Abstract
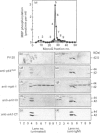
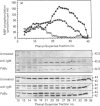
Cross-linking of membrane immunoglobulin (mIg), the B lymphocyte antigen receptor, with anti-receptor antibodies stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of a number of proteins, including one of 42 kDa. Proteins with a similar molecular mass are tyrosine-phosphorylated in response to receptor stimulation in other cell types and have been identified as serine/threonine kinases, termed mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases or extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs). The MAP kinases constitute a family of related kinases, at least three of which have molecular masses of 40-45 kDa. In this paper we show that mIg cross-linking stimulated the myelin basic protein phosphotransferase activity characteristic of MAP kinase in both mature and immature murine B cell lines. This enzyme activity co-purified on three different columns with a 42 kDa protein that was tyrosine-phosphorylated (pp42) in response to mIg cross-linking and which reacted with a panel of anti-(MAP kinase) antibodies. Although immunoblotting with the anti-(MAP kinase) antibodies showed that these B cell lines expressed both 42 kDa and 44 kDa forms of MAP kinase, only the 42 kDa form was activated and tyrosine-phosphorylated to a significant extent. Activation of protein kinase C (PKC) with phorbol esters also resulted in selective tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of the 42 kDa MAP kinase. This suggested that mIg-induced MAP kinase activation could be due to stimulation of PKC by mIg. However, mIg-stimulated MAP kinase activation and pp42 tyrosine phosphorylation was only partially blocked by a PKC inhibitor, the staurosporine analogue Compound 3. In contrast, Compound 3 completely blocked the ability of phorbol esters to stimulate MAP kinase activity and induce tyrosine phosphorylation of pp42. Thus mIg may activate MAP kinase by both PKC-dependent and -independent mechanisms.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn N. G., Seger R., Bratlien R. L., Diltz C. D., Tonks N. K., Krebs E. G. Multiple components in an epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein kinase cascade. In vitro activation of a myelin basic protein/microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4220–4227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez E., Northwood I. C., Gonzalez F. A., Latour D. A., Seth A., Abate C., Curran T., Davis R. J. Pro-Leu-Ser/Thr-Pro is a consensus primary sequence for substrate protein phosphorylation. Characterization of the phosphorylation of c-myc and c-jun proteins by an epidermal growth factor receptor threonine 669 protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15277–15285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Li P., Marsden L. A., Williams N., Roberts T. M., Sturgill T. W. Raf-1 is a potential substrate for mitogen-activated protein kinase in vivo. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 15;277(Pt 2):573–576. doi: 10.1042/bj2770573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Maller J. L., Tonks N. K., Sturgill T. W. Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):651–653. doi: 10.1038/343651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auger K. R., Cantley L. C. Novel polyphosphoinositides in cell growth and activation. Cancer Cells. 1991 Jul;3(7):263–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benhamou L. E., Cazenave P. A., Sarthou P. Anti-immunoglobulins induce death by apoptosis in WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jun;20(6):1405–1407. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird T. A., Sleath P. R., deRoos P. C., Dower S. K., Virca G. D. Interleukin-1 represents a new modality for the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases/microtubule-associated protein-2 kinases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22661–22670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Bos T. J., Admon A., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K., Tjian R. Human proto-oncogene c-jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2825349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Cobb M. H. Identification of multiple extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) with antipeptide antibodies. Cell Regul. 1991 May;2(5):357–371. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.5.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Gregory J. S., Cobb M. H. Purification and properties of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1, an insulin-stimulated microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 8;30(1):278–286. doi: 10.1021/bi00215a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Nye S. H., Robbins D. J., Ip N. Y., Radziejewska E., Morgenbesser S. D., DePinho R. A., Panayotatos N., Cobb M. H., Yancopoulos G. D. ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):663–675. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90098-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Yancopoulos G. D., Gregory J. S., Slaughter C., Moomaw C., Hsu J., Cobb M. H. An insulin-stimulated protein kinase similar to yeast kinases involved in cell cycle control. Science. 1990 Jul 6;249(4964):64–67. doi: 10.1126/science.2164259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunswick M., Samelson L. E., Mond J. J. Surface immunoglobulin crosslinking activates a tyrosine kinase pathway in B cells that is independent of protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1311–1314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt A. L., Brunswick M., Bolen J. B., Mond J. J. Anti-immunoglobulin stimulation of B lymphocytes activates src-related protein-tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Ransom J. T. Molecular mechanisms of transmembrane signaling in B lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:175–199. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. A., Sefton B. M. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation is induced in murine B lymphocytes in response to stimulation with anti-immunoglobulin. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2125–2131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. H., Park D. J., Rhee S. G., Fearon D. T. Tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C induced by membrane immunoglobulin in B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2745–2749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casillas A., Hanekom C., Williams K., Katz R., Nel A. E. Stimulation of B-cells via the membrane immunoglobulin receptor or with phorbol myristate 13-acetate induces tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of a 42-kDa microtubule-associated protein-2 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):19088–19094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Pelech S. L., Blenis J. Mitogen-activated Swiss mouse 3T3 RSK kinases I and II are related to pp44mpk from sea star oocytes and participate in the regulation of pp90rsk activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4981–4985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Sanghera J. S., Pelech S. L. Definition of a consensus sequence for peptide substrate recognition by p44mpk, the meiosis-activated myelin basic protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15180–15184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Boulton T. G., Robbins D. J. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases: ERKs in progress. Cell Regul. 1991 Dec;2(12):965–978. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.12.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Alessandrini A. A., Erikson R. L. Mouse Erk-1 gene product is a serine/threonine protein kinase that has the potential to phosphorylate tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8845–8849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. D., Hill C. H., Keech E., Lawton G., Nixon J. S., Sedgwick A. D., Wadsworth J., Westmacott D., Wilkinson S. E. Potent selective inhibitors of protein kinase C. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):61–63. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81494-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L. Molecular aspects of B-lymphocyte activation. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:143–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely C. M., Oddie K. M., Litz J. S., Rossomando A. J., Kanner S. B., Sturgill T. W., Parsons S. J. A 42-kD tyrosine kinase substrate linked to chromaffin cell secretion exhibits an associated MAP kinase activity and is highly related to a 42-kD mitogen-stimulated protein in fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):731–742. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ettehadieh E., Sanghera J. S., Pelech S. L., Hess-Bienz D., Watts J., Shastri N., Aebersold R. Tyrosyl phosphorylation and activation of MAP kinases by p56lck. Science. 1992 Feb 14;255(5046):853–855. doi: 10.1126/science.1311128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Martin G. S. Identification of a 42-kilodalton phosphotyrosyl protein as a serine(threonine) protein kinase by renaturation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3020–3026. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Zokas L., Kamps M. P. Monoclonal antibodies to phosphotyrosine. J Immunol Methods. 1988 May 9;109(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90253-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Chan V. W., Turck C. W., DeFranco A. L. Membrane Ig cross-linking regulates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2012–2022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Law D. A., DeFranco A. L. Stimulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation by the B-lymphocyte antigen receptor. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):810–813. doi: 10.1038/345810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Matsuuchi L., Kelly R. B., DeFranco A. L. Tyrosine phosphorylation of components of the B-cell antigen receptors following receptor crosslinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3436–3440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodnow C. C., Crosbie J., Adelstein S., Lavoie T. B., Smith-Gill S. J., Brink R. A., Pritchard-Briscoe H., Wotherspoon J. S., Loblay R. H., Raphael K. Altered immunoglobulin expression and functional silencing of self-reactive B lymphocytes in transgenic mice. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):676–682. doi: 10.1038/334676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez N., Cohen P. Dissection of the protein kinase cascade by which nerve growth factor activates MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):170–173. doi: 10.1038/353170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasbold J., Klaus G. G. Anti-immunoglobulin antibodies induce apoptosis in immature B cell lymphomas. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Aug;20(8):1685–1690. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempel W. M., Schatzman R. C., DeFranco A. L. Tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 2 upon cross-linking of membrane Ig on murine B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 May 15;148(10):3021–3027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi M., Nishida E., Sakai H. Activation of a Ca2+-inhibitable protein kinase that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 2 in vitro by growth factors, phorbol esters, and serum in quiescent cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5396–5401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchcroft J. E., Harrison M. L., Geahlen R. L. B lymphocyte activation is accompanied by phosphorylation of a 72-kDa protein-tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):14846–14849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. J., Kanellopoulos-Langevin C., Merwin R. M., Sachs D. H., Asofsky R. Establishment and characterization of BALB/c lymphoma lines with B cell properties. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):549–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. Factors affecting B-cell growth and differentiation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:133–157. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J. pp54 microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase. A novel serine/threonine protein kinase regulated by phosphorylation and stimulated by poly-L-lysine. