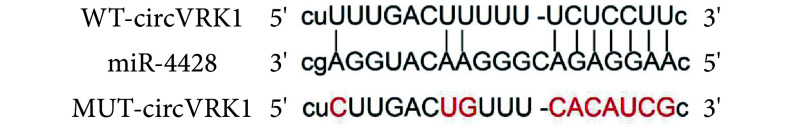Abstract
目的
分析circVRK1和miR-4428在急性淋巴细胞白血病(acute lymphoblastic leukemia, ALL)细胞增殖和凋亡中的关系。
方法
体外培养ALL细胞KOCL44,实验分组为:pcDNA、pcDNA-circVRK1、anti-miR-NC、anti-miR-4428、si-NC、si-circVRK1、pcDNA-circVRK1+miR-NC和pcDNA-circVRK1+miR-4428组。qRT-PCR检测细胞circVRK1和miR-4428的表达水平;CCK-8法、流式细胞术分别检测细胞增殖及凋亡;双荧光素酶报告实验检测circVRK1与miR-4428的靶向关系〔实验分为circVRK1野生型报告质粒(WT-circVRK1)+miR-NC、WT-circVRK1+miR-4428、circVRK1突变报告质粒(MUT-circVRK1)+miR-NC和MUT-circVRK1+ miR-4428组〕;Western blot检测Ki-67、cleaved caspase-3、cleaved caspase-9蛋白表达量。
结果
相较于pcDNA组,pcDNA-circVRK1组的circVRK1表达上调(P<0.05);与转染pcDNA或者转染anti-miR-NC相比,转染pcDNA-circVRK1或anti-miR-4428后,KOCL44细胞活力和Ki-67蛋白表达降低(P<0.05),凋亡率和cleaved caspase-3、cleaved caspase-9蛋白水平增加(P<0.05);circVRK1可负向调控miR-4428的表达,但该作用仅在转染WT-circVRK1的组别中体现;与pcDNA组相比,pcDNA-circVRK1组miR-4428表达降低(P<0.05);与si-NC组相比,si-circVRK1组miR-4428表达增加(P<0.05);与共转染pcDNA-circVRK1+miR-NC相比,共转染pcDNA-circVRK1+miR-4428后细胞活力升高(P<0.05),Ki-67蛋白表达增加(P<0.05),凋亡率和cleaved caspase-3、cleaved caspase-9蛋白水平降低(P<0.05)。
结论
circVRK1过表达可通过下调miR-4428表达而减弱ALL细胞增殖能力及诱导细胞凋亡。
Keywords: 急性淋巴细胞白血病, circVRK1, miR-4428, 细胞增殖, 细胞凋亡
Abstract
Objective
To elucidate the role of circVRK1 and its interaction with miR-4428 in regulating proliferation and apoptosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cells.
Methods
KOCL44 ALL cells were cultured in vitro, and experimental groups included pcDNA, pcDNA-circVRK1, anti-miR-NC, anti-miR-4428, si-NC, si-circVRK1, pcDNA-circVRK1+miR-NC, and pcDNA-circVRK1+miR-4428. The expression levels of circVRK1 and miR-4428 were detected using qRT-PCR. CCK-8 assays and flow cytometry were used to assess cell proliferation and apoptosis, respectively. The dual luciferase reporter assays were employed to investigate the interaction between circVRK1 and miR-4428, with groups categorized as WT-circVRK1+miR-NC, WT-circVRK1+miR-4428, MUT-circVRK1+miR-NC, and MUT-circVRK1+ miR-4428. Western blotting was utilized to detect the expression levels of Ki-67, cleaved caspase-3, and cleaved caspase-9 proteins.
