Abstract
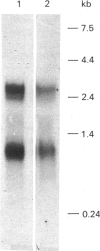
Phospholamban cDNA from pig stomach smooth muscle was cloned and sequenced. The 737-nucleotide-residue cDNA contained an open reading frame of 156 nucleotide residues encoding a peptide of 52 amino acid residues (Mr 6080). This peptide shares 100% sequence identity with dog cardiac-muscle phospholamban. It differs from rabbit cardiac-muscle and slow-twitch skeletal-muscle phospholamban only at position 2, which is a glutamic acid residue in rabbit phospholamban, but an aspartic acid residue in the pig smooth-muscle protein. Northern-blot analysis reveals the presence of several phospholamban mRNAs in smooth muscle, but a 900-nucleotide-residue and a 2800-nucleotide-residue transcript predominate.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii J., Lytton J., Tada M., MacLennan D. H. Rabbit cardiac and slow-twitch muscle express the same phospholamban gene. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 18;227(1):51–55. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81412-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii J., Ueno A., Kitano K., Tanaka S., Kadoma M., Tada M. Complete complementary DNA-derived amino acid sequence of canine cardiac phospholamban. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):301–304. doi: 10.1172/JCI112799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasa Y., Hosey M. M. Phosphorylation of cardiac sarcolemma proteins by the calcium-activated phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):534–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchberger M. A., Tada M. Effects of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase on sarcoplasmic reticulum isolated from cardiac and slow and fast contracting skeletal muscles. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 10;251(3):725–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Peuch C. J., Haiech J., Demaille J. G. Concerted regulation of cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium transport by cyclic adenosine monophosphate dependent and calcium--calmodulin-dependent phosphorylations. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 13;18(23):5150–5157. doi: 10.1021/bi00590a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeymaekers L., Hofmann F., Casteels R. Cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates phospholamban in isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum from cardiac and smooth muscle. Biochem J. 1988 May 15;252(1):269–273. doi: 10.1042/bj2520269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeymaekers L., Jones L. R. Evidence for the presence of phospholamban in the endoplasmic reticulum of smooth muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 19;882(2):258–265. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmerman H. K., Collins J. H., Theibert J. L., Wegener A. D., Jones L. R. Sequence analysis of phospholamban. Identification of phosphorylation sites and two major structural domains. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13333–13341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada M., Katz A. M. Phosphorylation of the sarcoplasmic reticulum and sarcolemma. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:401–423. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.002153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda A., Kitano K., Fujii J., Kadoma M., Tada M., Tanaka S. The cDNA sequence of the major phospholamban mRNA in canine cardiac ventricular muscle. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6738–6738. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]