Abstract
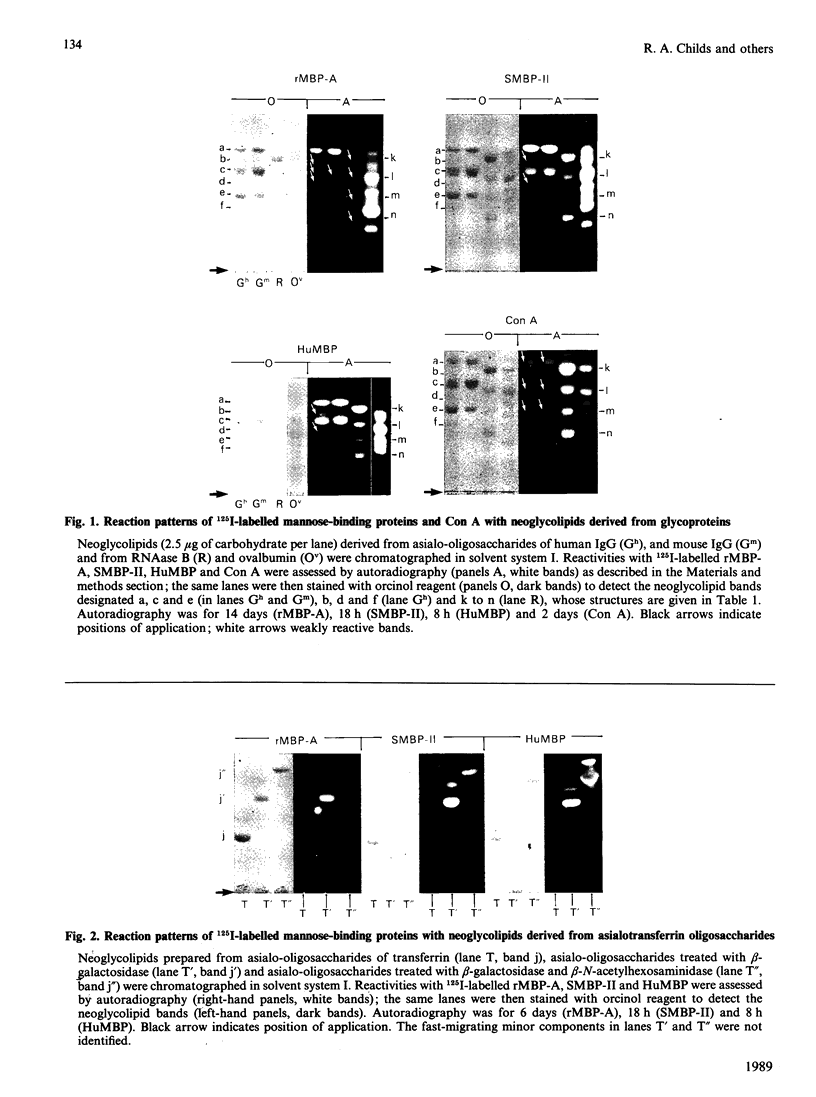
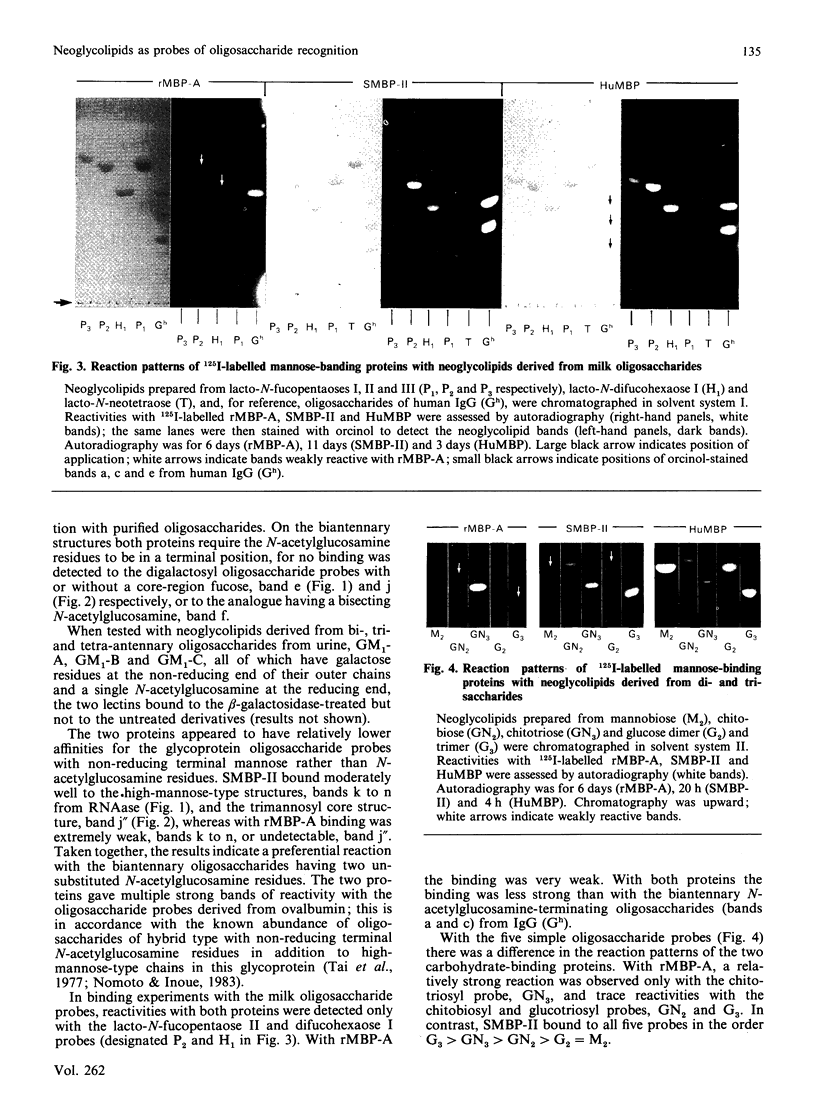
Oligosaccharide recognition by three mammalian mannose-binding proteins was investigated by using as probes a series of structurally characterized neoglycolipids in t.l.c. binding assays. The neoglycolipids were derived from N-linked oligosaccharides of complex, high-mannose and hybrid types and from human milk oligosaccharides and simple di- and tri-saccharides. The three proteins, namely the recombinant carbohydrate-recognition domain of rat mannose-binding Protein A and the multi-subunit forms of rat and human serum mannose-binding proteins, were shown to have in common reactivity with oligosaccharide probes containing one or more non-reducing terminal N-acetylglucosamine residue(s). Substitution with galactose masks reactivity. The three proteins also bound to non-reducing terminal mannose residues in high-mannose-type oligosaccharides, non-reducing terminal fucose residues in the sequence Fuc alpha 1-4(Gal beta 1-3)GlcNAc and non-reducing terminal glucose residues in dextran oligomers; the recombinant binding domain gave consistently weaker binding. The relative reactivities with the various probes differ for each protein. Overall, the reaction patterns of the three mammalian proteins differ from that of the plant lectin concanavalin A, which showed preferential binding to the high-mannose type, weak binding to biantennary complex type and no binding to the fuco-oligosaccharide and simple oligosaccharide probes. As a group, the three mammalian proteins resemble bovine serum conglutinin and behave as lectins with rather broad sugar specificities directed at certain non-reducing terminal N-acetylglucosamine, mannose, glucose and fucose residues, but with subtle differences in fine specificities. These results illustrate the potential of neoglycolipids in studies of oligosaccharide recognition by natural and recombinant proteins of diverse biological systems.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baenziger J. U., Fiete D. Structure of the complex oligosaccharides of fetuin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):789–795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drickamer K. Demonstration of carbohydrate-recognition activity in diverse proteins which share a common primary structure motif. Biochem Soc Trans. 1989 Feb;17(1):13–15. doi: 10.1042/bst0170013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drickamer K., Dordal M. S., Reynolds L. Mannose-binding proteins isolated from rat liver contain carbohydrate-recognition domains linked to collagenous tails. Complete primary structures and homology with pulmonary surfactant apoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6878–6887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drickamer K. Two distinct classes of carbohydrate-recognition domains in animal lectins. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9557–9560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekowitz R. A., Day L. E., Herman G. A. A human mannose-binding protein is an acute-phase reactant that shares sequence homology with other vertebrate lectins. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1034–1046. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feizi T. Demonstration by monoclonal antibodies that carbohydrate structures of glycoproteins and glycolipids are onco-developmental antigens. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):53–57. doi: 10.1038/314053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feizi T. Glycoprotein oligosaccharides as recognition structures. Ciba Found Symp. 1989;145:62-74, discussion 74-9. doi: 10.1002/9780470513828.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornstedt N., Porath J. Characterization studies on a new lectin found in seeds of Vicia ervilia. FEBS Lett. 1975 Sep 15;57(2):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80713-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda K., Sannoh T., Kawasaki N., Kawasaki T., Yamashina I. Serum lectin with known structure activates complement through the classical pathway. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7451–7454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki N., Kawasaki T., Yamashina I. Isolation and characterization of a mannan-binding protein from human serum. J Biochem. 1983 Sep;94(3):937–947. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki N., Kawasaki T., Yamashina I. Mannan-binding protein and conglutinin in bovine serum. J Biochem. 1985 Nov;98(5):1309–1320. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J. Conglutinin and immunoconglutinins. Adv Immunol. 1967;6:479–527. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60527-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loveless R. W., Feizi T., Childs R. A., Mizuochi T., Stoll M. S., Oldroyd R. G., Lachmann P. J. Bovine serum conglutinin is a lectin which binds non-reducing terminal N-acetylglucosamine, mannose and fucose residues. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 15;258(1):109–113. doi: 10.1042/bj2580109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynard Y., Baenziger J. U. Characterization of a mannose and N-acetylglucosamine-specific lectin present in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3788–3794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuochi T., Taniguchi T., Shimizu A., Kobata A. Structural and numerical variations of the carbohydrate moiety of immunoglobulin G. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2016–2020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori K., Kawasaki T., Yamashina I. Identification of the mannan-binding protein from rat livers as a hepatocyte protein distinct from the mannan receptor on sinusoidal cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Apr 15;222(2):542–552. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90552-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori K., Kawasaki T., Yamashina I. Isolation and characterization of endogenous ligands for liver mannan-binding protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Aug 1;264(2):647–656. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90331-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto H., Inoue Y. A novel glycoasparagine isolated from an ovalbumin glycopeptide fraction (GP-IV). Anion-exchange borate chromatography and structural analysis of GP-IV glycoasparagines. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Sep 15;135(2):243–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07644.