Abstract
Atrial fibrillation (AF) prediction and screening are of important clinical interest because of the potential to prevent serious adverse events. Devices capable of detecting short episodes of arrhythmia are now widely available. Although it has recently been suggested that some high-risk patients with AF detected on implantable devices may benefit from anticoagulation, long-term management remains challenging in lower-risk patients and in those with AF detected on monitors or wearable devices as the development of clinically meaningful arrhythmia burden in this group remains unknown. Identification and prediction of clinically relevant AF is therefore of unprecedented importance to the cardiologic community. Family history and underlying genetic markers are important risk factors for AF. Recent studies suggest a good predictive ability of polygenic risk scores, with a possible additive value to clinical AF prediction scores. Artificial intelligence, enabled by the exponentially increasing computing power and digital data sets, has gained traction in the past decade and is of increasing interest in AF prediction using a single or multiple lead sinus rhythm electrocardiogram. Integrating these novel approaches could help predict AF substrate severity, thereby potentially improving the effectiveness of AF screening and personalizing the management of patients presenting with conditions such as embolic stroke of undetermined source or subclinical AF. This review presents current evidence surrounding deep learning and polygenic risk scores in the prediction of incident AF and provides a futuristic outlook on possible ways of implementing these modalities into clinical practice, while considering current limitations and required areas of improvement.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation, Atrial fibrillation screening, Atrial fibrillation prediction scores, Artificial intelligence, Deep learning, Polygenic risk score
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract.
What’s new?
A comprehensive overview of innovations in genetics and artificial intelligence, exploring their potential use for predicting new-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) to enhance AF screening and personalize patient management.
The review emphasizes the need for further research to establish the feasibility, cost-effectiveness, and impact on clinical outcomes of these emerging tools.
Introduction
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia and increases risk for stroke, death, heart failure, hospitalization, and cognitive decline.1–6 Oral anticoagulation and early rhythm control strategies have been shown to reduce adverse cardiovascular outcomes.7–9 Atrial fibrillation screening may provide an opportunity to implement measures aimed at primary prevention of AF-related morbidity and mortality through early initiation of appropriate therapy, risk factor modification, and closer follow-up of higher-risk patients.10,11
Atrial fibrillation screening as recommended by most scientific guidelines is mainly opportunistic.12,13 However, this approach could easily overlook patients with paroxysmal or short-term persistent AF.14,15 Recent evidence favouring systematic AF screening in targeted populations has the potential to influence future guidelines and has been discussed in a recent consensus statement from the European Heart Rhythm Association.16–18 While modern screening tools such as implantable loop recorders (ILR) or wearables have become increasingly reliable and widely available, clinical implications and appropriate management of asymptomatic and screen-detected AF are still incompletely defined.19–23
An essential question in AF screening is not only how to screen but which population to screen. Improving the ability to identify individuals at high risk of developing clinically significant AF (i.e. AF leading to adverse outcomes) may help define populations that may benefit from screening and specialized downstream management. Recent technological advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and genetics offer the opportunity to develop new tools for a more individualized approach.
In this review, we provide an overview of the concepts of AF screening and available AF prediction scores, with a focus on emerging approaches. We discuss current developments in genetics and AI, including their potential value in refining clinical risk scores and elucidating the population of patients most likely to benefit from advanced AF screening.
Atrial fibrillation definitions relevant to screening
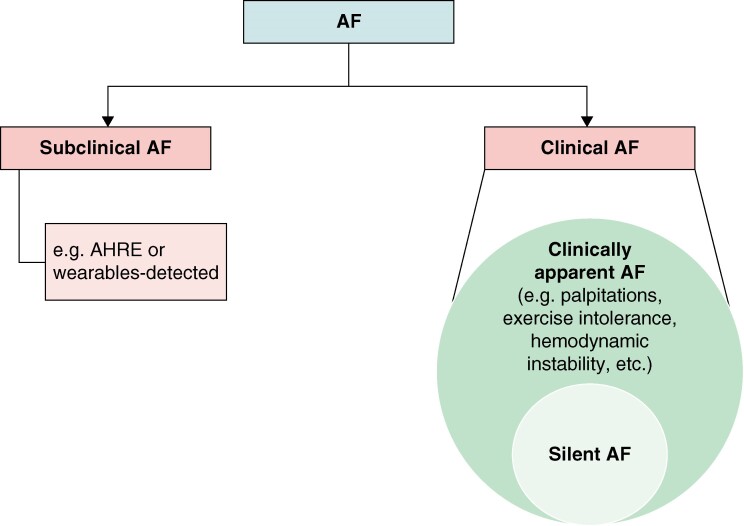
Multiple AF classification schemes have been used based on its temporal pattern, associated symptoms, and detection method.12 Figure 1 and Table 1 summarize the latest classification relevant to AF screening published in recent guidelines.12,24
Figure 1.
Atrial fibrillation classification adapted from recent guidelines.12,24 Symptoms attributable to AF range from non-specific palpitations to haemodynamic instability.12 Clinically apparent AF and silent AF are two presenting forms of clinical AF documented on a 12-lead ECG or ≥30 s rhythm strip. Subclinical AF is identified by continuous monitoring devices in asymptomatic individuals with no history of clinical AF. AF, atrial fibrillation; AHRE, atrial high-rate episodes; ECG, electrocardiogram.
Table 1.
Atrial fibrillation classification, definitions, and clinical implication adapted from recent guidelines12,24
| Definition | Clinical implication | |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical AF | AF diagnosed on a conventional 12-lead ECG tracing or rhythm strip showing AF for ≥30 s. It could be symptomatic or not | Established guideline-directed anticoagulation benefit irrespective of symptom status12 |
| Clinically apparent AF | Subset of clinical AF in patients with symptoms attributable to AF | Symptoms attributable to AF range from non-specific palpitations to haemodynamic instability12 |
| Silent AF | Subset of clinical AF in patients with no symptoms attributable to AF | Associated with increased morbidity and mortality compared with clinically apparent AF25 |
| SCAF | AF identified by continuous monitoring devices in asymptomatic individuals with no history of clinical AF | Management remains controversial, requiring a personalized, patient-centred approach that weighs the risks and benefits of OAC intiation19,26–28 |
| AHRE | Subset of SCAF defined as arrhythmia episodes with atrial rate ≥ 170–190 b.p.m. detected by CIEDs with an atrial lead | Needs to be inspected to rule out an artefactual signal |
AF, atrial fibrillation; AHRE, atrial high-rate episodes; CIED, cardiac implantable electronic device; ECG, electrocardiogram; OAC, oral anticoagulation; SCAF, subclinical atrial fibrillation.
Traditionally, ‘clinical AF’ is diagnosed by a conventional 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) or rhythm strip showing AF for ≥30 s.12 Patients with symptomatic clinical AF will be referred to as ‘clinically apparent AF’. It is estimated that 10–40% of patients with clinical AF are asymptomatic, defining ‘silent AF’.25 Silent AF was shown to be associated with increased morbidity and mortality compared with clinically apparent AF, possibly due to delayed arrhythmia diagnosis and management, thus providing the impetus for AF screening.12,25
Growing utilization of continuous cardiac monitoring devices has led to a rise in the occurrence of asymptomatic device-detected AF without documentation on 12-lead ECG, which is referred to as subclinical AF (SCAF).24 Monitoring strategies range from wearables to cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs). Atrial tachyarrhythmia detected by CIEDs with an atrial lead are termed atrial high-rate episodes (AHREs), which may be short in duration and are not restricted to AF.12,24 Multiple studies have demonstrated that continuous monitoring using CIEDs increases SCAF detection in patients at high risk of AF or stroke.21,29–31 Recent randomized clinical trials (RCTs) showed that in high-risk patients with AHREs longer than 6 min (detected mainly on pacemakers), oral anticoagulation (OAC) lowers the risk of stroke but increases the risk of major bleeding, thus highlighting the need for a personalized approach to balance the risks and benefits of OAC initiation.21,26,27,32,33 However, OAC did not show improved outcomes in ILR-screened SCAF in a similar high-risk population.21
Atrial fibrillation risk factors and clinical risk score
Risk factors for atrial fibrillation development
Current AF prediction tools rely almost exclusively on clinical risk factors. The most important clinical risk factor for AF is age, with 12% of individuals over age 80 affected.13 Other traditional risk factors include male sex, hypertension, hyperthyroidism, heart failure, and valvular and structural heart disease; others such as obstructive sleep apnoea, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and diabetes are more contested.13,34,35
Several lifestyle factors have also been associated with AF. Alcohol carries undoubtedly the greatest risk.13,34 Body mass index (BMI) has a linear relationship with AF incidence.36 Weight gain is correlated with an increase in AF incidence, independently of the actual BMI.37 Exercise shows a U-shaped association with AF.38 Smoking is debated as a risk factor with inconsistent findings in observational studies.13
Classical atrial fibrillation prediction scores
Currently available AF prediction scores all include combinations of clinical and lifestyle risk factors but differ mainly in the selection and weighting of these factors. Over 10 traditional AF prediction scores have been published (Table 2).39,40
Table 2.
Clinical risk scores to predict AF
| Score | CHADS241,42 | CHADS2Vasc41,42 | HATCH43 | C2HEST44 | FHS39 | ARIC40 | EHR45 | HARMS2-AF34 | CHARGE AF46 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk factors | (1) Congestive heart failure (1) HTN (1) Age > 75 (1) DM (2) Stroke/TIA |
(1) Congestive heart failure (1) HTN (1–2) Age (>75 = 2 points, >65 = 1 point) (1) DM (2) Stroke/TIA (1) Vascular disease (1) Sex (female) |
(1) Hypertension (1) Age > 75 (1) Stroke or TIA (1) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (1) Heart failure |
(1) CAD (1) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (1) HTN (2) Age > 75 (2) Systolic heart failure (1) Hyperthyroidism |
Age Sex BMI Systolic BP HTN treatment PR interval Cardiac murmur Heart failure |
Age Race Height Smoking Systolic BP HTN treatment Cardiac murmur LVH LA dilatation DM CAD Heart failure |
Sex Age Race Smoking Height Weight Diastolic BP HTN Hyperlipidaemia Heart failure CAD Valvular heart disease Prior stroke PAD CKD Hypothyroidism Quadratic terms for height, weight, and age |
(4) HTN (1–2) Age (>60 = 1 point, ≥65 = 2 points) (1) BMI > 30 (2) Male (2) OSA (1) Smoking (1–2) Alcohol (depending on quantity) |
Age Race Height Weight Systolic BP Diastolic BP Current smoking HTN treatment DM History of MI History of heart failure |
| AUC | 0.700 (Fauchier et al.)42 0.63 (Zuo et al.)41 0.66 (meta-analysis)47 |
0.706 (Fauchier et al.)42 0.63 (Zuo et al.)41 0.69 (meta-analysis)47 |
0.716 (internal) 0.67 (meta-analysis)47 |
0.75 (internal) 0.650–0.734 (external)44,48 |
0.78 (internal) 0.70 (meta-analysis)47 |
0.78 (internal) no external validation |
0.777 (internal) 0.808 (external)48 |
0.782 (internal) 0.757 (external) |
0.765 (internal) 0.664 (external) 0.806 (external)48 0.71 (meta-analysis)47 |
| Follow-up time or chosen time horizon for prediction | Mean 6.1 ± 1.5 years | Mean 6.1 ± 1.5 years | Mean 9.0 ± 2.2 years | Mean 7.9 ± 11.5 months | 10-year window | 10-year window | 5-year window | Median 12.9 years (IQR 12.1–13.7) | 5-year window |
| Comments | Developed to predict risk of stroke in AF patients and subsequently tested for the prediction of incident AF Fauchier et al.: score tested in stroke patients for prediction of AF Zuo: score tested in patients with arrhythmic symptoms |
Developed to predict risk of stroke in AF patients and subsequently tested for the prediction of incident AF Fauchier et al.: score tested in stroke patients for prediction of AF |
Tested in Taiwanese population First developed to predict progression from paroxysmal to persistent AF AF definition: discharge diagnosis or confirmed twice as outpatient diagnosis |
Derived and validated in East Asian cohort (Chinese/Korean) but externally also validated in European ancestry cohort DM correlated with AF on univariate analysis AF definition: hospital discharge diagnosis |
Long follow-up (10 years) Additional incorporation of echocardiographic data only slightly (although significantly) improved AUC to 0.79 in the internal validation data set |
US cohort of participants of European and of African ancestry Unconventional significance level for risk factors (P = 0.1) AF definition: follow-up ECGs, discharge diagnoses, death certificates |
Better than CHARGE AF, CHEST, and CHADS2VASc scores High AF risk also predicted high stroke risk |
Developed in UK Biobank and externally validated in the Framingham Heart Study population DM not associated with AF |
Derived in three US cohorts (Framingham, ARIC, CHS) and validated in two European cohorts AF definition: study ECGs or discharge diagnosis. ECG data did not improve model. Addition of BNP increased predictive ability49 |
Number in parenthesis indicates adjudicated score value for specific risk factors.
