Abstract
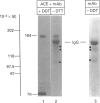
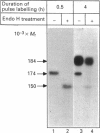
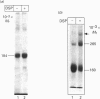
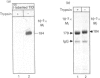
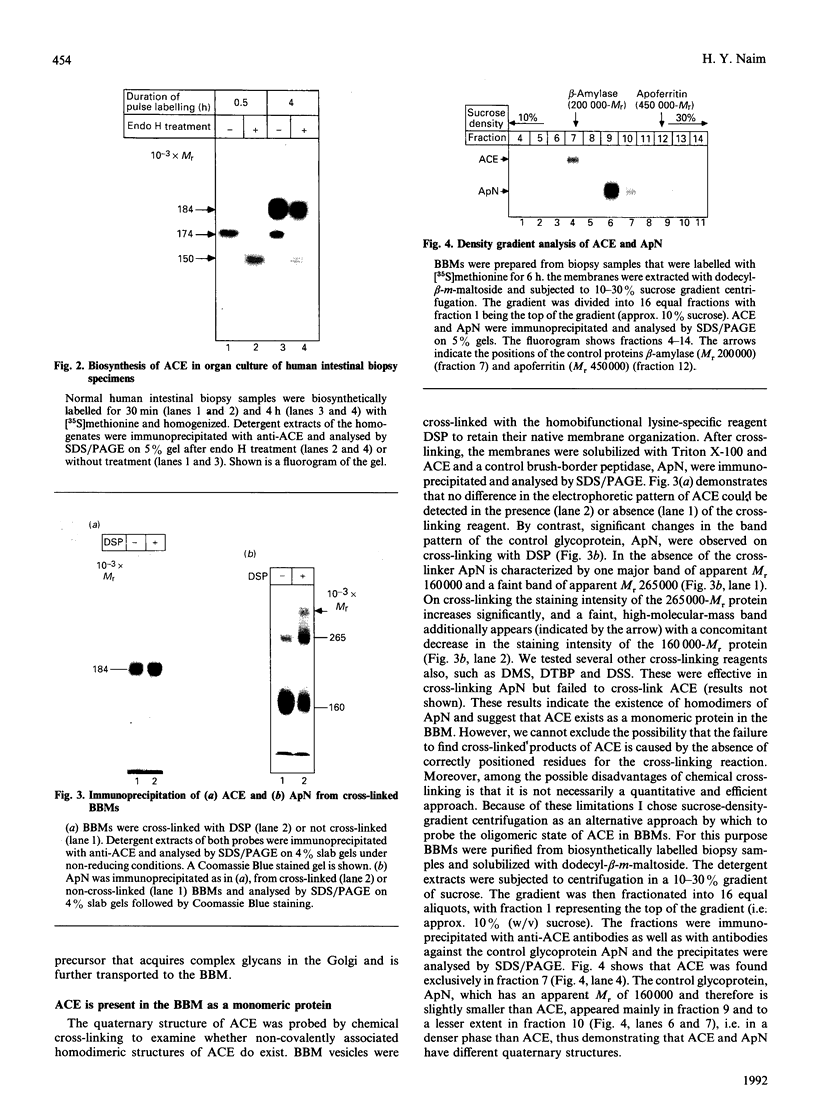
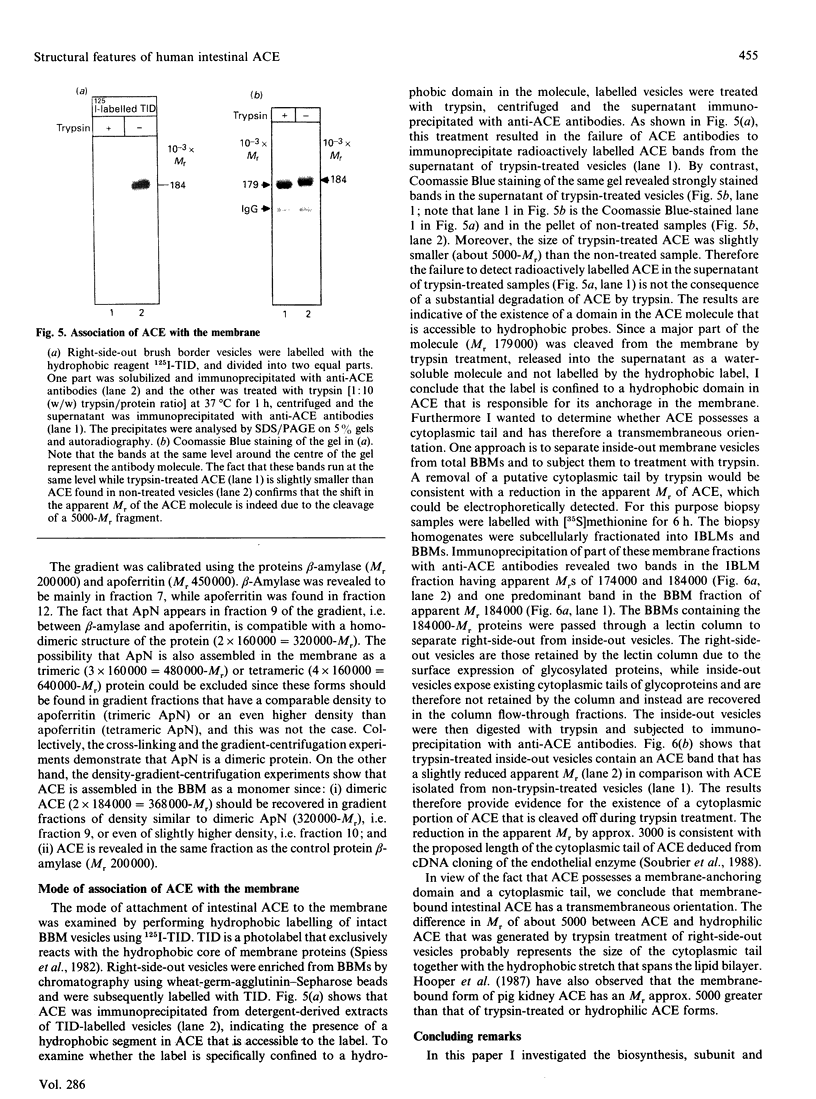
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) was isolated from detergent-derived extracts of human intestinal brush-border membranes (BBMs) by immunoprecipitation using a monoclonal antibody. Analysis of the immunoprecipitates by SDS/PAGE revealed a polypeptide of apparent M(r) 184,000 under reducing and non-reducing conditions, indicating that ACE does not contain intermolecular disulphide bridges. The quaternary structure of ACE was examined using cross-linking experiments with dithiobis[succinimidylpropionate] (DSP) and density gradient centrifugation on sucrose gradients. Both approaches demonstrated that ACE is assembled in the membrane as a monomer. By contrast, the control glycoprotein aminopeptidase N (ApN) exists as a dimer. Biosynthetic labelling experiments in intestinal tissue explants demonstrated that the 184,000-M(r) protein is generated from a single-polypeptide, mannose-rich precursor of ACE (M(r) 175,000) by modification of the carbohydrate side-chains in the Golgi apparatus. The mode of association of the mature form of the enzyme with BBMs was investigated by hydrophobic labelling of right-side-out brush-border vesicles with the photoactivatable carbene-generating reagent 125I-labelled 3-(trifluoromethyl)-3-(m[formylamino]phenyl)diazirine (125I-labelled TID), followed by treatment with trypsin at dilutions that do not cause substantial degradation of ACE. These studies demonstrated that ACE is associated with the membrane via a hydrophobic segment. Furthermore, treatment of 35S-labelled inside-out membrane vesicles with trypsin revealed that ACE possesses a cytoplasmic tail, and therefore has a transmembraneous orientation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asp N. G., Gudmand-Höyer E., Andersen B., Berg N. O., Dahlqvist A. Distribution of disaccharidases, alkaline phosphatase, and some intracellular enzymes along the human small intestine. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1975;10(6):647–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein K. E., Martin B. M., Edwards A. S., Bernstein E. A. Mouse angiotensin-converting enzyme is a protein composed of two homologous domains. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11945–11951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning T. H., Trier J. S. Organ culture of mucosal biopsies of human small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1423–1432. doi: 10.1172/JCI106108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. N., Riordan J. F. Identification of essential tyrosine and lysine residues in angiotensin converting enzyme: evidence for a single active site. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 20;29(46):10493–10498. doi: 10.1021/bi00498a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell G. M., Tranum-Jensen J., Sjöström H., Norén O. Topology and quaternary structure of pro-sucrase/isomaltase and final-form sucrase/isomaltase. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 15;237(2):455–461. doi: 10.1042/bj2370455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker A. D., Munday K. A. The effect of the renin-angiotensin system on mucosal water and sodium transfer in everted sacs of rat jejunum. J Physiol. 1970 Feb;206(2):323–333. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman D. W., Cheung H. S. Concentrations of angiotensin-converting enzyme in tissues of the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Oct;250(1):261–265. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsen E. M. Biosynthesis of intestinal microvillar proteins. Dimerization of aminopeptidase N and lactase-phlorizin hydrolase. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 9;29(1):305–308. doi: 10.1021/bi00453a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das M., Hartley J. L., Soffers R. L. Serum angiotensin-converting enzyme. Isolation and relationship to the pulmonary enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1316–1319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defendini R., Zimmerman E. A., Weare J. A., Alhenc-Gelas F., Erdös E. G. Angiotensin-converting enzyme in epithelial and neuroepithelial cells. Neuroendocrinology. 1983 Jul;37(1):32–40. doi: 10.1159/000123512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers M. R., Fox E. A., Strydom D. J., Riordan J. F. Molecular cloning of human testicular angiotensin-converting enzyme: the testis isozyme is identical to the C-terminal half of endothelial angiotensin-converting enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7741–7745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Dorry H. A., Bull H. G., Iwata K., Thornberry N. A., Cordes E. H., Soffer R. L. Molecular and catalytic properties of rabbit testicular dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14128–14133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Dorry H. A., Pickett C. B., MacGregor J. S., Soffer R. L. Tissue-specific expression of mRNAs for dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase isoenzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4295–4297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdös E. G., Skidgel R. A. The angiotensin I-converting enzyme. Lab Invest. 1987 Apr;56(4):345–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., McCammon K., Sambrook J. Expression of wild-type and mutant forms of influenza hemagglutinin: the role of folding in intracellular transport. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauri H. P., Sterchi E. E., Bienz D., Fransen J. A., Marxer A. Expression and intracellular transport of microvillus membrane hydrolases in human intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):838–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Keen J., Pappin D. J., Turner A. J. Pig kidney angiotensin converting enzyme. Purification and characterization of amphipathic and hydrophilic forms of the enzyme establishes C-terminal anchorage to the plasma membrane. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 1;247(1):85–93. doi: 10.1042/bj2470085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtley S. M., Helenius A. Protein oligomerization in the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:277–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igic R., Erdös E. G., Yeh H. S., Sorrells K., Nakajima T. Angiotensin I converting enzyme of the lung. Circ Res. 1972 Sep;31(9 Suppl):51–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jascur T., Matter K., Hauri H. P. Oligomerization and intracellular protein transport: dimerization of intestinal dipeptidylpeptidase IV occurs in the Golgi apparatus. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 19;30(7):1908–1915. doi: 10.1021/bi00221a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Maroux S. Topology of microvillar membrance hydrolases of kidney and intestine. Physiol Rev. 1982 Jan;62(1):91–128. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E., Lodish H. F. Oligomerization is essential for transport of vesicular stomatitis viral glycoprotein to the cell surface. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90075-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R. S., Kusari J., Roy S. N., Soffer R. L., Sen G. C. Structure of testicular angiotensin-converting enzyme. A segmental mosaic isozyme. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16754–16758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzillo J. J., Stevens J., Dasarathy Y., Yotsumoto H., Fanburg B. L. Angiotensin-converting enzyme from human tissues. Physicochemical, catalytic, and immunological properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):14938–14944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lattion A. L., Soubrier F., Allegrini J., Hubert C., Corvol P., Alhenc-Gelas F. The testicular transcript of the angiotensin I-converting enzyme encodes for the ancestral, non-duplicated form of the enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 31;252(1-2):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80897-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Rousseaux-Schmid M., Naim H. Y., MacDonald H. R., Bron C. Biosynthesis and maturation of the Lyt-2/3 molecular complex in mouse thymocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1937–1944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naim H. Y., Sterchi E. E., Lentze M. J. Biosynthesis and maturation of lactase-phlorizin hydrolase in the human small intestinal epithelial cells. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 15;241(2):427–434. doi: 10.1042/bj2410427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naim H. Y., Sterchi E. E., Lentze M. J. Biosynthesis of the human sucrase-isomaltase complex. Differential O-glycosylation of the sucrase subunit correlates with its position within the enzyme complex. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7242–7253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naim H. Y., Sterchi E. E., Lentze M. J. Structure, biosynthesis, and glycosylation of human small intestinal maltase-glucoamylase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19709–19717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng K. K., Vane J. R. Conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II. Nature. 1967 Nov 25;216(5117):762–766. doi: 10.1038/216762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patchett A. A., Cordes E. H. The design and properties of N-carboxyalkyldipeptide inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1985;57:1–84. doi: 10.1002/9780470123034.