Abstract
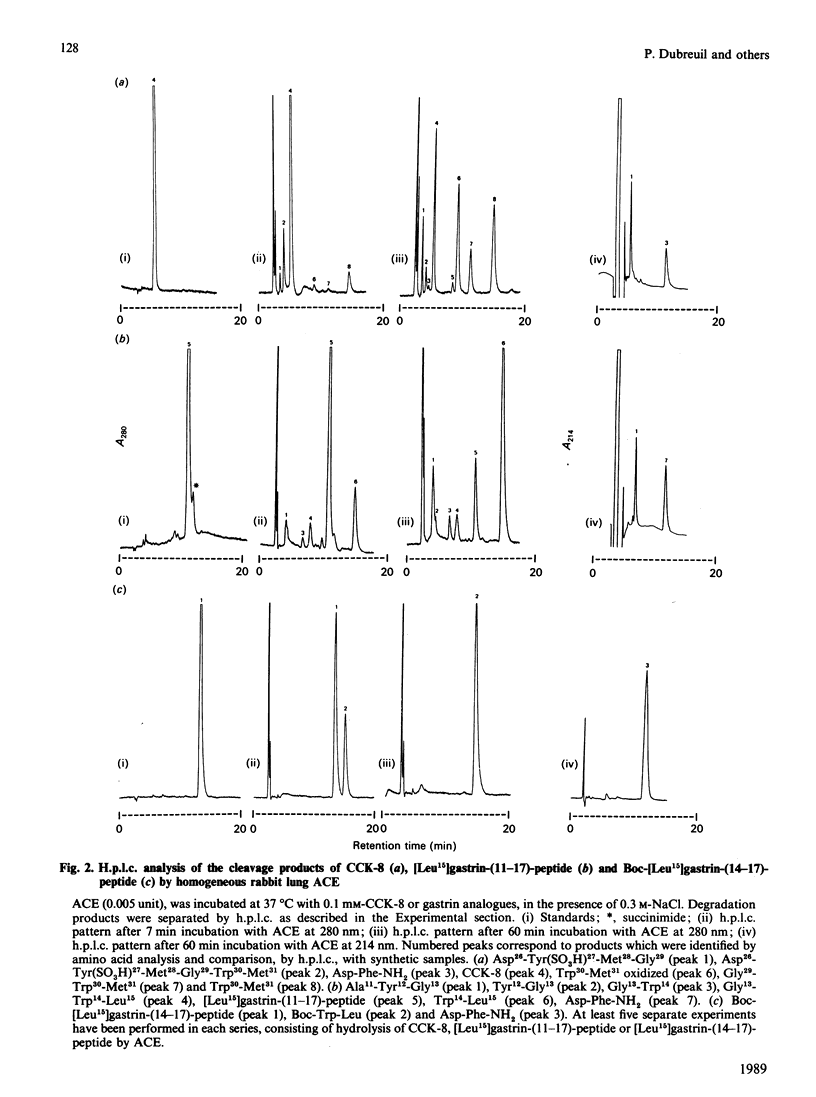
ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme; peptidyl dipeptidase A; EC 3.4.15.1), cleaves C-terminal dipeptides from active peptides containing a free C-terminus. We investigated the hydrolysis of cholecystokinin-8 [CCK-8; Asp-Tyr(SO3H)-Met-Gly-Trp-Met-Asp-Phe-NH2] and of various gastrin analogues by purified rabbit lung ACE. Although these peptides are amidated at their C-terminal end, they were metabolized by ACE to several peptide fragments. These fragments were analysed by h.p.l.c., isolated and identified by comparison with synthetic fragments, and by amino acid analysis. The initial and major site of hydrolysis was the penultimate peptide bond, which generated a major product, the C-terminal amidated dipeptide Asp-Phe-NH2. As a secondary cleavage, ACE subsequently released di- or tri-peptides from the C-terminal end of the remaining N-terminal fragments. The cleavage of CCK-8 and gastrin analogues was inhibited by ACE inhibitors (Captopril and EDTA), but not by other enzyme inhibitors (phosphoramidon, thiorphan, bestatin etc.). Hydrolysis of [Leu15]gastrin-(14-17)-peptide [Boc (t-butoxycarbonyl)-Trp-Leu-Asp-Phe-NH2] in the presence of ACE was found to be dependent on the chloride-ion concentration. Km values for the hydrolysis of CCK-8, [Leu15]gastrin-(11-17)-peptide and Boc-[Leu15]gastrin-(14-17)-peptide at an NaCl concentration of 300 mM were respectively 115, 420 and 3280 microM, and the catalytic constants were about 33, 115 and 885 min-1. The kcat/Km for the reactions at 37 degrees C was approx. 0.28 microM-1.min-1, which is approx. 35 times less than that reported for the cleavage of angiotensin I. These results suggest that ACE might be involved in the metabolism in vivo of CCK and gastrin short fragments.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bunnett N. W., Debas H. T., Turner A. J., Kobayashi R., Walsh J. H. Metabolism of gastrin and cholecystokinin by endopeptidase 24.11 from the pig stomach. Am J Physiol. 1988 Nov;255(5 Pt 1):G676–G684. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.255.5.G676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunnett N. W., Orloff M. S., Turner A. J. Catabolism of substance P in the stomach wall of the rat. Life Sci. 1985 Aug 19;37(7):599–606. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90426-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bünning P., Riordan J. F. Activation of angiotensin converting enzyme by monovalent anions. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 4;22(1):110–116. doi: 10.1021/bi00270a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cascieri M. A., Bull H. G., Mumford R. A., Patchett A. A., Thornberry N. A., Liang T. Carboxyl-terminal tripeptidyl hydrolysis of substance P by purified rabbit lung angiotensin-converting enzyme and the potentiation of substance P activity in vivo by captopril and MK-422. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;25(2):287–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman D. W., Cheung H. S. Concentrations of angiotensin-converting enzyme in tissues of the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Oct;250(1):261–265. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das M., Soffer R. L. Pulmonary angiotensin-converting enzyme. Structural and catalytic properties. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6762–6768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschodt-Lanckman M., Pauwels S., Najdovski T., Dimaline R., Dockray G. J. In vitro and in vivo degradation of human gastrin by endopeptidase 24.11. Gastroenterology. 1988 Mar;94(3):712–721. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90244-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorer F., Ryan J. W., Stewart J. M. Hydrolysis of bradykinin and its higher homologues by angiotensin-converting enzyme. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):915–917. doi: 10.1042/bj1410915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubreuil P., Lignon M. F., Magous R., Rodriguez M., Bali J. P., Martinez J. Degradation of a tetragastrin analogue by a membrane fraction from rat gastric mucosa. Drug Des Deliv. 