AF, atrial fibrillation; AUC, area under the receiver-operator curve; BMI, body-mass index; BP, blood pressure; BNP, Brain Natriuretic Peptide; CAD, coronary artery disease; CKD, chronic kidney disease; DM, diabetes mellitus; HTN, hypertension; IQR, interquartile range; LA, left atrium; LVH, left ventricular hypertrophy; MI, myocardial infarction; OSA, obstructive sleep apnoea; PAD, peripheral artery disease; TIA, transient ischemic attack.
HATCH and CHADS2/CHA2DS2-VASc scores were initially intended to predict progression of AF and stroke risk, respectively, but were later applied to the prediction of incident AF as well.41,43 While these scores were not intended for this purpose and were not specifically optimized for AF prediction,50 it is nevertheless interesting that their predictive ability is comparable to dedicated AF prediction scores.41,42 The C2HEST score was proposed as a simple score for predicting incident AF and includes the following risk factors: coronary artery disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hypertension, elderly (≥75 years), systolic heart failure, and hyperthyroidism. While prediction in the derivation cohort was good, the ability of differentiation in external validation cohorts was modest [area under the receiving operating characteristic curve (AUC) 0.65] and lower than other scores in direct comparisons [namely, CHARGE-AF and Electronic Health Records model for AF prediction (EHR-AF)] (Table 2).44,47,48,51 CHARGE-AF, specifically created to predict AF, is the most commonly cited score to predict new-onset AF.46 Beyond classical risk factors, it includes race (higher risk for Caucasians), as well as more contested factors (diabetes, smoking, height, and history of myocardial infarction).46,52 CHARGE-AF has been shown to be superior to CHA2DS2VASasc in predicting AF.53–56 The EHR-AF included the largest set of risk factors (19).45 This model performed significantly better in a direct comparison with CHARGE-AF and CHA2DS2-VASc scores.45 Most recently, HARMS2-AF was proposed.34 In contrast to other scores, HARMS2-AF includes alcohol consumption as a lifestyle factor. It has a comparable predictive value as CHARGE-AF.34 Comparison between scores is difficult though because the choice of predictive time windows was quite heterogeneous (Table 2).
Dedicated AF prediction scores perform somewhat better than scores that were derived to predict AF-related complications or AF progression. Some of the best-performing scores in head-to-head comparisons were CHARGE-AF, EHR-AF, and HARMS2-AF scores. C-statistics for these prediction models range approximately between 0.7 and 0.8. While this is generally considered to be fairly good for a predictive score, there might be added value in integrating additional information outside of the classical risk factors.
Traditional AF prediction scores mainly reflect the concept that more comorbidities lead to more AF. However, they may miss some of the underlying individual predisposition and therefore be less suited for some populations, e.g. patients with few or not in risk scores represented comorbidities. Furthermore, these scores remain with limited discriminative ability despite inclusion of multiple demographic and clinical risk markers, which might be part of the reason why they are rarely used in clinical practice. Importantly, none of the scores included family history. Novel approaches have been developed to predict AF beyond clinical risk scores, notably AI and genetics, which will be discussed in the following sections.
Atrial fibrillation prediction using artificial intelligence
Overview of artificial intelligence
The concept of machine learning (ML), a subset of AI (see Supplementary material online, Figure S1), has been around for decades. Instead of explicitly outlining the steps to resolve a task, a ML algorithm derives the solution based on data: this is referred to as the training or learning process (see Supplementary material online, Figure S2).57 Artificial neural networks have gained popularity through their ability to surpass other ML techniques in solving complex problems. They are composed of interconnected artificial ‘neurones’ that represent mathematical equations sequenced into different components: an input layer, several hidden layers, and an output layer.58 When they contain numerous hidden layers, they are referred to as deep neural networks (DNNs), also known as deep learning (DL) algorithms. Convolutional neural networks (CNN), inspired by the architecture of the visual cortex, are one of the most employed algorithms in the field of DL.59 Supervised learning is a type of ML in which algorithms are trained on labelled data sets. Inaccurate or inconsistent labelling can lead to poor model performance, underscoring the importance of expert involvement in the labelling process and the continuous refinement of the labelled data sets.
The performance of a model is usually measured using a process called ‘holdout strategy’. This involves splitting the whole data set into three separate parts—a training set, an internal validation set, and a test set. The training set helps learn the data, the validation set is used to optimize and select the best-performing settings (hyperparameters), and the test set allows the opportunity to gauge how the adjusted model performs (see Supplementary material online, Figure S3).60 Usually, the ‘C-statistic’ or AUC is used to gauge the performance of classifiers. However, if the data sets are unbalanced, which is often the case for detecting incident AF (only a minority of patients develop the outcome), then the area under the precision recall curve (AUPRC) should be used instead.61
Deep learning to predict atrial fibrillation using electrocardiograms
Recent studies reported on the development of incident AF prediction models using patients without previous history of AF and with ECG during normal sinus rhythm (NSR-ECG). The pathophysiological plausibility of such prediction can be based on the assumption of an underlying ECG signature of significant atrial myopathy (AM) representing a vulnerable substrate for AF.62–65 Attia et al.66 were the first to train a CNN on NSR-ECG of 144 642 adults to predict new-onset AF and achieved an AUC value of 0.87 on an independent test set (Table 3). However, this model is limited to predicting ‘imminent AF’ within 31 days of the analysed ECG. While this limited timeframe could be useful to stratify the risk of a short-term documentation of AF in patients presenting with palpitations, the opportunity to prevent stroke is limited. Moreover, AF diagnosis required documentation on a 12-lead ECG at Mayo Clinic. Notably, patients with AF diagnosis in the electronic health records (EHRs) but without ECG documentation were excluded, which could have introduced a selection bias. Raghunath et al.67 trained a CNN on NSR-ECG from more than 382 604 adults to predict incident AF within 1 year. Atrial fibrillation diagnosis relied on a 12-lead ECG documentation and on diagnoses in the EHR at Geisinger. This model demonstrated good discrimination on the holdout set with an AUC of 0.85 using NSR-ECG, age, and sex as inputs. The model also showed superior performance compared to CHARGE-AF on a subset of the holdout set (AUC 0.84 vs. 0.79). However, the prediction window in this model remains relatively short, potentially limiting timely primary prevention interventions. Further, the models developed by Attia et al. and Raghunath et al. lacked rigorous external validation to test generalizability. Lastly, incident AF was modelled as a binary classification task at a specific follow-up time which can be associated with a classification error given the paroxysmal nature of AF and irregular follow-up times.
Table 3.
Selected studies evaluating DL models in the prediction of AF
| Reference | Training population | Model type | Input | Output | Sample sizea | External validation | Key reported performance measuresb | Main innovations | Main limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attia et al. (2019)66 | Patients ≥ 18 years old with ≥1 NSR-ECG at Mayo Clinic (USA) | CNN | ECG | Paroxysmal/imminent AF within 31 days (binary classification) | 180 922 patients 649 931 ECGs |
No |
P = 8.4% patients AUC = 0.87 Sensitivity = 79% Specificity = 79.5% |
1. First ECG-AI model predicting paroxysmal AF 2. Prospective evaluation68 3. Enhanced explainability by showing an association between DL probability of paroxysmal AF with atrial myopathy65 |
1. Prediction is limited to paroxysmal/imminent AF 2. AF is only adjudicated using ECG at Mayo Clinic 3. Single-centre training data 4. Absence of external validation 5. ECG acquired for clinical indication |
| Raghunath et al. (2021)67 | Patients ≥ 18 years old with ≥1 NSR-ECG at Geisinger (USA) | CNN | ECG, age, sex | Incident AF at 1-year (binary classification) | 355 802 patients 1 348 940 ECGs |
No |
P = 3.5% patients AUC = 0.83 PRC = 0.17 Sensitivity = 69% Specificity = 81% |
1. Prediction extended to 1 year 2. AF is adjudicated using ECG and EHR 3. Exclusion of AF diagnoses following cardiac surgery or a diagnosis of hyperthyroidism 4. Superior performance compared to CHARGE-AF |
1. Single-centre training data 2. Absence of external validation 3. Absence of prospective evaluation 4. Binary outcome as opposed to a time-to-event outcome 5. ECG acquired for clinical indication |
| Khurshid et al. (2022)69 | Longitudinal primary care patients 18–90 years old at MGB (USA) | CNN and CPH | 12-lead ECG (input to CNN) CHARGE-AF score |
AF-free survival at 5 years (time-to-event) | 49 936 patients | UK Biobank (incident AF at 2 years) |
P = 4.2 per 1000 person-years AUC = 0.746 PRC = 0.059 Sensitivity = 95% Specificity = 30.4% PPV = 4.85% |
1. Targeted training population to primary care patients 2. Multimodal prediction: ECG signal and CHARGE-AF variables 3. Incident AF prediction at 5 years as a time-to-event outcome 4. External validation 5. Enhanced explainability using saliency maps, median waveforms, and genomic association/correlation analyses70 |
1. Single-centre (hospital network) training data 2. Absence of prospective evaluation |
| Yuan et al. (2023)71 | Outpatient Veteran Affairs hospital networks (USA) | CNN | 12-lead ECG | Concurrent paroxysmal AF within 31 days (binary classification) | 277 528 patients 907 858 ECGs |
Outpatients from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center (USA) |
P = 2.4% ECGs AUC = 0.93 Sensitivity = 87% Specificity = 87% PPV = 5% (at 90% sensitivity) |
1. Inclusion of ECGs from a multi-site outpatient population 2. Reporting of an overall consistent performance across subgroups (age, sex, ethnicity, CHA2DS2-VASc score) |
1. Prediction is limited to concurrent paroxysmal AF 2. Inclusion of patients with baseline AF in the test sets 3. Limited number of cases of incident AF at 1 year in the exploratory analysis 4. ECG acquired for clinical indication |
| Dupulthys et al. (2023)72 | Patients ≥ 40 years old at AZ Delta hospital (Belgium) |
CNN + self-attention units | Lead-I ECG EHR data (age, sex, MI, HTN, HF, VHD) |
Paroxysmal AF within 91 days before or up to 365 days after AF diagnosis (binary classification) | 32 988 patients 67 395 ECGs |
No |
P = 20% ECGs AUC = 0.76 |
1. Mitigation of class unbalance by including four age and sex matched controls per one positive case 2. Comparison between Lead-I ECG and 12-lead ECG inputs 3. Reporting of an overall consistent performance across subgroups (age, sex) |
1. Prediction is limited to paroxysmal/imminent AF 2. Single-centre training data 3. Absence of external validation 4. ECG acquired for clinical indication 5. Reported performance limited to AUC |
| Gadaleta et al. (2023)73 | Patients ≥ 18 years old prescribed single-lead patch monitoring up to 14 days | CNN, RNN | 24 h single-lead ECG recording Age, sex, ECG features (HRV, rhythm, ectopy) |
Near-term AF within 2 weeks | 269 889 recordings | No |
P = 4.3% recordings AUC = 0.80 Sensitivity = 80% Specificity = 65% PPV = 9% |
1. Use of single-lead continuous monitoring 2. Multimodal model input using ECG features 3. Report association of predicted risk with observed AF burden |
1. Prediction is limited to paroxysmal/imminent AF 2. Adjudication of AF diagnosis is limited to up to 14 days of continuous monitoring recording 3. Absence of external validation 4. ECG acquired for clinical indication |
| Hygrell et al. (2023)74 | STROKESTOP II cohort17 (Sweden) SAFER cohort75 (England) |
CNN | One-lead ECG | Paroxysmal AF (binary classification) | 6658 patients 248 964 ECGs |
STROKESTOP I cohort76 (Sweden) |
P = 4.2% patients AUC = 0.62 Sensitivity = 75% Specificity = 41% |
1. One-lead ECG acquired in the context of AF screening studies 2. Multicentre training data 3. External validation 4. Age-homogeneous testing cohort |
1. Prediction is limited to paroxysmal AF 2. Absence of prospective evaluation 3. Limited number of patients and low prevalence of AF in the training set |
| Hill et al. (2019)77 | CPRD primary care registry ≥ 30 years old (UK) |
Time-varying neural network | EHR | Incident AF at 1-year (binary classification) | 162 672 patients | DISCOVER primary care registry (UK)78 |
P = 3.19% patients AUC = 0.827 Sensitivity = 75% Specificity = 74.9% PPV = 11.5% |
1. EHR as input to predict incident AF 2. External validation78 3. Prospective evaluation79 |
1. ECG done for clinical indication limiting generalizability to AF screening 2. AF adjudicated only using primary care registries |
AF, atrial fibrillation; AUC, area under the receiver-operator curve; CNN, convolutional neural network; CPH, Cox proportional hazards; CPRD, Clinical Practice Research Datalink; EHR, electronic health records; HRV, heart rate variability; MGB, Massachusetts General Brigham; NSR-ECG, normal sinus rhythm electrocardiogram; P, prevalence/incidence of AF in the data set where performance metrics are reported; PPV, positive predictive value; RNN, recurrent neural network.
aIncludes the training, validation, and internal test sets.
bProvided only for the primary analysis on the test set or external validation set when available.
