Abstract
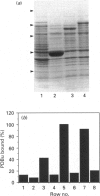
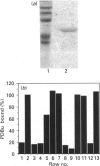
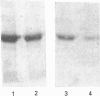
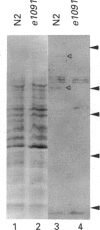
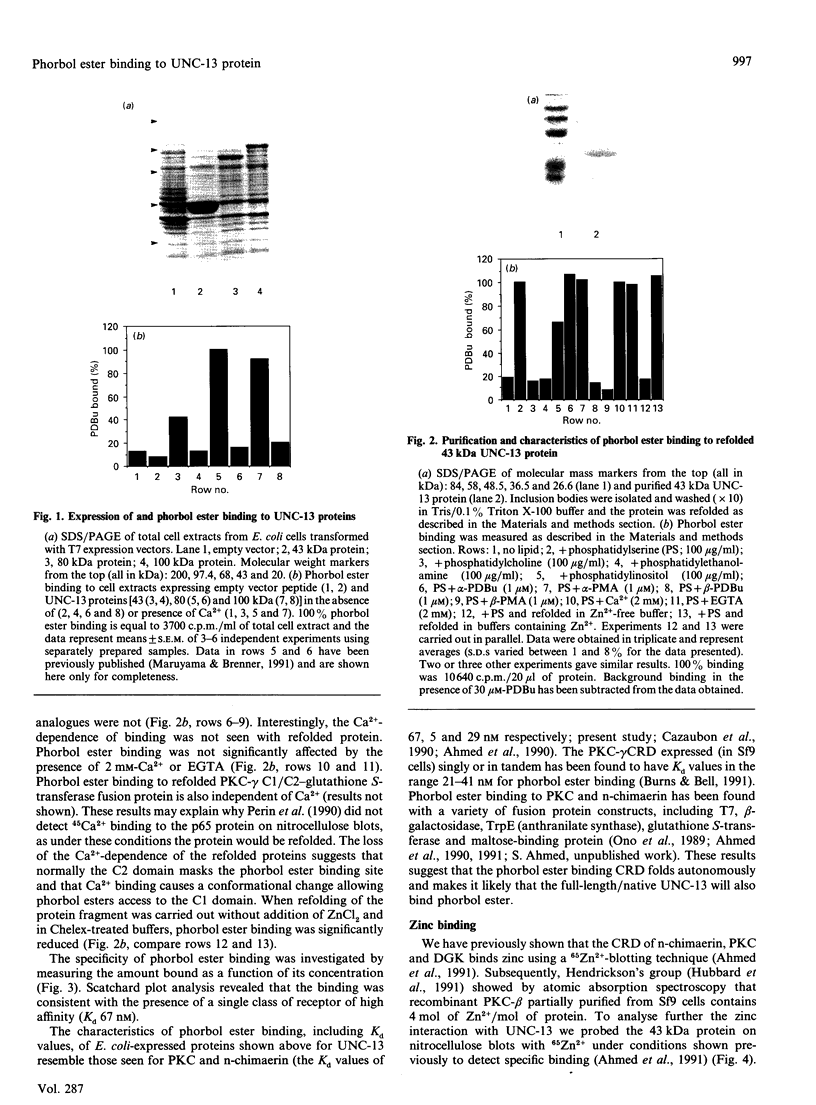
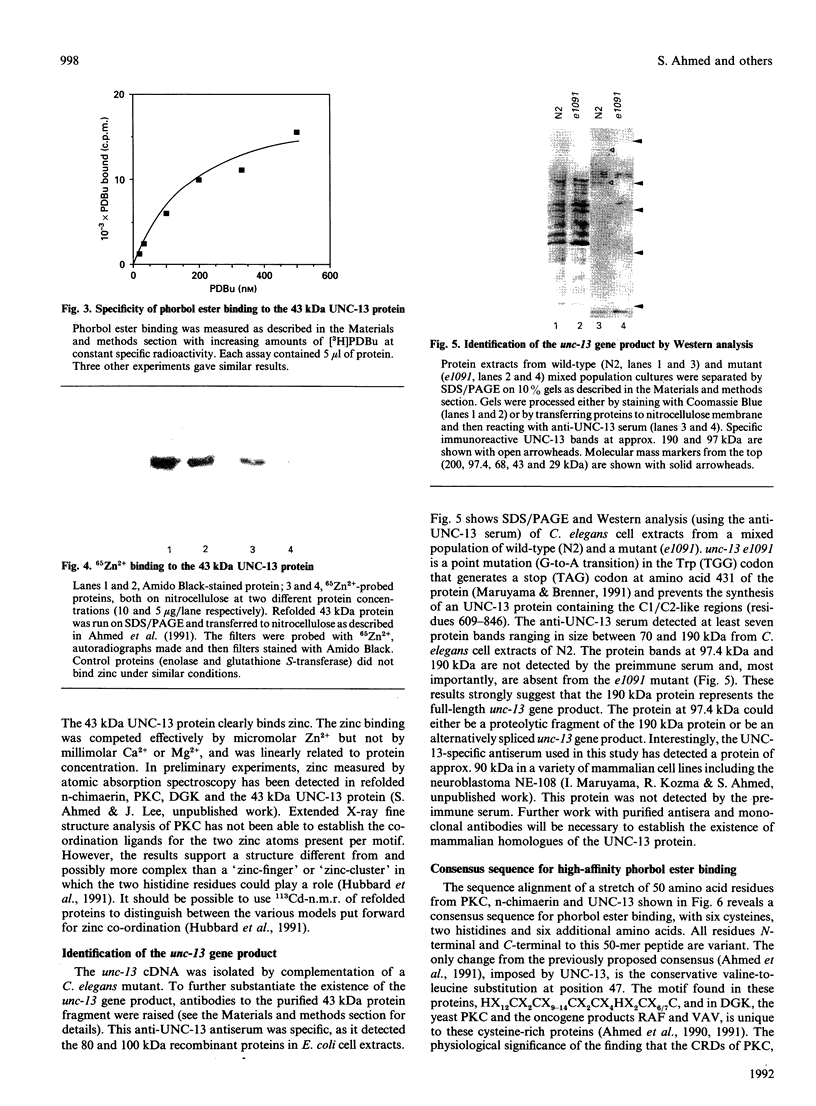
The Caenorhabditis elegans unc-13 mutant is a member of a class of mutants that have un-coordinated movement. Mutations of the unc-13 gene cause diverse defects in C. elegans, including abnormal neuronal connections and modified synaptic transmission in the nervous system. unc-13 cDNA encodes a protein (UNC-13) of 1734 amino acid residues with a predicted molecular mass of 198 kDa and sequence identity to the C1/C2 regions but not to the catalytic domain of the ubiquitously expressed protein kinase C family [Maruyama & Brenner (1991) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 5729-5733]. To characterize the phorbol ester binding site of the UNC-13 protein, cDNA encoding the C1/C2-like regions (amino acid residues 546-940) was expressed in Escherichia coli and the 43 kDa recombinant protein was purified. Phorbol ester binding to the 43 kDa protein was zinc- and phospholipid-dependent, stereospecific and of high affinity (Kd 67 nM). UNC-13 specific antisera detected a protein of approx. 190 kDa in wild-type (N2) but not in mutant (e1019) C. elegans cell extracts. We conclude that UNC-13 represents a novel class of phorbol ester receptor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed S., Kozma R., Lee J., Monfries C., Harden N., Lim L. The cysteine-rich domain of human proteins, neuronal chimaerin, protein kinase C and diacylglycerol kinase binds zinc. Evidence for the involvement of a zinc-dependent structure in phorbol ester binding. Biochem J. 1991 Nov 15;280(Pt 1):233–241. doi: 10.1042/bj2800233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed S., Kozma R., Monfries C., Hall C., Lim H. H., Smith P., Lim L. Human brain n-chimaerin cDNA encodes a novel phorbol ester receptor. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 15;272(3):767–773. doi: 10.1042/bj2720767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns D. J., Bell R. M. Protein kinase C contains two phorbol ester binding domains. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18330–18338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazaubon S., Webster C., Camoin L., Strosberg A. D., Parker P. Effector-dependent conformational changes in protein kinase C gamma through epitope mapping with inhibitory monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Dec 27;194(3):799–804. