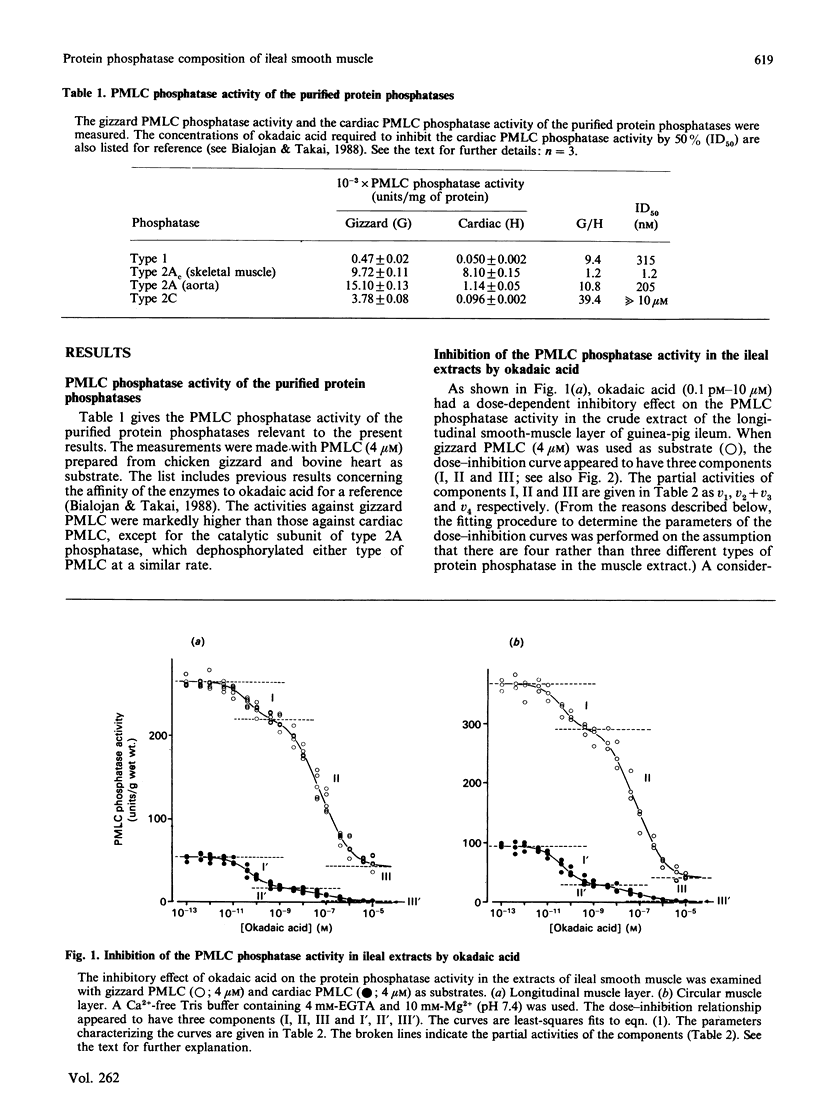
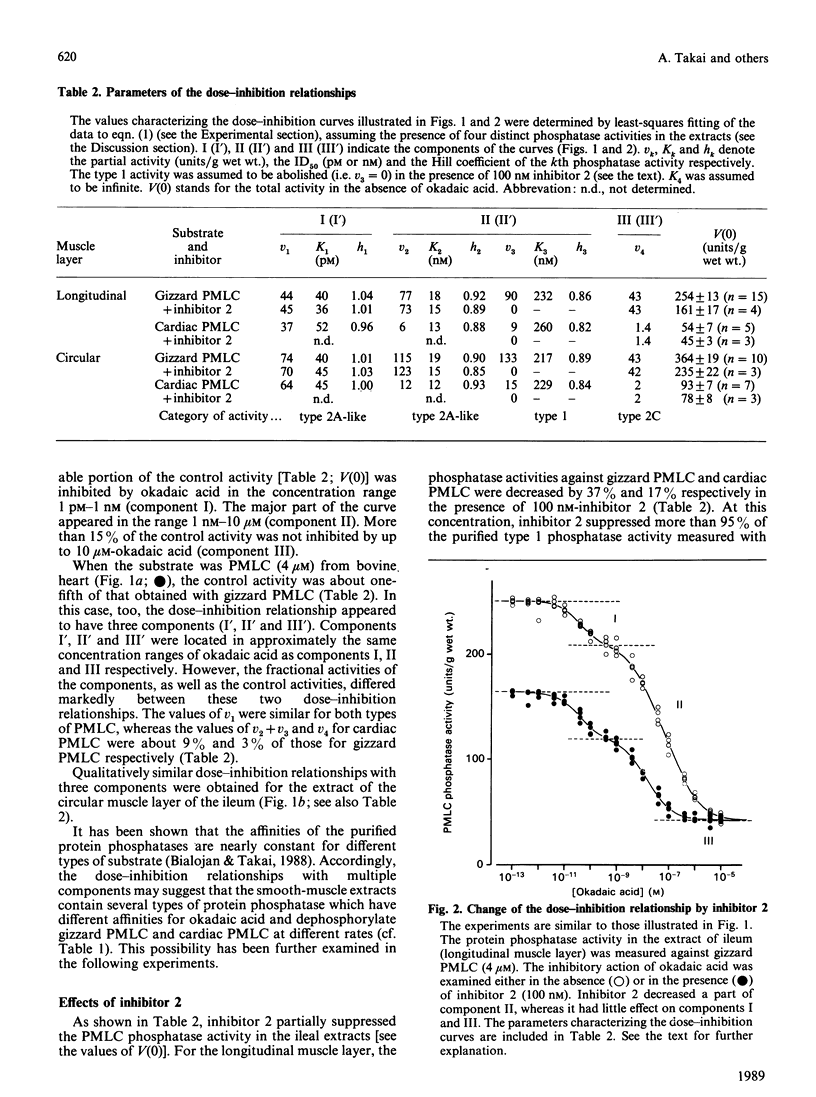
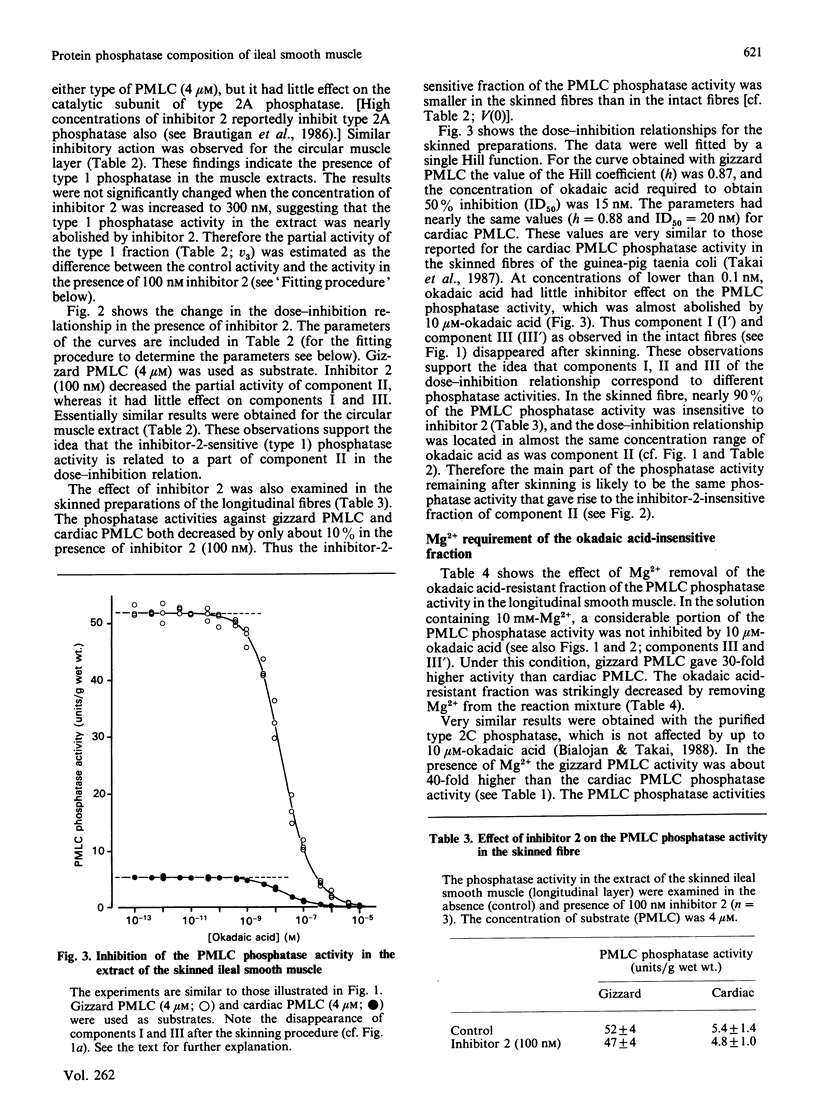
Abstract
Using okadaic acid, a potent inhibitor of type 2A and type 1 protein phosphatases, and inhibitor 2, an intrinsic inhibitory factor of type 1 phosphatase, we characterized the phosphorylated myosin light-chain (PMLC) phosphatase activity in the smooth-muscle extracts of guinea-pig ileum. In the intact fibres the control activity was 254 +/- 13 nmol of Pi/min per g wet wt. (n = 15) against 32P-labelled PMLC (4 microM) from chicken gizzard. The following phosphatase fractions were identified: an inhibitor-2-sensitive (type 1) fraction (fractional activity = 35%), a Mg2+-dependent and okadaic acid-insensitive (type 2C) fraction (17%), and two type 2A-like fractions that had different susceptibility to okadaic acid. The type 2A-like fraction with lower affinity to okadaic acid accounted for 30% of the control activity. After the cell membrane was permeabilized by Triton X-100, more than 60% of this fraction remained and accounted for about 90% of the total activity, whereas the other fractions were nearly abolished. The type 2A-like fraction may be bound to some intracellular structure such as contractile proteins.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bialojan C., Rüegg J. C., Takai A. Effects of okadaic acid on isometric tension and myosin phosphorylation of chemically skinned guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1988 Apr;398:81–95. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialojan C., Takai A. Inhibitory effect of a marine-sponge toxin, okadaic acid, on protein phosphatases. Specificity and kinetics. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):283–290. doi: 10.1042/bj2560283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brautigan D. L., Gruppuso P. A., Mumby M. Protein phosphatase type-1 and type-2 catalytic subunits both bind inhibitor-2 and monoclonal immunoglobulins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):14924–14928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Nimmo G. A., Antoniw J. F. Specificity of a protein phosphatase inhibitor from rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 15;162(2):435–444. doi: 10.1042/bj1620435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of protein phosphorylation in the hormonal control of enzyme activity. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 16;151(3):439–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins P., Lambert S. J. Myosin transitions in the bovine and human heart. A developmental and anatomical study of heavy and light chain subunits in the atrium and ventricle. Circ Res. 1986 Jun;58(6):846–858. doi: 10.1161/01.res.58.6.846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Salvo J., Gifford D., Bialojan C., Rüegg J. C. An aortic spontaneously active phosphatase dephosphorylates myosin and inhibits actin-myosin interaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 29;111(3):906–911. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiSalvo J., Gifford D., Jiang M. J. Properties and function of phosphatases from vascular smooth muscle. Fed Proc. 1983 Jan;42(1):67–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiSalvo J., Jiang M. J., Vandenheede J. R., Merlevede W. The ATPMg-dependent phosphatase is present in mammalian vascular smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Sep 30;108(2):534–540. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90861-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J., Brody T. M. Relationship between smooth muscle contraction and phosphorylase activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 May;152(2):212–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne D. J., Siemankowski R. F. Regulation of smooth muscle actomyosin. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:519–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haystead T. A., Sim A. T., Carling D., Honnor R. C., Tsukitani Y., Cohen P., Hardie D. G. Effects of the tumour promoter okadaic acid on intracellular protein phosphorylation and metabolism. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):78–81. doi: 10.1038/337078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Mieskes G., Rüegg J. C., Takai A., Trautwein W. Effects of a protein phosphatase inhibitor, okadaic acid, on membrane currents of isolated guinea-pig cardiac myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Aug;412(3):248–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00582504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang F. L., Glinsmann W. H. Separation and characterization of two phosphorylase phosphatase inhibitors from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 15;70(2):419–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingebritsen T. S., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. 1. Classification and substrate specificities. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 2;132(2):255–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingebritsen T. S., Foulkes J. G., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. 2. Glycogen metabolism. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 2;132(2):263–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07358.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan C. H., Cohen P. Identification of two isoenzymes of protein phosphatase 2C in both rabbit skeletal muscle and liver. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Aug 3;166(3):713–721. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13570.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namm D. H. The activation of glycogen phosphorylase in arterial smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Aug;178(2):299–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngai P. K., Carruthers C. A., Walsh M. P. Isolation of the native form of chicken gizzard myosin light-chain kinase. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 15;218(3):863–870. doi: 10.1042/bj2180863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi H., Umeda J., Uchiwa H., Watanabe S. Purification of gizzard myosin light-chain phosphatase, and reversible changes in the ATPase and superprecipitation activities of actomyosin in the presence of purified preparation of myosin light-chain phosphatase and kinase. J Biochem. 1982 Jan;91(1):265–271. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pato M. D., Adelstein R. S., Crouch D., Safer B., Ingebritsen T. S., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. 4. Classification of two homogeneous myosin light chain phosphatases from smooth muscle as protein phosphatase-2A1 and 2C, and a homogeneous protein phosphatase from reticulocytes active on protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-2 as protein phosphatase-2A2. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 2;132(2):283–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07360.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pato M. D., Adelstein R. S. Dephosphorylation of the 20,000-dalton light chain of myosin by two different phosphatases from smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6535–6538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pato M. D., Kerc E. Purification and characterization of a smooth muscle myosin phosphatase from turkey gizzards. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12359–12366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. J., Stull J. T. Regulation of myosin light chain and phosphorylase phosphorylation in tracheal smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6145–6150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. A., Ingebritsen T. S., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. 5. Purification and properties of a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase (2B) from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 2;132(2):289–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07361.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai A., Bialojan C., Troschka M., Rüegg J. C. Smooth muscle myosin phosphatase inhibition and force enhancement by black sponge toxin. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 8;217(1):81–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81247-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai A. Okadaic acid. Protein phosphatase inhibition and muscle contractile effects. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1988 Dec;9(6):563–565. doi: 10.1007/BF01738761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung H. Y., Resink T. J., Hemmings B. A., Shenolikar S., Cohen P. The catalytic subunits of protein phosphatase-1 and protein phosphatase 2A are distinct gene products. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Feb 1;138(3):635–641. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07962.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werth D. K., Haeberle J. R., Hathaway D. R. Purification of a myosin phosphatase from bovine aortic smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7306–7309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