Results
Compared to the pcDNA group, circVRK1 expression was up-regulated in the pcDNA-circVRK1 group (P<0.05). Compared to transfection with pcDNA or anti-miR-NC, transfection with pcDNA-circVRK1 or anti-miR-4428 led to decreased cell viability and Ki-67 protein levels in KOCL44 cells (P<0.05), and increased apoptosis rates and levels of cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved caspase-9 (P<0.05). circVRK1 was found to negatively regulate miR-4428 expression, with this effect observed only in the WT-circVRK1 group. miR-4428 levels were lower in the pcDNA-circVRK1 group compared to the pcDNA group (P<0.05) and higher in the si-circVRK1 group compared to the si-NC group (P<0.05). Co-transfection with pcDNA-circVRK1+miR-4428 resulted in increased cell viability (P<0.05) and Ki-67 expression (P<0.05), and decreased apoptosis rates and levels of cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved caspase-9 (P<0.05) compared to co-transfection with pcDNA-circVRK1+miR-NC.
Conclusion
Overexpression of circVRK1 reduces the proliferation ability of acute ALL cells and induces cell apoptosis by downregulating miR-4428 expression.
Keywords: Acute lymphocytic leukemia, circVRK1, miR-4428, Cell proliferation, Cell apoptosis
急性淋巴细胞白血病(acute lymphoblastic leukemia, ALL)是一种恶性疾病,主要是由于淋巴造血系统中的异常白细胞在骨髓中无法正常发育,进而在骨髓腔中聚集,抑制正常的造血功能,ALL患者预后较差[1-3]。环状RNA(circular RNA, circRNA)是一种特殊类型的非编码RNA,不像线性RNA那样具有5'端和3'端,它可直接结合特定微小RNA(microRNA, miRNA),调节其活性,进而解除miRNA对其靶基因的抑制作用[4]。先前的研究已经表明circRNA的异常表达与疾病的发生和进展密切相关[5]。据报道,circRNA还是某些血液恶性肿瘤病理过程中的关键调控因子[6]。早期的研究表明高表达circVRK1可促进骨肉瘤细胞的增殖和迁移[7]。但circVRK1在ALL进展中的角色还未见报道。本课题组通过StarBase预测发现circVRK1与miR-4428有互补序列,基于此,本研究进一步分析了circVRK1和miR-4428在ALL细胞增殖和凋亡中的关系,现报道如下。
1. 材料与方法
1.1. 主要材料
