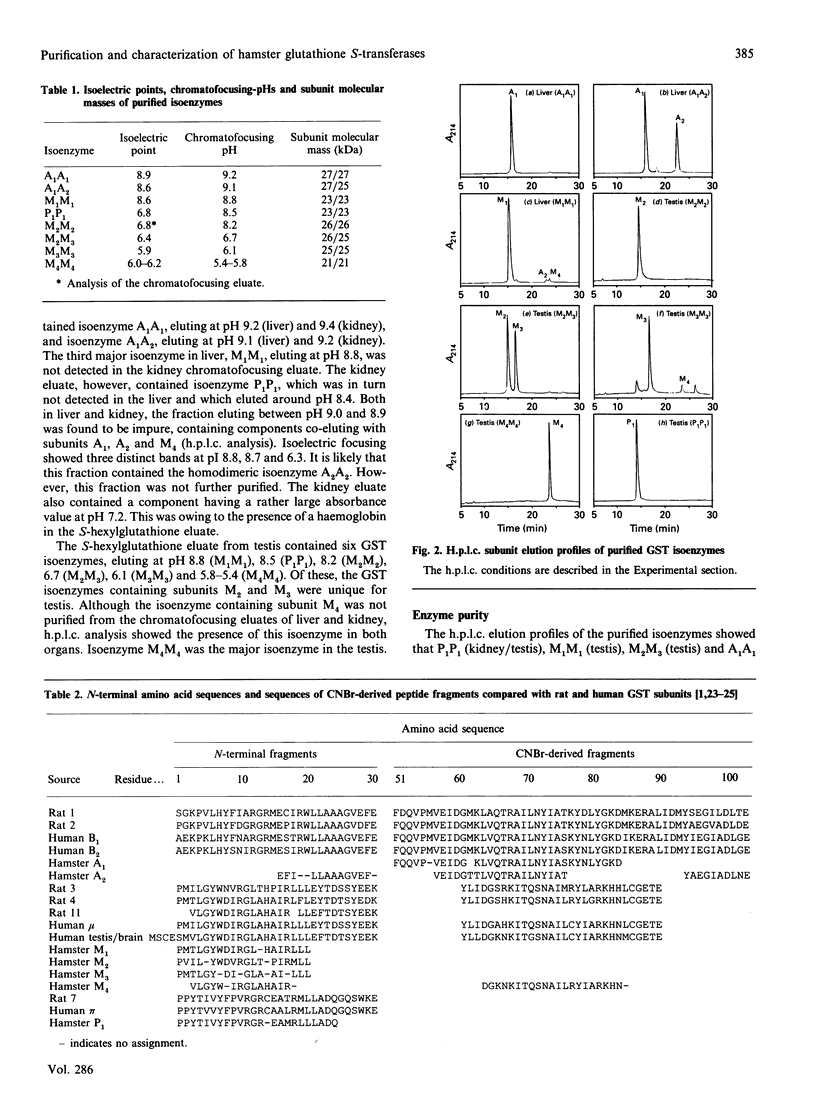
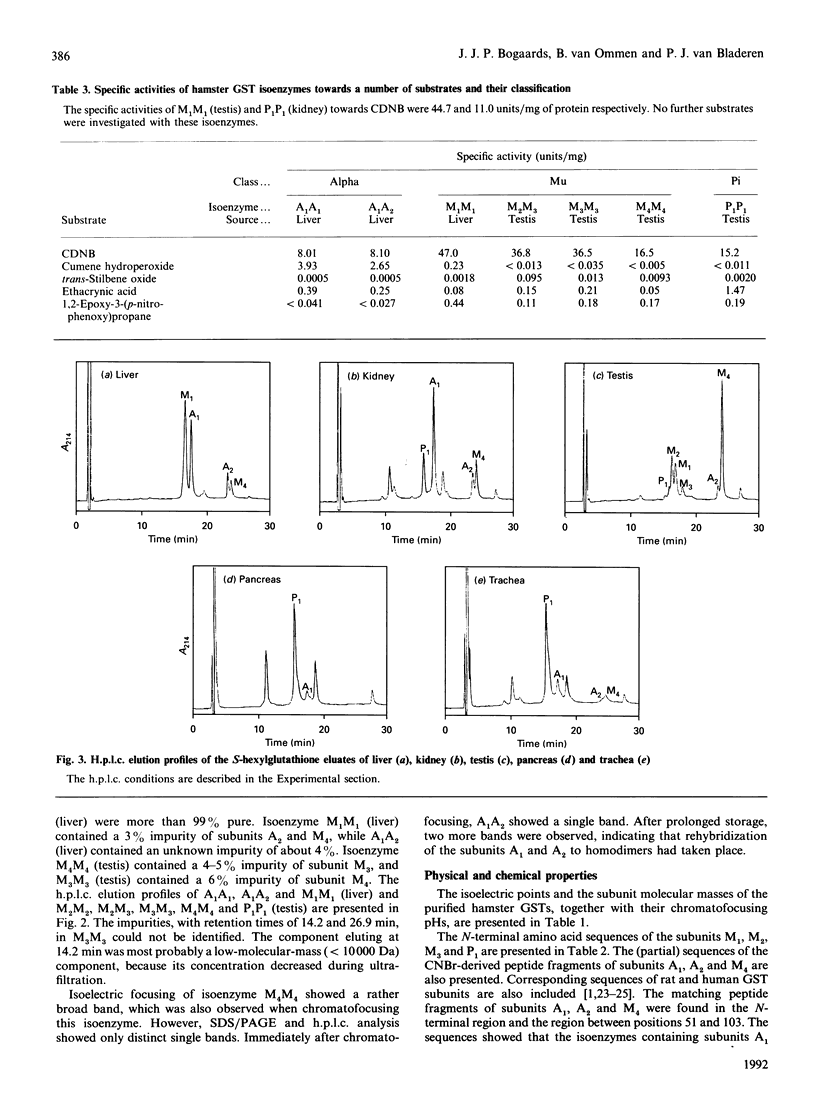


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alin P., Jensson H., Guthenberg C., Danielson U. H., Tahir M. K., Mannervik B. Purification of major basic glutathione transferase isoenzymes from rat liver by use of affinity chromatography and fast protein liquid chromatofocusing. Anal Biochem. 1985 May 1;146(2):313–320. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90545-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson A. M., Talalay P., Keen J. H., Jakoby W. B. Relationship between the soluble glutathione-dependent delta 5-3-ketosteroid isomerase and the glutathione S-transferases of the liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):158–162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogaards J. J., van Ommen B., van Bladeren P. J. An improved method for the separation and quantification of glutathione S-transferase subunits in rat tissue using high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1989 Jul 19;474(2):435–440. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)93940-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell E., Takahashi Y., Abramovitz M., Peretz M., Listowsky I. A distinct human testis and brain mu-class glutathione S-transferase. Molecular cloning and characterization of a form present even in individuals lacking hepatic type mu isoenzymes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9188–9193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fjellstedt T. A., Allen R. H., Duncan B. K., Jakoby W. B. Enzymatic conjugation of epoxides with glutathione. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3702–3707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habig W. H., Pabst M. J., Jakoby W. B. Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 25;249(22):7130–7139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. D. Selective elution of rodent glutathione S-transferases and glyoxalase I from the S-hexyglutathione-Sepharose affinity matrix. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 1;255(3):913–922. doi: 10.1042/bj2550913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi T., Tomihari N., Ohmori S., Ueno K., Kitagawa H., Satoh T. Comparison of glutathione S-transferases in mouse, guinea pig, rabbit and hamster liver cytosol to those in rat liver. Biochem Int. 1986 Oct;13(4):641–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakoby W. B., Ketterer B., Mannervik B. Glutathione transferases: nomenclature. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Aug 15;33(16):2539–2540. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90621-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen D. E., Mackay R. L. Rat, mouse and hamster isozyme specificity in the glutathione transferase-mediated denitrosation of nitrosoguanidinium compounds. Cancer Res. 1990 Mar 1;50(5):1440–1448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kispert A., Meyer D. J., Lalor E., Coles B., Ketterer B. Purification and characterization of a labile rat glutathione transferase of the Mu class. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 15;260(3):789–793. doi: 10.1042/bj2600789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence R. A., Burk R. F. Glutathione peroxidase activity in selenium-deficient rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 23;71(4):952–958. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90747-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannervik B., Danielson U. H. Glutathione transferases--structure and catalytic activity. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1988;23(3):283–337. doi: 10.3109/10409238809088226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannervik B., Guthenberg C. Glutathione transferase (human placenta). Methods Enzymol. 1981;77:231–235. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)77030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. J., Christodoulides L. G., Hong Tan K., Ketterer B. Isolation, properties and tissue distribution of rat glutathione transferase E. FEBS Lett. 1984 Aug 6;173(2):327–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80799-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostlund Farrants A. K., Meyer D. J., Coles B., Southan C., Aitken A., Johnson P. J., Ketterer B. The separation of glutathione transferase subunits by using reverse-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):423–428. doi: 10.1042/bj2450423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidegård J., Vorachek W. R., Pero R. W., Pearson W. R. Hereditary differences in the expression of the human glutathione transferase active on trans-stilbene oxide are due to a gene deletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7293–7297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh S. V., Creadon G., Das M., Mukhtar H., Awasthi Y. C. Glutathione S-transferases of mouse lung. Selective binding of benzo[a]pyrene metabolites by the subunits which are preferentially induced by t-butylated hydroxyanisole. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 15;243(2):351–358. doi: 10.1042/bj2430351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh S. V., Dao D. D., Partridge C. A., Theodore C., Srivastava S. K., Awasthi Y. C. Different forms of human liver glutathione S-transferases arise from dimeric combinations of at least four immunologically and functionally distinct subunits. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):781–790. doi: 10.1042/bj2320781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. J., Ohl V. S., Litwack G. Purification and properties of hamster liver ligandins, glutathione S-transferases. Cancer Res. 1980 Jun;40(6):1787–1790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderström M., Mannervik B., Orning L., Hammarström S. Leukotriene C4 formation catalyzed by three distinct forms of human cytosolic glutathione transferase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 16;128(1):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91673-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ujihara M., Tsuchida S., Satoh K., Sato K., Urade Y. Biochemical and immunological demonstration of prostaglandin D2, E2, and F2 alpha formation from prostaglandin H2 by various rat glutathione S-transferase isozymes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Aug 1;264(2):428–437. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90308-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warholm M., Guthenberg C., Mannervik B., von Bahr C. Purification of a new glutathione S-transferase (transferase mu) from human liver having high activity with benzo(alpha)pyrene-4,5-oxide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jan 30;98(2):512–519. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90870-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto T., Soberman R. J., Spur B., Austen K. F. Properties of highly purified leukotriene C4 synthase of guinea pig lung. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):866–871. doi: 10.1172/JCI113396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ommen B., Bogaards J. J., Peters W. H., Blaauboer B., van Bladeren P. J. Quantification of human hepatic glutathione S-transferases. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 1;269(3):609–613. doi: 10.1042/bj2690609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