More recently, Khurshid et al.69 trained a CNN on 45 770 patients to predict 5-year AF-free survival using NSR-ECG. Unlike previous studies, they used a discrete-time survival model using DNN, accounting for censoring (death or loss to follow-up).80 The innovative inclusion of CNN-predicted probability and CHARGE-AF as covariates in a Cox proportional hazards model improved incident AF discrimination with a 5-year AUC of 0.838 and 0.777 on two internal data sets, respectively, and a 2-year AUC of 0.746 on the UK Biobank external data set. This study suggests that ECG-AI provides predictive value above and beyond standard clinical factors. Furthermore, the authors used saliency maps, an AI model interpretation technique to highlight features such as the ECG P wave and its surrounding regions which had contributed the most on the model's AF risk estimates.
A common limitation in the three aforementioned studies lies in training DL models on single-institution ECGs for clinical purposes which may not extrapolate well to AF screening in the general population. For instance, in the study by Khurshid et al., the training set's AF incidence rate was 12.8 per 1000 person-years vs. 4.2 in the UK Biobank, which probably contributes to the limited generalizability.69
In a recent study, Hygrell et al.74,75,81 trained a CNN model using data from the STROKESTOP II and SAFER AF screening studies. Electrocardiograms from 80% of participants in both SAFER and STROKESTOP II were utilized for model training. The remaining 20% were allocated to the test set, along with all the ECGs from STROKESTOP I, another AF screening study randomizing 75–76-year-olds in Sweden.76 The model performed better in the age-diverse SAFER data set (AUC 0.80) compared to the age-homogeneous cohorts in STROKESTOP I (AUC 0.62) and STOKESTOP II (AUC 0.62). The authors hypothesized that the higher accuracy in SAFER can be attributed to the identification of age-related patterns on the ECG by the CNN, since there is a strong association between age and AF, and ECGs were shown to effectively estimate a person's age.82 The low prevalence of AF in the training set (2.6%) could have also negatively affected model performance. Two other studies notably used single-lead ECGs combined with clinical data for predicting near-term or paroxysmal AF and achieved good classification performance.72,73 However, those models were not validated on external data sets. Additionally, some authors presented the AUC as the performance metric, which may overestimate the model's predictive power since only a minority of patients developed incident AF. For instance, while Yuan et al.71 achieved an AUC of 0.93 in predicting paroxysmal AF using 12-lead ECGs; the reported positive predictive value (PPV) is only 5%. Future studies should present PPV, negative predictive values, and the AUPRC to provide a more comprehensive evaluation of the model's classification performance.
In 2022, Noseworthy et al.68 published the first prospective non-randomized interventional trial evaluating the performance of a previously developed model in the prediction of paroxysmal AF based on NSR-ECG (Table 4). This study showed a benefit in increased detection of AF on continuous monitoring using AI-based risk stratification [odds ratio (OR) = 4.98, P = 0.0002]. Although AF was defined as an episode ≥30 s, ODs remained statistically significant for episodes ≥6 min (P = 0.0015) but not for episodes ≥24 h (P = 0.091), possibly due to limited power.
Table 4.
Prospective trials assessing DL models predicting incident AF
| Author, year, country | Design | Population and setting | Intervention | Comparator | Follow-up | Outcome | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hill et al. (2022)79 | Prospective randomized multicentre controlled trial (UK) | UK general practices at high risk for AF based on DL model | 12-lead ECG and 2-week one-lead ECG monitoring twice daily (n = 906) | Routine care (n = 974) | 20 months | Diagnosis of AF, atrial flutter, or fast atrial tachycardia | OR = 1.15 (0.77–1.73) P = 0.486 |
| Noseworthy et al. (2022)68 | Prospective non-randomized single-centre interventional trial (USA) | Mayo Clinic patients with ≥1 ECG. CHA2DS2-VASc ≥ 2 (men) or ≥3 (women) | High risk for AF based on DL model (n = 633) | Low risk for AF based on DL model (n = 370) | Mean of 22.3 days | Diagnosis of AF ≥ 30 s on continuous ambulatory monitoring for up to 30 days | OR = 4.98 (2.11–11.75) P = 0.0002 |
AF, atrial fibrillation; DL, deep learning; ECG, electrocardiogram; OR, odds ratio.
Deep learning to predict atrial fibrillation using electronic health record data
Electronic health record data is a promising substrate for big data analytic approaches such as DL. In 2019, Hill et al.77 trained and validated a neural network which predicts the incidence of AF in primary care patients within 1-year follow-up. The model was trained on a cohort of adults aged ≥30 years in the UK. The final model included baseline variables, such as patient demographics and comorbidities, and considered time-varying information to capture the evolution of AF risk factors. The model was externally validated in a subsequent study demonstrating an AUC of 0.87.78 In 2022, Hill et al.79 published a multicentre RCT assessing whether the deployment of their model could identify patients at high risk for AF who may benefit from downstream screening (Table 4). The study population included adult primary care patients in the UK. The screening intervention consisted of a 12-lead ECG followed by a 2-week one-lead ECG monitoring twice daily. Of the 906 high-risk patients in the intervention arm, 255 patients (28.1%) accepted the screening invitation and only 148 patients (16.3%) completed the intervention per protocol. The observed OR of the primary outcome (any atrial arrhythmia ≥ 30 s in high-risk patients) was not statistically significant but was significant in the per protocol analysis (OR = 3.07, P = 0.001). This trial was the first to evaluate the performance of a DL-based AF risk prediction tool using solely clinical variables collected in a primary care setting. However, the evaluation of the model was limited by the poor response in the intervention group. Moreover, the generalizability of the study findings to varied practices in diverse healthcare systems and using different EHR modalities is uncertain.
Polygenic scores in atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation and genetics
Genetic predisposition is a major risk factor for AF. A first-degree relative of a patient with AF has a greater than four-fold relative risk of experiencing AF compared to an individual with a negative family history.83 It has been estimated that genetic factors account for more than 20% of the risk for developing AF.84 Therefore, genetic risk scores may play an important role in predicting incident AF.
Association of rare genetic variants with atrial fibrillation
In familial AF, inheritance can follow a Mendelian pattern and rare variants (e.g. present in <0.01% of the population) can explain some of the heritability. The first AF-associated mutation was found in the ion channel gene KCNQ1, which is also responsible for long QT syndrome type 1.85 Several other rare variants in ion channel genes (e.g. KCNH2, SCN5A, and KCNA5) and in genes involved in atrial function, such as myocyte contraction (sarcomeric proteins MYL4 and TTN), hormonal regulation (NPPA), transcription factors (TBX5), and gap junctions (GJA1 and GJA5), have been discovered.86 Importantly, significant overlap between AF and genetic cardiomyopathies (CM) exists.87–90 Indeed, in patients with early-onset AF (<45 or ≤65 years of age), the prevalence of pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants in CM or arrhythmia genes was 10–24%.91,92 Affected genes included TTN, RBM20, MYH7, MYH6, LMNA, and KCNQ1. Gene-positive patients were found to have a 50% increased mortality hazard, independent of left ventricular ejection fraction.93 Based on these data, the recent AF guidelines of the American Heart Association state that it may be reasonable to perform genetic testing for rare pathogenic variants in patients with an onset of AF before age 45 without obvious AF risk factors.24 Notably, although rare genetic variants may importantly increase risk for AF, the rarity of these variants renders them accountable for a smaller portion of genetic susceptibility to AF at a population level compared to common polygenic factors.94
Basic concepts of polygenic risk scores
While early studies looked at familial clustering and used linkage analyses to identify rare variants, AF most commonly occurs in its sporadic form and the largest proportion of heritability in the general population is explained by common variants (e.g. present in >1% of the population).94,95 Common variants in isolation have small effect sizes, but if many of them accumulate in one individual, they may increase AF susceptibility. On this concept rely polygenic risk scores (PRSs) (Figure 2).
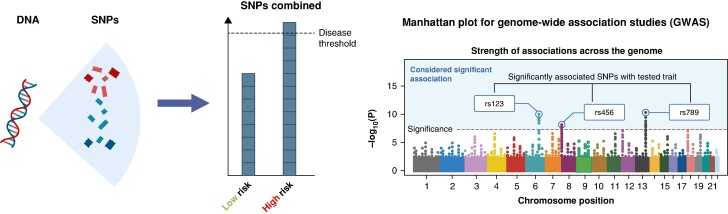
Figure 2.
Polygenic risk and GWASs. Left panel depicts the theoretical basis underlying polygenic risk. DNA contains a vast number of SNPs. The accumulation of several of these common DNA variants makes up an individual's polygenic risk. If a certain threshold is surpassed, the disease is more likely to develop. Right panel shows a graphical depiction of a Manhattan plot for a GWAS. The dots represent all the analysed SNPs at their specific chromosome position (X axis). SNPs above the level of significance (indicated by a dashed line on the Y axis) are significantly associated with the disease under investigation, e.g. AF. SNPs are commonly referred to with their reference SNP (rs) number.
Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have led to the discovery of >150 different loci associated with AF, and this number is increasing over time with larger GWAS.96,97 Using high-throughput genotyping arrays, millions of SNPs can be analysed quickly. The results can be visualized on so-called Manhattan plots; SNPs above the significance threshold are considered associated with AF (Figure 2).
One of the first AF susceptibility loci detected by GWAS and replicated in multiple studies and across ancestries is located at chromosome 4q25.95,96,98–100 PITX2, the likely causal gene at this locus, codes for a transcription factor that is key in determining the differentiation of the left atrium and the development of the pulmonary myocardial sleeves.101,102 Many other candidate genes have been identified, e.g. ZFHX3 (16q22), KCNN3 (1q21), and IL6R (1q21).96,100,103–106 While GWASs do not provide any evidence of a causal relationship, they lead to the identification of promising candidate genes associated with AF. At present, the function of most loci remains to be elucidated, and investigations to unravel pathological pathways are underway.
