Abstract
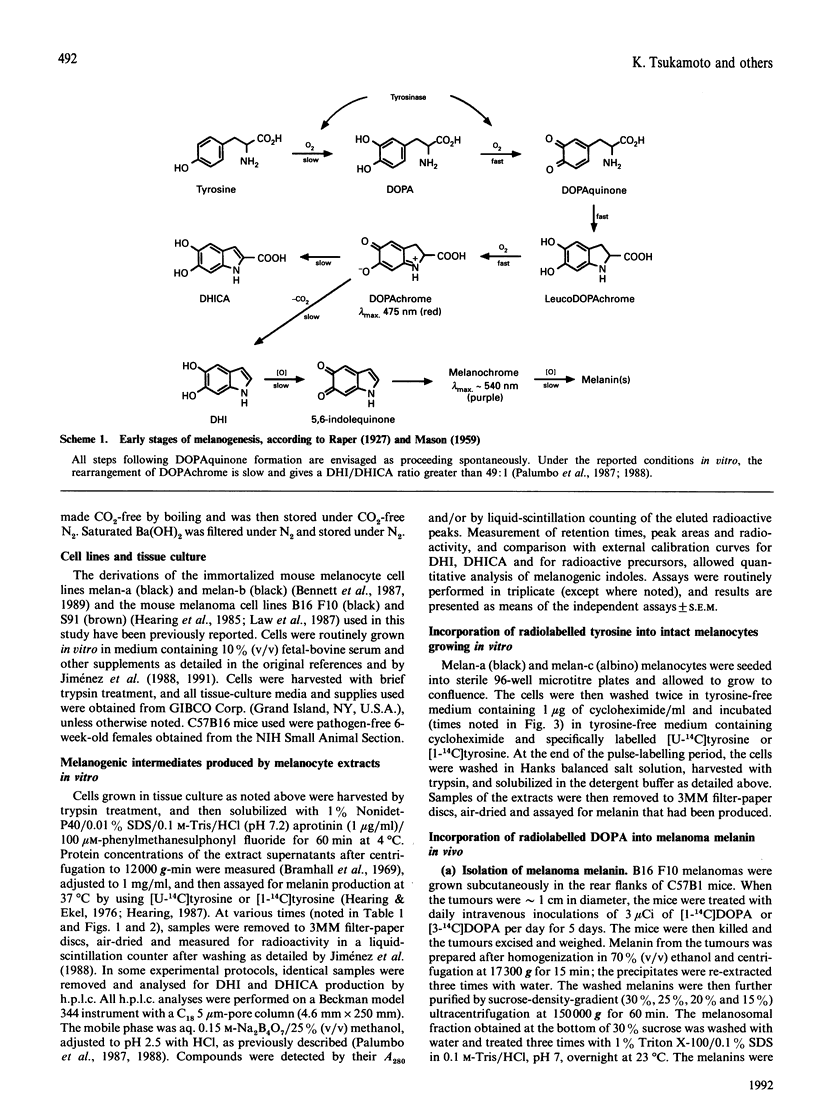
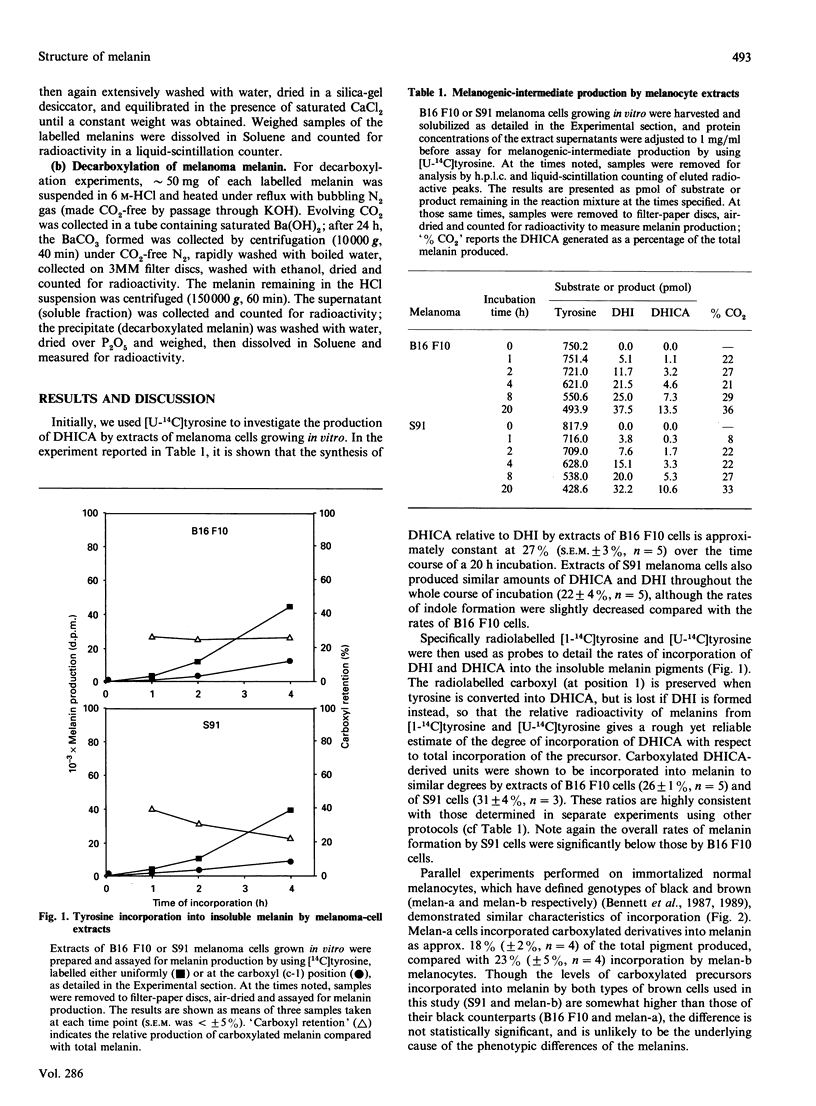
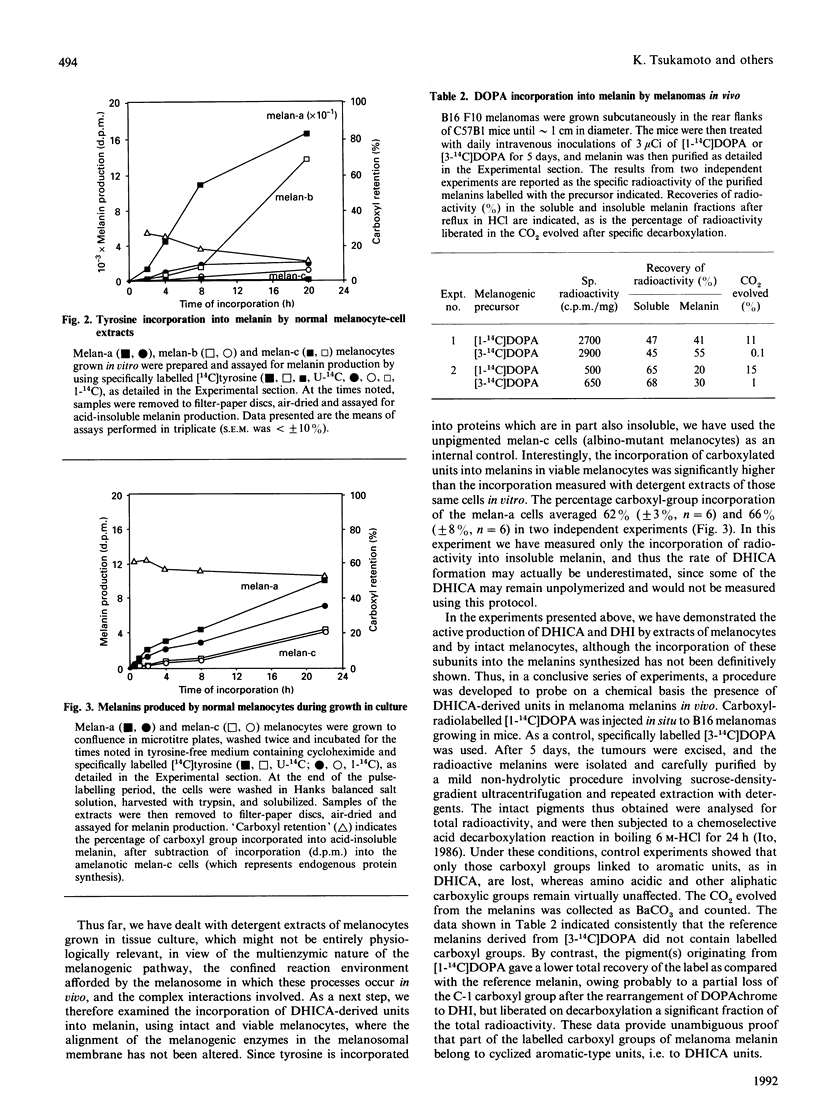
The role of 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid (DHICA) in the biosynthesis of melanins has been studied by using the incorporation of specifically radiolabelled melanogenic precursors into melanins formed by melanocytes growing in vitro and in vivo. Extracts of mouse melanocytes and intact viable melanocytes were found to incorporate into melanin from 25% to more than 60% of [1-14C]tyrosine. Melanins from melanoma tumours grown in mice were radiolabelled with 3,4-dihydroxy[1-14C]phenylalanine, purified and chemoselectively decarboxylated. Determination of the 14CO2 evolved showed that at least 20% of the precursor incorporated in vivo retains the label in the form of non-aminoacidic aromatic-type carboxyl groups. These results provide the first unambiguous demonstration that DHICA is incorporated in physiologically relevant amounts in mammalian melanins.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aroca P., Garcia-Borron J. C., Solano F., Lozano J. A. Regulation of mammalian melanogenesis. I: Partial purification and characterization of a dopachrome converting factor: dopachrome tautomerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 14;1035(3):266–275. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(90)90088-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber J. I., Townsend D., Olds D. P., King R. A. Dopachrome oxidoreductase: a new enzyme in the pigment pathway. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Aug;83(2):145–149. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12263381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett D. C., Cooper P. J., Dexter T. J., Devlin L. M., Heasman J., Nester B. Cloned mouse melanocyte lines carrying the germline mutations albino and brown: complementation in culture. Development. 1989 Feb;105(2):379–385. doi: 10.1242/dev.105.2.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett D. C., Cooper P. J., Hart I. R. A line of non-tumorigenic mouse melanocytes, syngeneic with the B16 melanoma and requiring a tumour promoter for growth. Int J Cancer. 1987 Mar 15;39(3):414–418. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910390324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramhall S., Noack N., Wu M., Loewenberg J. R. A simple colorimetric method for determination of protein. Anal Biochem. 1969 Oct 1;31(1):146–148. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90251-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty A. K., Mishima Y., Inazu M., Hatta S., Ichihashi M. Melanogenic regulatory factors in coated vesicles from melanoma cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Nov;93(5):616–620. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12319736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatta S., Mishima Y., Ichihashi M., Ito S. Melanin monomers within coated vesicles and premelanosomes in melanin synthesizing cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Aug;91(2):181–184. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12464454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J., Ekel T. M. Mammalian tyrosinase. A comparison of tyrosine hydroxylation and melanin formation. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):549–557. doi: 10.1042/bj1570549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J., Jiménez M. Mammalian tyrosinase--the critical regulatory control point in melanocyte pigmentation. Int J Biochem. 1987;19(12):1141–1147. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(87)90095-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J., Jr, Ekel T. M., Montague P. M., Nicholson J. M. Mammalin tyrosinase. Stoichiometry and measurement of reaction products. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 14;611(2):251–268. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J., Jr Mammalian monophenol monooxygenase (tyrosinase): purification, properties, and reactions catalyzed. Methods Enzymol. 1987;142:154–165. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)42024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J., Tsukamoto K. Enzymatic control of pigmentation in mammals. FASEB J. 1991 Nov;5(14):2902–2909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J., Vieira W. D., Law L. W. Malignant melanoma: cross-reacting (common) tumor rejection antigens. Int J Cancer. 1985 Mar 15;35(3):403–409. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910350317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S. Reexamination of the structure of eumelanin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Aug 6;883(1):155–161. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90146-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez M., Kameyama K., Maloy W. L., Tomita Y., Hearing V. J. Mammalian tyrosinase: biosynthesis, processing, and modulation by melanocyte-stimulating hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3830–3834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez M., Tsukamoto K., Hearing V. J. Tyrosinases from two different loci are expressed by normal and by transformed melanocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1147–1156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Körner A., Pawelek J. Mammalian tyrosinase catalyzes three reactions in the biosynthesis of melanin. Science. 1982 Sep 17;217(4565):1163–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.6810464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson B., Tjälve H. Studies on the mechanism of drug-binding to melanin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Apr 1;28(7):1181–1187. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90326-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law L. W., Vieira W. D., Kameyama K., Hearing V. J. A unique tumor rejection antigen from the S91 murine malignant melanoma. Cancer Res. 1987 Nov 15;47(22):5841–5845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard L. J., Townsend D., King R. A. Function of dopachrome oxidoreductase and metal ions in dopachrome conversion in the eumelanin pathway. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 9;27(16):6156–6159. doi: 10.1021/bi00416a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link E. M., Brown I., Carpenter R. N., Mitchell J. S. Uptake and therapeutic effectiveness of 125I- and 211At-methylene blue for pigmented melanoma in an animal model system. Cancer Res. 1989 Aug 1;49(15):4332–4337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palumbo A., Solano F., Misuraca G., Aroca P., Garcia Borron J. C., Lozano J. A., Prota G. Comparative action of dopachrome tautomerase and metal ions on the rearrangement of