Abstract
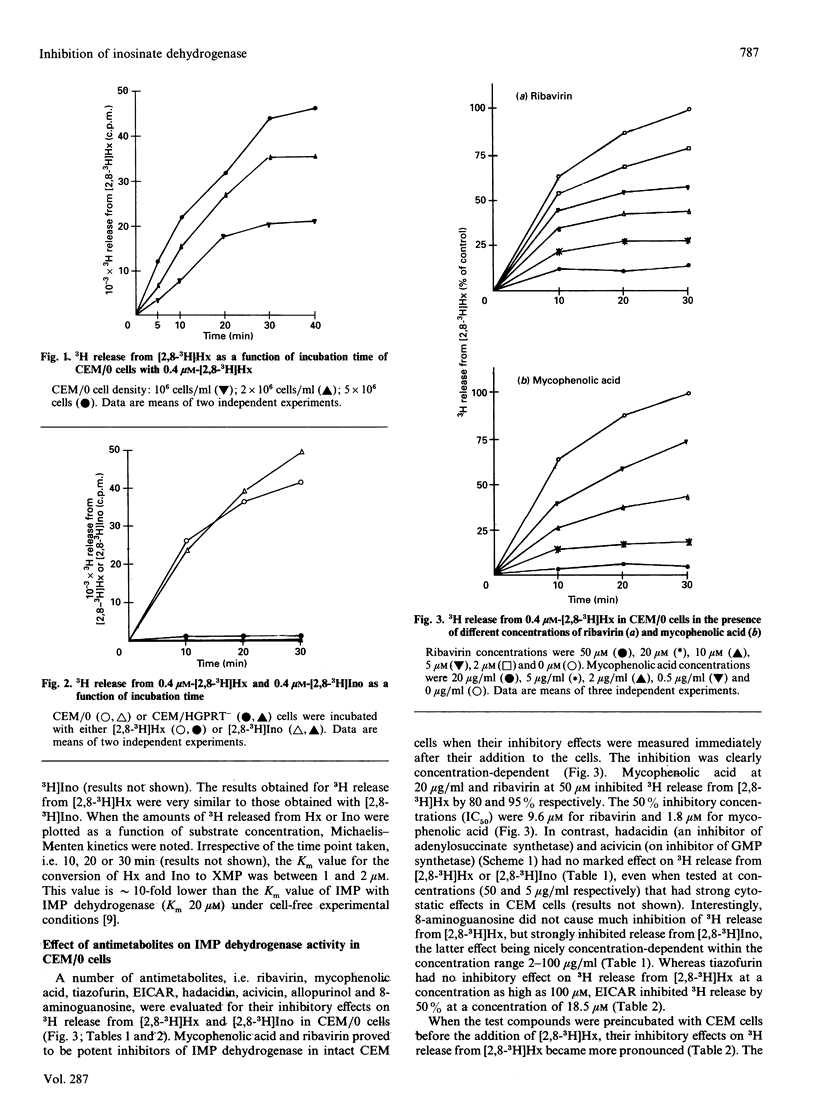
A rapid and convenient method has been developed to monitor the inhibition of inosinate (IMP) dehydrogenase by antimetabolites in intact human CEM lymphocytes. This method is based on the determination of 3H release from [2,8-3H]hypoxanthine ([2,8-3H]Hx) or [2,8-3H]inosine ([2,8-3H]Ino). The validity of this procedure was assessed by evaluating IMP dehydrogenase inhibition in intact CEM cells by the well-known IMP dehydrogenase inhibitors ribavirin, mycophenolic acid and tiazofurin. As reference materials, several compounds that are targeted at other enzymes in de novo purine nucleotide anabolism (i.e. hadacidine, acivicin) or catabolism (i.e. 8-aminoguanosine, allopurinol) were evaluated. There was a strong correlation between the inhibitory effects of the IMP dehydrogenase inhibitors (ribavirin, mycophenolic acid, tiazofurin) on 3H release from [2,8-3H]Hx and [2,8-3H]Ino in intact CEM cells and their ability to decrease intracellular GTP pool levels. The other compounds (hadacidine, acivicin, 8-aminoguanosine, allopurinol) had no marked effect on 3H release from [2,8-3H]Hx. Using this method, we demonstrated that the novel ribavirin analogue, 5-ethynyl-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylimidazole-4-carboxamide, is a potent inhibitor of IMP dehydrogenase in intact cells.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahluwalia G. S., Cooney D. A., Marquez V. E., Jayaram H. N., Johns D. G. Studies on the mechanism of action of tiazofurin (2-beta-D-ribofuranosylthiazole-4-carboxamide). VI. Biochemical and pharmacological studies on the degradation of thiazole-4-carboxamide adenine dinucleotide (TAD). Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Nov 1;35(21):3783–3790. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90665-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. H., Sartorelli A. C. Inosinic acid dehydrogenase of sarcoma 180 cells. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 25;243(18):4762–4768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balzarini J., Lee C. K., Herdewijn P., De Clercq E. Mechanism of the potentiating effect of ribavirin on the activity of 2',3'-dideoxyinosine against human immunodeficiency virus. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21509–21514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balzarini J., Lee C. K., Schols D., De Clercq E. 1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide (ribavirin) and 5-ethynyl-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylimidazole-4-carboxamide (EICAR) markedly potentiate the inhibitory effect of 2',3'-dideoxyinosine on human immunodeficiency virus in peripheral blood lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jul 31;178(2):563–569. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90145-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney D. A., Jayaram H. N., Glazer R. I., Kelley J. A., Marquez V. E., Gebeyehu G., Van Cott A. C., Zwelling L. A., Johns D. G. Studies on the mechanism of action of tiazofurin metabolism to an analog of NAD with potent IMP dehydrogenase-inhibitory activity. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1983;21:271–303. