Abstract
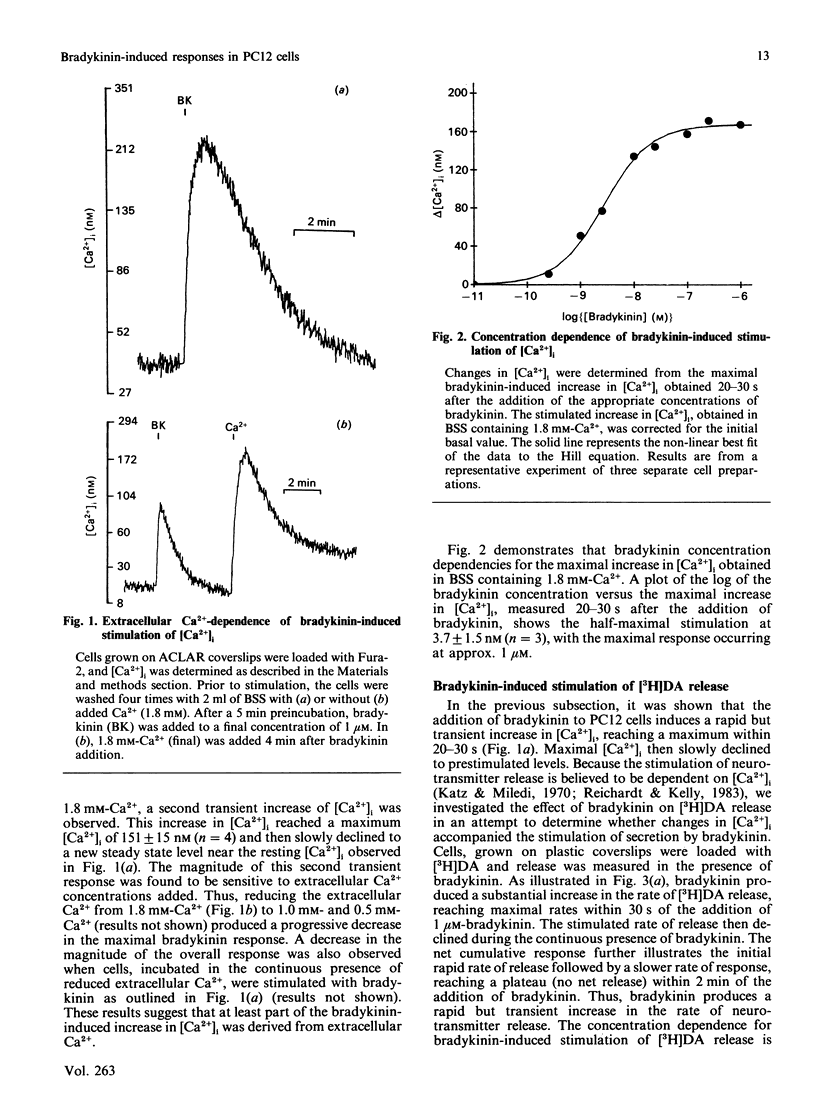
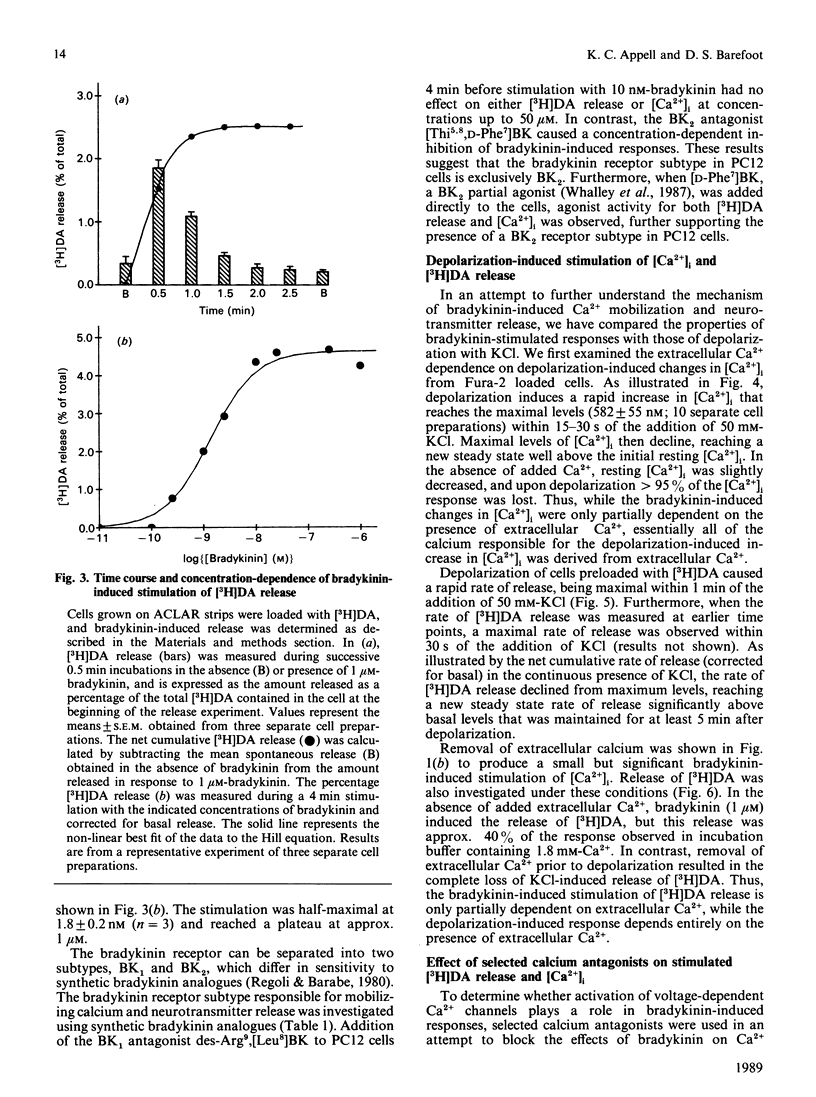
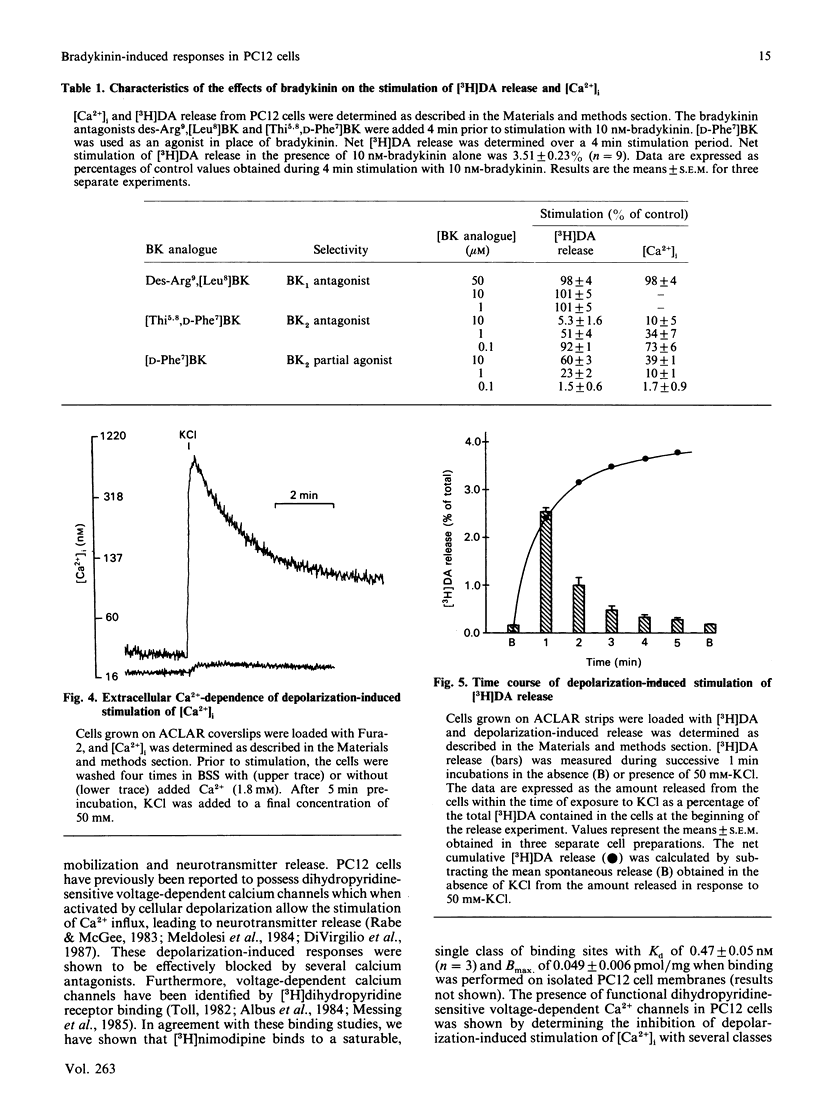
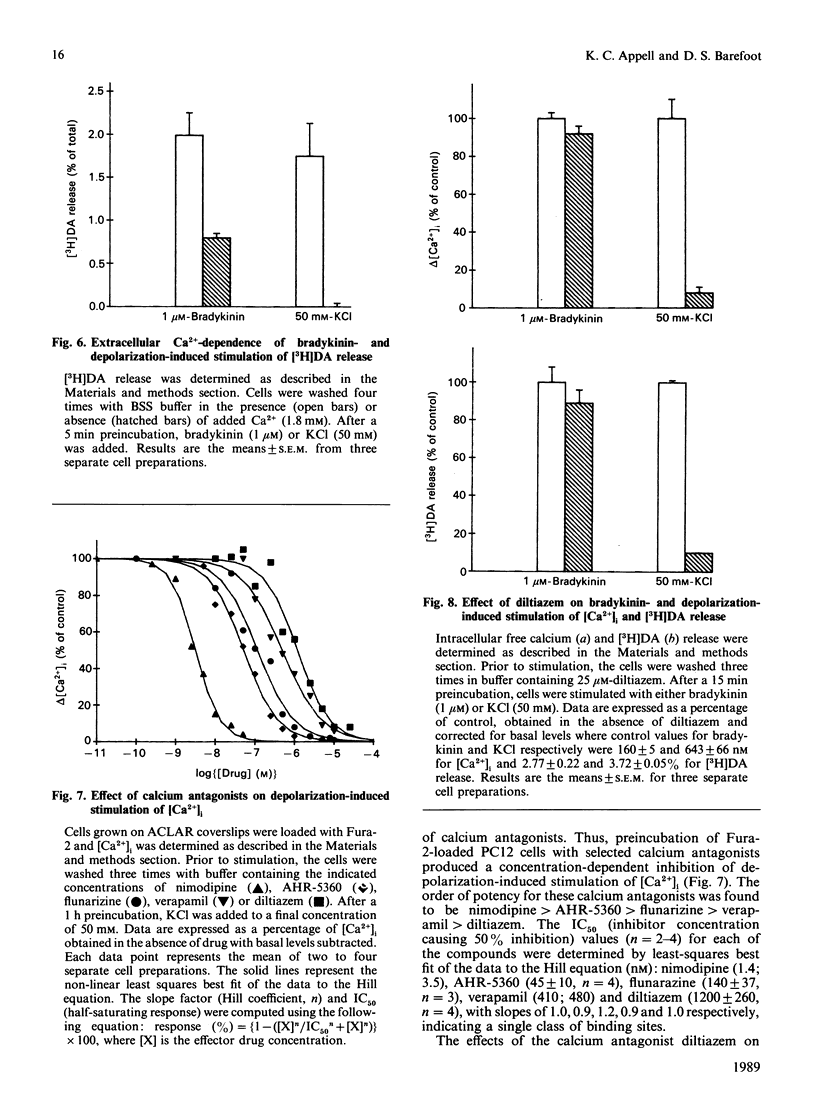
The effect of bradykinin on intracellular free Ca2+ and neurotransmitter secretion was investigated in the rat pheochromocytoma cell line PC12. Bradykinin was shown to induce a rapid, but transient, increase in intracellular free Ca2+ which could be separated into an intracellular Ca2+ release component and an extracellular Ca2+ influx component. The bradykinin-induced stimulation of intracellular free Ca2+ displayed a similar time course, concentration dependencies and extracellular Ca2+ dependence as that found for neurotransmitter release, indicating an association between intracellular free Ca2+ levels and neurotransmitter secretion. The selective BK1-receptor antagonist des-Arg9,[Leu8]BK (where BK is bradykinin) did not significantly affect the stimulation of intracellular free Ca2+ or neurotransmitter release. In contrast, these effects of bradykinin were effectively blocked by the selective BK2-receptor antagonist [Thi5,8,D-Phe7]BK, and mimicked by the BK2 partial agonist [D-Phe7]BK in a concentration-dependent manner. The stimulation of intracellular free Ca2+ and neurotransmitter release induced by bradykinin was shown not to involve voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels, since calcium antagonists had no effect on either response at concentrations which effectively inhibit depolarization-induced responses. These results indicate that bradykinin, acting through the interaction with the BK2 receptor, stimulates an increase in intracellular free Ca2+ leading to neurotransmitter secretion. Furthermore, bradykinin-induced responses involve the release of intracellular Ca2+ and the influx of extracellular Ca2+ that is not associated with the activation of voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albus U., Habermann E., Ferry D. R., Glossmann H. Novel 1,4-dihydropyridine (Bay K 8644) facilitates calcium-dependent [3H]noradrenaline release from PC 12 cells. J Neurochem. 