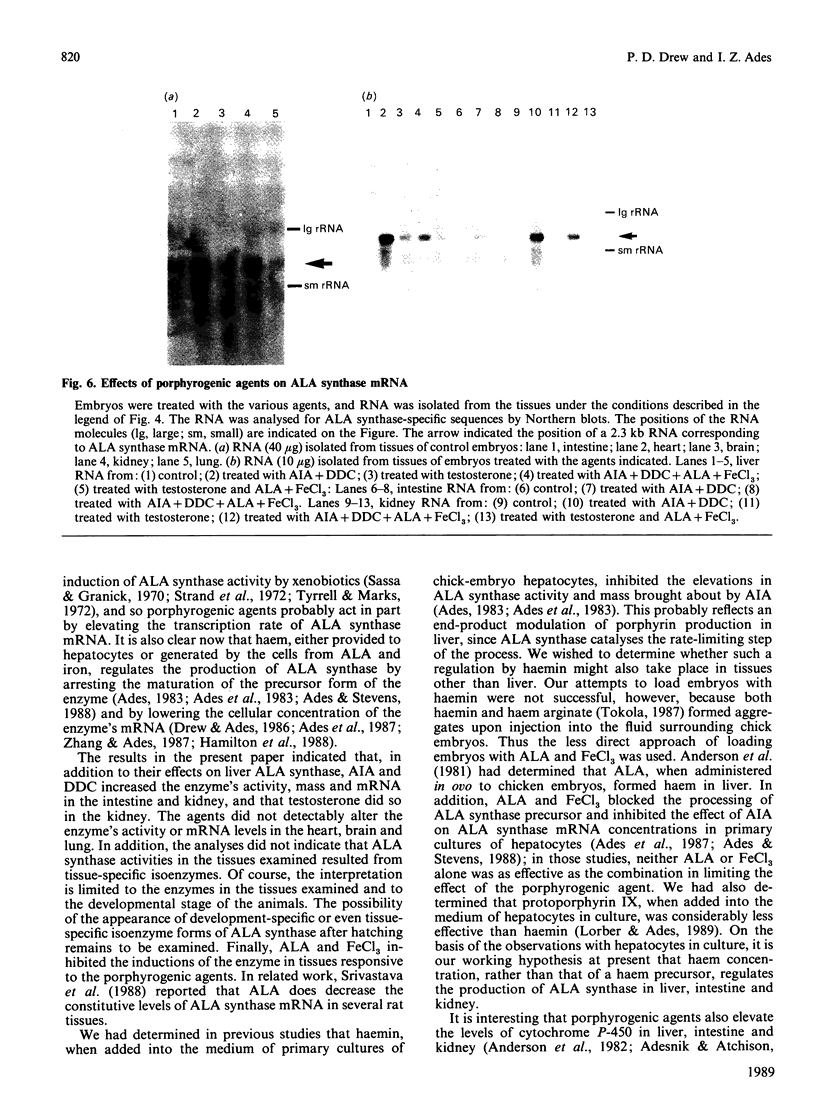
Abstract
Studies conducted by several groups have established that porphyrogenic agents which caused elevations in chick-embryo liver delta-aminolaevulinate (ALA) synthase activity also increased the concentrations of the enzyme's RNA, and that haemin inhibited these elevations. We have determined in this study, using immune-blot analyses, that administration in ovo of allylisopropylacetamide (AIA) in combination with diethyl 1,4-dihydro-2,4,6-trimethyl,3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate (DDC) increased the mass of ALA synthase in intestine and kidney of chick embryos. Furthermore, the molecular mass of the subunit of the enzyme in those tissues appeared identical with that of liver ALA synthase. Using a synthetic oligonucleotide complementary to ALA synthase mRNA, we determined by solution hybridization and Northern-blot analyses that AIA and DDC also increased the concentrations of ALA synthase mRNA in intestine and kidney and that testosterone elevated the concentration of the RNA in kidney. In analyses of RNA obtained from chick-embryo liver, intestine, kidney, heart, brain and lung, the probe bound primarily in each case to a single 2.3 kb RNA. Finally, the haem precursors ALA and FeCl3, when injected together into the fluid surrounding embryos, inhibited both the elevations in ALA synthase mass and RNA concentration brought about by porphyrogenic agents in liver, kidney and intestine. Thus the results indicated that: (1) certain porphyrogenic agents increased ALA synthase mass and RNA in chick-embryo intestine and kidney, in addition to liver; (2) ALA and FeCl3 inhibited the elevations; and (3) the sizes of ALA synthase's subunit as well as the enzyme's mRNA appeared identical, in each case, in all tissues examined.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ades I. Z. Biogenesis of mitochondrial proteins regulation of maturation of delta-aminolevulinate synthase by hemin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 14;110(1):42–47. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91257-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ades I. Z., Harpe K. G. Biogenesis of mitochondrial proteins. Identification of the mature and precursor forms of the subunit of delta-aminolevulinate synthase from embryonic chick liver. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9329–9333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ades I. Z., Harpe K. G., Stevens T. M. Biogenesis of mitochondrial proteins. Regulation of production of delta-aminolaevulinate synthase by haemin in embryonic-chick liver. Biochem J. 1983 Sep 15;214(3):967–974. doi: 10.1042/bj2140967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ades I. Z., Stevens T. M., Drew P. D. Biogenesis of embryonic chick liver delta-aminolevulinate synthase: regulation of the level of mRNA by hemin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Mar;253(2):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90182-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ades I. Z., Stevens T. M. Maturation of embryonic chick liver delta-aminolevulinate synthase: precursor pools and regulation by intra-cellularly produced heme. Int J Biochem. 1988;20(9):959–964. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(88)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adesnik M., Atchison M. Genes for cytochrome P-450 and their regulation. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;19(3):247–305. doi: 10.3109/10409238609084657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. E., Drummond G. S., Freddara U., Sardana M. K., Sassa S. Porphyrogenic effects and induction of heme oxygenase in vivo by delta-aminolevulinic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 4;676(3):289–299. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90162-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. E., Freddara U., Kappas A. Induction of hepatic cytochrome P-450 by natural steroids: relationship to the induction of delta-aminolevulinate synthase and porphyrin accumulation in the avian embryo. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Sep;217(2):597–608. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90542-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. F., Kitchen H., Wood W. A. Evidence for erythroid and nonerythroid forms of delta-aminolevulinate synthetase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Feb;206(2):380–391. