Abstract
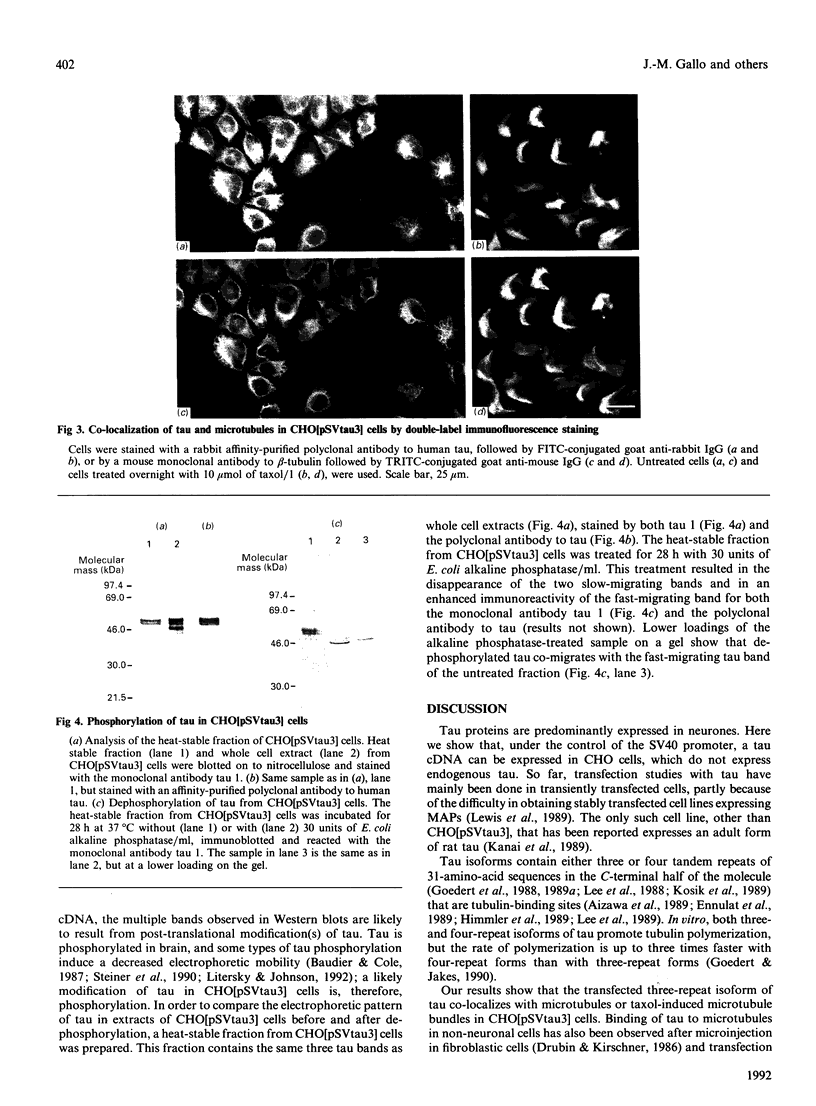
The neuronal microtubule-associated protein, tau, is expressed as a set of isoforms containing either three or four tandemly repeated 31-amino-acid motifs in the C-terminal half of the molecule that can bind to microtubules. Three-repeat forms are the only ones expressed early in development. A single three-repeat isoform of tau has been stably expressed in non-neuronal cells which do not express endogenous tau. Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells were transfected with a full-length cDNA coding for the foetal form of human tau cloned downstream of the simian virus 40 (SV40) promoter, and a cell line constitutively expressing tau, CHO[pSVtau3], was isolated. Double-label immunofluorescence microscopy reveals that tau co-localizes with the microtubular network of normal or taxol-treated CHO[pSVtau3] cells, without inducing any dramatic change in cell morphology. Tau is expressed in CHO[pSVtau3] cells as three bands in SDS/PAGE recognized by antibodies to tau, the slow-migrating tau species being the most abundant. Tau also appears as three bands in a heat-stable fraction from CHO[pSVtau3] cells, but a single band of enhanced immunoreactivity is detected following treatment of this fraction with alkaline phosphatase. This single band co-migrates with the fast-migrating band of untreated fractions or whole-cell extracts. In conclusion, a three-repeat isoform of tau is capable of binding to microtubules in transfected non-neuronal cells; furthermore, in this system, the protein is phosphorylated in at least two different states inducing a reduced electrophoretic mobility.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aizawa H., Kawasaki H., Murofushi H., Kotani S., Suzuki K., Sakai H. A common amino acid sequence in 190-kDa microtubule-associated protein and tau for the promotion of microtubule assembly. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5885–5890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baas P. W., Black M. M., Banker G. A. Changes in microtubule polarity orientation during the development of hippocampal neurons in culture. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):3085–3094. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baas P. W., Deitch J. S., Black M. M., Banker G. A. Polarity orientation of microtubules in hippocampal neurons: uniformity in the axon and nonuniformity in the dendrite. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8335–8339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudier J., Cole R. D. Phosphorylation of tau proteins to a state like that in Alzheimer's brain is catalyzed by a calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase and modulated by phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17577–17583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder L. I., Frankfurter A., Rebhun L. I. The distribution of tau in the mammalian central nervous system. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1371–1378. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brion J. P., Guilleminot J., Couchie D., Flament-Durand J., Nunez J. Both adult and juvenile tau microtubule-associated proteins are axon specific in the developing and adult rat cerebellum. Neuroscience. 1988 Apr;25(1):139–146. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caceres A., Kosik K. S. Inhibition of neurite polarity by tau antisense oligonucleotides in primary cerebellar neurons. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):461–463. doi: 10.1038/343461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caceres A., Potrebic S., Kosik K. S. The effect of tau antisense oligonucleotides on neurite formation of cultured cerebellar macroneurons. J Neurosci. 1991 Jun;11(6):1515–1523. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-06-01515.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Miller P. E., Navone F., Theurkauf W. E., Vallee R. B. Distribution of microtubule-associated protein 2 in the nervous system of the rat studied by immunofluorescence. Neuroscience. 1984 Apr;11(4):817–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinsmore J. H., Solomon F. Inhibition of MAP2 expression affects both morphological and cell division phenotypes of neuronal differentiation. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):817–826. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90510-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotti C. G., Banker G. A., Binder L. I. The expression and distribution of the microtubule-associated proteins tau and microtubule-associated protein 2 in hippocampal neurons in the rat in situ and in cell culture. Neuroscience. 1987 Oct;23(1):121–130. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90276-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G., Kirschner M. W. Tau protein function in living cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2739–2746. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennulat D. J., Liem R. K., Hashim G. A., Shelanski M. L. Two separate 18-amino acid domains of tau promote the polymerization of tubulin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5327–5330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flament S., Delacourte A. Abnormal tau species are produced during Alzheimer's disease neurodegenerating process. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81337-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francon J., Lennon A. M., Fellous A., Mareck A., Pierre M., Nunez J. Heterogeneity of microtubule-associated proteins and brain development. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec 15;129(2):465–471. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Jakes R. Expression of separate isoforms of human tau protein: correlation with the tau pattern in brain and effects on tubulin polymerization. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4225–4230. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07870.