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata S., Muramatsu T., Kobata A. Fractionation of glycopeptides by affinity column chromatography on concanavalin A-sepharose. J Biochem. 1975 Oct;78(4):687–696. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka S., Ikeda K., Kawasaki T., Yamashina I. Isolation and characterization of two distinct mannan-binding proteins from rat serum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jan;260(1):257–266. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90448-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka S., Itoh N., Kawasaki T., Yamashina I. Primary structure of rat liver mannan-binding protein deduced from its cDNA sequence. J Biochem. 1987 Jan;101(1):135–144. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd V. L., Lee Y. C., Schlesinger P. H., Stahl P. D. L-Fucose-terminated glycoconjugates are recognized by pinocytosis receptors on macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1019–1022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl P. D., Rodman J. S., Miller M. J., Schlesinger P. H. Evidence for receptor-mediated binding of glycoproteins, glycoconjugates, and lysosomal glycosidases by alveolar macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1399–1403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll M. S., Mizuochi T., Childs R. A., Feizi T. Improved procedure for the construction of neoglycolipids having antigenic and lectin-binding activities, from reducing oligosaccharides. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 1;256(2):661–664. doi: 10.1042/bj2560661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai T., Yamashita K., Ito S., Kobata A. Structures of the carbohydrate moiety of ovalbumin glycopeptide III and the difference in specificity of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases CII and H. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6687–6694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasaki S., Mizuochi T., Kobata A. Hydrazinolysis of asparagine-linked sugar chains to produce free oligosaccharides. Methods Enzymol. 1982;83:263–268. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)83019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang P. W., Gool H. C., Hardy M., Lee Y. C., Feizi T. Novel approach to the study of the antigenicities and receptor functions of carbohydrate chains of glycoproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Oct 30;132(2):474–480. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91158-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe S. J., Bellairs R., Feizi T. Developmental patterning of carbohydrate antigens during early embryogenesis of the chick: expression of antigens of the poly-N-acetyllactosamine series. Development. 1988 Jan;102(1):193–210. doi: 10.1242/dev.102.1.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild J., Robinson D., Winchester B. Isolation of mannose-binding proteins from human and rat liver. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 15;210(1):167–174. doi: 10.1042/bj2100167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita K., Mizuochi T., Kobata A. Analysis of oligosaccharides by gel filtration. Methods Enzymol. 1982;83:105–126. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)83008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]