1984 Apr;42(4):1186–1189. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb12729.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. L., Baenziger N. L., Majerus P. W. Bradykinin-stimulated release of arachidonate from phosphatidyl inositol in mouse fibrosarcoma cells. Prostaglandins. 1980 Aug;20(2):269–274. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(80)80045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossley I., Swann K., Chambers E., Whitaker M. Activation of sea urchin eggs by inositol phosphates is independent of external calcium. Biochem J. 1988 May 15;252(1):257–262. doi: 10.1042/bj2520257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Virgilio F., Milani D., Leon A., Meldolesi J., Pozzan T. Voltage-dependent activation and inactivation of calcium channels in PC12 cells. Correlation with neurotransmitter release. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9189–9195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Rein G. Release, storage and uptake of catecholamines by a clonal cell line of nerve growth factor (NGF) responsive pheo-chromocytoma cells. Brain Res. 1977 Jul 1;129(2):247–263. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Moor R. M. Micro-injection of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate activates sea urchin eggs by a mechanism dependent on external Ca2+. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):917–920. doi: 10.1042/bj2400917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Spontaneous and evoked activity of motor nerve endings in calcium Ringer. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(3):689–706. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. C., Snyder S. H., Kachur J. F., Miller R. J., Field M. Bradykinin receptor-mediated chloride secretion in intestinal function. Nature. 