Abstract
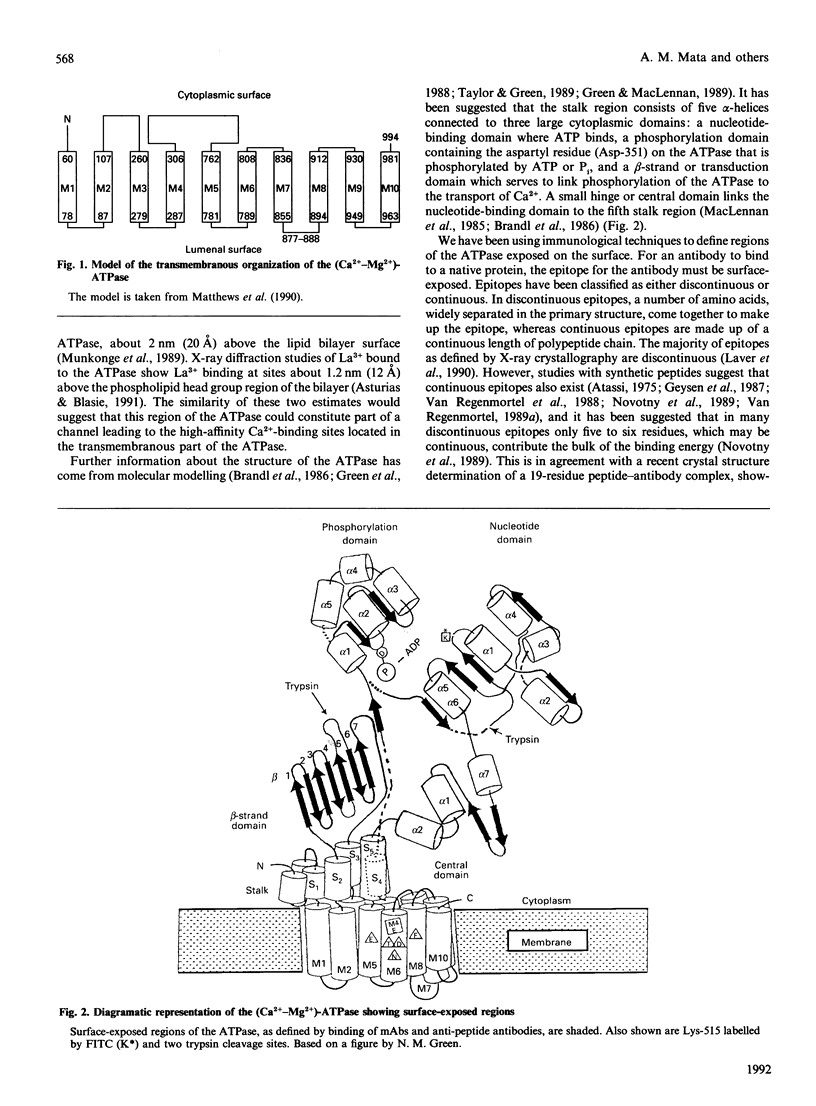
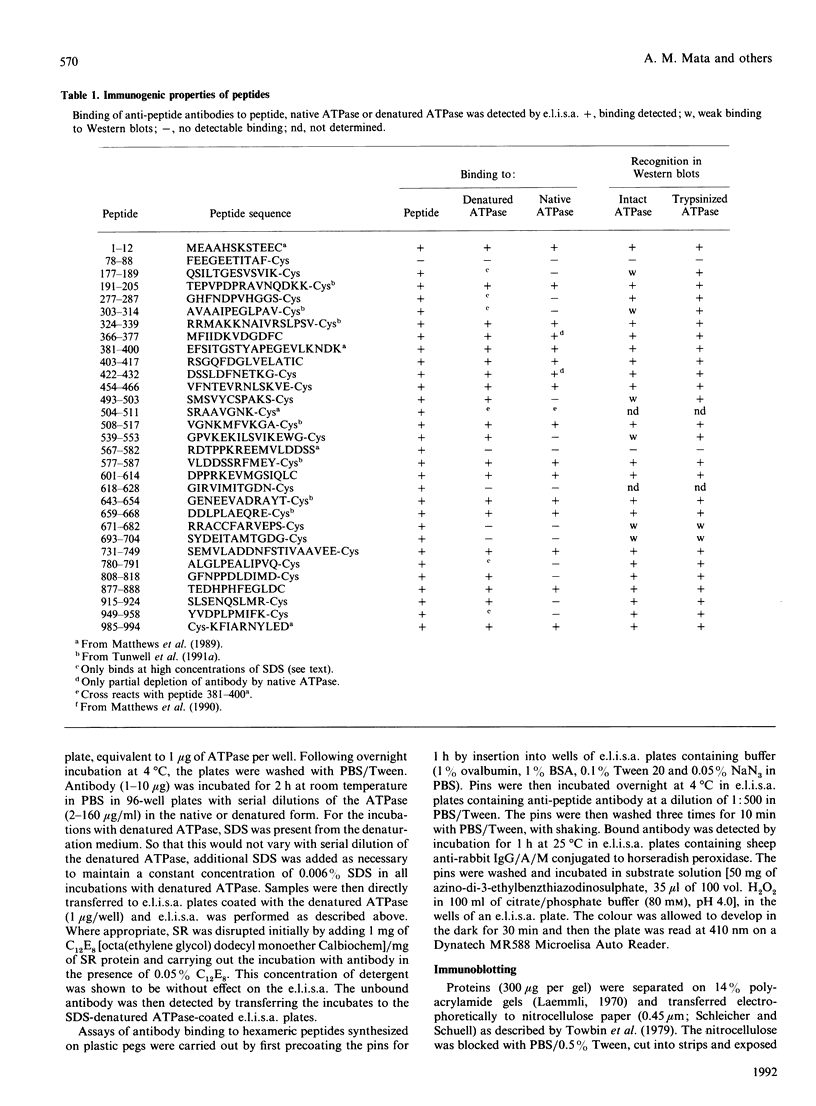
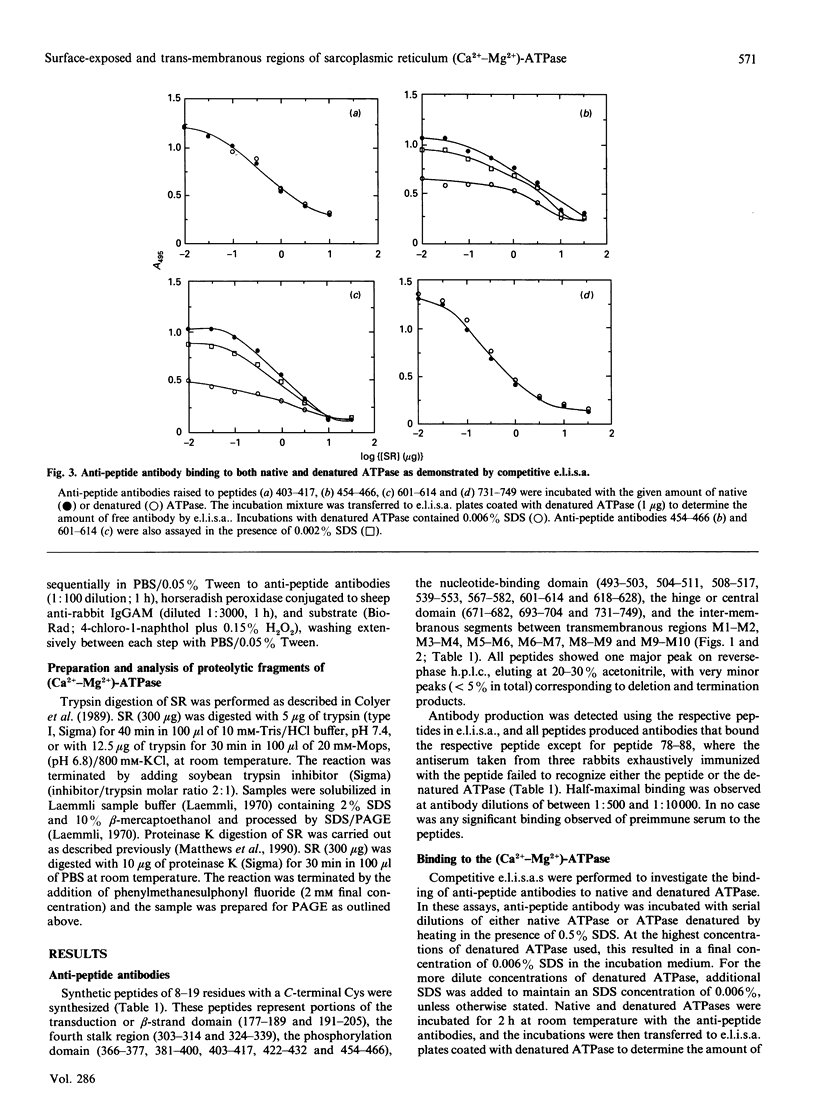
Peptides have been synthesized representing parts of the transduction, phosphorylation, nucleotide-binding and hinge domains of the (Ca(2+)-Mg2+)-ATPase of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), and corresponding to segments of all of the postulated short inter-membranous loops of the (Ca(2+)-Mg2+)-ATPase (residues 77-88, 277-287, 780-791, 808-818, 915-924 and 949-958). A number of antibodies raised to these peptides have been shown to bind to the ATPase, defining surface-exposed regions. Many of these are concentrated in the phosphorylation and nucleotide-binding domains, suggesting that these domains could be exposed on the top surface of the ATPase. The cytoplasmic location of the loop containing residues 808-818 was confirmed by the finding that proteinase K treatment of intact SR vesicles enhanced the binding of antibodies against this segment. These findings support the 10-alpha-helix model of the ATPase. These results also suggest that only inter-membranous loops larger than about 20 residues are likely to be detected by immunological methods in transmembranous proteins. Binding of anti-peptide antibodies to proteolytic fragments of the ATPase has been used to define the domain structure of the enzyme. Some of the anti-peptide antibodies have been characterized by studying their binding to sets of hexameric peptides synthesized on plastic pegs. A wide pattern of responses is observed, with a restricted range of epitopes being recognized by each anti-peptide antibody.
Full text
PDF



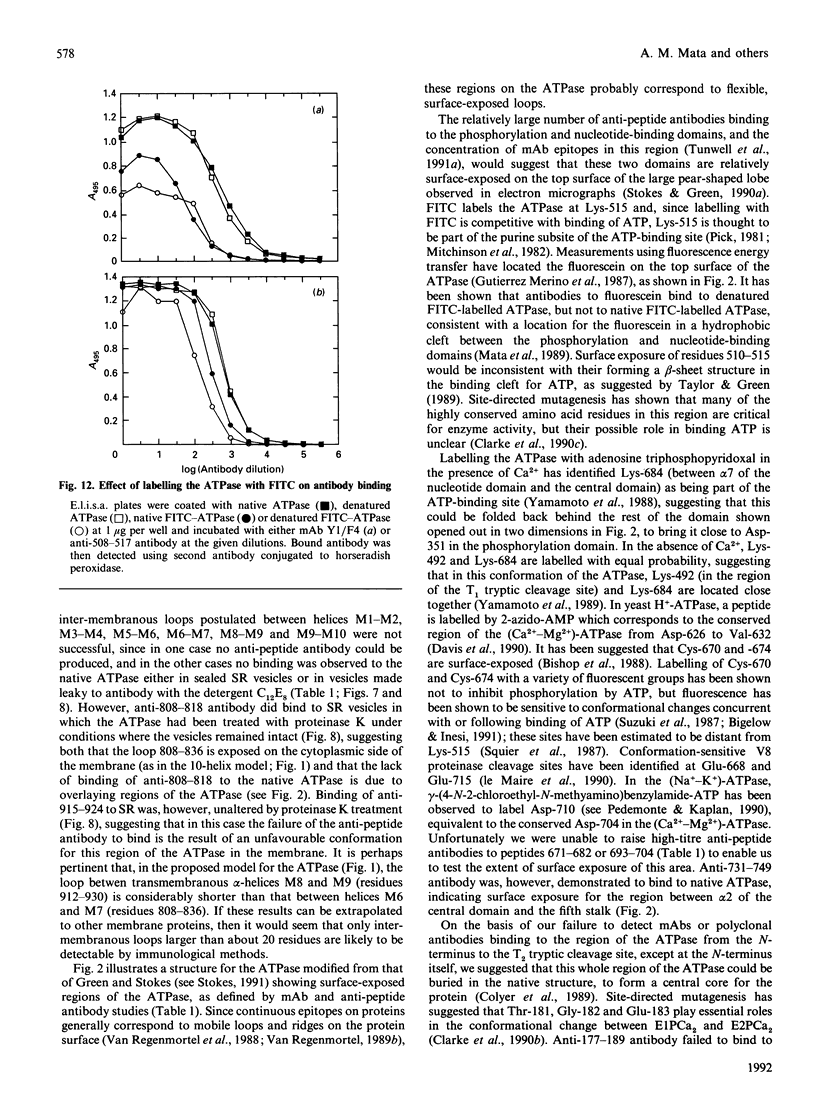


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antolovic R., Brüller H. J., Bunk S., Linder D., Schoner W. Epitope mapping by amino-acid-sequence-specific antibodies reveals that both ends of the alpha subunit of Na+/K(+)-ATPase are located on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jul 1;199(1):195–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asturias F. J., Blasie J. K. Location of high-affinity metal binding sites in the profile structure of the Ca+2-ATPase in the sarcoplasmic reticulum by resonance x-ray diffraction. Biophys J. 1991 Feb;59(2):488–502. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82242-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atassi M. Z. Antigenic structure of myoglobin: the complete immunochemical anatomy of a protein and conclusions relating to antigenic structures of proteins. Immunochemistry. 1975 May;12(5):423–438. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(75)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigelow D. J., Inesi G. Frequency-domain fluorescence spectroscopy resolves the location of maleimide-directed spectroscopic probes within the tertiary structure of the Ca-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 26;30(8):2113–2125. doi: 10.1021/bi00222a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. E., Squier T. C., Bigelow D. J., Inesi G. (Iodoacetamido)fluorescein labels a pair of proximal cysteines on the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):5233–5240. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandl C. J., Green N. M., Korczak B., MacLennan D. H. Two Ca2+ ATPase genes: homologies and mechanistic implications of deduced amino acid sequences. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):597–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90269-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke D. M., Loo T. W., Inesi G., MacLennan D. H. Location of high affinity Ca2+-binding sites within the predicted transmembrane domain of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):476–478. doi: 10.1038/339476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke D. M., Loo T. W., MacLennan D. H. Functional consequences of alterations to amino acids located in the nucleotide binding domain of the Ca2(+)-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22223–22227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke D. M., Loo T. W., MacLennan D. H. Functional consequences of mutations of conserved amino acids in the beta-strand domain of the Ca2(+)-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14088–14092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke D. M., Loo T. W., MacLennan D. H. The epitope for monoclonal antibody A20 (amino acids 870-890) is located on the luminal surface of the Ca2(+)-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17405–17408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colyer J., Mata A. M., Lee A. G., East J. M. Effects on ATPase activity of monoclonal antibodies raised against (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase from rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum and their correlation with epitope location. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):439–447. doi: 10.1042/bj2620439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. B., Smith K. E., Campbell B. N., Jr, Hammes G. G. The ATP binding site of the yeast plasma membrane proton-translocating ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1300–1305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froud R. J., East J. M., Rooney E. K., Lee A. G. Binding of long-chain alkyl derivatives to lipid bilayers and to (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7535–7544. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froud R. J., Lee A. G. Conformational transitions in the Ca2+ + Mg2+-activated ATPase and the binding of Ca2+ ions. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):197–206. doi: 10.1042/bj2370197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Meloen R. H., Barteling S. J. Use of peptide synthesis to probe viral antigens for epitopes to a resolution of a single amino acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3998–4002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Rodda S. J., Mason T. J., Tribbick G., Schoofs P. G. Strategies for epitope analysis using peptide synthesis. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Sep 24;102(2):259–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90085-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., Colyer J., East J. M., Lee A. G. Silver ions trigger Ca2+ release by interaction with the (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase in reconstituted systems. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7676–7679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M., MacLennan D. H. ATP driven ion pumps: an evolutionary mosaic. Biochem Soc Trans. 1989 Oct;17(5):819–822. doi: 10.1042/bst0170819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M., Taylor W. R., MacLennan D. H. A consensus structure for cation pumps. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;273:15–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Alexander H., Olson A., Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Immunogenic structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez-Merino C., Munkonge F., Mata A. M., East J. M., Levinson B. L., Napier R. M., Lee A. G. The position of the ATP binding site on the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Feb 26;897(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90417-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura Y., Kawakita M. Purification of limited tryptic fragments of Ca2+,Mg2+-adenosine triphosphatase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum and identification of conformation-sensitive cleavage sites. J Biochem. 1989 May;105(5):775–781. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachigian L. M., Evin G., Morgan F. J., Owensby D. A., Chesterman C. N. A crossreactive antipeptide monoclonal antibody with specificity for lysyl-lysine. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Jul 5;140(2):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90378-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Air G. M., Webster R. G., Smith-Gill S. J. Epitopes on protein antigens: misconceptions and realities. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):553–556. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90464-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Brandl C. J., Korczak B., Green N. M. Amino-acid sequence of a Ca2+ + Mg2+-dependent ATPase from rabbit muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum, deduced from its complementary DNA sequence. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):696–700. doi: 10.1038/316696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Clarke D. M., Fujii J., Loo T. W., MacLennan D. H. Expression and mutation of Ca2+ ATPases of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;14(1):26–34. doi: 10.1002/cm.970140107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mata A. M., Lee A. G., East J. M. Probing the nucleotide-binding site of sarcoplasmic reticulum (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase with anti-fluorescein antibodies. FEBS Lett. 1989 Aug 14;253(1-2):273–275. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80974-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews I., Colyer J., Mata A. M., Green N. M., Sharma R. P., Lee A. G., East J. M. Evidence for the cytoplasmic location of the N- and C-terminal segments of sarcoplasmic reticulum (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 15;161(2):683–688. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92653-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews I., Sharma R. P., Lee A. G., East J. M. Transmembranous organization of (Ca2(+)-Mg2+)-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Evidence for lumenal location of residues 877-888. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18737–18740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield B. Solid phase synthesis. Science. 1986 Apr 18;232(4748):341–347. doi: 10.1126/science.3961484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchinson C., Wilderspin A. F., Trinnaman B. J., Green N. M. Identification of a labelled peptide after stoicheiometric reaction of fluorescein isothiocyanate with the Ca2+ -dependent adenosine triphosphatase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 6;146(1):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80710-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munkonge F., East J. M., Lee A. G. Positions of the sites labeled by N-cyclohexyl-N'-(4-dimethylamino-1-naphthyl)carbodiimide on the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 13;979(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90530-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny J., Bruccoleri R. E., Saul F. A. On the attribution of binding energy in antigen-antibody complexes McPC 603, D1.3, and HyHEL-5. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4735–4749. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny J. Protein antigenicity: a thermodynamic approach. Mol Immunol. 1991 Mar;28(3):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90062-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Arzamazova N. M., Arystarkhova E. A., Gevondyan N. M., Aldanova N. A., Modyanov N. N. Detailed structural analysis of exposed domains of membrane-bound Na+,K+-ATPase. A model of transmembrane arrangement. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 15;217(2):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80676-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Luneva N. M., Arystarkhova E. A., Gevondyan N. M., Arzamazova N. M., Kozhich A. T., Nesmeyanov V. A., Modyanov N. N. Topology of Na+,K+-ATPase. Identification of the extra- and intracellular hydrophilic loops of the catalytic subunit by specific antibodies. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 25;227(2):230–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80904-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Modyanov N. N., Broude N. E., Petrukhin K. E., Grishin A. V., Arzamazova N. M., Aldanova N. A., Monastyrskaya G. S., Sverdlov E. D. Pig kidney Na+,K+-ATPase. Primary structure and spatial organization. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jun 9;201(2):237–245. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80616-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palfreyman J. W., Aitcheson T. C., Taylor P. Guidelines for the production of polypeptide specific antisera using small synthetic oligopeptides as immunogens. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Dec 31;75(2):383–393. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90122-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmero I., Sastre L. Complementary DNA cloning of a protein highly homologous to mammalian sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase from the crustacean Artemia. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 20;210(4):737–748. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90106-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedemonte C. H., Kaplan J. H. Chemical modification as an approach to elucidation of sodium pump structure-function relations. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 1):C1–23. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petithory J. R., Jencks W. P. Phosphorylation of the calcium adenosinetriphosphatase of sarcoplasmic reticulum: rate-limiting conformational change followed by rapid phosphoryl transfer. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 12;25(16):4493–4497. doi: 10.1021/bi00364a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U. Interaction of fluorescein isothiocyanate with nucleotide-binding sites of the Ca-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Dec;121(1):187–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoofs P. G., Geysen H. M., Jackson D. C., Brown L. E., Tang X. L., White D. O. Epitopes of an influenza viral peptide recognized by antibody at single amino acid resolution. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 15;140(2):611–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott T. L. Distances between the functional sites of the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14421–14423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R. Structure and function of proton translocating ATPase in plasma membranes of plants and fungi. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 24;947(1):1–28. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squier T. C., Bigelow D. J., Garcia de Ancos J., Inesi G. Localization of site-specific probes on the Ca-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum using fluorescence energy transfer. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4748–4754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield R. L., Fieser T. M., Lerner R. A., Wilson I. A. Crystal structures of an antibody to a peptide and its complex with peptide antigen at 2.8 A. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):712–719. doi: 10.1126/science.2333521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes D. L., Green N. M. Comparison of frozen-hydrated and negatively stained crystals of Ca-ATPase suggests a shape for the intramembranous domain. Biochem Soc Trans. 1990 Oct;18(5):841–843. doi: 10.1042/bst0180841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes D. L., Green N. M. Structure of CaATPase: electron microscopy of frozen-hydrated crystals at 6 A resolution in projection. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 5;213(3):529–538. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80213-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Obara M., Kuwayama H., Kanazawa T. A conformational change of N-iodoacetyl-N'-(5-sulfo-1-naphthyl)ethylenediamine-labeled sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase upon ATP binding to the catalytic site. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15448–15456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K., Dux L., Martonosi A. Structure of the vanadate-induced crystals of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 25;174(1):193–204. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90372-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. R., Green N. M. The predicted secondary structures of the nucleotide-binding sites of six cation-transporting ATPases lead to a probable tertiary fold. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 15;179(1):241–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14547.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Green N. M. Studies on the location and orientation of proteins in the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Dec 17;40(2):403–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunwell R. E., Conlan J. W., Matthews I., East J. M., Lee A. G. Definition of surface-exposed epitopes on the (Ca(2+)-Mg2+)-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J. 1991 Oct 1;279(Pt 1):203–212. doi: 10.1042/bj2790203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunwell R. E., O'Connor C. D., Mata A. M., East J. M., Lee A. G. Mapping epitopes on the (Ca(2+)-Mg2+)-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum using fusion proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 9;1073(3):585–592. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(91)90234-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Regenmortel M. H. Structural and functional approaches to the study of protein antigenicity. Immunol Today. 1989 Aug;10(8):266–272. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90140-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Regenmortel M. H. The concept and operational definition of protein epitopes. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1989 Jun 12;323(1217):451–466. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1989.0023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. E. The use of monoclonal antibodies and limited proteolysis in elucidation of structure-function relationships in proteins. Methods Biochem Anal. 1991;35:207–250. doi: 10.1002/9780470110560.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Imamura Y., Tagaya M., Fukui T., Kawakita M. Ca2(+)-dependent conformational change of the ATP-binding site of Ca2(+)-transporting ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum as revealed by an alteration of the target-site specificity of adenosine triphosphopyridoxal. J Biochem. 1989 Dec;106(6):1121–1125. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Tagaya M., Fukui T., Kawakita M. Affinity labeling of the ATP-binding site of Ca2+-transporting ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum by adenosine triphosphopyridoxal: identification of the reactive lysyl residue. J Biochem. 1988 Mar;103(3):452–457. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki K., Sano N., Ohe M., Yamamoto T. Determination of the primary structure of intermolecular cross-linking sites on the Ca2(+)-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum using 14C-labeled N,N'-(1,4-phenylene)bismaleimide or N-ethylmaleimide. J Biochem. 1990 Dec;108(6):918–925. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- le Maire M., Lund S., Viel A., Champeil P., Moller J. V. Ca2(+)-induced conformational changes and location of Ca2+ transport sites in sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2(+)-ATPase as detected by the use of proteolytic enzyme (V8). J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):1111–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]