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Spillantini M. G., Jakes R., Rutherford D., Crowther R. A. Multiple isoforms of human microtubule-associated protein tau: sequences and localization in neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 1989 Oct;3(4):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90210-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Spillantini M. G., Potier M. C., Ulrich J., Crowther R. A. Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding an isoform of microtubule-associated protein tau containing four tandem repeats: differential expression of tau protein mRNAs in human brain. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):393–399. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Wischik C. M., Crowther R. A., Walker J. E., Klug A. Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding a core protein of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer disease: identification as the microtubule-associated protein tau. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4051–4055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S. G., Davies P. A preparation of Alzheimer paired helical filaments that displays distinct tau proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5827–5831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagestedt T., Lichtenberg B., Wille H., Mandelkow E. M., Mandelkow E. Tau protein becomes long and stiff upon phosphorylation: correlation between paracrystalline structure and degree of phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1643–1651. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanger D. P., Brion J. P., Gallo J. M., Cairns N. J., Luthert P. J., Anderton B. H. Tau in Alzheimer's disease and Down's syndrome is insoluble and abnormally phosphorylated. Biochem J. 1991 Apr 1;275(Pt 1):99–104. doi: 10.1042/bj2750099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmler A., Drechsel D., Kirschner M. W., Martin D. W., Jr Tau consists of a set of proteins with repeated C-terminal microtubule-binding domains and variable N-terminal domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1381–1388. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai Y., Takemura R., Oshima T., Mori H., Ihara Y., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T., Hirokawa N. Expression of multiple tau isoforms and microtubule bundle formation in fibroblasts transfected with a single tau cDNA. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1173–1184. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knops J., Kosik K. S., Lee G., Pardee J. D., Cohen-Gould L., McConlogue L. Overexpression of tau in a nonneuronal cell induces long cellular processes. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):725–733. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Finch E. A. MAP2 and tau segregate into dendritic and axonal domains after the elaboration of morphologically distinct neurites: an immunocytochemical study of cultured rat cerebrum. J Neurosci. 1987 Oct;7(10):3142–3153. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-10-03142.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Orecchio L. D., Bakalis S., Neve R. L. Developmentally regulated expression of specific tau sequences. Neuron. 1989 Apr;2(4):1389–1397. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowall N. W., Kosik K. S. Axonal disruption and aberrant localization of tau protein characterize the neuropil pathology of Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1987 Nov;22(5):639–643. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G., Cowan N., Kirschner M. The primary structure and heterogeneity of tau protein from mouse brain. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):285–288. doi: 10.1126/science.3122323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G., Neve R. L., Kosik K. S. The microtubule binding domain of tau protein. Neuron. 1989 Jun;2(6):1615–1624. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. M., Balin B. J., Otvos L., Jr, Trojanowski J. Q. A68: a major subunit of paired helical filaments and derivatized forms of normal Tau. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):675–678. doi: 10.1126/science.1899488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Ivanov I. E., Lee G. H., Cowan N. J. Organization of microtubules in dendrites and axons is determined by a short hydrophobic zipper in microtubule-associated proteins MAP2 and tau. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):498–505. doi: 10.1038/342498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Wang D. H., Cowan N. J. Microtubule-associated protein MAP2 shares a microtubule binding motif with tau protein. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):936–939. doi: 10.1126/science.3142041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindwall G., Cole R. D. Phosphorylation affects the ability of tau protein to promote microtubule assembly. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5301–5305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litersky J. M., Johnson G. V. Phosphorylation by cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibits the degradation of tau by calpain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1563–1568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matus A., Bernhardt R., Hugh-Jones T. High molecular weight microtubule-associated proteins are preferentially associated with dendritic microtubules in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3010–3014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff P. B., Horwitz S. B. Taxol stabilizes microtubules in mouse fibroblast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1561–1565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner B., Mandelkow E. M., Biernat J., Gustke N., Meyer H. E., Schmidt B., Mieskes G., Söling H. D., Drechsel D., Kirschner M. W. Phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein tau: identification of the site for Ca2(+)-calmodulin dependent kinase and relationship with tau phosphorylation in Alzheimer tangles. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3539–3544. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten M. D., Lockwood A. H., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]