Abstract
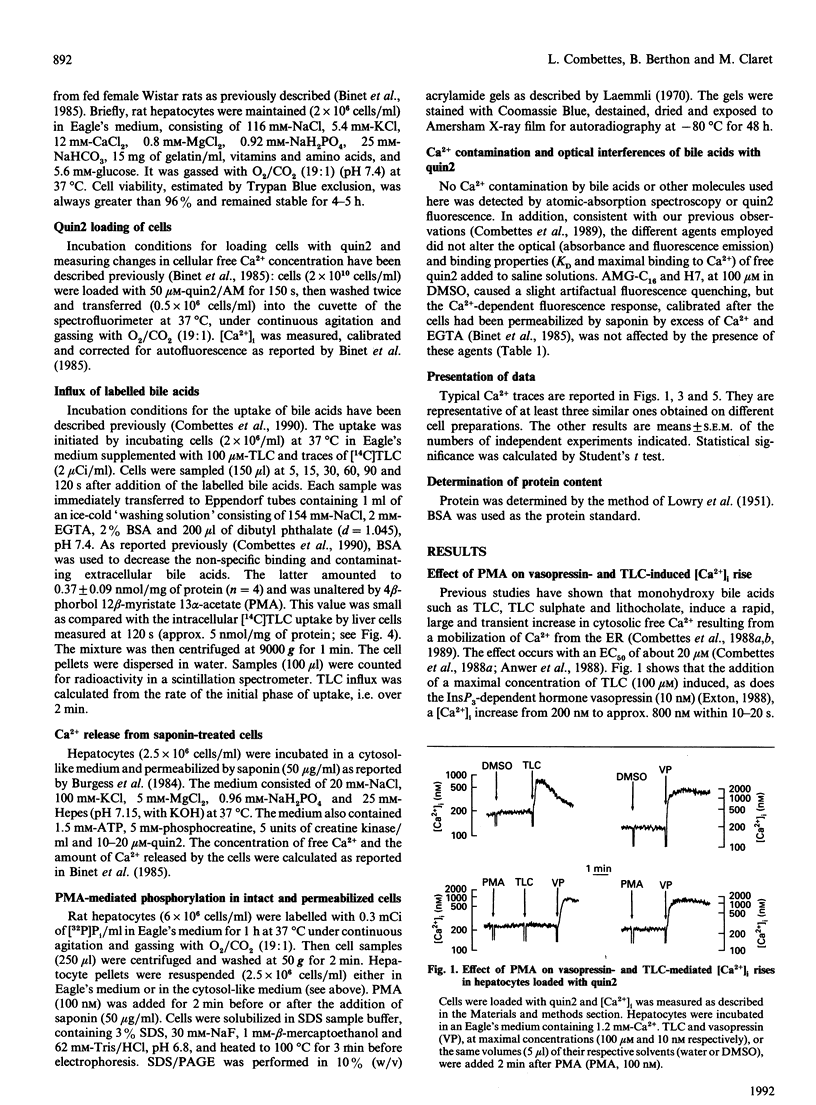
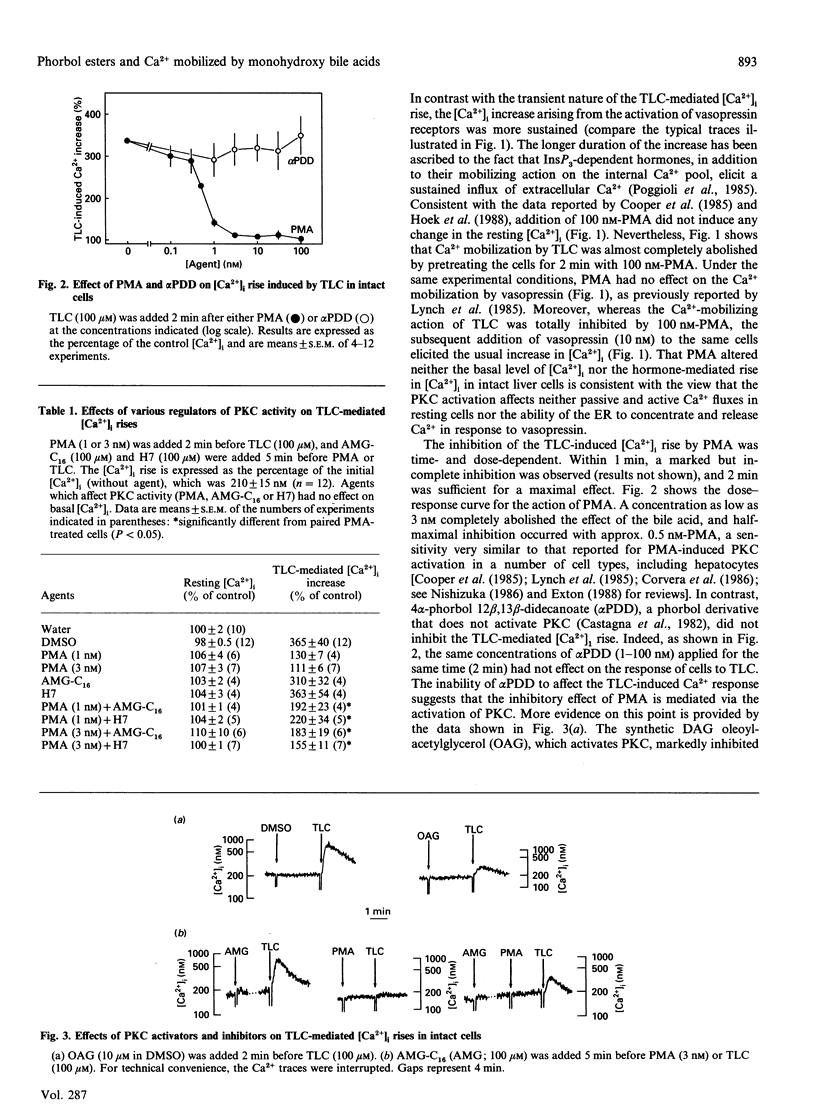
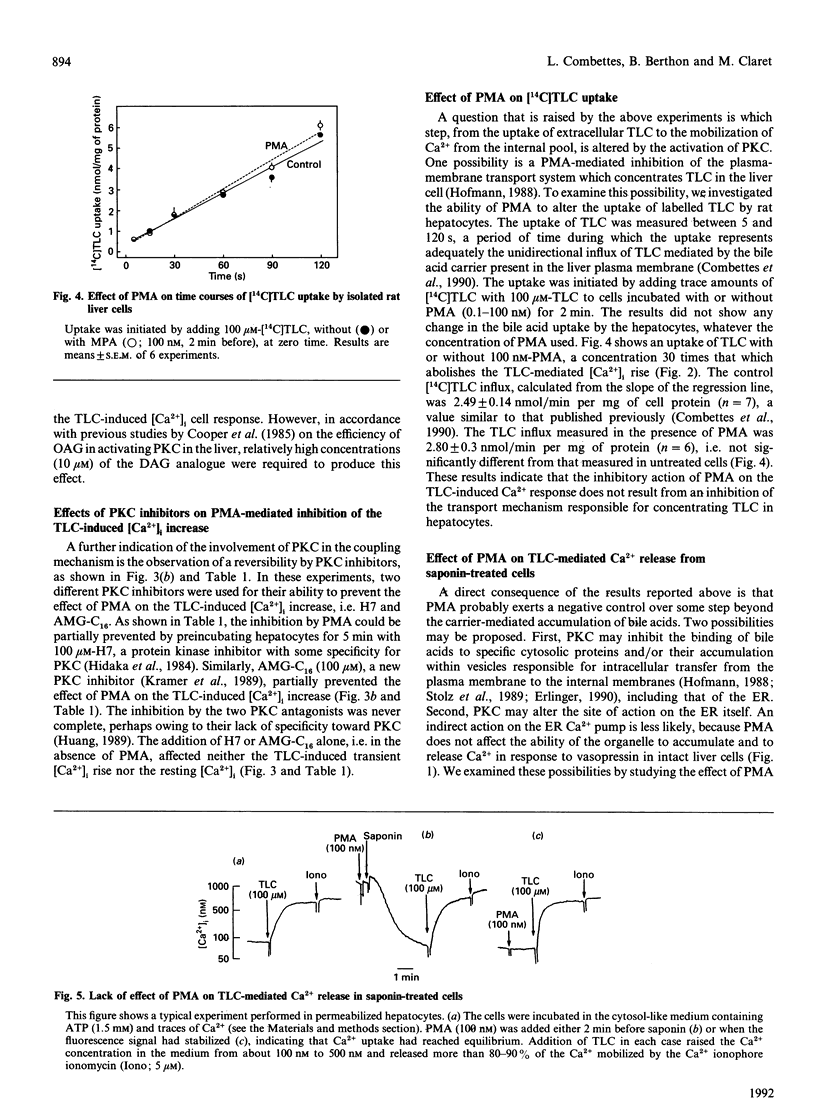
The monohydroxy bile acid taurolithocholate (TLC) causes a rapid and transient increase in free cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) in suspensions of rat hepatocytes similar to that elicited by the InsP3-dependent hormone vasopressin. The effect of the bile acid is due to a mobilization of Ca2+, independent of InsP3, from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Short-term preincubation of cells with the phorbol ester 4 beta-phorbol 12 beta-myristate 13 alpha-acetate (PMA), which activates protein kinase C (PKC), blocked the increase in [Ca2+]i induced by TLC, but did not alter that mediated by vasopressin. We obtained the following results, indicating that the effect of PMA is mediated by the activation of PKC. (1) Phorbol esters were effective over a concentration range where they activate PKC (IC50 = 0.5 nM); (2) phorbol esters that do not activate PKC did not inhibit the effects of TLC; (3) the permeant analogue oleoylacetylglycerol mimicked the inhibitory effect of PMA; (4) lastly, the inhibition of the TLC-induced Ca2+ mobilization by phorbol esters was partially prevented by preincubating the cells with the PKC inhibitors H7 and AMG-C16. Preincubating hepatocytes with PMA had no effect on the cell uptake of labelled TLC, indicating that the phorbol ester does not interfere with the transport system responsible for the accumulation of bile acids. In saponin-treated liver cells, PMA added before or after permeabilization failed to abolish TLC-induced Ca2+ release from the ER. The possibility is discussed that PMA, via PKC activation, may alter the intracellular binding or the transfer of bile acids in the liver.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anwer M. S., Engelking L. R., Nolan K., Sullivan D., Zimniak P., Lester R. Hepatotoxic bile acids increase cytosolic Ca++ activity of isolated rat hepatocytes. Hepatology. 1988 Jul-Aug;8(4):887–891. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binet A., Berthon B., Claret M. Hormone-induced increase in free cytosolic calcium and glycogen phosphorylase activation in rat hepatocytes incubated in normal and low-calcium media. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 15;228(3):565–574. doi: 10.1042/bj2280565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capiod T., Combettes L., Noel J., Claret M. Evidence for bile acid-evoked oscillations of Ca2(+)-dependent K+ permeability unrelated to a D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate effect in isolated guinea pig liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):268–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combettes L., Berthon B., Doucet E., Erlinger S., Claret M. Bile acids mobilise internal Ca2+ independently of external Ca2+ in rat hepatocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 5;190(3):619–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15617.