Abstract
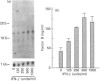
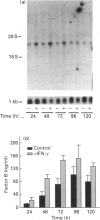
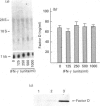
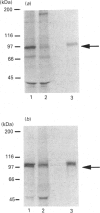
In this paper, we demonstrate the synthesis of the complement component C2 and factors B and D by the human astroglioma cell line U105-MG. All three components were structurally and antigenically similar to their serum counterparts, as determined by biosynthetic labelling studies or Western blot analysis. Northern blot analysis demonstrated that the mRNAs of all three components had the same apparent sizes as the equivalent mRNAs from hepatocyte and monocyte cell lines. Interestingly, U105-MG cells produce two C2 transcripts with sizes of approximately 2.8 and 2.3 kb. Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) enhanced the expression of C2 and factor B mRNA and protein in a dose- and time-dependent fashion, while factor D expression was refractory to IFN-gamma. IFN-gamma appeared to predominantly enhance the expression of the large (2.8 kb) C2 transcript. Kinetic studies demonstrated peak C2 and factor B expression in 48 h in response to IFN-gamma, similar to the acute-phase response of factor B in serum. These data are the first to demonstrate the synthesis of C2 and factor D by astroglioma cells. Combined with previous reports documenting the synthesis of C3 by astrocytes, our data suggest that endogenous synthesis of complement proteins, and particularly of alternative pathway activation components (C3, factors B and D), may play an important role in host defence in the central nervous system.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antras J., Lasnier F., Pairault J. Adipsin gene expression in 3T3-F442A adipocytes is posttranscriptionally down-regulated by retinoic acid. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1157–1161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnum S. R., Niemann M. A., Kearney J. F., Volanakis J. E. Quantitation of complement factor D in human serum by a solid-phase radioimmunoassay. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Mar 16;67(2):303–309. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90470-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnum S. R., Volanakis J. E. In vitro biosynthesis of complement protein D by U937 cells. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1799–1803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. R., Porter R. R. Isolation of cDNA clones for human complement component C2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1212–1215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste E. N. Cytokines: influence on glial cell gene expression and function. Chem Immunol. 1992;52:106–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignami A., Eng L. F., Dahl D., Uyeda C. T. Localization of the glial fibrillary acidic protein in astrocytes by immunofluorescence. Brain Res. 1972 Aug 25;43(2):429–435. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90398-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigner D. D., Bigner S. H., Pontén J., Westermark B., Mahaley M. S., Ruoslahti E., Herschman H., Eng L. F., Wikstrand C. J. Heterogeneity of Genotypic and phenotypic characteristics of fifteen permanent cell lines derived from human gliomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1981 May;40(3):201–229. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198105000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell R. D. The molecular genetics and polymorphism of C2 and factor B. Br Med Bull. 1987 Jan;43(1):37–49. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Campbell R. D., Bentley D. R., Porter R. R. A molecular map of the human major histocompatibility complex class III region linking complement genes C4, C2 and factor B. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):237–241. doi: 10.1038/307237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook K. S., Groves D. L., Min H. Y., Spiegelman B. M. A developmentally regulated mRNA from 3T3 adipocytes encodes a novel serine protease homologue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6480–6484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook K. S., Min H. Y., Johnson D., Chaplinsky R. J., Flier J. S., Hunt C. R., Spiegelman B. M. Adipsin: a circulating serine protease homolog secreted by adipose tissue and sciatic nerve. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):402–405. doi: 10.1126/science.3299705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielson P. E., Forss-Petter S., Brow M. A., Calavetta L., Douglass J., Milner R. J., Sutcliffe J. G. p1B15: a cDNA clone of the rat mRNA encoding cyclophilin. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):261–267. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falus A., Beuscher H. U., Auerbach H. S., Colten H. R. Constitutive and IL 1-regulated murine complement gene expression is strain and tissue specific. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):856–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton A. O., Jones L., Morrison L., Whaley K. Modulation of monocyte complement synthesis by interferons. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 15;242(3):809–815. doi: 10.1042/bj2420809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi T., Macon K. J., Kidd V. J., Volanakis J. E. Translational regulation of complement protein C2 expression by differential utilization of the 5'-untranslated region of mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6521–6524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi T., Macon K. J., Kidd V. J., Volanakis J. E. cDNA cloning and expression of human complement component C2. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):2105–2111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa N., Nonaka M., Wetsel R. A., Colten H. R. Murine complement C2 and factor B genomic and cDNA cloning reveals different mechanisms for multiple transcripts of C2 and B. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):19040–19046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz Y., Cole F. S., Strunk R. C. Synergism between gamma interferon and lipopolysaccharide for synthesis of factor B, but not C2, in human fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):1–14. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz Y., Strunk R. C. Synovial fibroblast-like cells synthesize seven proteins of the complement system. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Nov;31(11):1365–1370. doi: 10.1002/art.1780311104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lappin D. F., Birnie G. D., Whaley K. Interferon-mediated transcriptional and post-transcriptional modulation of complement gene expression in human monocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 26;194(1):177–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesavre P. H., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Mechanism of action of factor D of the alternative complement pathway. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1498–1509. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littman B. H., Dastvan F. F., Carlson P. L., Sanders K. M. Regulation of monocyte/macrophage C2 production and HLA-DR expression by IL-4 (BSF-1) and IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):520–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévi-Strauss M., Mallat M. Primary cultures of murine astrocytes produce C3 and factor B, two components of the alternative pathway of complement activation. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2361–2366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min H. Y., Spiegelman B. M. Adipsin, the adipocyte serine protease: gene structure and control of expression by tumor necrosis factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):8879–8892. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.8879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Ishikawa N., Passwell J., Natsuume-Sakai S., Colten H. R. Tissue-specific initiation of murine complement factor B mRNA transcription. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1377–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oglesby T. J., Schultz D. R., Schein R. M., Sprung C. L., Volanakis J. E. Measurement of complement proteins C2 and B in systemic lupus erythematosus and septic shock. Complement Inflamm. 1989;6(1):27–35. doi: 10.1159/000463069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter D. H., Cole F. S., Goldberger G., Colten H. R. Distinct primary translation products from human liver mRNA give rise to secreted and cell-associated forms of complement protein C2. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10380–10385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter D. H., Colten H. R. Molecular immunobiology of complement biosynthesis: a model of single-cell control of effector-inhibitor balance. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:231–251. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.001311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders K. M., Littman B. H. Lymphokine stimulation of human macrophage C2 production is partially due to interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 1;137(3):876–879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strunk R. C., Cole F. S., Perlmutter D. H., Colten H. R. gamma-Interferon increases expression of class III complement genes C2 and factor B in human monocytes and in murine fibroblasts transfected with human C2 and factor B genes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15280–15285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidovic M., Sparacio S. M., Elovitz M., Benveniste E. N. Induction and regulation of class II major histocompatibility complex mRNA expression in astrocytes by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Neuroimmunol. 1990 Dec;30(2-3):189–200. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(90)90103-T. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volanakis J. E., Barnum S. R., Giddens M., Galla J. H. Renal filtration and catabolism of complement protein D. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 14;312(7):395–399. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502143120702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaley K. Biosynthesis of the complement components and the regulatory proteins of the alternative complement pathway by human peripheral blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):501–516. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]