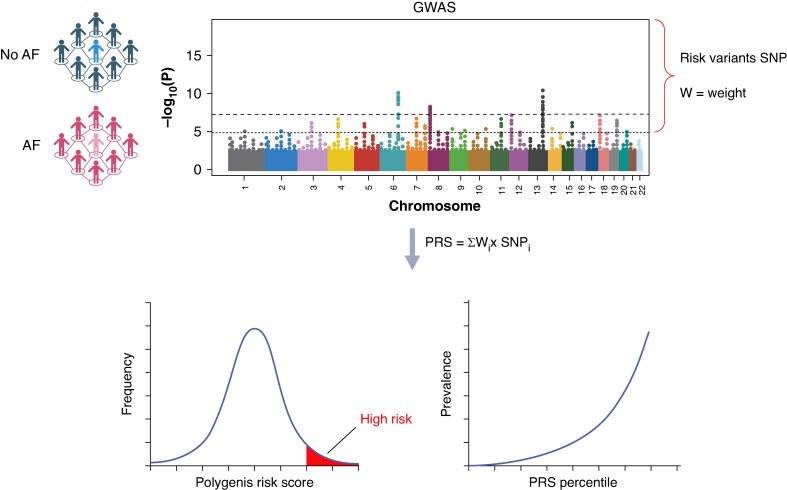
A genetic risk score includes a variable number of SNPs, as little as a handful up to millions, selected based on GWAS results. A PRS can then be calculated by summing up the number of risk alleles present in an individual and adjusting to the relative effect size of the association of each allele with the trait. The individual effect sizes for each SNP are usually very small, but if many are present, they can lead to a high PRS and consequently to a high relative disease risk (Figure 3). Commonly, ORs are indicated to describe risk of the top of the distribution curve vs. the rest of the population (e.g. PRS in the top 5% vs. the rest), or, alternatively, highest vs. lowest percentile.107,108
Figure 3.
Polygenic risk score derivation from genome wide association studies (GWASs). Development of a polygenic risk score (PRS) is done by first analysing DNA of a patient cohort with the trait (i.e. AF) and a control cohort. The GWAS indicates all the single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) or common variants which are significantly associated with AF. The relative genome-wide effect size of the association of each SNP (i.e. weight) can be determined. By summing up all the significant SNPs, each multiplied by their respective weight, a PRS is obtained. A PRS is normally distributed in the population; the right end indicates a high polygenic risk and can be compared to the rest of the population.
A PRS should be tested in an external population to help mitigate biases and overinflation related to the selected cohort and avoid a possible correlation between genetic and environmental risk.109 Initially, GWASs were performed in cohorts from often only one geographic location, which can lead to confounding due to heterogeneous genetic architecture between populations.109 To develop widely applicable scores, the general tendency has shifted to derive and test PRSs in ethnically diverse populations.96,110
Current data on polygenic scores in atrial fibrillation
First attempts to create PRSs to predict incident AF were undertaken just a decade ago and included only the top variant at each disease susceptibility locus, hence consisting of merely a handful of genetic loci (Table 5).111 While it had been shown that PRSs could be superior to family history in predicting disease risk in multiple common diseases, an early theoretical model by Do et al.112 failed to show this benefit for AF. In 2014, Lubitz et al.113 investigated a PRS comprising 12 SNPs observing a five-fold risk increase for the development of AF in individuals with the highest compared to those with the lowest number of risk alleles.
Table 5.
Selection of important studies using genetic risk scores to predict incident or prevalent AF
| Study | Do et al. (2012)112 | Smith et al. (2012)114 | Lubitz et al. (2014)113 | Tada et al. (2014)115 | Lubitz et al. (2016)116 | Khera et al. (2018)108 | Weng et al. (2018)117 | Muse et al. (2018)118 | Lazarte et al. (2021)119 | Börschel et al. (2021)120 | Kurshid et al. (2021)121 | Miyazawa et al. (2023)96 | Marsten et al. (2023)107 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of adjudication (incident vs. prevalent AF) | Theoretical model | Prospective | Incident and prevalent AF | Prospective | Prospective | Prevalent AF | Prospective | Prospective | Prevalent AF | Prospective | Prospective | Prevalent AF | Prospective |
| Number of SNPs included in score | 3 | 2 | 12 | 12 | 719 | 6 730 541 | 986 | 12 | 6 730 541 and 1168 | 145 | 1168 | 4520 | 6 730 541 |
| Discovery GWAS | 4976 individuals (Gudbjartsson et al. 2007),98 and 40 518 individuals (Benjamin et al. 2009)104 | Weight of SNPs on chromosome 4q25 was derived from the study population itself; for the remaining SNPs, a previously published GWAS was used (59 133 individuals), Ellinor et al. (2012)122 | ≈200 000 individuals, derived from six GWAS analyses or candidate SNP testing | 59 133 individuals122 | 133 073 individuals (Christophersen et al. 2017)100 | 133 073 individuals (Christophersen et al. 2017)100 Weights derived from a validation cohort of 120 286 individuals (UK Biobank) |
≈200 000 individuals, derived from six GWAS analyses or candidate SNP testing | 133 073 individuals (Christophersen et al. 2017)100 | Derived from 3 GWAS including 1 619 026 individuals from European, Japanese, African American, Brazilian, and Hispanic populations99,123 | 133 073 individuals (Christophersen et al. 2017)100 | 1 244 730 individuals from Biobank Japan, FinnGen, and a European meta-analysis (AFGen consortium, UK Biobank, Discov-EHR, deCODE, HUNT, MGI) | 133 073 individuals (Christophersen et al. 2017)100 | |
| Participants | 26 946 | 64 683 (3869 incident and 3302 prevalent AF cases) | 27 471 | 18 919 | 120 280 (validation data set) 288 978 (independent testing data set) |
5131 (individuals from the Framingham and Framingham offspring cohort) | 904 | 609 | 6945 | 543 093 | 21 194 (testing data set) | 36 662 | |
| Population | European ancestry (Sweden) Mean age: 58.1 Female: 60.6% |
European ancestry Mean age: 60 Female: 69.4% |
European ancestry (Malmö Diet and Cancer Study, Sweden) Mean age: 58 Female: 60.6% |
European ancestry Mean age range: 58–75 years Female (range): 47–52% |
European ancestry (UK Biobank) | European ancestry Mean age: 62 Female: 56% |
Predominantly European (92.6%) with a minority of African American, Asian, and Native Americans Mean age: 66 Female: 62% |
European ancestry Mean age: 44.3 Female: 18.8% |
Finnish ancestry (FINNRISK study) Median age: 47.3 Female: 52.1% |
Predominantly European ancestry and Finnish ancestry Mean age range: 47–59 Female (range): 52–66% |
Japanese ancestry Mean age: 62.8 Female: 45.6% (Japanese GWAS cohort) |
European ancestry and an additional analysis in 4873 individuals of non-European ancestry Mean age: 64.1 Female sex: 25.3% |
|
| Follow-up time or chosen time horizon for prediction | n.a. | Median 14.1 years (IQR 12.9–15.7) | n.a. | Median 14.4 years | 5-year follow-up window | n.a. | Median 9.4 years (IQR 4.4–14.3) | AF detection during 2 weeks of ambulatory cardiac rhythm monitoring | n.a. | Median 17.8 years | 5-year window | median 8.4 years (IQR 6.8–9.9) | 3-year window |
| Predictability of score (AUC) (alternatively, RR, OR of HR if AUC not available) | 0.593 | 0.743 | RR = 5 (comparing individuals with lowest vs. highest number of risk alleles) | HR = 2.00 (top quintile vs. bottom quintile) | HR (range) = 1.28–1.65 (highest vs. lowest quartile) AUC for clinical risk factor model without PRS ranged from 0.615 to 0.802 and was improved by adding PRS by 0.009 and 0.017 |
0.77 OR = 3.22 (top 5% of PRS distribution vs. remaining 95%) |
Main effects of clinical and polygenic risk score on AF after adjustment for competing risk of death (HR): 2.26 vs. 1.13 | 0.719 Adjusted OR = 3.11 (top quintile vs. bottom quintile) |
0.76 and 0.70 OR for top 10% of AF cases vs. controls: OR = 4.64 and OR = 3.16 (both for the polygenic scores including 6.7 million and 1168 SNPs, respectively) |
0.829 HR = 2.18 (per unit of PRS increase) |
0.749–0.831 (combining PRS and clinical risk) (vs. 0.720–0.824 for clinical risk score only) | 0.738 | 0.70 (combining PRS, clinical risk, and biomarkers) HR = 1.40 (per SD increase of PRS) HR = 2.45 (highest vs. lowest genetic risk tertile) HR = 2.15 (per SD increase of PRS) in the non-European ancestry subgroup |
| Comments | Family history outperformed SNP-based risk score with an AUC of 0.701 Combination of SNPs + family history yielded AUC of 0.712 |
AUC was calculated for a model including age and sex in its predictors. It had similar predictability to conventional risk factors alone (AUC 0.750). In a model including conventional risk factors and the two SNPs, AUC was slightly, but not significantly improved at 0.755 | Included subjects from 8 prospective cohort and 12 case-control studies Relative risk increased four-fold between lowest number (3–4) vs. highest number (15–16) of AF risk alleles Replicated in an independent Japanese Biobank sample of 11 309 individuals |
PRS also associated with incident embolic stroke (HR = 1.23) | Included populations from five prospective studies (Malmö Diet and Cancer Study), Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA), Prevention of Renal and Vascular Endstage Disease (PREVEND), PROspective Study of Pravastatin in the Elderly at Risk (PROSPER), Vanderbilt University de-identified DNA biobank (BioVU) Model was adjusted for CHARGE-AF clinical risk factors |
Largest number of included SNPs of any PRS. However, no comparisons to established clinical risk factors/scores and biomarkers were performed, and added value of the PRS over these factors was not assessed | Clinical risk estimated with CHARGE-AF score. Compared by tertiles of genetic and clinical risk score. Genetic and clinical risk independently contributed to AF risk Lifetime AF risk according to low vs. high polygenic score (cumulative incidence):
Lifetime AF risk with low genetic and low clinical score: 22.3% vs. high genetic and high clinical score: 48.2% |
AUC of PRS was superior compared to risk score comprising only clinical parameters (AUC 0.687) For inclusion, patients had to have at least one clinical risk factor for AF (defined as: hypertension, ischemic stroke, BMI > 30 kg/m2, history of heart failure, clinically significant murmur, first-degree atrioventricular block, chronic kidney disease, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, congenital heart disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, obstructive sleep apnoea, diabetes mellitus, regular excess alcohol consumption, or a family history of AF) |
A population with ‘lone AF’ was assessed in this study The more inclusive genetic score using 6.7 million SNPs was superior to the more restrictive genetic score (P = 0.002) |
The predictive abilities for incident AF were analysed using four different models, including combinations of clinical risk factors, biomarkers, and PRS. Best predictive ability was achieved with a model comprising clinical risk factors, biomarkers, and the PRS (AUC 0.83) Validated in the PREVEND cohort, same model comprising all three of clinical risk factors, biomarkers, and the PRS achieved an AUC of 0.85 (Dutch Prevention of REnal and Vascular ENd-stage Disease) |
Validation cohort was comprised of population of three studies (FINNRISK, Geisinger MyCode Initiative, and Framingham Heart Study117) AF risk was estimated using the CHARGE-AF score and a combination of CHARGE-AF and a PRS (Predict-AF) |
PRS based on cross-ancestry GWAS including populations from three different ancestries (Japanese + European + Finnish) performed better compared to single-population GWAS or the combination of only two of the mentioned ancestries PRS also associated with embolic stroke and stroke mortality |
Predictive ability of clinical risk factors (CHARGE-AF), biomarker (NT-proBNP), and PRS was compared. AUC for AF prediction by CHARGE-AF alone was 0.65, with inclusion of NT-proBNP improved to 0.67 and increased further to 0.70 with the addition of the AF PRS Populations included in this study had established cardiovascular disease (included individuals were drawn from four TIMI trials: SOLID-TIMI 52, SAVOR-TIMI 53, PEGASUS-TIMI 54, FOURIER-TIMI 59) |
AF, atrial fibrillation; AUC, area under the receiver-operator curve; BMI, body mass index; BNP, brain natriuretic peptide; ECG, electrocardiogram; GWAS, genome-wide association study; HR, hazard ratio; IQR, interquartile range; OR, odds ratio; PRS, polygenic risk score; RR, risk ratio; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism.