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew P. D., Ades I. Z. Regulation of production of embryonic chick liver delta-aminolevulinate synthase: effects of testosterone and of hemin on the mRNA of the enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Oct 15;140(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink C. J., Srivastava G., Maguire D. J., Borthwick I. A., May B. K., Elliott W. H. A unique gene for 5-aminolevulinate synthase in chickens. Evidence for expression of an identical messenger RNA in hepatic and erythroid tissues. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):3988–3992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. W., Bement W. J., Sinclair P. R., Sinclair J. F., Wetterhahn K. E. Expression of 5-aminolaevulinate synthase and cytochrome P-450 mRNAs in chicken embryo hepatocytes in vivo and in culture. Effect of porphyrinogenic drugs and haem. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):267–275. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorber B. J., Ades I. Z. Regulation of biogenesis of liver delta-aminolevulinate synthase: effects of structural modifications of heme on the enzyme's RNA. Int J Biochem. 1989;21(4):439–443. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(89)90369-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks G. S. Exposure to toxic agents: the heme biosynthetic pathway and hemoproteins as indicator. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1985;15(2):151–179. doi: 10.3109/10408448509029323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks G. S., McCluskey S. A., Mackie J. E., Riddick D. S., James C. A. Disruption of hepatic heme biosynthesis after interaction of xenobiotics with cytochrome P-450. FASEB J. 1988 Sep;2(12):2774–2783. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.12.3044903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassa S., Granick S. Induction of -aminolevulinic acid synthetase in chick embryo liver cells in cluture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):517–522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassa S., Kappas A., Bernstein S. E., Alvares A. P. Heme biosynthesis and drug metabolism in mice with hereditary hemolytic anemia. Heme oxygenase induction as an adaptive response for maintaining cytochrome P-450 in chronic hemolysis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):729–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenhaut D. S., Curtis P. J. Nucleotide sequence of mouse 5-aminolevulinic acid synthase cDNA and expression of its gene in hepatic and erythroid tissues. Gene. 1986;48(1):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava G., Borthwick I. A., Maguire D. J., Elferink C. J., Bawden M. J., Mercer J. F., May B. K. Regulation of 5-aminolevulinate synthase mRNA in different rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5202–5209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand L. J., Manning J., Marver H. S. The induction of -aminolevulinic acid synthetase in cultured liver cells. The effects of end product and inhibitors of heme synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2820–2827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokola O. Effects of repeated intravenous administration of haem arginate upon hepatic metabolism of foreign compounds in rats and dogs. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr;90(4):661–668. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11218.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber P. G., Chianale J., Florence R., Kim K., Wojcik E., Gumucio J. J. Expression of cytochrome P450b and P450e genes in small intestinal mucosa of rats following treatment with phenobarbital, polyhalogenated biphenyls, and organochlorine pesticides. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9449–9455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell D. L., Marks G. S. Drug-induced porphyrin biosynthesis. V. Effect of protohemin on the transcriptional and post-transcriptional phases of -aminolevulinic acid synthetase induction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Aug 1;21(15):2077–2093. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe N., Hayashi N., Kikuchi G. delta-Aminolevulinate synthase isozymes in the liver and erythroid cells of chicken. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jun 15;113(2):377–383. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91737-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting M. J., Granick S. Delta-Aminolevulinic acid synthase from chick embryo liver mitochondria. I. Purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1340–1346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]