ALL细胞KOCL44购自武汉普诺赛;pcDNA、pcDNA-circVRK1购自上海吉满生物;LipofectamineTM 3000 Transfection Reagent转染试剂购自美国Invitrogen;DMEM培养液与胎牛血清购自美国Gibco;pGL3质粒购自美国Promega;Trizol试剂和反转录与荧光定量PCR试剂盒购自美国Thermo Fisher;基因定量试剂购自北京天根生化;一抗购自武汉艾美捷;二抗购自美国Santa Cruz;miR-4428模拟物(miR-4428 mimics, 记为miR-4428)和抑制剂(anti-miR-4428)、circVRK1小干扰RNA(si-circVRK1)以及相应的对照miR-NC、anti-miR-NC、si-NC购自广州锐博生物;CCK-8试剂、细胞凋亡检测试剂、胰蛋白酶溶液、磷酸缓冲液、蛋白电泳液、双荧光素酶活性检测试剂盒、细胞裂解液、蛋白预制胶、转膜液购自北京索莱宝;BeyoECL Plus化学发光试剂盒购自江苏碧云天生物有限公司。
1.2. 研究方法
1.2.1. 实验分组
KOCL44细胞放入含有胎牛血清、青霉素和链霉素的DMEM培养基,于37 ℃、体积分数5%CO2培养箱内培养,待细胞生长汇合度达到80%时进行转染,采用脂质体转染法(参照LipofectamineTM 3000 Transfection Reagent转染试剂说明书)将pcDNA、pcDNA-circVRK1、anti-miR-NC、anti-miR-4428、si-circVRK1、si-NC分别转染至KOCL44细胞,分别记为pcDNA组、pcDNA-circVRK1组、anti-miR-NC组、anti-miR-4428组、si-circVRK1组及si-NC组。采用脂质体转染法将pcDNA-circVRK1和miR-NC或miR-4428 mimics共转染至细胞,分别记为pcDNA-circVRK1+miR-NC组、pcDNA-circVRK1+miR-4428组。
1.2.2. qRT-PCR检测circVRK1和miR-4428的表达水平
转染48 h后,采用Trizol试剂分别提取各组KOCL44细胞总RNA,依据紫外分光光度计测定RNA浓度。随后,其反转录体系如下:2 μL 5×gDNA Buffer,2 μL 10×King RT Buffer,1 μL FastKing RT Enzyme Mix,2 μL FQ-RT Primer Mix,2 μg RNA;反应条件:42 ℃ 15 min,95 ℃ 3 min。然后,以cDNA为模板,ABI StepOnePlus荧光定量PCR仪进行qRT-PCR扩增,反应程序:95 ℃ 2 min,95 ℃ 15 s,60 ℃ 1 min,72 ℃ 30 s(循环40次)。circVRK1和miR-4428的相对表达量通过2−ΔΔCt法计算。
1.2.3. CCK-8实验检测细胞增殖
将KOCL44细胞在96孔板中传代。转染48 h后,收集各组KOCL44细胞,按照说明书指南用制备的CCK-8溶液处理细胞4 h,使用酶标仪测量450 nm处的吸光度值。
1.2.4. 流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡率
转染48 h后,收集各组KOCL44细胞,调整至所需密度(1×106)。根据Annexin Ⅴ-FITC/PI试剂盒说明书,在黑暗中将细胞凋亡检测试剂添加到每孔中,然后添加磷酸盐缓冲液。将细胞放至冰上,流式细胞仪分析早期凋亡率+晚期凋亡率。
1.2.5. 双荧光素酶报告实验检测circVRK1与miR-4428的靶向关系
circVRK1的序列中含有与miR-4428互补的核苷酸序列,见图1。将circVRK1序列中含有miR-4428结合位点的区域通过聚合酶链反应扩增,扩增的序列由上海擎科生物鉴定。将克隆序列导入pGL3载体,构建circVRK1野生型报告质粒(WT-circVRK1)。突变circVRK1序列中和miR-4428互补的位点,将突变的circVRK1序列克隆到pGL3载体,构建circVRK1突变报告质粒(MUT-circVRK1)。按上述转染方法将WT-circVRK1、MUT-circVRK1分别与miR-4428或miR-NC共转染至KOCL44细胞,分组:WT-circVRK1+miR-NC、WT-circVRK1+ miR-4428、MUT-circVRK1+miR-NC和MUT-circVRK1+ miR-4428组。然后,将细胞置于培养箱内培养24 h,使用双荧光素酶活性检测试剂盒分析发光情况。
图 1.