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(83)90019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Cools M., Balzarini J., Snoeck R., Andrei G., Hosoya M., Shigeta S., Ueda T., Minakawa N., Matsuda A. Antiviral activities of 5-ethynyl-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylimidazole-4- carboxamide and related compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Apr;35(4):679–684. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.4.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebeyehu G., Marquez V. E., Van Cott A., Cooney D. A., Kelley J. A., Jayaram H. N., Ahluwalia G. S., Dion R. L., Wilson Y. A., Johns D. G. Ribavirin, tiazofurin, and selenazofurin: mononucleotides and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide analogues. Synthesis, structure, and interactions with IMP dehydrogenase. J Med Chem. 1985 Jan;28(1):99–105. doi: 10.1021/jm00379a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert B. E., Knight V. Biochemistry and clinical applications of ribavirin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):201–205. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda A., Minakawa N., Sasaki T., Ueda T. The design, synthesis and antileukemic activity of 5-alkynyl-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylimidazole-4-carboxamides. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1988 Jul;36(7):2730–2733. doi: 10.1248/cpb.36.2730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick J. B., King I. J., Webb P. A., Scribner C. L., Craven R. B., Johnson K. M., Elliott L. H., Belmont-Williams R. Lassa fever. Effective therapy with ribavirin. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jan 2;314(1):20–26. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198601023140104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidwell R. W., Huffman J. H., Khare G. P., Allen L. B., Witkowski J. T., Robins R. K. Broad-spectrum antiviral activity of Virazole: 1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide. Science. 1972 Aug 25;177(4050):705–706. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4050.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeter D. G., Witkowski J. T., Khare G. P., Sidwell R. W., Bauer R. J., Robins R. K., Simon L. N. Mechanism of action of 1- -D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide (Virazole), a new broad-spectrum antiviral agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1174–1178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tricot G., Jayaram H. N., Weber G., Hoffman R. Tiazofurin: biological effects and clinical uses. Int J Cell Cloning. 1990 May;8(3):161–170. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530080303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G. Biochemical strategy of cancer cells and the design of chemotherapy: G. H. A. Clowes Memorial Lecture. Cancer Res. 1983 Aug;43(8):3466–3492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G., Natsumeda Y., Pillwein K. Targets and markers of selective action of tiazofurin. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1985;24:45–65. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(85)90069-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis R. C., Carson D. A., Seegmiller J. E. Adenosine kinase initiates the major route of ribavirin activation in a cultured human cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3042–3044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



