Abstract
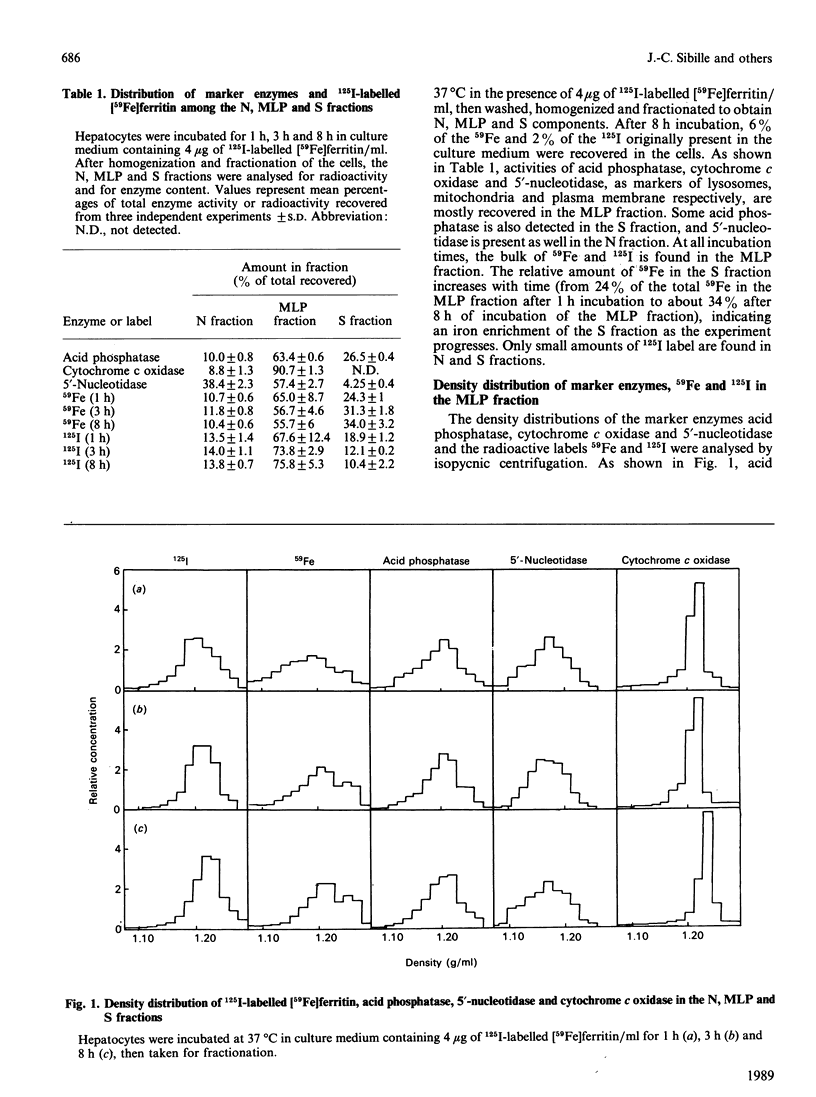
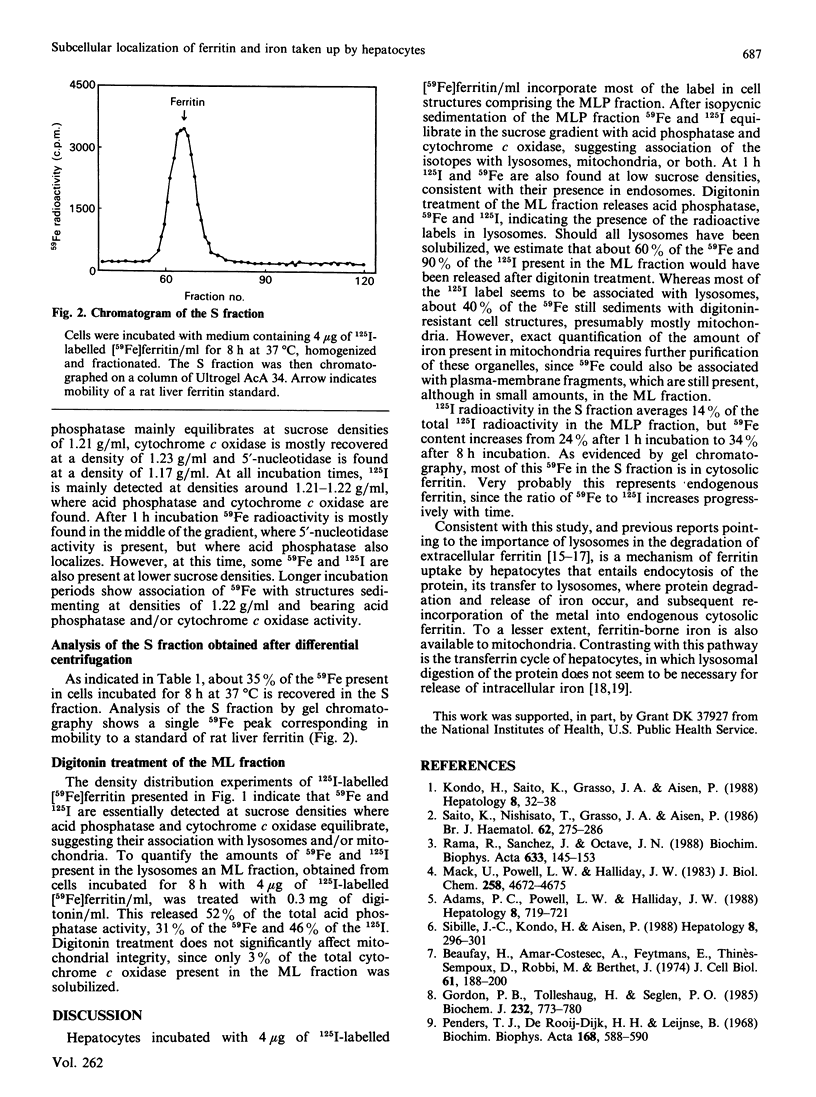
The subcellular localization of ferritin and its iron taken up by rat hepatocytes was investigated by sucrose-density-gradient ultracentrifugation of cell homogenates. After incubation of hepatocytes with 125I-labelled [59Fe]ferritin, cells incorporate most of the labels into structures equilibrating at densities where acid phosphatase and cytochrome c oxidase are found, suggesting association of ferritin and its iron with lysosomes or mitochondria. Specific solubilization of lysosomes by digitonin treatment indicates that, after 8 h incubation, most of the 125I is recovered in lysosomes, whereas 59Fe is found in mitochondria as well as in lysosomes. As evidenced by gel chromatography of supernatant fractions, 59Fe accumulates with time in cytosolic ferritin. To account for these results a model is proposed in which ferritin, after being endocytosed by hepatocytes, is degraded in lysosomes, and its iron is released and re-incorporated into cytosolic ferritin and, to a lesser extent, into mitochondria.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. C., Powell L. W., Halliday J. W. Isolation of a human hepatic ferritin receptor. Hepatology. 1988 Jul-Aug;8(4):719–721. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch J., Wallach D. F. Preparation and properties of plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum fragments from isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 13;233(2):334–347. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaufay H., Amar-Costesec A., Feytmans E., Thinès-Sempoux D., Wibo M., Robbi M., Berthet J. Analytical study of microsomes and isolated subcellular membranes from rat liver. I. Biochemical methods. J Cell Biol. 1974 Apr;61(1):188–200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blight G. D., Morgan E. H. Transferrin and ferritin endocytosis and recycling in guinea-pig reticulocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 15;929(1):18–24. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90236-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPERSTEIN S. J., LAZAROW A. A microspectrophotometric method for the determination of cytochrome oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1951 Apr;189(2):665–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon P. B., Tolleshaug H., Seglen P. O. Use of digitonin extraction to distinguish between autophagic-lysosomal sequestration and mitochondrial uptake of [14C]sucrose in hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):773–780. doi: 10.1042/bj2320773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo H., Saito K., Grasso J. P., Aisen P. Iron metabolism in the erythrophagocytosing Kupffer cell. Hepatology. 