More recently, a shift towards genome-wide PRSs comprised of millions of SNPs has taken place. This method uses less stringent criteria on genome-wide significance levels and on linkage disequilibrium and has been suggested to lead to better performance than early PRSs.124 Khera et al.108 conducted a seminal study in 2018 in which a PRS including more than 6 million SNPs was derived. The group successfully demonstrated that a high PRS was significantly associated with prevalent AF: in the top 1% of the tested population, risk was 4.63-fold increased, compared to the bottom 99%. The AUC for this score was 0.77, which is comparable to the best clinical AF prediction scores.108 Recent data also suggest that the implication of polygenic risk is particularly important in lone AF: one study found that 26.3–33.3% of lone AF patients vs. only 10% of controls had a high PRS.125
An important observation underscoring the importance of genetics in the development of AF and the additive value of a PRS to a purely clinical AF prediction score was made by Weng et al.126 To assess the differential contribution of clinical and genetic risk in AF, the authors used the CHARGE-AF score and a PRS comprised of 986 SNPs. Both risk scores were strongly associated with AF incidence and earlier onset. At age 55, the lifetime risk for AF was ∼22% with a low PRS and ∼48% with a high PRS, and a lower clinical risk score was associated with delayed AF onset within each PRS stratum.126
A limitation of current GWAS and PRS is that most were performed in single-ancestry cohorts. The added value of cross-ancestry cohorts was demonstrated in a recent study by Miyazawa et al.96 Thirty-five new AF-associated loci were identified across a GWAS including Japanese, Finnish, and European ancestry cohorts. Indeed, a PRS based on the multi-ancestry cohort (AUC 0.738) performed better than single-ancestry cohorts and confirmed previous observations of an association between higher PRS and earlier AF onset. These findings will likely prompt additional multi-ancestry genetic studies to overcome current limitations.
Integrating genetic risk and artificial intelligence in atrial fibrillation prediction models
Atrial fibrillation screening has the potential to identify patients at risk for adverse clinical outcomes and can allow initiating pre-emptive treatment or risk factor modification.23 However, AF screening is encumbered by the arrhythmia's often asymptomatic and paroxysmal nature. To avoid overdiagnosis and subsequently overtreatment while minimizing the non-detection of patients at risk, it has become paramount to identify the ideal population to screen. For a screening strategy to achieve a meaningful benefit, it must not only detect the disease but also lead to a reduction in disease-associated risk by subsequent clinically useful interventions.127
Much effort has been directed towards developing clinical risk scores for AF prediction. To date, no model has been widely implemented into routine clinical practice. This may be due to moderate predictive ability, a lack of evidence of clinical benefit, and/or lack of generalized streamline implementation of such scores in electronic medical records.
The importance of genetics in the development of AF has been well established making PRS attractive tools to complement current models. It has indeed been shown that genetics and clinical factors are independent contributors to AF development and therefore would be expected to have additive value for AF risk estimation.126 With cost and time of genetic analyses having come down drastically, it seems increasingly feasible to set up the infrastructure to use PRSs in clinical practice, not only for AF prediction but as part of multiple actionable disease prediction.128 A finding of major clinical interest was reported by Miyazawa et al.,96 demonstrating that a multi-ancestry PRS for AF showed a significant relationship with hard clinical AF–related outcomes. These outcomes included cardiovascular death, stroke, and cardioembolic stroke, with hazard ratios of 1.06, 1.04, and 1.35, respectively, in patients who were not diagnosed with AF but had a high genetic predisposition.96 Although these results are encouraging for potential future applicability of PRSs, an added value over a simple clinical risk score has yet to be proven.126
Combining AI and genetic scores, Wang et al.70 have recently shown in a genetic correlation analysis that incident AF risk prediction using DL has a higher correlation with established AF susceptibility loci compared to a model solely based on clinical variables. Those recent studies suggest that DL model prediction of incident AF risk using NSR-ECG could be a biomarker of a clinically significant underlying AM or inherited predisposition to AF. Hence, ECG-AI models are a promising tool to identify patients at high risk of incident AF.
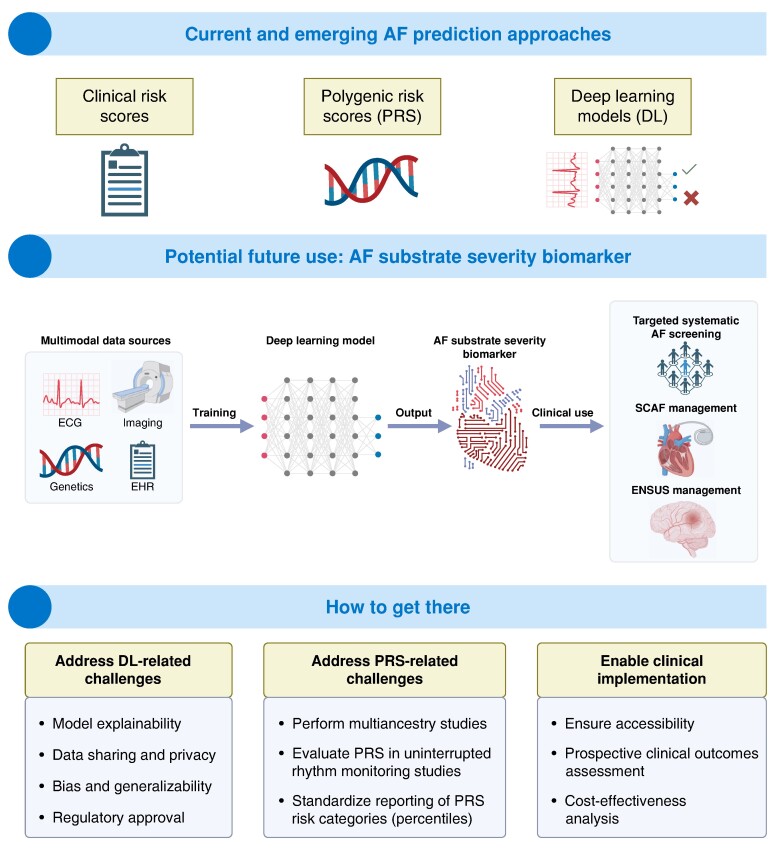
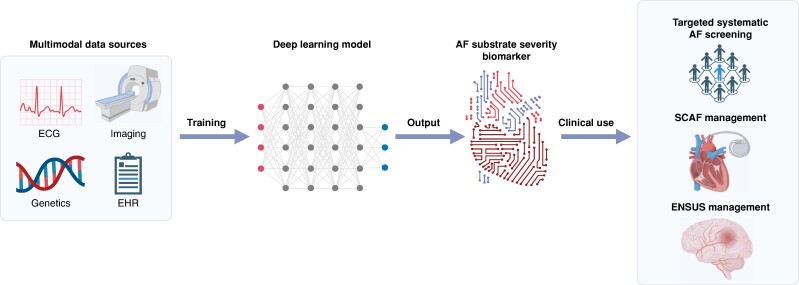
Given the potential additive predictive value of clinical risk factors, ECG data, and genetics, it would be ideal to develop a multimodal AF prediction model. Recent advances in AI carry the potential to integrate this heterogeneous data using large language models (LLMs) and output an AF substrate severity biomarker, capable of predicting clinically significant AF at risk for adverse events (Figure 4).129 In addition to better population targeting in AF screening, such a multimodal approach might also prove useful in SCAF management. Subclinical AF has become an issue of increasing importance due to the exponentially growing number of continuous monitoring devices. While recent trials and guidelines addressed OAC indication in patients with CIEDs presenting with AHREs, the management of AF detected by consumer-based wearables is yet to be defined.24 Another area of much controversy is embolic stroke of undetermined source (ESUS) management where OAC was not shown to be associated with positive outcomes compared to aspirin.130,131 Recent trials also showed no benefit when targeting enriched ESUS patients with suggestive risk factors for cardiac embolism.132,133 The identification of a clinically significant AF substrate could help better stratify patients presenting with ESUS or SCAF and possibly personalize management and OAC indication in these complex conditions.134
Figure 4.
Future DL methods combining multimodal data sources to predict AF substrate severity. AF, atrial fibrillation; EHR, electronic health records; ESUS, embolic stroke from undetermined source; SCAF, subclinical atrial fibrillation.
Another potential area of application would be the prediction of recurrent AF after catheter ablation. A few results from smaller studies support the hypothesis that genetic factors can predict ablation failure.135,136 However, the largest PRS study for AF recurrence so far, conducted by Shoemaker et al.,137 did not find any significant association. Recent work on AI suggested that ECG-based algorithms could predict AF recurrence after ablation.135,138 A prospective randomized trial to guide selection of patients for AF ablation is currently underway (AI-PAFA).139 However, AF recurrence after ablation is a multifaceted issue that is dependent, in part, on procedural circumstances and patient characteristics such that the role of genetic factors remains uncertain.
Several limitations and challenges are associated with the use of digital health solutions in cardiology and involve multiple stakeholders including patients, healthcare professionals, and product developers.140 Those challenges need to be addressed to enable using such novel approaches in AF screening. Lack of algorithm explainability is one of the main barriers to integrating DL in healthcare.141–143 Although recent studies suggest that DL model prediction of incident AF risk using NSR-ECG may identify underlying AM or inherited predisposition to AF, replication of those exploratory findings and additional research in AI algorithm explainability will be necessary in order to facilitate clinical implementation by increasing clinician and patient trust in the model. Furthermore, transparency of DL algorithms is particularly important since DL has the potential to reinforce inherent biases in training data features such as race and sex.144 To address this issue, performance should be reported by subgroup at a minimum, and the training process should take these potential confounders into account. Furthermore, to enhance the quality of AI models in cardiology, five minimal quality criteria were recently proposed to guide the development of new models: complete reporting, clearly defined intended use, rigorous validation, sufficient sample size, and transparency of code and software.145 Additionally, while LLMs offer the opportunity to integrate multimodal data, their large-scale deployment requires addressing central issues in the implementation of AI into healthcare, specifically data sharing and privacy, algorithm standardization, and generalizability across healthcare systems.141,142
A further limiting factor of currently available GWAS and PRS is that most have been derived and tested in ethnically homogeneous populations. As reported above, research is shifting towards multi-ancestry studies.96 Another important limitation is the ascertainment of AF in available PRS studies: AF diagnosis was mainly based on either hospital diagnoses, single ECG, or short-term ECG monitoring. Assessment of PRS performance in patients with uninterrupted rhythm monitoring is yet to be conducted. Another limitation of GWASs is that they do not identify genes. The discovered loci may be found in proximity to candidate genes, which might be related to AF. However, no clear pathological pathway has been identified so far from GWAS studies, and causal relationship remains hypothetical for now. Several studies evaluating the effect of candidate genes are underway. Future work should tackle questions on implementation in clinical care pathways (Table 6). These novel approaches in AF screening and prediction will need to be tested prospectively to establish their feasibility and demonstrate cost-effectiveness, safety, and improved hard clinical endpoints including mortality, hospitalization, and stroke. Ultimately, AF prediction is of limited value if the detected AF is clinically insignificant.
Table 6.
Future research needs towards clinical implementation of AI and PRS in AF screening and management (AF, atrial fibrillation; GWAS, genome wide association study; OAC, oral anticoagulation; PRS, polygenic risk score; RCT, randomized controlled trial)
| Phase | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Development | Develop and adopt a standardized and gated technology development framework145 (e.g. technology readiness levels146) |
| Enhance explainability to enable causal inference | |
| Identify and mitigate bias | |
| Develop multi-ancestry GWAS/PRS | |
| Standardize reporting for PRS risk categories (percentiles) | |
| Deployment | Establish level of evidence required prior to deployment (e.g. RCT vs. observational prospective data) |
| Identify a target population | |
| Establish clinical relevance of AF detected via such methods (e.g. risk of stroke vs. clinical AF) | |
| Establish downstream management pathways (e.g. more intensive AF screening vs. OAC) | |
| Evaluate cost-effectiveness | |
| Establish infrastructure for more accessible genetic testing |
AF, atrial fibrillation; GWAS, genome wide association study; OAC, oral anticoagulation; PRS, polygenic risk score; RCT, randomized controlled trial.
Finally, cost implications need to be considered when assessing the utility of new tools for predicting incident AF. Electrocardiograms are relatively inexpensive and widely available, making them a cost-attractive initial screening tool. In contrast, genetic analysis involves higher costs due to the need for specialized equipment and expert interpretation. Nevertheless, in recent years, genetic sequencing costs have decreased drastically such that cost-effectiveness analyses have demonstrated the potential benefit of genetic screening for certain conditions.147,148 Importantly, the potential additional costs associated with ECG-AI or genetic testing would need to be offset by savings in downstream management and/or reduction of adverse outcomes to qualify as cost-effective (e.g. obviate the need for regular ECG/Holter screening, and ILR implantation).
