Abstract
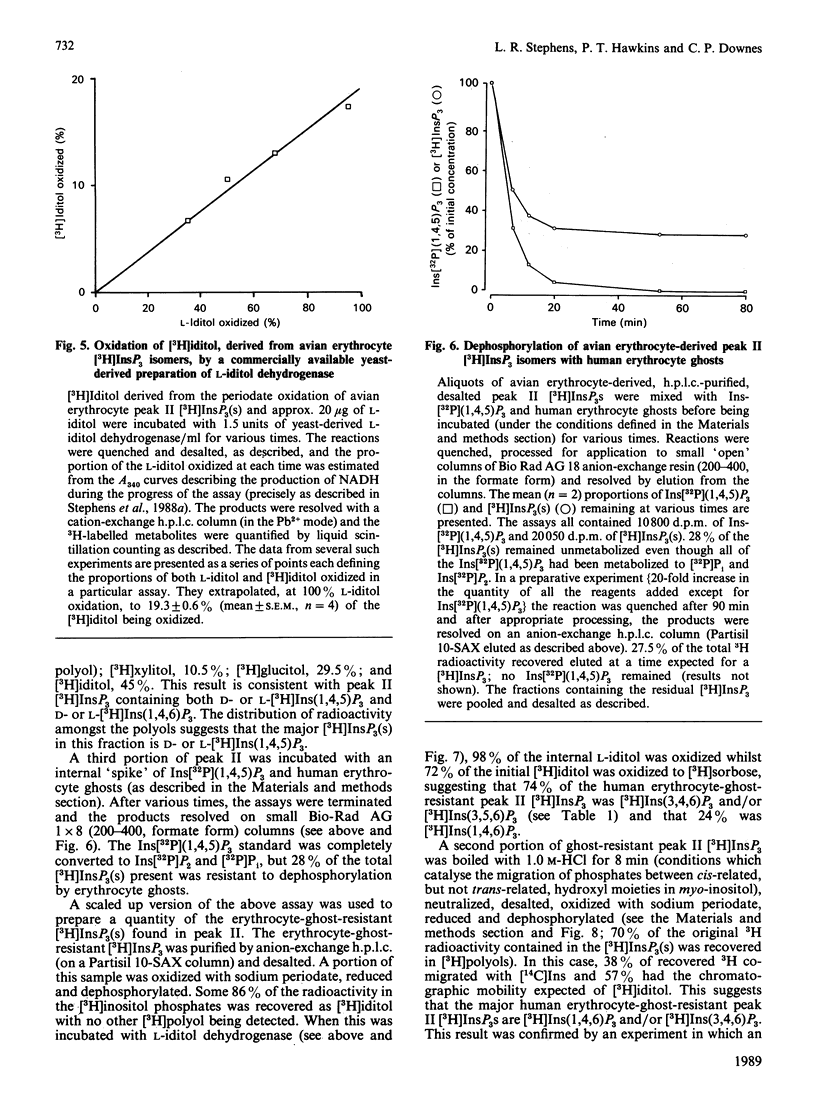
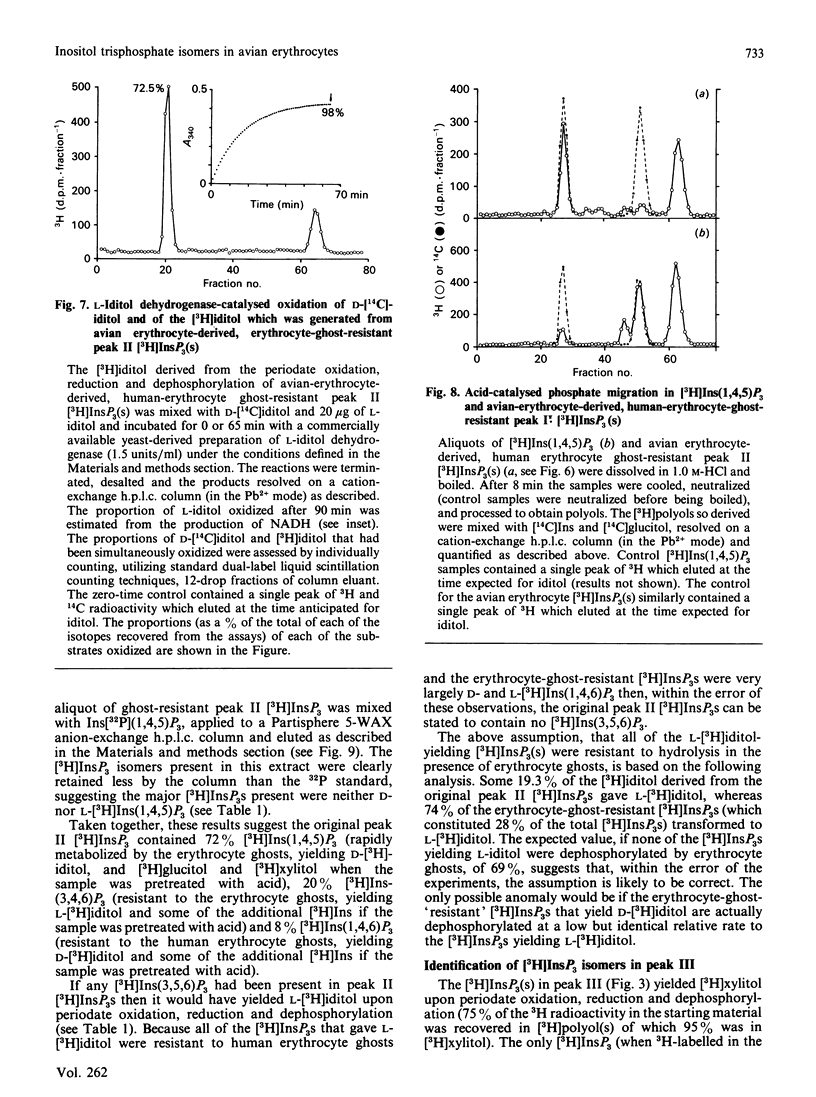
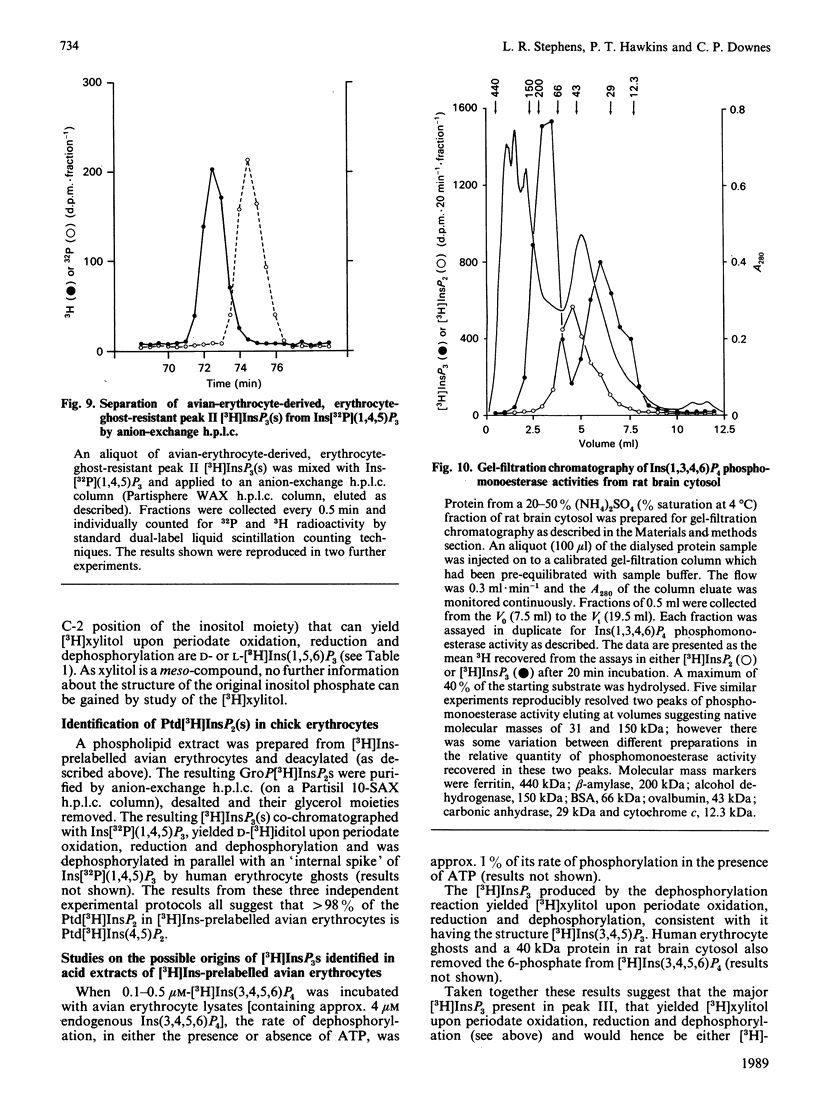
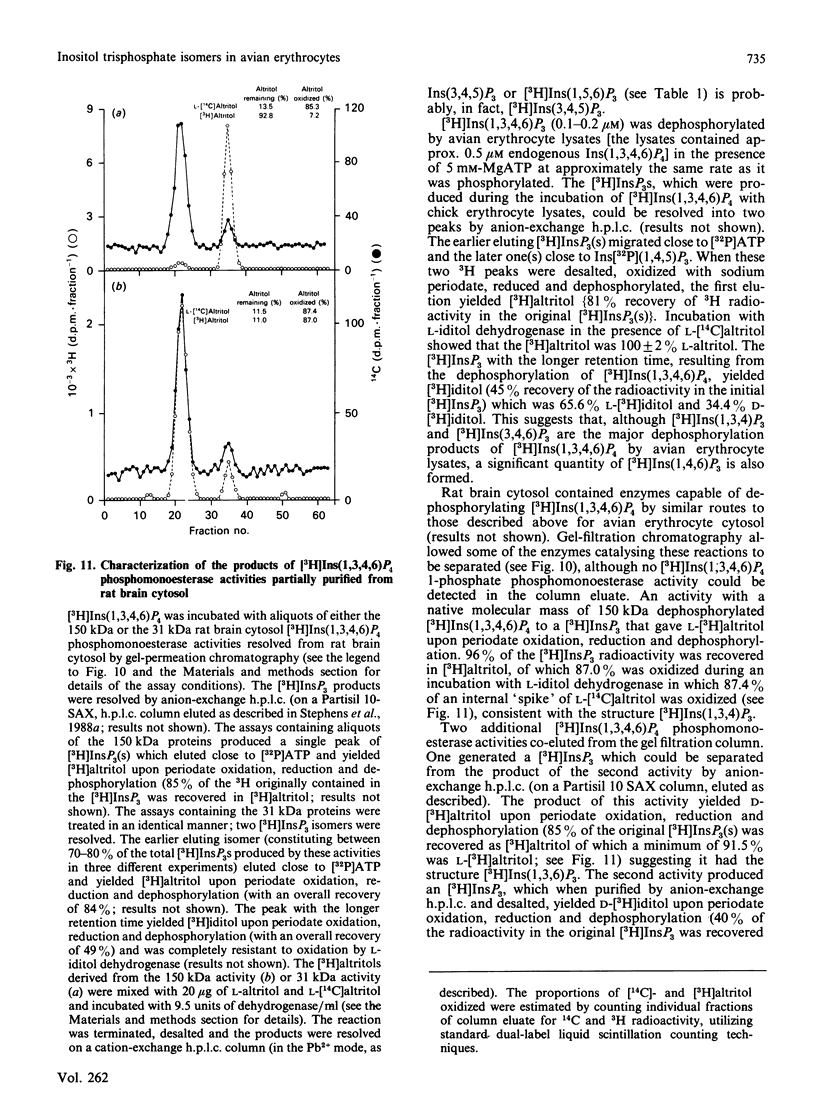
Evidence is presented to show that acid extracts of avian erythrocytes prelabelled for 24-48 h with myo-[3H]inositol contain the following myo-[3H]inositol trisphosphates (expressed as a percentage of total myo-[3H]inositol trisphosphates extracted): 36% myo-[3H]inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate; 33.7% myo-[3H]inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate; 13% myo-[3H]inositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate; 9.7% myo-[3H]inositol 3,4,6-trisphosphate; 4.4% myo-[3H]inositol 1,4,6-trisphosphate and 3.3% myo-[3H]inositol 1,3,6-trisphosphate. The only phosphatidyl-myo-[3H]inositol bisphosphate that could be detected in [3H]Ins-prelabelled avian erythrocytes was phosphatidyl-myo-[3H]inositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Cellular myo-[3H]inositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate may be synthesized by dephosphorylation of myo-[3H]inositol 3,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate. D- and L-myo-[3H]inositol 1,4,6-trisphosphate and D- and L-myo-[3H]inositol 1,3,6-trisphosphate may be dephosphorylation products of myo-[3H]inositol 1,3,4,6-tetrakisphosphate.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balla T., Guillemette G., Baukal A. J., Catt K. J. Metabolism of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate to a new tetrakisphosphate isomer in angiotensin-stimulated adrenal glomerulosa cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):9952–9955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batty I. R., Nahorski S. R., Irvine R. F. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate following muscarinic receptor stimulation of rat cerebral cortical slices. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):211–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2320211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. M., Stewart J. C. The structure of triphosphoinositide from beef brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 7;125(3):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(66)90029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Thompson W. The triphosphoinositide phosphomonoesterase of brain tissue. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):244–250. doi: 10.1042/bj0910244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. F., Hokin L. E. Inositol 1,2-cyclic 4,5-trisphosphate concentration relative to inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in pancreatic minilobules on stimulation with carbamylcholine in the absence of lithium. Possible role as a second messenger in long- but not short-term responses. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):13892–13895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Irvine R. F. Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and not phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate is the probable precursor of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in agonist-stimulated parotid gland. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):501–506. doi: 10.1042/bj2380501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. T., Berrie C. P., Morris A. J., Downes C. P. Inositol 1,2-cyclic 4,5-trisphosphate is not a product of muscarinic receptor-stimulated phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis in rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 1;243(1):211–218. doi: 10.1042/bj2430211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. T., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. A simple assay method for determination of the specific radioactivity of the gamma-phosphate group of 32P-labelled ATP. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 15;210(3):717–720. doi: 10.1042/bj2100717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Heslop J. P., Berridge M. J. The inositol tris/tetrakisphosphate pathway--demonstration of Ins(1,4,5)P3 3-kinase activity in animal tissues. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):631–634. doi: 10.1038/320631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Downes C. P. Inositol trisphosphates in carbachol-stimulated rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2230237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharps E. S., McCarl R. L. A high-performance liquid chromatographic method to measure 32P incorporation into phosphorylated metabolites in cultured cells. Anal Biochem. 1982 Aug;124(2):421–424. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shears S. B., Parry J. B., Tang E. K., Irvine R. F., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. Metabolism of D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate by rat liver, including the synthesis of a novel isomer of myo-inositol tetrakisphosphate. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 15;246(1):139–147. doi: 10.1042/bj2460139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Hawkins P. T., Barker C. J., Downes C. P. Synthesis of myo-inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate from inositol phosphates generated by receptor activation. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):721–733. doi: 10.1042/bj2530721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Hawkins P. T., Morris A. J., Downes P. C. L-myo-inositol 1,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate (3-hydroxy)kinase. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):283–292. doi: 10.1042/bj2490283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L., Hawkins P. T., Carter N., Chahwala S. B., Morris A. J., Whetton A. D., Downes P. C. L-myo-inositol 1,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate is present in both mammalian and avian cells. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):271–282. doi: 10.1042/bj2490271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L., Hawkins P. T., Downes C. P. Metabolic and structural evidence for the existence of a third species of polyphosphoinositide in cells: D-phosphatidyl-myo-inositol 3-phosphate. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 1;259(1):267–276. doi: 10.1042/bj2590267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W., Dawson R. M. The hydrolysis of triphosphoinositide by extracts of ox brain. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):233–236. doi: 10.1042/bj0910233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W., Dawson R. M. The triphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase of brain tissue. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj0910237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong N. S., Barker C. J., Shears S. B., Kirk C. J., Michell R. H. Inositol 1:2(cyclic),4,5-trisphosphate is not a major product of inositol phospholipid metabolism in vasopressin-stimulated WRK1 cells. Biochem J. 1988 May 15;252(1):1–5. doi: 10.1042/bj2520001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



