Abstract
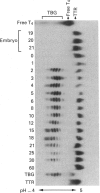
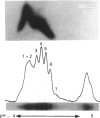
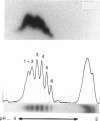
Thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG), the major carrier of thyroid hormones in human and murine sera, is in the rat a developmentally regulated protein, showing a large surge during post-natal growth followed by virtual disappearance in adults. Here we study as a function of age, from the 19-day embryo to 60 days after birth, the structural and binding characteristics of rat TBG microheterogeneity. Serum obtained throughout development, when pre-incubated with 125I-thyroxine (T4), was shown by isoelectric focusing (IEF; pH range 4-5) to contain six labelled isoforms of TBG, with isoelectric points between 4.25 and 4.55. These isoforms differ in their sialic acid content. The relative labelling densities of the isoforms show age-related changes: in neonates, the bulk of T4 is bound to the most alkaline (least sialylated) TBG isoforms; then, with advancing age, it shifts to the most acidic isoforms. To understand whether this progressive transfer of ligand reflects developmental changes in the relative abundance of isoforms, we submitted sera from rats of different ages to crossed immunoelectrofocusing analysis. We demonstrate that the relative proportions of the TBG isoforms remain fairly constant, independent of the level of total TBG. The most acidic forms always represented the majority (approximately 50%), with the most alkaline ones only representing 15% of total TBG. Experiments based on IEF of charcoal-treated sera, supplemented or not with lipidic serum extracts, further demonstrate that the paradoxical low labelling seen in the neonates for the most abundant highly sialylated isoforms is due to inhibition of their binding abilities by liposoluble components, which are particularly concentrated in the sera at the earlier post-natal ages. These studies represent the first analysis of concentration versus binding functions of rat TBG isoforms in the physiological conditions of normal ontogeny. Our results point to an important influence for the serum environment on the binding properties of TBG isoforms. The physiological significance of such interactions remains to be clarified.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ain K. B., Mori Y., Refetoff S. Reduced clearance rate of thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) with increased sialylation: a mechanism for estrogen-induced elevation of serum TBG concentration. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Oct;65(4):689–696. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-4-689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S., Morrone S., Robbins J. Effect of deglycosylation on the binding and immunoreactivity of human thyroxine-binding globulin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8830–8835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delorme J., Benassayag C., Christeff N., Vallette G., Savu L., Nunez E. Age-dependent responses of the serum non-esterified fatty acids to adrenalectomy and ovariectomy in developing rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 17;792(1):6–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90275-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feizi T., Childs R. A. Carbohydrates as antigenic determinants of glycoproteins. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 1;245(1):1–11. doi: 10.1042/bj2450001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flink I. L., Bailey T. J., Gustafson T. A., Markham B. E., Morkin E. Complete amino acid sequence of human thyroxine-binding globulin deduced from cloned DNA: close homology to the serine antiproteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7708–7712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON A. H., GROSS J., O'CONNOR D., PITT-RIVERS R. Nature of the circulating thyroid hormone-plasma protein complex. Nature. 1952 Jan 5;169(4288):19–20. doi: 10.1038/169019a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershengorn M. C., Cheng S. Y., Lippoldt R. E., Lord R. S., Robbins J. Characterization of human thyroxine-binding globulin. Evidence for a single polypeptide chain. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8713–8718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershengorn M. C., Lippoldt R. E., Edelhoch H., Robbins J. Structure and stability of human thyroxine-binding globulin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8719–8723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gärtner R., Henze R., Horn K., Pickardt C. R., Scriba P. C. Thyroxine-binding globulin: investigation of microheterogeneity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Apr;52(4):657–664. doi: 10.1210/jcem-52-4-657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Electroimmuno assay. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:21–37. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leoni S., Marino M., Devirgiliis L. C., Spagnuolo S., Beninati S., Mangiantini M. T. Age-related changes of glycosylation pattern in isolated rat hepatocytes. Mech Ageing Dev. 1990 Nov;56(2):169–178. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(90)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. S., Pensky J., Green A. M. Studies on human thyroxine-binding globulin. VI. The nature of slow thyroxine-binding globulin. J Clin Invest. 1972 Dec;51(12):3173–3181. doi: 10.1172/JCI107144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. S., Pensky J., Williams S. Studies on human thyroxine-binding globulin. 8. Isoelectric focusing evidence for microheterogeneity of thyroxine-binding globulin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jun;156(2):456–462. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90294-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin Ansart M. C., Vacher D., Girard-Globa A. Lipoproteins of the newborn rat. Reciprocal development of low density lipoproteins and apoprotein E-rich high density lipoproteins. J Dev Physiol. 1988 Aug;10(4):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premachandra B. N., Perlstein I. B., Blumenthal H. T. Studies on obesity. II. Slow-moving thyroxine binding globulin in the sera of normal and obese subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 Jun;30(6):752–762. doi: 10.1210/jcem-30-6-752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly C. P., Wellby M. L. Slow thyroxine binding globulin in the pathogenesis of increased dialysable fraction of thyroxine in nonthyroidal illnesses. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Jul;57(1):15–18. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savu L., Vranckx R., Maya M., Nunez E. A. A thyroxine binding globulin (TBG)-like protein in the sera of developing and adult rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 13;148(3):1165–1173. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80255-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savu L., Vranckx R., Maya M., Nunez E. A. Binding activities of thyroxine binding globulin versus thyroxine binding prealbumin in rat sera: differential modulation by thyroid hormone ligands, oleic acid and pharmacological drugs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 31;159(3):919–926. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92196-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savu L., Vranckx R., Rouaze-Romet M., Maya M., Nunez E. A., Tréton J., Flink I. L. A senescence up-regulated protein: the rat thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jul 26;1097(1):19–22. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(91)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabachnick M., Korcek L. Effect of long-chain fatty acids on the binding of thyroxine and triiodothyronine to human thyroxine-binding globulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Apr 11;881(2):292–296. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasaki T., Pardridge W. M. Differential binding of thyroxine and triiodothyronine to acidic isoforms of thyroid hormone binding globulin in human serum. Biochemistry. 1988 May 17;27(10):3624–3628. doi: 10.1021/bi00410a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vranckx R., Rouaze M., Savu L., Nunez E. A., Beaumont C., Flink I. L. The hepatic biosynthesis of rat thyroxine binding globulin (TBG): demonstration, ontogenesis, and up-regulation in experimental hypothyroidism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Feb 28;167(1):317–322. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91767-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vranckx R., Savu L., Maya M., Nunez E. A. Characterization of a major development-regulated serum thyroxine-binding globulin in the euthyroid mouse. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 15;271(2):373–379. doi: 10.1042/bj2710373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vranckx R., Savu L., Maya M., Rouaze-Romet M., Nunez E. A. Immunological quantitation of rat and mouse thyroxine-binding globulins. Ontogenesis and sex-dependence of the circulating levels of the thyroxine-binding globulins. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1990 Dec;123(6):649–656. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1230649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vranckx R., Savu L., Nunez E. A. The microheterogeneity of rat TBG. FEBS Lett. 1989 Feb 27;244(2):343–346. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80559-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P., Dubois J. D., Dussault J. H. Free thyroid hormone concentrations during postnatal development in the rat. Pediatr Res. 1980 Mar;14(3):247–249. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198003000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Meyers B., Alex S., Fang S. L., Braverman L. E. Thyroxine binding to serum thyronine-binding globulin in thyroidectomized adult and normal neonatal rats. Endocrinology. 1988 May;122(5):2318–2323. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-5-2318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn A. B., Marshall J. S., Carlson D. M. Carbohydrate structures of thyroxine-binding globulin and their effects on hepatocyte membrane binding. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6768–6773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]