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combettes L., Berthon B., Doucet E., Erlinger S., Claret M. Characteristics of bile acid-mediated Ca2+ release from permeabilized liver cells and liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):157–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combettes L., Dumont M., Berthon B., Erlinger S., Claret M. Effect of the bile acid taurolithocholate on cell calcium in saponin-treated rat hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 25;227(2):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80889-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combettes L., Dumont M., Berthon B., Erlinger S., Claret M. Release of calcium from the endoplasmic reticulum by bile acids in rat liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2299–2303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. H., Coll K. E., Williamson J. R. Differential effects of phorbol ester on phenylephrine and vasopressin-induced Ca2+ mobilization in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3281–3288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coquil J. F., Berthon B., Chomiki N., Combettes L., Jourdon P., Schteingart C., Erlinger S., Claret M. Effects of taurolithocholate, a Ca2(+)-mobilizing agent, on cell Ca2(+) in rat hepatocytes, human platelets and neuroblastoma NG108-15 cell line. Biochem J. 1991 Jan 1;273(Pt 1):153–160. doi: 10.1042/bj2730153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corasanti J. G., Smith N. D., Gordon E. R., Boyer J. L. Protein kinase C agonists inhibit bile secretion independently of effects on the microcirculation in the isolated perfused rat liver. Hepatology. 1989 Jul;10(1):8–13. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvera S., Schwarz K. R., Graham R. M., García-Sáinz J. A. Phorbol esters inhibit alpha 1-adrenergic effects and decrease the affinity of liver cell alpha 1-adrenergic receptors for (-)-epinephrine. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):520–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlinger S. Role of intracellular organelles in the hepatic transport of bile acids. Biomed Pharmacother. 1990;44(8):409–416. doi: 10.1016/0753-3322(90)90045-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Role of phosphoinositides in the regulation of liver function. Hepatology. 1988 Jan-Feb;8(1):152–166. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Tawada Y., Shigekawa M. Protein kinase C activation stimulates plasma membrane Ca2+ pump in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4844–4849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoek J. B., Rubin R., Thomas A. P. Ethanol-induced phospholipase C activation is inhibited by phorbol esters in isolated hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1988 May 1;251(3):865–871. doi: 10.1042/bj2510865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. P. The mechanism of protein kinase C activation. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Nov;12(11):425–432. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Thomas A. P., Williams R. J., Irvine R. F., Williamson J. R. myo-Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. A second messenger for the hormonal mobilization of intracellular Ca2+ in liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3077–3081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer I. M., van der Bend R. L., Tool A. T., van Blitterswijk W. J., Roos D., Verhoeven A. J. 1-O-hexadecyl-2-Q-methylglycerol, a novel inhibitor of protein kinase C, inhibits the respiratory burst in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5876–5884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagast H., Pozzan T., Waldvogel F. A., Lew P. D. Phorbol myristate acetate stimulates ATP-dependent calcium transport by the plasma membrane of neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):878–883. doi: 10.1172/JCI111284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch C. J., Charest R., Bocckino S. B., Exton J. H., Blackmore P. F. Inhibition of hepatic alpha 1-adrenergic effects and binding by phorbol myristate acetate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2844–2851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montrose M. H., Lester R., Zimniak P., Anwer M. S., Murer H. Bile acids increase cellular free calcium in cultured kidney cells (LLC-PK). Pflugers Arch. 1988 Jul;412(1-2):164–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00583746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson M. H., Boyer J. L. Mechanisms and regulation of bile secretion. Hepatology. 1991 Sep;14(3):551–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poggioli J., Mauger J. P., Guesdon F., Claret M. A regulatory calcium-binding site for calcium channel in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3289–3294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimniak P., Little J. M., Radominska A., Oelberg D. G., Anwer M. S., Lester R. Taurine-conjugated bile acids act as Ca2+ ionophores. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 3;30(35):8598–8604. doi: 10.1021/bi00099a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