1982 Sep 16;299(5880):256–259. doi: 10.1038/299256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldolesi J., Huttner W. B., Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T. Free cytoplasmic Ca2+ and neurotransmitter release: studies on PC12 cells and synaptosomes exposed to alpha-latrotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):620–624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing R. O., Carpenter C. L., Greenberg D. A. Mechanism of calcium channel inhibition by phenytoin: comparison with classical calcium channel antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Nov;235(2):407–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry D. C., Snyder S. H. Identification of bradykinin in mammalian brain. J Neurochem. 1984 Oct;43(4):1072–1080. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb12846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabe C. S., Delorme E., Weight F. F. Muscarine-stimulated neurotransmitter release from PC12 cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Nov;243(2):534–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabe C. S., McGee R., Jr Regulation of depolarization-dependent release of neurotransmitters by adenosine: cyclic AMP-dependent enhancement of release from PC12 cells. J Neurochem. 1983 Dec;41(6):1623–1634. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb00873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Barabé J., Park W. K. Receptors for bradykinin in rabbit aortae. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;55(4):855–867. doi: 10.1139/y77-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Barabé J. Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Mar;32(1):1–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt L. F., Kelly R. B. A molecular description of nerve terminal function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:871–926. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.004255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds E. E., Dubyak G. R. Agonist-induced calcium transients in cultured smooth muscle cells: measurements with fura-2 loaded monolayers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 14;136(3):927–934. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90421-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie A. K. Catecholamine secretion in a rat pheochromocytoma cell line: two pathways for calcium entry. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:541–561. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H. Brain peptides as neurotransmitters. Science. 1980 Aug 29;209(4460):976–983. doi: 10.1126/science.6157191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toll L. Calcium antagonists High-affinity binding and inhibition of calcium transport in a clonal cell line. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13189–13192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicentini L. M., Ambrosini A., Di Virgilio F., Pozzan T., Meldolesi J. Muscarinic receptor-induced phosphoinositide hydrolysis at resting cytosolic Ca2+ concentration in PC12 cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;100(4):1330–1333. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.4.1330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalley E. T., Nwator I. A., Stewart J. M., Vavrek R. J. Analysis of the receptors mediating vascular actions of bradykinin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;336(4):430–433. doi: 10.1007/BF00164878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Calker D., Assmann K., Greil W. Stimulation by bradykinin, angiotensin II, and carbachol of the accumulation of inositol phosphates in PC-12 pheochromocytoma cells: differential effects of lithium ions on inositol mono- and polyphosphates. J Neurochem. 1987 Nov;49(5):1379–1385. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb01003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


