Abstract
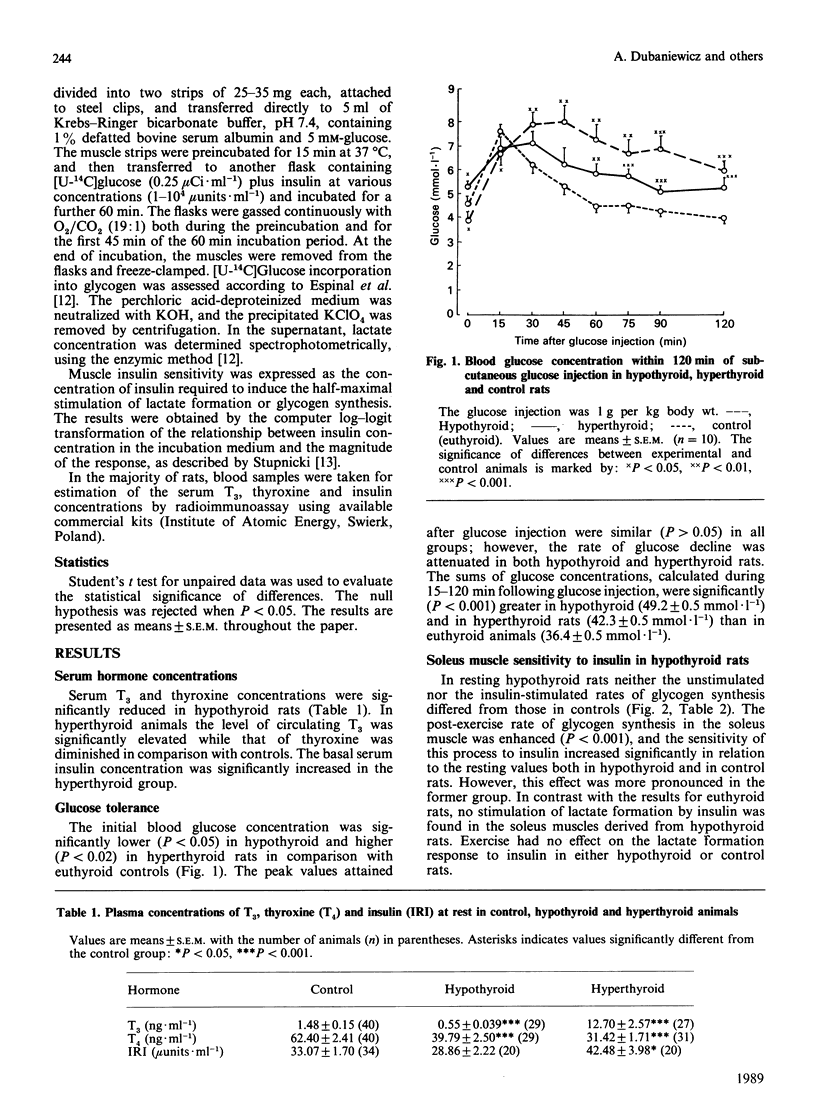
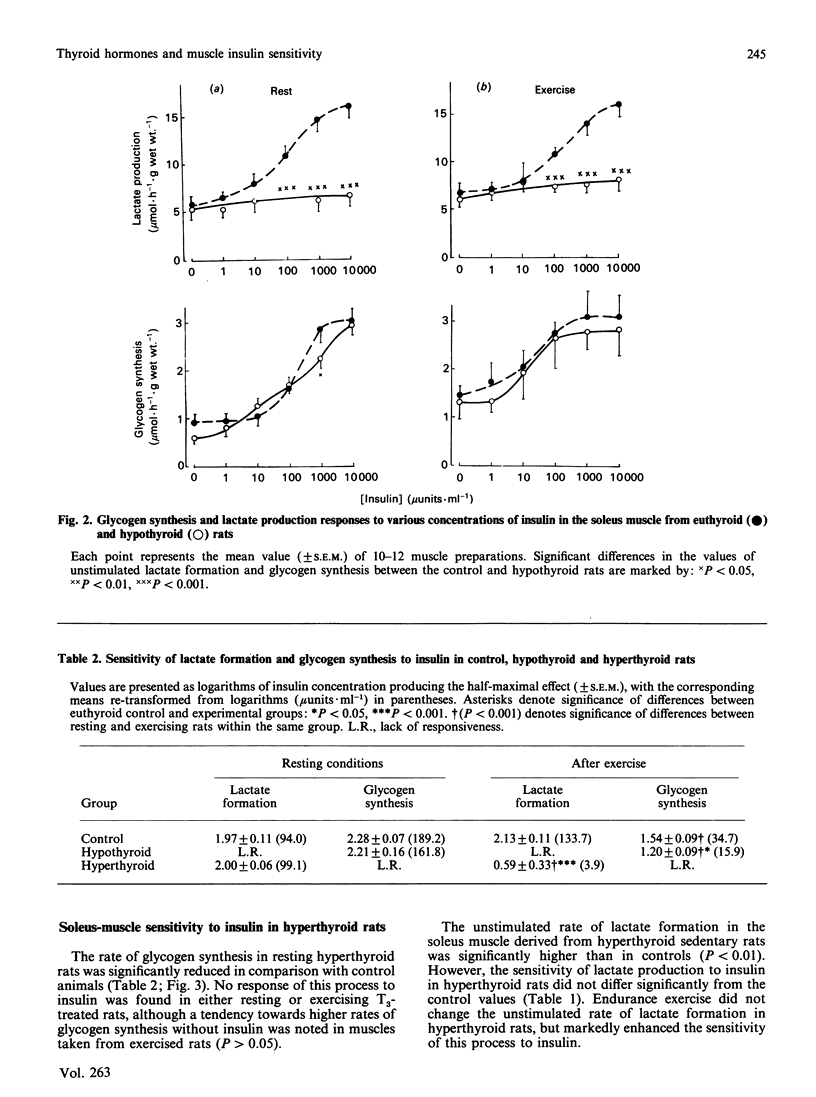
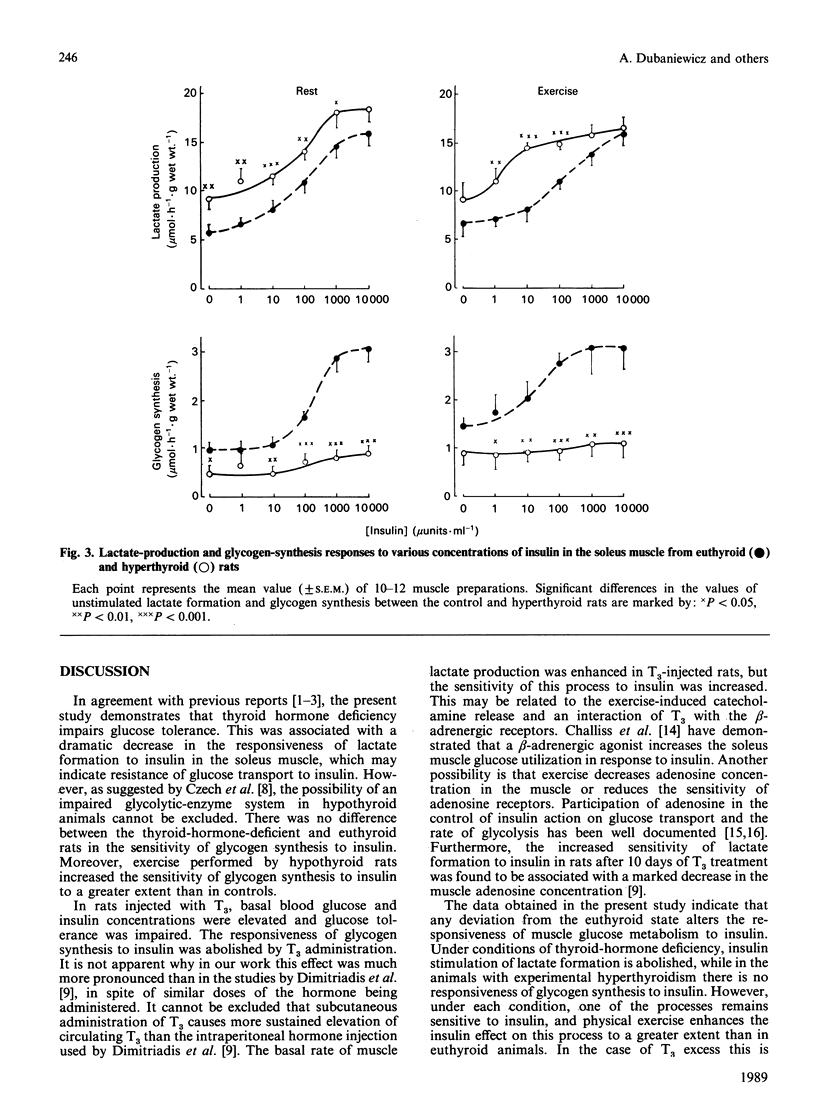
1. The effects of hypothyroidism (caused by surgical thyroidectomy followed by treatment for 1 month with propylthiouracil) and of hyperthyroidism [induced by subcutaneous administration of L-tri-iodothyronine (T3)] on glucose tolerance and skeletal-muscle sensitivity to insulin were examined in rats. Glucose tolerance was estimated during 2 h after subcutaneous glucose injection (1 g/kg body wt.). The sensitivity of the soleus muscle to insulin was studied in vitro in sedentary and acutely exercised animals. 2. Glucose tolerance was impaired in both hypothyroid and hyperthyroid rats in comparison with euthyroid controls. 3. In the soleus muscle, responsiveness of the rate of lactate formation to insulin was abolished in hypothyroid rats, whereas the sensitivity of the rate of glycogen synthesis to insulin was unchanged. In hyperthyroid animals, opposite changes were found, i.e. responsiveness of the rate of glycogen synthesis was inhibited and the sensitivity of the rate of lactate production did not differ from that in control sedentary rats. 4. A single bout of exercise for 30 min potentiated the stimulatory effect of insulin on lactate formation in hyperthyroid rats and on glycogen synthesis in hypothyroid animals. 5. The data suggest that thyroid hormones exert an interactive effect with insulin in skeletal muscle. This is likely to be at the post-receptor level, inhibiting the effect of insulin on glycogen synthesis and stimulating oxidative glucose utilization.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Budohoski L., Challiss R. A., Dubaniewicz A., Kaciuba-Usciłko H., Leighton B., Lozeman F. J., Nazar K., Newsholme E. A., Porta S. Effects of prolonged elevation of plasma adrenaline concentration in vivo on insulin-sensitivity in soleus muscle of the rat. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 15;244(3):655–660. doi: 10.1042/bj2440655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budohoski L., Challiss R. A., McManus B., Newsholme E. A. Effects of analogues of adenosine and methyl xanthines on insulin sensitivity in soleus muscle of the rat. FEBS Lett. 1984 Feb 13;167(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80820-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Budohoski L., Newsholme E. A., Sennitt M. V., Cawthorne M. A. Effect of a novel thermogenic beta-adrenoceptor agonist (BRL 26830) on insulin resistance in soleus muscle from obese Zucker rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 30;128(2):928–935. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90135-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Malbon C. C., Kerman K., Gitomer W., Pilch P. F. Effect of thyroid status on insulin action in rat adipocytes and skeletal muscle. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):574–582. doi: 10.1172/JCI109889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitriadis G. D., Leighton B., Vlachonikolis I. G., Parry-Billings M., Challiss R. A., West D., Newsholme E. A. Effects of hyperthyroidism on the sensitivity of glycolysis and glycogen synthesis to insulin in the soleus muscle of the rat. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 1;253(1):87–92. doi: 10.1042/bj2530087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitriadis G., Baker B., Marsh H., Mandarino L., Rizza R., Bergman R., Haymond M., Gerich J. Effect of thyroid hormone excess on action, secretion, and metabolism of insulin in humans. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):E593–E601. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.5.E593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doar J. W., Stamp T. C., Wynn V., Audhya T. K. Effects of oral and intravenous glucose loading in thyrotoxicosis. Studies of plasma glucose, free fatty acid, plasma insulin and blood pyruvate levels. Diabetes. 1969 Sep;18(9):633–639. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.9.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espinal J., Dohm G. L., Newsholme E. A. Sensitivity to insulin of glycolysis and glycogen synthesis of isolated soleus-muscle strips from sedentary, exercised and exercise-trained rats. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):453–458. doi: 10.1042/bj2120453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsilambros N., Ziegler R., Schatz H., Hinz M., Naier V., Pfeiffer E. F. Intravenous glucose tolerance and insulin secretion in the rat after thyroidectomy. Horm Metab Res. 1972 Sep;4(5):377–379. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1094037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamberg B. A. Glucose metabolism in thyroid disease. Acta Med Scand. 1965 Sep;178(3):351–362. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1965.tb04279.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langfort J., Budohoski L., Newsholme E. A. Effect of various types of acute exercise and exercise training on the insulin sensitivity of rat soleus muscle measured in vitro. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Jul;412(1-2):101–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00583737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. J., Seitz H. J. In vivo glucose turnover in hypo- and hyperthyroid starved rat. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Jul;386(1):47–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00584186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Ui M. Metabolism of glucose in hyper- and hypo-thyroid rats in vivo. Glucose-turnover values and futile-cycle activities obtained with 14C- and 3H-labelled glucose. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 15;182(2):565–575. doi: 10.1042/bj1820565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renauld A., Sverdlik R. C., Andrade L. L., Rodríguez R. R. Studies on the effect of thyroxine replacement therapy on the increased insulin response to hyperglycemia in the thyroidectomized dog. Horm Metab Res. 1972 Sep;4(5):373–376. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1094036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stupnicki R. A single-parameter quality control in radioimmunoassays. Endokrinologie. 1982 Jul;80(1):48–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