Targeted complementary sequences of circVRK1 and miR-4428
circVRK1和miR-4428的靶向互补序列
1.2.6. Western blot检测Ki-67、cleaved caspase-3、cleavedcaspase-9 蛋白表达量
各组细胞转染48 h后, 使用预冷的细胞裂解缓冲液制备细胞裂解液,并离心去除颗粒细胞碎片。上清液中的蛋白质样品在高温下变性,并根据其相对分子质量使用聚丙烯酰胺凝胶分离。在使用脱脂牛奶防止非特异性结合之前,将分离的蛋白质转移到硝化纤维素膜上。采用Ki-67(1∶800)、cleaved caspase-3(1∶1000)、cleaved caspase-9(1∶1000)一抗与内参GAPDH抗体(1∶3000)稀释液孵育硝化纤维素膜,去除未结合的一抗后,用酶偶联二抗与膜孵育。通过BeyoECL Plus化学发光试剂盒可视化膜上的蛋白条带。成像的蛋白条带经Image J软件分析灰度值,结果以目的蛋白与内参蛋白GAPDH灰度值的比值表示目的蛋白的相对表达量。
1.3. 统计学方法
采用SPSS21.0统计学软件分析数据,计量资料以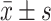 表示,正态分布的数据两组间比较采用独立样本t检验并使用bonferroni法进行P值校正,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,两两比较使用Dunnet t法,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
表示,正态分布的数据两组间比较采用独立样本t检验并使用bonferroni法进行P值校正,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,两两比较使用Dunnet t法,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1. circVRK1过表达对KOCL44细胞增殖的影响
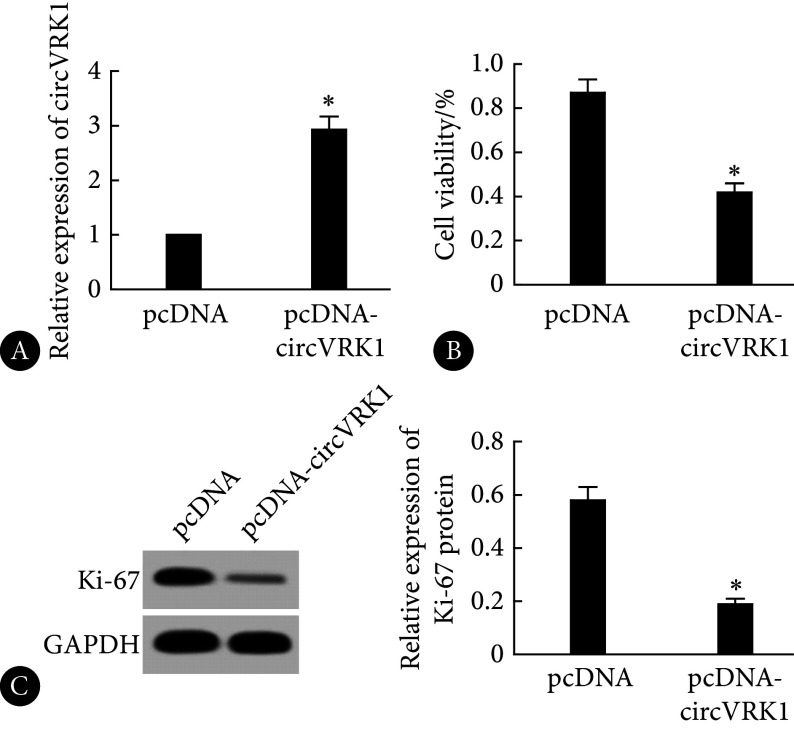
相较于pcDNA组,pcDNA-circVRK1组的circVRK1表达上调,KOCL44细胞活力和Ki-67蛋白表达水平降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见图2。
图 2.
Effects of circVRK1 overexpression on KOCL44 cell proliferation and related protein expression
circVRK1过表达对KOCL44细胞增殖及相关蛋白表达的影响
A, The expression level of circVRK1 assessed by qRT-PCR (n=9); B, CCK-8 assay performed to evaluate cell viability (n=9); C, Western blot performed to determine Ki-67 protein expression (the relative molecular mass of Ki-67 and GAPDH proteins is 358×103 and 37×103, respectively. n=3). * P<0.05, vs. pcDNA.