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17355–17363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane P. J., McConnell F. M., Schieven G. L., Clark E. A., Ledbetter J. A. The role of class II molecules in human B cell activation. Association with phosphatidyl inositol turnover, protein tyrosine phosphorylation, and proliferation. J Immunol. 1990 May 15;144(10):3684–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyasaka T., Chao M. V., Sherline P., Saltiel A. R. Nerve growth factor stimulates a protein kinase in PC-12 cells that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein-2. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4730–4735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay N. K., Price D. J., Kyriakis J. M., Pelech S., Sanghera J., Avruch J. An array of insulin-activated, proline-directed serine/threonine protein kinases phosphorylate the p70 S6 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3325–3335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nel A. E., Hanekom C., Rheeder A., Williams K., Pollack S., Katz R., Landreth G. E. Stimulation of MAP-2 kinase activity in T lymphocytes by anti-CD3 or anti-Ti monoclonal antibody is partially dependent on protein kinase C. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2683–2689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemazee D. A., Bürki K. Clonal deletion of B lymphocytes in a transgenic mouse bearing anti-MHC class I antibody genes. Nature. 1989 Feb 9;337(6207):562–566. doi: 10.1038/337562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J. Cellular mechanisms of immunologic tolerance. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:33–62. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.000341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. M., DeFranco A. L. Antigen receptor-induced cell cycle arrest in WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells depends on the duration of signaling before the G1 phase restriction point. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3003–3012. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S., Daya-Makin M. Protein kinase cascades in meiotic and mitotic cell cycle control. Biochem Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;68(12):1297–1330. doi: 10.1139/o90-194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S., Paddon H. B., Quayle K. A., Brownsey R. W. Identification of a major maturation-activated acetyl-CoA carboxylase kinase in sea star oocytes as p44mpk. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 15;274(Pt 3):759–767. doi: 10.1042/bj2740759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M., Sanghera J. S., Pelech S. L., Nigg E. A. Mitogen-activated protein kinases phosphorylate nuclear lamins and display sequence specificity overlapping that of mitotic protein kinase p34cdc2. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Apr 1;205(1):287–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16779.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posada J., Cooper J. A. Requirements for phosphorylation of MAP kinase during meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):212–215. doi: 10.1126/science.1313186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Rapid stimulation by insulin of a serine/threonine kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 2 in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1502–1506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossomando A. J., Payne D. M., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Evidence that pp42, a major tyrosine kinase target protein, is a mitogen-activated serine/threonine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6940–6943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossomando A. J., Sanghera J. S., Marsden L. A., Weber M. J., Pelech S. L., Sturgill T. W. Biochemical characterization of a family of serine/threonine protein kinases regulated by tyrosine and serine/threonine phosphorylations. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20270–20275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanghera J. S., Paddon H. B., Bader S. A., Pelech S. L. Purification and characterization of a maturation-activated myelin basic protein kinase from sea star oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):52–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanghera J. S., Paddon H. B., Pelech S. L. Role of protein phosphorylation in the maturation-induced activation of a myelin basic protein kinase from sea star oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6700–6707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. W., Livnat D., Pennell C. A., Keng P. Lymphoma models for B cell activation and tolerance. III. Cell cycle dependence for negative signalling of WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells by anti-mu. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):156–164. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Ahn N. G., Boulton T. G., Yancopoulos G. D., Panayotatos N., Radziejewska E., Ericsson L., Bratlien R. L., Cobb M. H., Krebs E. G. Microtubule-associated protein 2 kinases, ERK1 and ERK2, undergo autophosphorylation on both tyrosine and threonine residues: implications for their mechanism of activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6142–6146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Ray L. B., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):715–718. doi: 10.1038/334715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Wu J. Recent progress in characterization of protein kinase cascades for phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 17;1092(3):350–357. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(97)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Kobayashi T., Kondo J., Takahashi K., Nakamura H., Suzuki J., Nagai K., Yamada T., Nakamura S., Yamamura H. Molecular cloning of a porcine gene syk that encodes a 72-kDa protein-tyrosine kinase showing high susceptibility to proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15790–15796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Kakiuchi T., Mizuguchi J., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Association of B cell antigen receptor with protein tyrosine kinase Lyn. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):192–194. doi: 10.1126/science.1702903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]