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Doms R. W. Regulation of protein export from the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:257–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J., Preiser H., Maestracci D., Ghosh B. K., Cerda J. J., Crane R. K. Purification of the human intestinal brush border membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 27;323(1):98–112. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90434-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenza G. Anchoring and biosynthesis of stalked brush border membrane proteins: glycosidases and peptidases of enterocytes and renal tubuli. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:255–313. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skeggs L. T., Dorer F. E., Kahn J. R., Lentz K. E., Levine M. The biochemistry of the renin-angiotensin system and its role in hypertension. Am J Med. 1976 May 31;60(6):737–748. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90888-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soffer R. L. Angiotensin-converting enzyme and the regulation of vasoactive peptides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:73–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.000445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soubrier F., Alhenc-Gelas F., Hubert C., Allegrini J., John M., Tregear G., Corvol P. Two putative active centers in human angiotensin I-converting enzyme revealed by molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9386–9390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiess M., Brunner J., Semenza G. Hydrophobic labeling, isolation, and partial characterization of the NH2-terminal membranous segment of sucrase-isomaltase complex. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2370–2377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterchi E. E., Woodley J. F. Peptide hydrolases of the human small intestinal mucosa: distribution of activities between brush border membranes and cytosol. Clin Chim Acta. 1980 Mar 14;102(1):49–56. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(80)90432-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. E., Sheridan M. A., Hammon K. J., Erdös E. G. Angiotensin I converting enzyme (kininase II) of the brush border of human and swine intestine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Jun 1;29(11):1525–1529. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90603-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. Y., Erdös E. G., Levin Y. A dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase that converts angiotensin I and inactivates bradykinin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 21;214(2):374–376. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka M., Erickson R. H., Woodley J. F., Gulli R., Guan D., Kim Y. S. Role of rat intestinal brush-border membrane angiotensin-converting enzyme in dietary protein digestion. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 1):G781–G786. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.253.6.G781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]