dopachrome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Nov 14;1115(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(91)90003-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palumbo A., d'Ischia M., Misuraca G., Prota G. Effect of metal ions on the rearrangement of dopachrome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Aug 13;925(2):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(87)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palumbo A., d'Ischia M., Misuraca G., Prota G., Schultz T. M. Structural modifications in biosynthetic melanins induced by metal ions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 17;964(2):193–199. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(88)90166-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawelek J. M., Körner A. M. The biosynthesis of mammalian melanin. Am Sci. 1982 Mar-Apr;70(2):136–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawelek J., Körner A., Bergstrom A., Bologna J. New regulators of melanin biosynthesis and the autodestruction of melanoma cells. Nature. 1980 Aug 7;286(5773):617–619. doi: 10.1038/286617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prota G. Progress in the chemistry of melanins and related metabolites. Med Res Rev. 1988 Oct-Dec;8(4):525–556. doi: 10.1002/med.2610080405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prota G., Thomson R. H. Melanin pigmentation in mammals. Endeavour. 1976 Jan;35(224):32–38. doi: 10.1016/0160-9327(76)90060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raper H. S. The Tyrosinase-tyrosine Reaction: Production from Tyrosine of 5: 6-Dihydroxyindole and 5: 6-Dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic Acid-the Precursors of Melanin. Biochem J. 1927;21(1):89–96. doi: 10.1042/bj0210089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarna T., Hyde J. S., Swartz H. M. Ion-exchange in melanin: an electron spin resonance study with lanthanide probes. Science. 1976 Jun 11;192(4244):1132–1134. doi: 10.1126/science.179142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swan G. A. Structure, chemistry, and biosynthesis of the melanins. Fortschr Chem Org Naturst. 1974;31(0):521–582. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-7094-6_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