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. D., Lin L. L., Kriz R. W., Ramesha C. S., Sultzman L. A., Lin A. Y., Milona N., Knopf J. L. A novel arachidonic acid-selective cytosolic PLA2 contains a Ca(2+)-dependent translocation domain with homology to PKC and GAP. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90556-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto Y., Shudo K. Cytosolic-nuclear tumor promoter-specific binding protein (CN-TPBP) in human promyelocytic leukemia cells HL-60. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Feb 14;166(3):1126–1132. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90983-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. R., Bishop W. R., Kirschmeier P., George S. J., Cramer S. P., Hendrickson W. A. Identification and characterization of zinc binding sites in protein kinase C. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1776–1779. doi: 10.1126/science.1763327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama I. N., Brenner S. A phorbol ester/diacylglycerol-binding protein encoded by the unc-13 gene of Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5729–5733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Akita Y., Konno Y., Imajoh S., Suzuki K. A novel phorbol ester receptor/protein kinase, nPKC, distantly related to the protein kinase C family. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):731–741. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90091-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Ogita K., Kikkawa U., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C zeta subspecies from rat brain: its structure, expression, and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3099–3103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perin M. S., Fried V. A., Mignery G. A., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Phospholipid binding by a synaptic vesicle protein homologous to the regulatory region of protein kinase C. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):260–263. doi: 10.1038/345260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane F., Yamada K., Kanoh H., Yokoyama C., Tanabe T. Porcine diacylglycerol kinase sequence has zinc finger and E-F hand motifs. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):345–348. doi: 10.1038/344345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]