Abstract
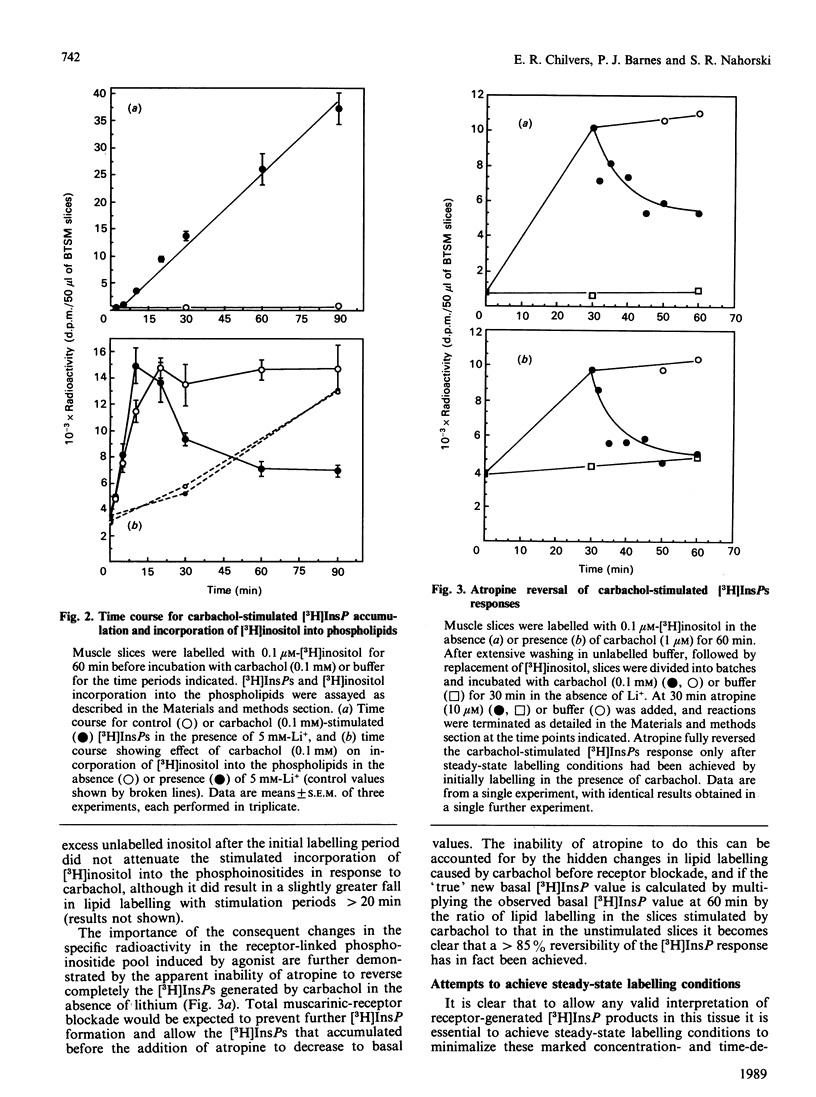
The effects of the muscarinic agonist carbachol, histamine and bradykinin on incorporation of [3H]inositol into the phosphoinositides and the formation of [3H]InsPs were examined in bovine tracheal smooth-muscle (BTSM) slices labelled with [3H]inositol. These agonists result in substantial and dose-related increases in the incorporation of [3H]inositol into the phospholipids. Carbachol and histamine stimulated the incorporation of [3H]inositol into the phospholipids to the same degree, despite histamine being only 35% as effective as carbachol on [3H]InsP accumulation. Histamine and carbachol, at maximal concentrations, were non-additive with respect to both the stimulated incorporation of [3H]inositol and [3H]InsP formation. For carbachol this effect on incorporation was found to occur to a similar extent in PtdInsP and PtdInsP2 as well as PtdIns. The initial effect of carbachol on [3H]inositol incorporation was rapid (maximal by 10 min); however, with prolonged stimulation large secondary declines in PtdInsP and PtdInsP2 labelling were observed, with depletion of the much larger PtdIns pool only evident in the presence of Li+. Lowering buffer [Ca2+] increased the incorporation of [3H]inositol under basal conditions, but did not attenuate the subsequent agonist-stimulated incorporation effect. The large changes in specific radioactivity of the phosphoinositides, and consequently the [3H]InsP products, after carbachol stimulation resulted in the apparent failure of atropine to reverse the [3H]InsP response completely. Labelling muscle slices with [3H]inositol in the presence of carbachol or labelling for longer periods (greater than 6 h) prevented subsequent carbachol-stimulated effects on incorporation without significantly altering the dose-response relationship for carbachol-stimulated [3H]InsP formation and resulted in steady-state labelling conditions confirmed by the ability of atropine to reverse fully the [3H]InsP response to carbachol. This study demonstrates the profound effects of a number of agonists on [3H]inositol incorporation into the phospho- and polyphosphoinositides in BTSM with important consequent changes in the specific radioactivity of these lipids and the resulting [3H]InsP products. In addition, a selective depletion of PtdInsP and PtdInsP2 over PtdIns has been demonstrated with prolonged muscarinic-receptor stimulation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison J. H., Blisner M. E. Inhibition of the effect of lithium on brain inositol by atropine and scopolamine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 23;68(4):1332–1338. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90342-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aub D. L., Putney J. W., Jr Metabolism of inositol phosphates in parotid cells: implications for the pathway of the phosphoinositide effect and for the possible messenger role of inositol trisphosphate. Life Sci. 1984 Apr 2;34(14):1347–1355. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird J. G., Chilvers E. R., Kennedy E. D., Nahorski S. R. Changes in extracellular calcium within the physiological range influence receptor-mediated inositol phosphate responses in brain and tracheal smooth muscle slices. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Mar;339(3):247–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00173572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron C. B., Cunningham M., Strauss J. F., 3rd, Coburn R. F. Pharmacomechanical coupling in smooth muscle may involve phosphatidylinositol metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6899–6903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Downes C. P., Hanley M. R. Lithium amplifies agonist-dependent phosphatidylinositol responses in brain and salivary glands. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):587–595. doi: 10.1042/bj2060587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E., Kendall D. A., Nahorski S. R. Inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in rat cerebral cortical slices: I. Receptor characterisation. J Neurochem. 1984 May;42(5):1379–1387. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Dibner M. D., Hanley M. R. Sympathetic denervation impairs agonist-stimulated phosphatidylinositol metabolism in rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1983 Sep 15;214(3):865–870. doi: 10.1042/bj2140865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Stone M. A. Lithium-induced reduction in intracellular inositol supply in cholinergically stimulated parotid gland. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 15;234(1):199–204. doi: 10.1042/bj2340199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Wusteman M. M. Breakdown of polyphosphoinositides and not phosphatidylinositol accounts for muscarinic agonist-stimulated inositol phospholipid metabolism in rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 15;216(3):633–640. doi: 10.1042/bj2160633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R. A., Krzanowski J. J., Jr, Davis J. S., Polson J. B., Coffey R. G., Shimoda T., Szentivanyi A. Polyphosphoinositide metabolism in canine tracheal smooth muscle (CTSM) in response to a cholinergic stimulus. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Feb 1;36(3):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90286-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egawa K., Takenawa T., Sacktor B. Inhibition by Ca2+ of the incorporation of myo-inositol into phosphatidylinositol. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1981 Jan;21(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(81)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek B., Nahorski S. Muscarinic receptor coupling to inositol phospholipid metabolism in guinea-pig cerebral cortex, parotid gland and ileal smooth muscle. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Dec 1;37(23):4461–4467. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90661-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandordy B. M., Cuss F. M., Sampson A. S., Palmer J. B., Barnes P. J. Phosphatidylinositol response to cholinergic agonists in airway smooth muscle: relationship to contraction and muscarinic receptor occupancy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Jul;238(1):273–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandordy B. M., Frossard N., Rhoden K. J., Barnes P. J. Tachykinin-induced phosphoinositide breakdown in airway smooth muscle and epithelium: relationship to contraction. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 May;33(5):515–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin H. D., Hawthorne J. N. Calcium-activated hydrolysis of phosphatidyl-myo-inositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidyl-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate in guinea-pig synaptosomes. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 15;176(2):541–552. doi: 10.1042/bj1760541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN M. R., HOKIN L. E. Enzyme secretion and the incorporation of P32 into phospholipides of pancreas slices. J Biol Chem. 1953 Aug;203(2):967–977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall I. P., Hill S. J. Beta-adrenoceptor stimulation inhibits histamine-stimulated inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in bovine tracheal smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1204–1212. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11757.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanley M. R., Lee C. M., Michell R. H., Jones L. M. Similar effects of substance P and related peptides on salivation and on phosphatidylinositol turnover in rat salivary glands. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Jul;18(1):78–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto T., Hirata M., Ito Y. A role for inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in the initiation of agonist-induced contractions of dog tracheal smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Sep;86(1):191–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb09449.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. D., Wusteman M., Downes C. P. Muscarinic receptors and hydrolysis of inositol phospholipids in rat cerebral cortex and parotid gland. J Neurochem. 1985 Feb;44(2):465–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb05437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Michell R. H. Breakdown of phosphatidylinositol provoked by muscarinic cholinergic stimulation of rat parotid-gland fragments. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):583–590. doi: 10.1042/bj1420583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall D. A., Nahorski S. R. Inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in rat cerebral cortical slices: II. Calcium requirement. J Neurochem. 1984 May;42(5):1388–1394. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02799.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco M. E. The phosphatidylinositol cycle in WRK-1 cells. Evidence for a separate, hormone-sensitive phosphatidylinositol pool. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2137–2139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park S., Rasmussen H. Activation of tracheal smooth muscle contraction: synergism between Ca2+ and activators of protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8835–8839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Barrett P. Q. Calcium messenger system: an integrated view. Physiol Rev. 1984 Jul;64(3):938–984. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.3.938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney T. A., Nahorski S. R. Regional characterization of agonist and depolarization-induced phosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Dec;239(3):873–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. P., Walker J. W., Goldman Y. E., Trentham D. R., Kobayashi S., Kitazawa T., Somlyo A. V. Inositol trisphosphate, calcium and muscle contraction. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 26;320(1199):399–414. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takenawa T., Egawa K. CDP-diglyceride:inositol transferase from rat liver. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5419–5423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takuwa Y., Takuwa N., Rasmussen H. Carbachol induces a rapid and sustained hydrolysis of polyphosphoinositide in bovine tracheal smooth muscle measurements of the mass of polyphosphoinositides, 1,2-diacylglycerol, and phosphatidic acid. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14670–14675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




