Abstract
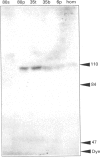
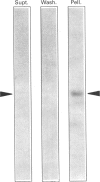
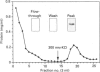
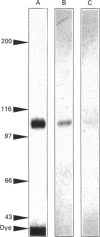
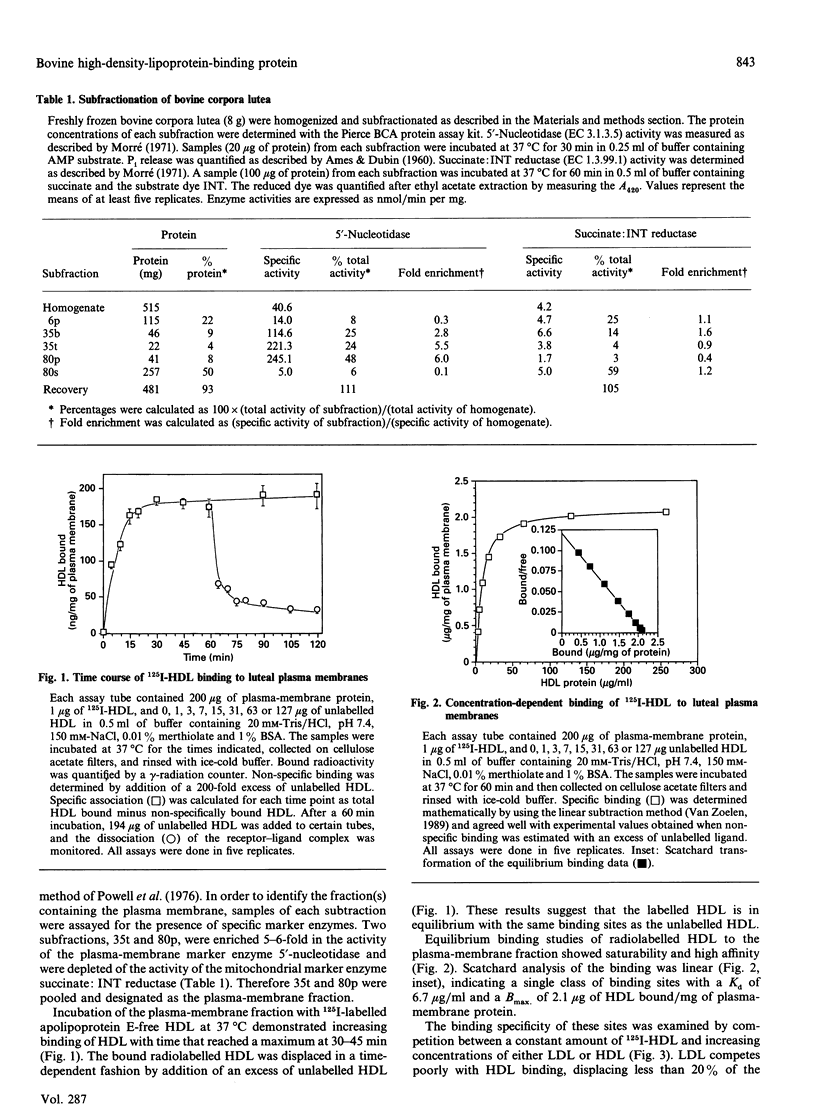
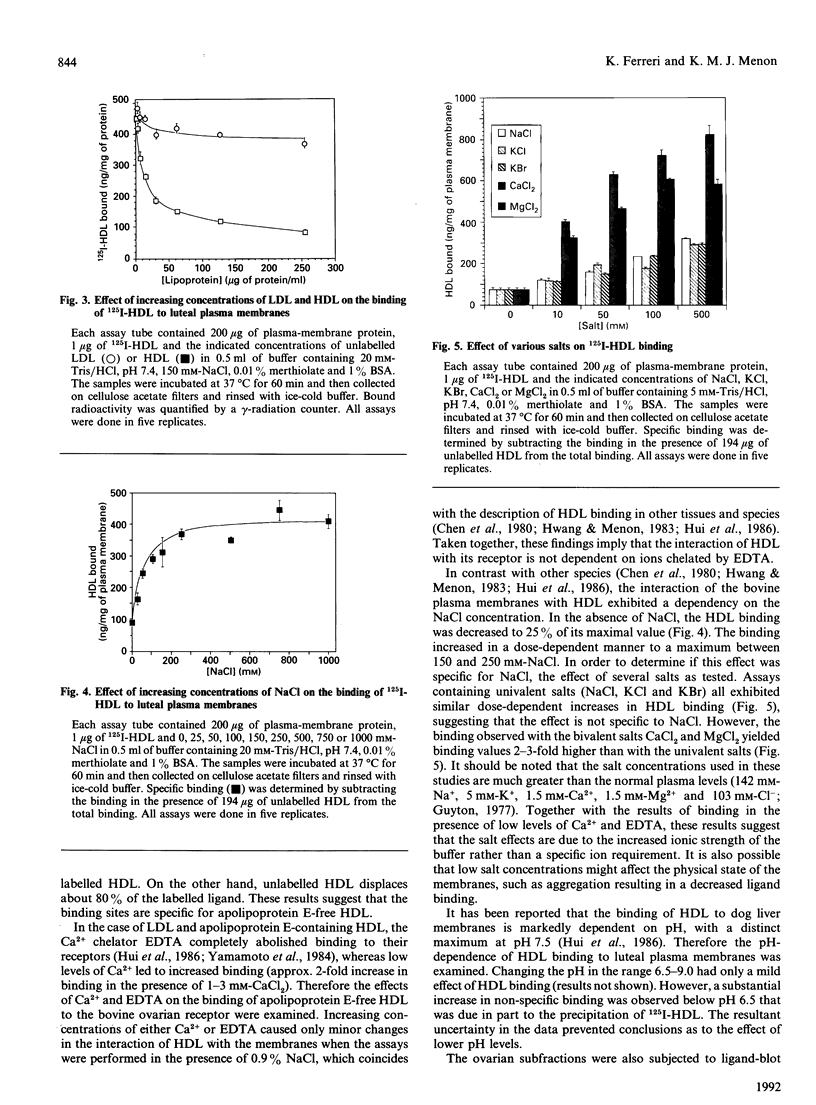
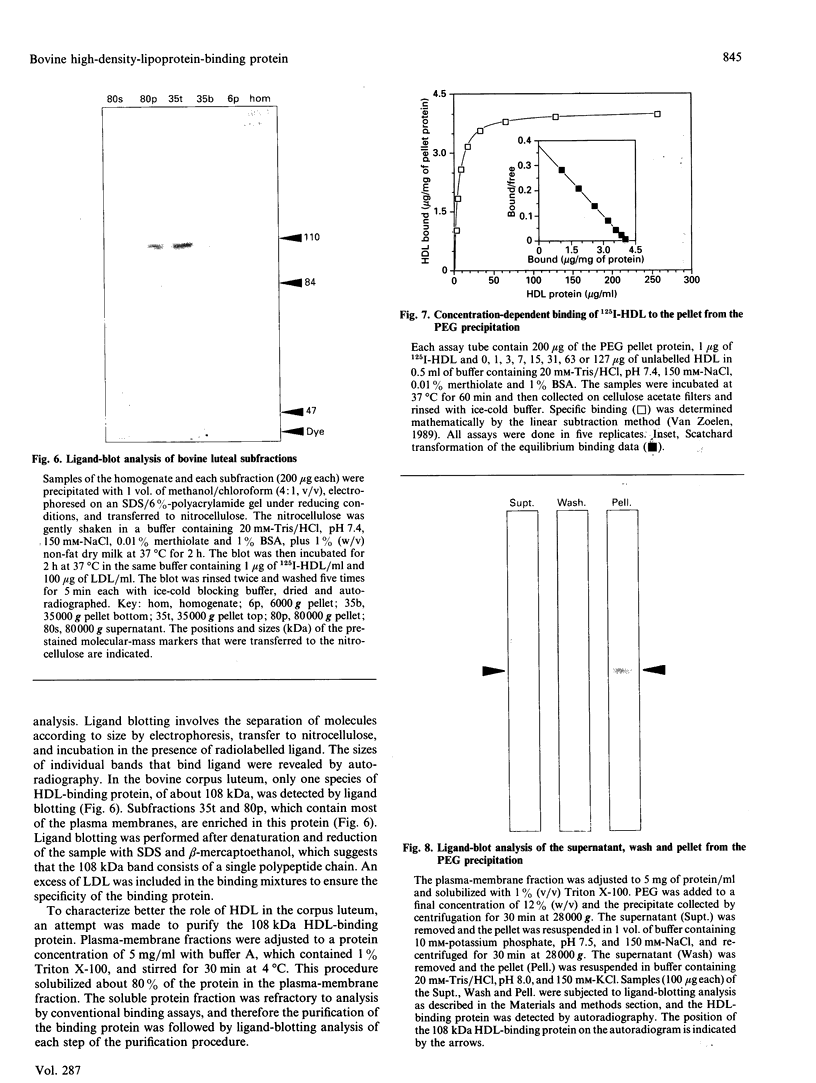
The ovary uses the cholesterol from high-density lipoproteins (HDL) as a substrate source for steroid hormone production. It is not clear, however, how ovarian cells acquire the lipoprotein cholesterol. This study describes the characterization and isolation of a high-affinity-binding protein for apolipoprotein E-free HDL from the plasma-membrane fraction of bovine corpora lutea. Plasma membranes were prepared by differential centrifugation with 5-6-fold enrichment of 5'-nucleotidase activity. The binding of 125I-HDL to the plasma membranes was time-dependent, and there appeared to be a single high-affinity site with a Kd of 6.7 micrograms of HDL/ml of assay buffer. The binding was not affected by high concentrations of low-density lipoproteins or the Ca2+ chelator EDTA, nor by changes in pH in the range 6.5-9.0. The binding was affected by the salt concentration in the buffer, with a dose-dependent increase that reached a maximum at 150-250 mM-NaCl. Binding was increased in the presence of high concentrations of KCl and KBr, and most significantly increased by high concentrations of bivalent metal ions. Ligand-blot analysis under reducing conditions revealed that the binding protein was a single polypeptide of about 108 kDa that was associated with the plasma-membrane fraction. This HDL-binding protein was purified to homogeneity by solubilization with Triton X-100, poly(ethylene glycol) precipitation, DEAE-Sephadex chromatography, and preparative SDS/PAGE. The purified binding protein is a single polypeptide of 108 kDa that retains high affinity and specificity for HDL as assayed by ligand blotting.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen J. M., Dietschy J. M. Kinetic parameters of the lipoprotein transport systems in the adrenal gland of the rat determined in vivo. Comparison of low and high density lipoproteins of human and rat origin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7362–7370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen J. M., Dietschy J. M. Relative importance of high and low density lipoproteins in the regulation of cholesterol synthesis in the adrenal gland, ovary, and testis of the rat. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):9024–9032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbaras R., Puchois P., Fruchart J. C., Pradines-Figueres A., Ailhaud G. Purification of an apolipoprotein A binding protein from mouse adipose cells. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 1;269(3):767–773. doi: 10.1042/bj2690767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond H. M., Morrone G., Venuta S., Howell K. E. Characterization and purification of proteins which bind high-density lipoprotein. A putative cell-surface receptor. Biochem J. 1991 Nov 1;279(Pt 3):633–641. doi: 10.1042/bj2790633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):34–47. doi: 10.1126/science.3513311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. D., Kraemer F. B., Reaven G. M. Identification of specific high density lipoprotein-binding sites in rat testis and regulation of binding by human chorionic gonadotropin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9162–9167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darbon J. M., Tournier J. F., Tauber J. P., Bayard F. Possible role of protein phosphorylation in the mitogenic effect of high density lipoproteins on cultured vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):8002–8008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreri K., Menon K. M. Detection of a 58-kilodalton high density lipoprotein-binding protein in the membrane fraction of luteinized rat ovaries. Endocrinology. 