Abstract
Saporin-S6, a ribosome-inactivating protein (RIP) from Saponaria officinalis released more than 1 mol of adenine/mol of ribosomes from house fly (Musca domestica) larvae and from rat liver. The release of adenine from rat liver ribosomes by several RIPs (plant enzymes with RNA N-glycosidase activity) was examined. Saporins, pokeweed antiviral protein from roots of Phytolacca americana (PAP-R), and trichokirin from Trichosanthes kirilowii seeds depurinated rat liver ribosomes at more than one site. Up to 33 mol of adenine were released from 1 mol of ribosomes. This property is not common to all RIPS.
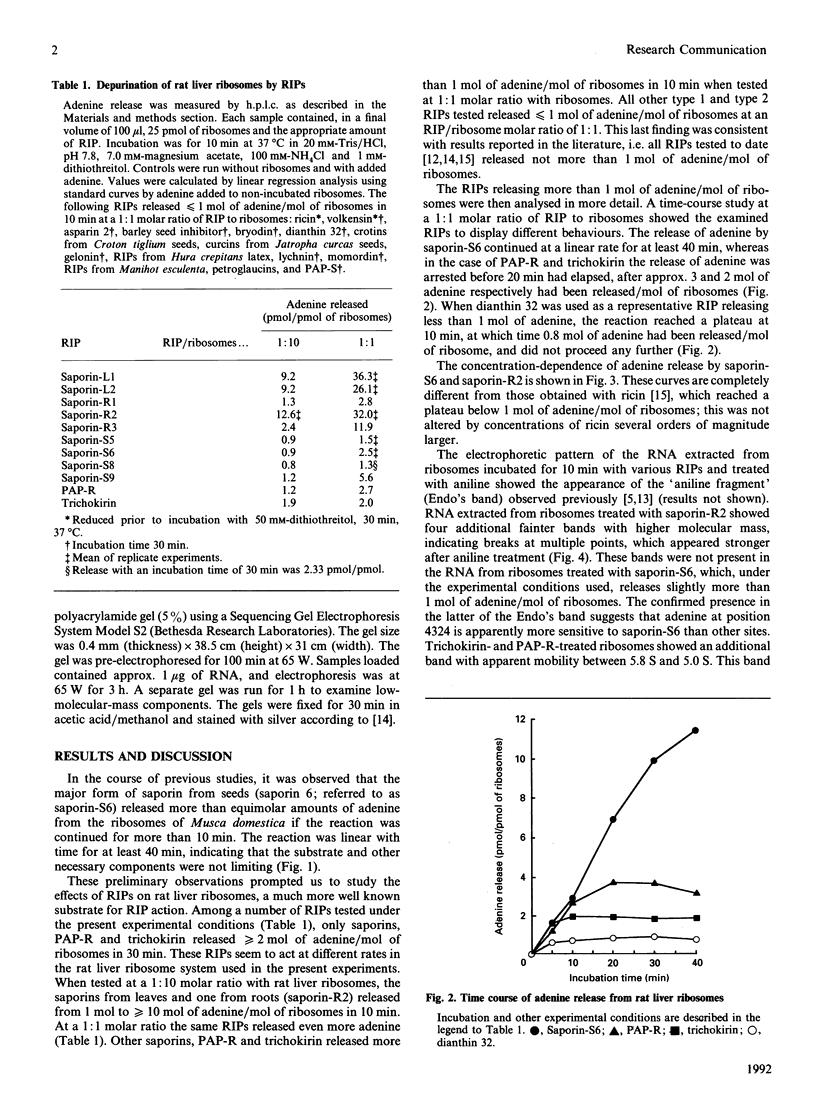
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry M. J., Samuel C. E. Detection of subnanogram amounts of RNA in polyacrylamide gels in the presence and absence of protein by staining with silver. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jul 15;124(1):180–184. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnicelli D., Brigotti M., Montanaro L., Sperti S. Differential requirement of ATP and extra-ribosomal proteins for ribosome inactivation by eight RNA N-glycosidases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jan 31;182(2):579–582. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91771-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Glück A., Wool I. G. Ribosomal RNA identity elements for ricin A-chain recognition and catalysis. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 5;221(1):193–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80214-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Mitsui K., Motizuki M., Tsurugi K. The mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes. The site and the characteristics of the modification in 28 S ribosomal RNA caused by the toxins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5908–5912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K. The RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. The characteristics of the enzymatic activity of ricin A-chain with ribosomes and with rRNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8735–8739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari C., Barbieri L., Stirpe F. Effects of plant ribosome-inactivating proteins on ribosomes from Musca domestica. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1991;100(2):223–227. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(91)90365-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habuka N., Miyano M., Kataoka J., Noma M. Escherichia coli ribosome is inactivated by Mirabilis antiviral protein which cleaves the N-glycosidic bond at A2660 of 23 S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 5;221(3):737–743. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80168-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley M. R., Legname G., Osborn R., Chen Z., Lord J. M. Single-chain ribosome inactivating proteins from plants depurinate Escherichia coli 23S ribosomal RNA. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 23;290(1-2):65–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81227-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann W. P., Hall L. M., Siler W., Barton N., Whitley R. J. High-pressure liquid chromatographic methods for determining arabinosyladenine-5'-monophosphate, arabinosyladenine, and arabinosylhypoxanthine in plasma and urine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):265–273. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prestle J., Hornung E., Schönfelder M., Mundry K. W. Mechanism and site of action of a ribosome-inactivating protein type 1 from Dianthus barbatus which inactivates Escherichia coli ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 10;297(3):250–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80549-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperti S., Zamboni M., Brigotti M., Rambelli F., Montanaro L. Alpha-sarcin impairs the N-glycosidase activity of ricin on ribosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 28;160(2):857–861. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92513-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Bailey S., Miller S. P., Bodley J. W. Modification of ribosomal RNA by ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1349–1357. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Barbieri L., Battelli M. G., Soria M., Lappi D. A. Ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants: present status and future prospects. Biotechnology (N Y) 1992 Apr;10(4):405–412. doi: 10.1038/nbt0492-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Hughes R. C. Specificity of ribosome-inactivating proteins with RNA N-glycosidase activity. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 15;262(3):1001–1002. doi: 10.1042/bj2621001b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh T. A., Morgan A. E., Hey T. D. Characterization and molecular cloning of a proenzyme form of a ribosome-inactivating protein from maize. Novel mechanism of proenzyme activation by proteolytic removal of a 2.8-kilodalton internal peptide segment. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23422–23427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamboni M., Brigotti M., Rambelli F., Montanaro L., Sperti S. High-pressure-liquid-chromatographic and fluorimetric methods for the determination of adenine released from ribosomes by ricin and gelonin. Biochem J. 1989 May 1;259(3):639–643. doi: 10.1042/bj2590639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