1987 Sep;2(1):49–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durieux C., Charpentier B., Pelaprat D., Roques B. P. Investigation on the metabolism of CCK8 analogues by rat brain slices. Neuropeptides. 1986 Jan;7(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(86)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdos E. G., Yang H. Y. An enzyme in microsomal fraction of kidney that inactivates bradykinin. Life Sci. 1967 Mar 15;6(6):569–574. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcrand P., Rodriguez M., Galas M. C., Lignon M. F., Laur J., Aumelas A., Martinez J. 2-Phenylethyl ester and 2-phenylethyl amide derivative analogues of the C-terminal hepta- and octapeptide of cholecystokinin. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1988 Nov;32(5):384–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1988.tb01273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh L. B., Gafford J. T., Powers J. C., Tanaka T., Erdös E. G. Novel substrates for angiotensin I converting enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 27;110(2):654–659. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91199-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Turner A. J. Isolation of two differentially glycosylated forms of peptidyl-dipeptidase A (angiotensin converting enzyme) from pig brain: a re-evaluation of their role in neuropeptide metabolism. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 1;241(3):625–633. doi: 10.1042/bj2410625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J., Bali J. P., Rodriguez M., Castro B., Magous R., Laur J., Lignon M. F. Synthesis and biological activities of some pseudo-peptide analogues of tetragastrin: the importance of the peptide backbone. J Med Chem. 1985 Dec;28(12):1874–1879. doi: 10.1021/jm00150a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J., Rodriguez M., Bali J. P., Laur J. Phenethyl ester derivative analogues of the C-terminal tetrapeptide of gastrin as potent gastrin antagonists. J Med Chem. 1986 Nov;29(11):2201–2206. doi: 10.1021/jm00161a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J., Rodriguez M., Bali J. P., Laur J. Phenylethylamide derivatives of the C-terminal tetrapeptide of gastrin. Potent inhibitors of gastrin-stimulated acid secretion. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1986 Nov;28(5):529–535. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1986.tb03288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondetti M. A., Rubin B., Cushman D. W. Design of specific inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme: new class of orally active antihypertensive agents. Science. 1977 Apr 22;196(4288):441–444. doi: 10.1126/science.191908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patchett A. A., Cordes E. H. The design and properties of N-carboxyalkyldipeptide inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1985;57:1–84. doi: 10.1002/9780470123034.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKEGGS L. T., Jr, KAHN J. R., SHUMWAY N. P. The preparation and function of the hypertensin-converting enzyme. J Exp Med. 1956 Mar 1;103(3):295–299. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.3.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidgel R. A., Engelbrecht S., Johnson A. R., Erdös E. G. Hydrolysis of substance p and neurotensin by converting enzyme and neutral endopeptidase. Peptides. 1984 Jul-Aug;5(4):769–776. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(84)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidgel R. A., Erdös E. G. Novel activity of human angiotensin I converting enzyme: release of the NH2- and COOH-terminal tripeptides from the luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1025–1029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. Y., Erdös E. G. Second kininase in human blood plasma. Nature. 1967 Sep 23;215(5108):1402–1403. doi: 10.1038/2151402a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokosawa H., Endo S., Ogura Y., Ishii S. A new feature of angiotensin-converting enzyme in the brain: hydrolysis of substance P. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Oct 31;116(2):735–742. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90586-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