1990 Apr;126(4):2137–2144. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-4-2137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong B. S., Salter A. M., Jimenez J., Angel A. The role of apolipoprotein A-I and apolipoprotein A-II in high-density lipoprotein binding to human adipocyte plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 31;920(2):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90249-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh D. K., Menon K. M. Induction of high-density-lipoprotein receptors in rat corpus luteum by human choriogonadotropin. Evidence of protein synthesis de novo. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 1;244(2):471–479. doi: 10.1042/bj2440471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotto A. M., Jr, Pownall H. J., Havel R. J. Introduction to the plasma lipoproteins. Methods Enzymol. 1986;128:3–41. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)28061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. L., Oram J. F. Identification and characterization of a high density lipoprotein-binding protein in cell membranes by ligand blotting. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7439–7442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui D. Y., Brecht W. J., Hall E. A., Friedman G., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Isolation and characterization of the apolipoprotein E receptor from canine and human liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4256–4267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang J., Menon K. M. Binding of apolipoprotein A-I and A-II after recombination with phospholipid vesicles to the high density lipoprotein receptor of luteinized rat ovary. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5660–5668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang J., Menon K. M. Characterization of low density and high density lipoprotein receptors in the rat corpus luteum and regulation by gonadotropin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8020–8027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. J., Mahlberg F. H., Chacko G. K., Phillips M. C., Rothblat G. H. The influence of cellular and lipoprotein cholesterol contents on the flux of cholesterol between fibroblasts and high density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14099–14106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin J. B., Johnson W. J., Benedict C. R., Chacko G. K., Phillips M. C., Rothblat G. H. Cholesterol flux between cells and high density lipoprotein. Lack of relationship to specific binding of the lipoprotein to the cell surface. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12557–12564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalazar A., Weisgraber K. H., Rall S. C., Jr, Giladi H., Innerarity T. L., Levanon A. Z., Boyles J. K., Amit B., Gorecki M., Mahley R. W. Site-specific mutagenesis of human apolipoprotein E. Receptor binding activity of variants with single amino acid substitutions. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3542–3545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall S., Heidenreich K. A., Horikoshi H. Stoichiometric translocation of adipocyte insulin receptors from the cell-surface to the cell-interior. Studies using a novel method to rapidly remove detergent and concentrate soluble receptors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4128–4135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. Efficient trace-labelling of proteins with iodine. Nature. 1958 Jul 5;182(4627):53–53. doi: 10.1038/182053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel C. M., Kunitake S. T., Kane J. P. Discrimination between subclasses of human high-density lipoproteins by the HDL binding sites of bovine liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 3;875(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez A. J., Oram J. F., Bierman E. L. Protein kinase C as a mediator of high density lipoprotein receptor-dependent efflux of intracellular cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10104–10111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer M. J., Oram J. F., Bierman E. L. Up-regulation of high density lipoprotein receptor activity by gamma-interferon associated with inhibition of cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19318–19323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. F., Johnson C. J., Brown T. A. Interaction of high density lipoprotein with its receptor on cultured fibroblasts and macrophages. Evidence for reversible binding at the cell surface without internalization. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2405–2410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. F. Receptor-mediated transport of cholesterol between cultured cells and high-density lipoproteins. Methods Enzymol. 1986;129:645–659. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)29096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paavola L. G., Strauss J. F., 3rd Uptake of lipoproteins by in situ perfused rat ovaries: identification of binding sites for high density lipoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):593–606. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell W. S., Hammerström S., Samuelsson B. Localization of a prostaglandin F2alpha receptor in bovine Corpus luteum plasma membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jan 15;61(2):605–611. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahim A. T., Miyazaki A., Morino Y., Horiuchi S. Biochemical demonstration of endocytosis and subsequent resecretion of high-density lipoprotein by rat peritoneal macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 12;1082(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(91)90194-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajan V. P., Menon K. M. Involvement of microtubules in lipoprotein degradation and utilization for steroidogenesis in cultured rat luteal cells. Endocrinology. 1985 Dec;117(6):2408–2416. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-6-2408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajan V. P., Menon K. M. Metabolism of high-density lipoproteins in cultured rat luteal cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Sep 4;921(1):25–37. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90166-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran K. G., Hwang J., Menon K. M. Binding, degradation, and utilization of plasma high density and low density lipoproteins for progesterone production in cultured rat luteal cells. Endocrinology. 1983 May;112(5):1746–1753. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-5-1746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifici V. A., Eder H. A. A hepatocyte receptor for high-density lipoproteins specific for apolipoprotein A-I. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13814–13818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber J. R., Nakamura K., Weinstein D. B. Degradation of rat and human lipoproteins by cultured rat ovary granulosa cells. Endocrinology. 1982 Jan;110(1):55–63. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-1-55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slotte J. P., Oram J. F., Bierman E. L. Binding of high density lipoproteins to cell receptors promotes translocation of cholesterol from intracellular membranes to the cell surface. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):12904–12907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss J. F., 3rd, MacGregor L. C., Gwynne J. T. Uptake of high density lipoproteins by rat ovaries in vivo and dispersed ovarian cells in vitro. Direct correlation of high density lipoprotein uptake with steroidogenic activity. J Steroid Biochem. 1982 Apr;16(4):525–531. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(82)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talavera F., Menon K. M. Regulation of rat luteal cell high density lipoprotein receptors: up-regulation in response to changes in intracellular cholesterol concentration. Endocrinology. 1989 Oct;125(4):2015–2021. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-4-2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tozuka M., Fidge N. Purification and characterization of two high-density-lipoprotein-binding proteins from rat and human liver. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 1;261(1):239–244. doi: 10.1042/bj2610239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tóth I. E., Szabó D., Bácsy E., Szalay K. S., Hesz A., Szollár L. G. Morphological evidence of lysosomal uptake of high-density lipoproteins by rat adrenocortical cells in vitro. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1986 Feb;44(2):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(86)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tóth I. E., Szabó D., Szalay K. S., Gyévai A., Szollár L. G., Gláz E. Colloidal gold-labeled lipoprotein binding and internalization in adrenocortical cells in vitro. Clin Biochem. 1988 Apr;21(2):101–105. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9120(88)80096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel D., Flügge U. I. A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90782-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Brown M. S., Schneider W. J., Casey M. L., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. The human LDL receptor: a cysteine-rich protein with multiple Alu sequences in its mRNA. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zoelen E. J. Receptor-ligand interaction: a new method for determining binding parameters without a priori assumptions on non-specific binding. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):549–556. doi: 10.1042/bj2620549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]