1988 Jan-Feb;8(1):32–38. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack U., Powell L. W., Halliday J. W. Detection and isolation of a hepatic membrane receptor for ferritin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4672–4675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niitsu Y., Adachi C., Takahashi F., Goto Y., Kohgo Y., Urushizaki I., Listowsky I. Concentration-dependent sedimentation properties of ferritin: implications for estimation of iron contents of serum ferritins. Am J Hematol. 1985 Apr;18(4):363–371. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830180405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penders T. J., de Rooij-Dijk H. H., Leijnse B. Rapid isolation of ferritin by means of ultracentrifugation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Dec 3;168(3):588–590. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90198-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito K., Nishisato T., Grasso J. A., Aisen P. Interaction of transferrin with iron-loaded rat peritoneal macrophages. Br J Haematol. 1986 Feb;62(2):275–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1986.tb02930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibille J. C., Kondo H., Aisen P. Interactions between isolated hepatocytes and Kupffer cells in iron metabolism: a possible role for ferritin as an iron carrier protein. Hepatology. 1988 Mar-Apr;8(2):296–301. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibille J. C., Octave J. N., Schneider Y. J., Trouet A., Crichton R. Subcellular localization of transferrin protein and iron in the perfused rat liver. Effect of Triton WR 1339, digitonin and temperature. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 17;155(1):47–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger A., Hershko C. Hepatocellular uptake of ferritin in the rat. Br J Haematol. 1974 Oct;28(2):169–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb06651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. P., Roberts S., Bomford A. Intracellular processing of transferrin and iron by isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):819–823. doi: 10.1042/bj2320819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