Conclusion
Prediction of AF is a topic of important contemporary interest. New technologies allow for easy detection of arrhythmia with uncertain clinical benefits. Polygenic risk scores may be an important component in refining any current prediction score. Artificial intelligence would be expected to enable the integration of different modalities, including genetics, to better characterize AF substrate severity and draw a more reliable picture of the risk of developing clinically relevant AF. Such novel prediction models have the potential to enhance population targeting in systematic AF screening and further individualize AF management, with the ultimate objective of preventing related adverse events. This promising multimodal approach deserves further development and testing in future clinical trials to evaluate clinical outcomes, potential additional benefits, and the cost-effectiveness of these novel tools.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
A.M.P. was supported by the Research Scholarship of the Austrian Society of Cardiology and is supported by the George Mines Travelling Fellowship of the Canadian Heart Rhythm Society. R.A. is supported by the ‘Fonds de la recherche en santé du Québec’ (grant 312758), by the Canadian Institute for Advanced Research (CIFAR), by the Montreal Heart Institute Research Centre, the Montreal Heart Institute Foundation, and by the Des Groseillers-Bérard Research Chair. R.T. is supported by the Canada Research Chairs programme. Figures 2, 3, and 4; Supplementary material online, Figure S2; and the graphical abstract were created with Biorender.com.
Contributor Information
Adrian M Petzl, Electrophysiology Service, Department of Medicine, Montreal Heart Institute, Université de Montréal, 5000 rue Bélanger, Montreal, QC H1T 1C8, Canada; Cardiovascular Genetics Center, Montreal Heart Institute, Université de Montréal, 5000 rue Bélanger, Montreal, QC H1T 1C8, Canada.
Gilbert Jabbour, Electrophysiology Service, Department of Medicine, Montreal Heart Institute, Université de Montréal, 5000 rue Bélanger, Montreal, QC H1T 1C8, Canada; Heartwise (heartwise.ai), Montreal Heart Institute, Montreal, Canada.
Julia Cadrin-Tourigny, Electrophysiology Service, Department of Medicine, Montreal Heart Institute, Université de Montréal, 5000 rue Bélanger, Montreal, QC H1T 1C8, Canada; Cardiovascular Genetics Center, Montreal Heart Institute, Université de Montréal, 5000 rue Bélanger, Montreal, QC H1T 1C8, Canada.
Helmut Pürerfellner, Department of Internal Medicine 2/Cardiology, Ordensklinikum Linz Elisabethinen, Linz, Austria.
Laurent Macle, Electrophysiology Service, Department of Medicine, Montreal Heart Institute, Université de Montréal, 5000 rue Bélanger, Montreal, QC H1T 1C8, Canada.
Paul Khairy, Electrophysiology Service, Department of Medicine, Montreal Heart Institute, Université de Montréal, 5000 rue Bélanger, Montreal, QC H1T 1C8, Canada.
Robert Avram, Heartwise (heartwise.ai), Montreal Heart Institute, Montreal, Canada; Department of Medicine, Montreal Heart Institute, Université de Montréal, Montreal, Canada.
Rafik Tadros, Electrophysiology Service, Department of Medicine, Montreal Heart Institute, Université de Montréal, 5000 rue Bélanger, Montreal, QC H1T 1C8, Canada; Cardiovascular Genetics Center, Montreal Heart Institute, Université de Montréal, 5000 rue Bélanger, Montreal, QC H1T 1C8, Canada.
Supplementary material
Supplementary material is available at Europace online.
Data availability
No new data were generated or analysed in support of this research.
References
- 1. Tsao CW, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, Anderson CAM, Arora P, Avery CL et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2023 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023;147:e93–621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Goette A, Kalman JM, Aguinaga L, Akar J, Cabrera JA, Chen SA et al. EHRA/HRS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus on atrial cardiomyopathies: definition, characterization, and clinical implication. Europace 2016;18:1455–90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Qin D, Mansour MC, Ruskin JN, Heist EK. Atrial fibrillation-mediated cardiomyopathy. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2019;12:e007809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Santhanakrishnan R, Wang N, Larson MG, Magnani JW, McManus DD, Lubitz SA et al. Atrial fibrillation begets heart failure and vice versa: temporal associations and differences in preserved versus reduced ejection fraction. Circulation 2016;133:484–92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Koh YH, Lew LZW, Franke KB, Elliott AD, Lau DH, Thiyagarajah A et al. Predictive role of atrial fibrillation in cognitive decline: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 2.8 million individuals. Europace 2022;24:1229–39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Papanastasiou CA, Theochari CA, Zareifopoulos N, Arfaras-Melainis A, Giannakoulas G, Karamitsos TD et al. Atrial fibrillation is associated with cognitive impairment, all-cause dementia, vascular dementia, and Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gen Intern Med 2021;36:3122–35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Hart RG, Pearce LA, Aguilar MI. Meta-analysis: antithrombotic therapy to prevent stroke in patients who have nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Ann Intern Med 2007;146:857–67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Ruff CT, Giugliano RP, Braunwald E, Hoffman EB, Deenadayalu N, Ezekowitz MD et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet 2014;383:955–62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Kirchhof P, Camm AJ, Goette A, Brandes A, Eckardt L, Elvan A et al. Early rhythm-control therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2020;383:1305–16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Freedman B, Camm J, Calkins H, Healey JS, Rosenqvist M, Wang J et al. Screening for atrial fibrillation: a report of the AF-SCREEN International Collaboration. Circulation 2017;135:1851–67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Mairesse GH, Moran P, Van Gelder IC, Elsner C, Rosenqvist M, Mant J et al. Screening for atrial fibrillation: a European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) consensus document endorsed by the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS), and Sociedad Latinoamericana de Estimulacion Cardiaca y Electrofisiologia (SOLAECE). Europace 2017;19:1589–623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, Arbelo E, Bax JJ, Blomström-Lundqvist C et al. 2020 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): the task force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J 2021;42:373–498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Andrade JG, Aguilar M, Atzema C, Bell A, Cairns JA, Cheung CC et al. The 2020 Canadian Cardiovascular Society/Canadian Heart Rhythm Society comprehensive guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation. Can J Cardiol 2020;36:1847–948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Lubitz SA, Atlas SJ, Ashburner JM, Lipsanopoulos ATT, Borowsky LH, Guan W et al. Screening for atrial fibrillation in older adults at primary care visits: VITAL-AF randomized controlled trial. Circulation 2022;145:946–54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Uittenbogaart SB, Verbiest-van Gurp N, Lucassen WAM, Winkens B, Nielen M, Erkens PMG et al. Opportunistic screening versus usual care for detection of atrial fibrillation in primary care: cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2020;370:m3208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Schnabel RB, Marinelli EA, Arbelo E, Boriani G, Boveda S, Buckley CM et al. Early diagnosis and better rhythm management to improve outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation: the 8th AFNET/EHRA consensus conference. Europace 2023;25:6–27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Svennberg E, Friberg L, Frykman V, Al-Khalili F, Engdahl J, Rosenqvist M. Clinical outcomes in systematic screening for atrial fibrillation (STROKESTOP): a multicentre, parallel group, unmasked, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2021;398:1498–506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Svennberg E, Tjong F, Goette A, Akoum N, Di Biase L, Bordachar P et al. How to use digital devices to detect and manage arrhythmias: an EHRA practical guide. Europace 2022;24:979–1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Noseworthy PA, Kaufman ES, Chen LY, Chung MK, Elkind MSV, Joglar JA et al. Subclinical and device-detected atrial fibrillation: pondering the knowledge gap: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019;140:e944–63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Diederichsen SZ, Haugan KJ, Brandes A, Lanng MB, Graff C, Krieger D et al. Natural history of subclinical atrial fibrillation detected by implanted loop recorders. J Am Coll Cardiol 2019;74:2771–81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Svendsen JH, Diederichsen SZ, Højberg S, Krieger DW, Graff C, Kronborg C et al. Implantable loop recorder detection of atrial fibrillation to prevent stroke (The LOOP Study): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2021;398:1507–16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Svennberg E, Caiani EG, Bruining N, Desteghe L, Han JK, Narayan SM et al. The digital journey: 25 years of digital development in electrophysiology from an Europace perspective. Europace 2023;25:euad176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Brandes A, Stavrakis S, Freedman B, Antoniou S, Boriani G, Camm AJ et al. Consumer-led screening for atrial fibrillation: frontier review of the AF-SCREEN International Collaboration. Circulation 2022;146:1461–74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Joglar JA, Chung MK, Armbruster AL, Benjamin EJ, Chyou JY, Cronin EM et al. 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS guideline for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2023;149:e1–156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Arnar DO, Mairesse GH, Boriani G, Calkins H, Chin A, Coats A et al. Management of asymptomatic arrhythmias: a European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) consensus document, endorsed by the Heart Failure Association (HFA), Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS), Cardiac Arrhythmia Society of Southern Africa (CASSA), and Latin America Heart Rhythm Society (LAHRS). Europace 2019;21:844–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Boriani G, Gerra L, Mei DA, Bonini N, Vitolo M, Proietti M et al. Detection of subclinical atrial fibrillation with cardiac implanted electronic devices: what decision making on anticoagulation after the NOAH and ARTESiA trials? Eur J Intern Med 2024;123:37–41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Sanders P, Svennberg E, Diederichsen SZ, Crijns H, Lambiase PD, Boriani G, et al. Great debate: device-detected subclinical atrial fibrillation should be treated like clinical atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J 2024;45:2594–2603. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehae365 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Bertaglia E, Blank B, Blomström-Lundqvist C, Brandes A, Cabanelas N, Dan GA et al. Atrial high-rate episodes: prevalence, stroke risk, implications for management, and clinical gaps in evidence. Europace 2019;21:1459–67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Healey JS, Connolly SJ, Gold MR, Israel CW, Van Gelder IC, Capucci A et al. Subclinical atrial fibrillation and the risk of stroke. N Engl J Med 2012;366:120–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Sanna T, Diener HC, Passman RS, Di Lazzaro V, Bernstein RA, Morillo CA et al. Cryptogenic stroke and underlying atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2014;370:2478–86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Reiffel JA, Verma A, Kowey PR, Halperin JL, Gersh BJ, Wachter R et al. Incidence of previously undiagnosed atrial fibrillation using insertable cardiac monitors in a high-risk population: the REVEAL AF study. JAMA Cardiol 2017;2:1120–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Kirchhof P, Toennis T, Goette A, Camm AJ, Diener HC, Becher N et al. Anticoagulation with edoxaban in patients with atrial high-rate episodes. N Engl J Med 2023;389:1167–79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. McIntyre WF, Benz AP, Becher N, Healey JS, Granger CB, Rivard L et al. Direct oral anticoagulants for stroke prevention in patients with device-detected atrial fibrillation: a study-level meta-analysis of the NOAH-AFNET 6 and ARTESiA trials. Circulation 2024;149:981–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Segan L, Canovas R, Nanayakkara S, Chieng D, Prabhu S, Voskoboinik A et al. New-onset atrial fibrillation prediction: the HARMS2-AF risk score. Eur Heart J 2023;44:3443–52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Chung MK, Eckhardt LL, Chen LY, Ahmed HM, Gopinathannair R, Joglar JA et al. Lifestyle and risk factor modification for reduction of atrial fibrillation: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020;141:e750–72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Vyas V, Lambiase P. Obesity and atrial fibrillation: epidemiology, pathophysiology and novel therapeutic opportunities. Arrhythm Electrophysiol Rev 2019;8:28–36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Jones NR, Taylor KS, Clare JT, Aveyard P. Weight change and the risk of incident atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart 2019;105:1799–805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Mozaffarian D, Furberg CD, Psaty BM, Siscovick D. Physical activity and incidence of atrial fibrillation in older adults. Circulation 2008;118:800–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Schnabel RB, Sullivan LM, Levy D, Pencina MJ, Massaro JM, D'Agostino RB Sr et al. Development of a risk score for atrial fibrillation (Framingham Heart Study): a community-based cohort study. Lancet 2009;373:739–45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Chamberlain AM, Agarwal SK, Folsom AR, Soliman EZ, Chambless LE, Crow R et al. A clinical risk score for atrial fibrillation in a biracial prospective cohort (from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities [ARIC] study). Am J Cardiol 2011;107:85–91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Zuo ML, Liu S, Chan KH, Lau KK, Chong BH, Lam KF et al. The CHADS2 and CHA 2DS 2-VASc scores predict new occurrence of atrial fibrillation and ischemic stroke. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 2013;37:47–54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Fauchier L, Clementy N, Pelade C, Collignon C, Nicolle E, Lip GY. Patients with ischemic stroke and incident atrial fibrillation: a nationwide cohort study. Stroke 2015;46:2432–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Suenari K, Chao TF, Liu CJ, Kihara Y, Chen TJ, Chen SA. Usefulness of HATCH score in the prediction of new-onset atrial fibrillation for Asians. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e5597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Li YG, Bisson A, Bodin A, Herbert J, Grammatico-Guillon L, Joung B et al. C(2) HEST score and prediction of incident atrial fibrillation in poststroke patients: a French nationwide study. J Am Heart Assoc 2019;8:e012546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Hulme OL, Khurshid S, Weng LC, Anderson CD, Wang EY, Ashburner JM et al. Development and validation of a prediction model for atrial fibrillation using electronic health records. JACC Clin Electrophysiol 2019;5:1331–41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Alonso A, Krijthe BP, Aspelund T, Stepas KA, Pencina MJ, Moser CB et al. Simple risk model predicts incidence of atrial fibrillation in a racially and geographically diverse population: the CHARGE-AF consortium. J Am Heart Assoc 2013;2:e000102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Himmelreich JCL, Veelers L, Lucassen WAM, Schnabel RB, Rienstra M, van Weert H et al. Prediction models for atrial fibrillation applicable in the community: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Europace 2020;22:684–94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Khurshid S, Kartoun U, Ashburner JM, Trinquart L, Philippakis A, Khera AV et al. Performance of atrial fibrillation risk prediction models in over 4 million individuals. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2021;14:e008997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Sinner MF, Stepas KA, Moser CB, Krijthe BP, Aspelund T, Sotoodehnia N et al. B-type natriuretic peptide and C-reactive protein in the prediction of atrial fibrillation risk: the CHARGE-AF consortium of community-based cohort studies. Europace 2014;16:1426–33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Nielsen JC, Lin YJ, de Oliveira Figueiredo MJ, Sepehri Shamloo A, Alfie A, Boveda S et al. European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA)/Heart Rhythm Society (HRS)/Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS)/Latin American Heart Rhythm Society (LAHRS) expert consensus on risk assessment in cardiac arrhythmias: use the right tool for the right outcome, in the right population. Europace 2020;22:1147–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Li YG, Pastori D, Farcomeni A, Yang PS, Jang E, Joung B et al. A simple clinical risk score (C(2)HEST) for predicting incident atrial fibrillation in Asian subjects: derivation in 471,446 Chinese subjects, with internal validation and external application in 451,199 Korean subjects. Chest 2019;155:510–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Ashburner JM, Wang X, Li X, Khurshid S, Ko D, Trisini Lipsanopoulos A et al. Re-CHARGE-AF: recalibration of the CHARGE-AF model for atrial fibrillation risk prediction in patients with acute stroke. J Am Heart Assoc 2021;10:e022363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Christophersen IE, Yin X, Larson MG, Lubitz SA, Magnani JW, McManus DD et al. A comparison of the CHARGE-AF and the CHA2DS2-VASc risk scores for prediction of atrial fibrillation in the Framingham Heart Study. Am Heart J 2016;178:45–54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Alonso A, Roetker NS, Soliman EZ, Chen LY, Greenland P, Heckbert SR. Prediction of atrial fibrillation in a racially diverse cohort: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). J Am Heart Assoc 2016;5:e003077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Pfister R, Brägelmann J, Michels G, Wareham NJ, Luben R, Khaw KT. Performance of the CHARGE-AF risk model for incident atrial fibrillation in the EPIC Norfolk cohort. Eur J Prev Cardiol 2015;22:932–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Shulman E, Kargoli F, Aagaard P, Hoch E, Di Biase L, Fisher J et al. Validation of the framingham heart study and CHARGE-AF risk scores for atrial fibrillation in Hispanics, African-Americans, and non-Hispanic Whites. Am J Cardiol 2016;117:76–83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Samuel AL. Some studies in machine learning using the game of checkers. Ibm J Res Dev 1959;3:211–29. [Google Scholar]
- 58. LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature 2015;521:436–44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Nagarajan VD, Lee SL, Robertus JL, Nienaber CA, Trayanova NA, Ernst S. Artificial intelligence in the diagnosis and management of arrhythmias. Eur Heart J 2021;42:3904–16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Géron A; O'Reilly Media, Inc . Hands-on machine learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow: concepts, tools, and techniques to build intelligent systems. Beijing: O’Reilly; 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 61. Avram R, Olgin JE, Tison GH. The rise of open-sourced machine learning in small and imbalanced datasets: predicting in-stent restenosis. Can J Cardiol 2020;36:1574–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Rivner H, Mitrani RD, Goldberger JJ. Atrial myopathy underlying atrial fibrillation. Arrhythm Electrophysiol Rev 2020;9:61–70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Andrade J, Khairy P, Dobrev D, Nattel S. The clinical profile and pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation: relationships among clinical features, epidemiology, and mechanisms. Circ Res 2014;114:1453–68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Kottkamp H. Human atrial fibrillation substrate: towards a specific fibrotic atrial cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J 2013;34:2731–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Verbrugge FH, Reddy YNV, Attia ZI, Friedman PA, Noseworthy PA, Lopez-Jimenez F et al. Detection of left atrial myopathy using artificial intelligence-enabled electrocardiography. Circ Heart Fail 2022;15:e008176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Attia ZI, Noseworthy PA, Lopez-Jimenez F, Asirvatham SJ, Deshmukh AJ, Gersh BJ et al. An artificial intelligence-enabled ECG algorithm for the identification of patients with atrial fibrillation during sinus rhythm: a retrospective analysis of outcome prediction. Lancet 2019;394:861–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Raghunath S, Pfeifer JM, Ulloa-Cerna AE, Nemani A, Carbonati T, Jing L et al. Deep neural networks can predict new-onset atrial fibrillation from the 12-lead ECG and help identify those at risk of atrial fibrillation-related stroke. Circulation 2021;143:1287–98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Noseworthy PA, Attia ZI, Behnken EM, Giblon RE, Bews KA, Liu S et al. Artificial intelligence-guided screening for atrial fibrillation using electrocardiogram during sinus rhythm: a prospective non-randomised interventional trial. Lancet 2022;400:1206–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Khurshid S, Friedman S, Reeder C, Di Achille P, Diamant N, Singh P et al. ECG-based deep learning and clinical risk factors to predict atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2022;145:122–33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Wang X, Khurshid S, Choi SH, Friedman S, Weng LC, Reeder C et al. Genetic susceptibility to atrial fibrillation identified via deep learning of 12-lead electrocardiograms. Circ Genom Precis Med 2023;16:340–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Yuan N, Duffy G, Dhruva SS, Oesterle A, Pellegrini CN, Theurer J et al. Deep learning of electrocardiograms in sinus rhythm from US veterans to predict atrial fibrillation. JAMA Cardiol 2023;8:1131–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Dupulthys S, Dujardin K, Anné W, Pollet P, Vanhaverbeke M, McAuliffe D et al. Single-lead ECG AI model with risk factors detects atrial fibrillation during sinus rhythm. Europace 2023;26:euad354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Gadaleta M, Harrington P, Barnhill E, Hytopoulos E, Turakhia MP, Steinhubl SR et al. Prediction of atrial fibrillation from at-home single-lead ECG signals without arrhythmias. NPJ Digit Med 2023;6:229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Hygrell T, Viberg F, Dahlberg E, Charlton PH, Kemp Gudmundsdottir K, Mant J et al. An artificial intelligence-based model for prediction of atrial fibrillation from single-lead sinus rhythm electrocardiograms facilitating screening. Europace 2023;25:1332–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Williams K, Modi RN, Dymond A, Hoare S, Powell A, Burt J et al. Cluster randomised controlled trial of screening for atrial fibrillation in people aged 70 years and over to reduce stroke: protocol for the pilot study for the SAFER trial. BMJ Open 2022;12:e065066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Svennberg E, Engdahl J, Al-Khalili F, Friberg L, Frykman V, Rosenqvist M. Mass screening for untreated atrial fibrillation: the STROKESTOP study. Circulation 2015;131:2176–84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Hill NR, Ayoubkhani D, McEwan P, Sugrue DM, Farooqui U, Lister S et al. Predicting atrial fibrillation in primary care using machine learning. PLoS One 2019;14:e0224582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Sekelj S, Sandler B, Johnston E, Pollock KG, Hill NR, Gordon J et al. Detecting undiagnosed atrial fibrillation in UK primary care: validation of a machine learning prediction algorithm in a retrospective cohort study. Eur J Prev Cardiol 2021;28:598–605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Hill NR, Groves L, Dickerson C, Ochs A, Pang D, Lawton S et al. Identification of undiagnosed atrial fibrillation using a machine learning risk-prediction algorithm and diagnostic testing (PULsE-AI) in primary care: a multi-centre randomized controlled trial in England. Eur Heart J Digit Health 2022;3:195–204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Gensheimer MF, Narasimhan B. A scalable discrete-time survival model for neural networks. PeerJ 2019;7:e6257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Kemp Gudmundsdottir K, Fredriksson T, Svennberg E, Al-Khalili F, Friberg L, Frykman V et al. Stepwise mass screening for atrial fibrillation using N-terminal B-type natriuretic peptide: the STROKESTOP II study. Europace 2020;22:24–32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Attia ZI, Friedman PA, Noseworthy PA, Lopez-Jimenez F, Ladewig DJ, Satam G et al. Age and sex estimation using artificial intelligence from standard 12-lead ECGs. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2019;12:e007284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Arnar DO, Thorvaldsson S, Manolio TA, Thorgeirsson G, Kristjansson K, Hakonarson H et al. Familial aggregation of atrial fibrillation in Iceland. Eur Heart J 2006;27:708–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Weng LC, Choi SH, Klarin D, Smith JG, Loh PR, Chaffin M et al. Heritability of atrial fibrillation. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 2017;10:e001838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Chen YH, Xu SJ, Bendahhou S, Wang XL, Wang Y, Xu WY et al. KCNQ1 gain-of-function mutation in familial atrial fibrillation. Science 2003;299:251–4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86. Andersen JH, Andreasen L, Olesen MS. Atrial fibrillation—a complex polygenetic disease. Eur J Hum Genet 2021;29:1051–60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87. Johnson JN, Tester DJ, Perry J, Salisbury BA, Reed CR, Ackerman MJ. Prevalence of early-onset atrial fibrillation in congenital long QT syndrome. Heart Rhythm 2008;5:704–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Vlachos K, Mascia G, Martin CA, Bazoukis G, Frontera A, Cheniti G et al. Atrial fibrillation in Brugada syndrome: current perspectives. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2020;31:975–84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89. Falasconi G, Pannone L, Slavich M, Margonato A, Fragasso G, Spoladore R. Atrial fibrillation in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: pathophysiology, diagnosis and management. Am J Cardiovasc Dis 2020;10:409–18. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90. Buckley BJR, Harrison SL, Gupta D, Fazio-Eynullayeva E, Underhill P, Lip GYH. Atrial fibrillation in patients with cardiomyopathy: prevalence and clinical outcomes from real-world data. J Am Heart Assoc 2021;10:e021970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91. Goodyer WR, Dunn K, Caleshu C, Jackson M, Wylie J, Moscarello T et al. Broad genetic testing in a clinical setting uncovers a high prevalence of titin loss-of-function variants in very early onset atrial fibrillation. Circ Genom Precis Med 2019;12:e002713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92. Yoneda ZT, Anderson KC, Quintana JA, O'Neill MJ, Sims RA, Glazer AM et al. Early-onset atrial fibrillation and the prevalence of rare variants in cardiomyopathy and arrhythmia genes. JAMA Cardiol 2021;6:1371–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93. Yoneda ZT, Anderson KC, Ye F, Quintana JA, O'Neill MJ, Sims RA et al. Mortality among patients with early-onset atrial fibrillation and rare variants in cardiomyopathy and arrhythmia genes. JAMA Cardiol 2022;7:733–41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94. Choi SH, Jurgens SJ, Weng LC, Pirruccello JP, Roselli C, Chaffin M et al. Monogenic and polygenic contributions to atrial fibrillation risk: results from a national biobank. Circ Res 2020;126:200–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95. Pensa AV, Baman JR, Puckelwartz MJ, Wilcox JE. Genetically based atrial fibrillation: current considerations for diagnosis and management. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2022;33:1944–53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96. Miyazawa K, Ito K, Ito M, Zou Z, Kubota M, Nomura S et al. Cross-ancestry genome-wide analysis of atrial fibrillation unveils disease biology and enables cardioembolic risk prediction. Nat Genet 2023;55:187–97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97. Roselli C, Rienstra M, Ellinor PT. Genetics of atrial fibrillation in 2020: GWAS, genome sequencing, polygenic risk, and beyond. Circ Res 2020;127:21–33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98. Gudbjartsson DF, Arnar DO, Helgadottir A, Gretarsdottir S, Holm H, Sigurdsson A et al. Variants conferring risk of atrial fibrillation on chromosome 4q25. Nature 2007;448:353–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99. Roselli C, Chaffin MD, Weng L-C, Aeschbacher S, Ahlberg G, Albert CM et al. Multi-ethnic genome-wide association study for atrial fibrillation. Nat Genet 2018;50:1225–33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100. Christophersen IE, Rienstra M, Roselli C, Yin X, Geelhoed B, Barnard J et al. Large-scale analyses of common and rare variants identify 12 new loci associated with atrial fibrillation. Nat Genet 2017;49:946–52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101. Logan M, Pagán-Westphal SM, Smith DM, Paganessi L, Tabin CJ. The transcription factor Pitx2 mediates situs-specific morphogenesis in response to left-right asymmetric signals. Cell 1998;94:307–17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102. Mommersteeg MTM, Brown NA, Prall OWJ, de Gier-de Vries C, Harvey RP, Moorman AFM et al. Pitx2c and Nkx2-5 are required for the formation and identity of the pulmonary myocardium. Circ Res 2007;101:902–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103. Gudbjartsson DF, Holm H, Gretarsdottir S, Thorleifsson G, Walters GB, Thorgeirsson G et al. A sequence variant in ZFHX3 on 16q22 associates with atrial fibrillation and ischemic stroke. Nat Genet 2009;41:876–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104. Benjamin EJ, Rice KM, Arking DE, Pfeufer A, van Noord C, Smith AV et al. Variants in ZFHX3 are associated with atrial fibrillation in individuals of European ancestry. Nat Genet 2009;41:879–81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105. Ellinor PT, Lunetta KL, Glazer NL, Pfeufer A, Alonso A, Chung MK et al. Common variants in KCNN3 are associated with lone atrial fibrillation. Nat Genet 2010;42:240–4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106. Sinner MF, Tucker NR, Lunetta KL, Ozaki K, Smith JG, Trompet S et al. Integrating genetic, transcriptional, and functional analyses to identify 5 novel genes for atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2014;130:1225–35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107. Marston NA, Garfinkel AC, Kamanu FK, Melloni GM, Roselli C, Jarolim P et al. A polygenic risk score predicts atrial fibrillation in cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J 2023;44:221–31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108. Khera AV, Chaffin M, Aragam KG, Haas ME, Roselli C, Choi SH et al. Genome-wide polygenic scores for common diseases identify individuals with risk equivalent to monogenic mutations. Nat Genet 2018;50:1219–24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109. Choi SW, Mak TS, O’Reilly PF. Tutorial: a guide to performing polygenic risk score analyses. Nat Protoc 2020;15:2759–72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110. Tam V, Patel N, Turcotte M, Bossé Y, Paré G, Meyre D. Benefits and limitations of genome-wide association studies. Nat Rev Genet 2019;20:467–84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111. Huang HD, Darbar D. Genetic risk scores for atrial fibrillation: do they improve risk estimation? Can J Cardiol 2017;33:422–4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112. Do CB, Hinds DA, Francke U, Eriksson N. Comparison of family history and SNPs for predicting risk of complex disease. PLoS Genet 2012;8:e1002973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113. Lubitz SA, Lunetta KL, Lin H, Arking DE, Trompet S, Li G et al. Novel genetic markers associate with atrial fibrillation risk in Europeans and Japanese. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014;63:1200–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114. Smith JG, Newton-Cheh C, Almgren P, Melander O, Platonov PG. Genetic polymorphisms for estimating risk of atrial fibrillation in the general population: a prospective study. Arch Intern Med 2012;172:742–4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115. Tada H, Shiffman D, Smith JG, Sjögren M, Lubitz SA, Ellinor PT et al. Twelve-single nucleotide polymorphism genetic risk score identifies individuals at increased risk for future atrial fibrillation and stroke. Stroke 2014;45:2856–62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116. Lubitz SA, Yin X, Lin HJ, Kolek M, Smith JG, Trompet S et al. Genetic risk prediction of atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2017;135:1311–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117. Weng L-C, Preis SR, Hulme OL, Larson MG, Choi SH, Wang B et al. Genetic predisposition, clinical risk factor burden, and lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2018;137:1027–38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118. Muse ED, Wineinger NE, Spencer EG, Peters M, Henderson R, Zhang Y et al. Validation of a genetic risk score for atrial fibrillation: a prospective multicenter cohort study. PLoS Med 2018;15:e1002525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119. Lazarte J, Dron JS, McIntyre AD, Skanes AC, Gula LJ, Tang AS et al. Evaluating polygenic risk scores in “lone” atrial fibrillation. CJC Open 2021;3:751–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120. Börschel CS, Ohlrogge AH, Geelhoed B, Niiranen T, Havulinna AS, Palosaari T et al. Risk prediction of atrial fibrillation in the community combining biomarkers and genetics. Europace 2021;23:674–81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121. Khurshid S, Mars N, Haggerty CM, Huang Q, Weng LC, Hartzel DN et al. Predictive accuracy of a clinical and genetic risk model for atrial fibrillation. Circ Genom Precis Med 2021;14:e003355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122. Ellinor PT, Lunetta KL, Albert CM, Glazer NL, Ritchie MD, Smith AV et al. Meta-analysis identifies six new susceptibility loci for atrial fibrillation. Nat Genet 2012;44:670–5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123. Nielsen JB, Thorolfsdottir RB, Fritsche LG, Zhou W, Skov MW, Graham SE et al. Biobank-driven genomic discovery yields new insight into atrial fibrillation biology. Nat Genet 2018;50:1234–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124. Lambert SA, Abraham G, Inouye M. Towards clinical utility of polygenic risk scores. Hum Mol Genet 2019;28:R133–42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125. Lazarte J, Dron JS, McIntyre AD, Skanes AC, Gula LJ, Tang AS et al. Role of common genetic variation in lone atrial fibrillation. Circ Genom Precis Med 2021;14:e003179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126. Weng LC, Preis SR, Hulme OL, Larson MG, Choi SH, Wang B et al. Genetic predisposition, clinical risk factor burden, and lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation Circulation. Circulation 2018;137:1027–38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127. Wilson JMG, Jungner G. Principles and practice of screening for disease. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1968. [Google Scholar]
- 128. Vassy JL, Brunette CA, Lebo MS, MacIsaac K, Yi T, Danowski ME et al. The GenoVA study: equitable implementation of a pragmatic randomized trial of polygenic-risk scoring in primary care. Am J Hum Genet 2023;110:1841–52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129. Boonstra MJ, Weissenbacher D, Moore JH, Gonzalez-Hernandez G, Asselbergs FW. Artificial intelligence: revolutionizing cardiology with large language models. Eur Heart J 2024;45:332–45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130. Hart RG, Sharma M, Mundl H, Kasner SE, Bangdiwala SI, Berkowitz SD et al. Rivaroxaban for stroke prevention after embolic stroke of undetermined source. N Engl J Med 2018;378:2191–201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131. Diener HC, Sacco RL, Easton JD, Granger CB, Bernstein RA, Uchiyama S et al. Dabigatran for prevention of stroke after embolic stroke of undetermined source. N Engl J Med 2019;380:1906–17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132. Geisler T, Keller T, Martus P, Poli K, Serna-Higuita LM, Schreieck J et al. Apixaban versus aspirin for embolic stroke of undetermined source. NEJM Evid 2024;3:EVIDoa2300235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133. Kamel H, Longstreth WT Jr, Tirschwell DL, Kronmal RA, Marshall RS, Broderick JP et al. Apixaban to prevent recurrence after cryptogenic stroke in patients with atrial cardiopathy: the ARCADIA randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2024;331:573–81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134. Choi J, Kim JY, Cho MS, Kim M, Kim J, Oh IY, et al. Artificial intelligence predicts undiagnosed atrial fibrillation in patients with embolic stroke of undetermined source using sinus rhythm electrocardiograms. Heart Rhythm 2024:S1547-5271(24)00274-1. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2024.03.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135. Jiang J, Deng H, Liao H, Fang X, Zhan X, Wei W et al. An artificial intelligence-enabled ECG algorithm for predicting the risk of recurrence in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation. J Clin Med 2023;12:1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136. Choe W-S, Kang JH, Choi E-K, Shin SY, Lubitz SA, Ellinor PT et al. A genetic risk score for atrial fibrillation predicts the response to catheter ablation. Korean Circ J 2019;49:338–49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137. Shoemaker MB, Husser D, Roselli C, Al Jazairi M, Chrispin J, Kühne M et al. Genetic susceptibility for atrial fibrillation in patients undergoing atrial fibrillation ablation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2020;13:e007676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138. Shade JK, Ali RL, Basile D, Popescu D, Akhtar T, Marine JE et al. Preprocedure application of machine learning and mechanistic simulations predicts likelihood of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation recurrence following pulmonary vein isolation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2020;13:e008213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139. Yonsei University . 2021. Artificial Intelligence Guided Patient Selection for Atrial Fibrillation Catheter Ablation: Randomized Clinical Trial (AI-PAFA Trial). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04997824
- 140. Leclercq C, Witt H, Hindricks G, Katra RP, Albert D, Belliger A et al. Wearables, telemedicine, and artificial intelligence in arrhythmias and heart failure: proceedings of the European Society of Cardiology Cardiovascular Round Table. Europace 2022;24:1372–83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141. National Science and Technology Council Select Committee on Artificial Intelligence . National Artificial Intelligence Research and Development Strategic Plan: 2023 Update. The White House; 2023. Retrieved from https://www.whitehouse.gov/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/National-Artificial-Intelligence-Research-and-Development-Strategic-Plan-2023-Update.pdf
- 142. He J, Baxter SL, Xu J, Xu J, Zhou X, Zhang K. The practical implementation of artificial intelligence technologies in medicine. Nat Med 2019;25:30–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143. Gill SK, Karwath A, Uh HW, Cardoso VR, Gu Z, Barsky A et al. Artificial intelligence to enhance clinical value across the spectrum of cardiovascular healthcare. Eur Heart J 2023;44:713–25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144. Char DS, Shah NH, Magnus D. Implementing machine learning in health care—addressing ethical challenges. N Engl J Med 2018;378:981–3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145. van Royen FS, Asselbergs FW, Alfonso F, Vardas P, van Smeden M. Five critical quality criteria for artificial intelligence-based prediction models. Eur Heart J 2023;44:4831–4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146. Lavin A, Gilligan-Lee CM, Visnjic A, Ganju S, Newman D, Ganguly S et al. Technology readiness levels for machine learning systems. Nat Commun 2022;13:6039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147. Guzauskas GF, Garbett S, Zhou Z, Schildcrout JS, Graves JA, Williams MS et al. Population genomic screening for three common hereditary conditions : a cost-effectiveness analysis. Ann Intern Med 2023;176:585–95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148. Wetterstrand K. DNA Sequencing Costs: Data from the NHGRI Genome Sequencing Program (GSP). www.genome.gov/sequencingcostsdata (8 June 2024 last accessed).
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
No new data were generated or analysed in support of this research.