2.2. circVRK1过表达对KOCL44细胞凋亡的影响
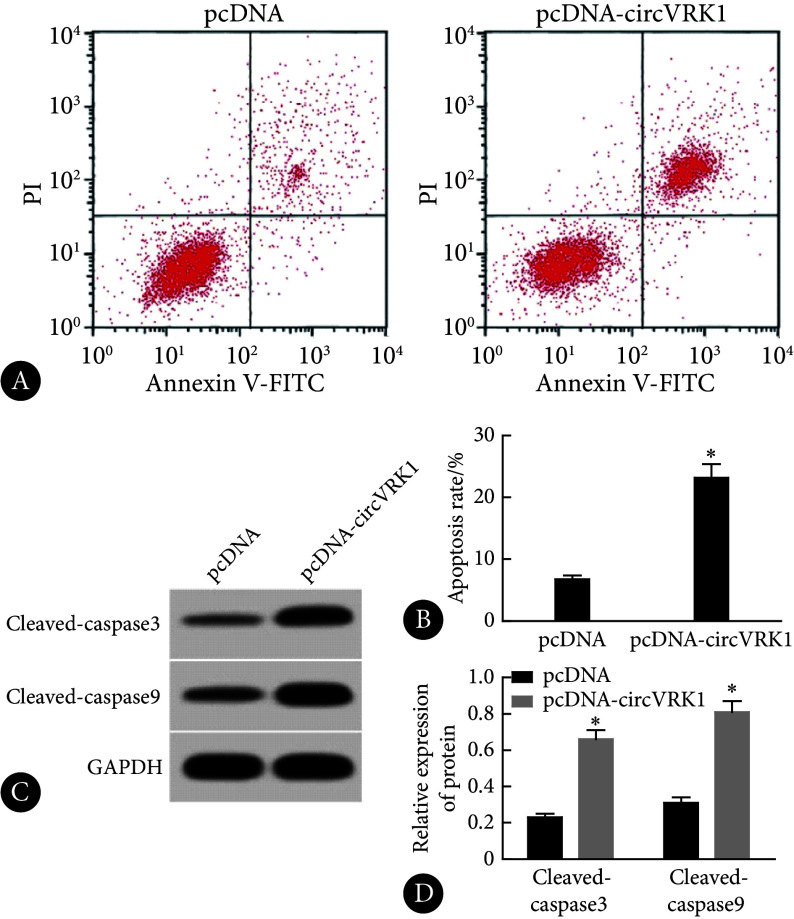
与pcDNA组比较,pcDNA-circVRK1组中KOCL44细胞凋亡率和cleaved caspase-3、cleaved caspase-9蛋白水平升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见图3。
图 3.
High expression of circVRK1 promoted apoptosis of KOCL44 cells
circVRK1高表达促进KOCL44细胞凋亡
A, Flow cytometry; B, apoptosis rate determined by flow cytometry (n=9); C, Western blot (the relative molecular mass of cleaved caspase-3, cleaved caspase-9, and GAPDH proteins is 17×103, 35×103, and 37×103, respectively); D, relative expression of proteins assessed by Western blot (n=3). * P<0.05, vs. pcDNA.
2.3. circVRK1靶向调控miR-4428的表达
与miR-NC相比,miR-4428模拟物转染抑制了WT-circVRK1组细胞的荧光素酶活性,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),但不影响MUT-circVRK1组,见表1。此外,circVRK1过表达抑制miR-4428的表达,而circVRK1沉默则促进miR-4428的表达,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表2。
表 1. Dual luciferase report assay (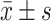 ).
).
双荧光素酶报告实验(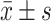 )
)
| Group | n | Relative luciferase activity | t | P | |
| miR-NC | miR-4428 | ||||
| WT-circVRK1 | 9 | 0.96±0.06 | 0.42±0.04 | 22.465 | <0.001 |
| MUT-circVRK1 | 9 | 0.99±0.07 | 0.98±0.05 | 0.349 | 0.732 |
表 2. Regulation of miR-4428 expression by circVRK1 (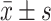 ).
).
circVRK1调控miR-4428的表达(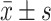 )
)
| Group | n | miR-4428 |
| * P<0.05, vs. pcDNA group; # P<0.05, vs. si-NC group. | ||
| pcDNA | 9 | 1.00±0.00 |
| pcDNA-circVRK1 | 9 | 0.51±0.04* |
| si-NC | 9 | 1.02±0.07 |
| si-circVRK1 | 9 | 3.14±0.26# |
2.4. miR-4428低表达抑制KOCL44细胞增殖、促进细胞凋亡
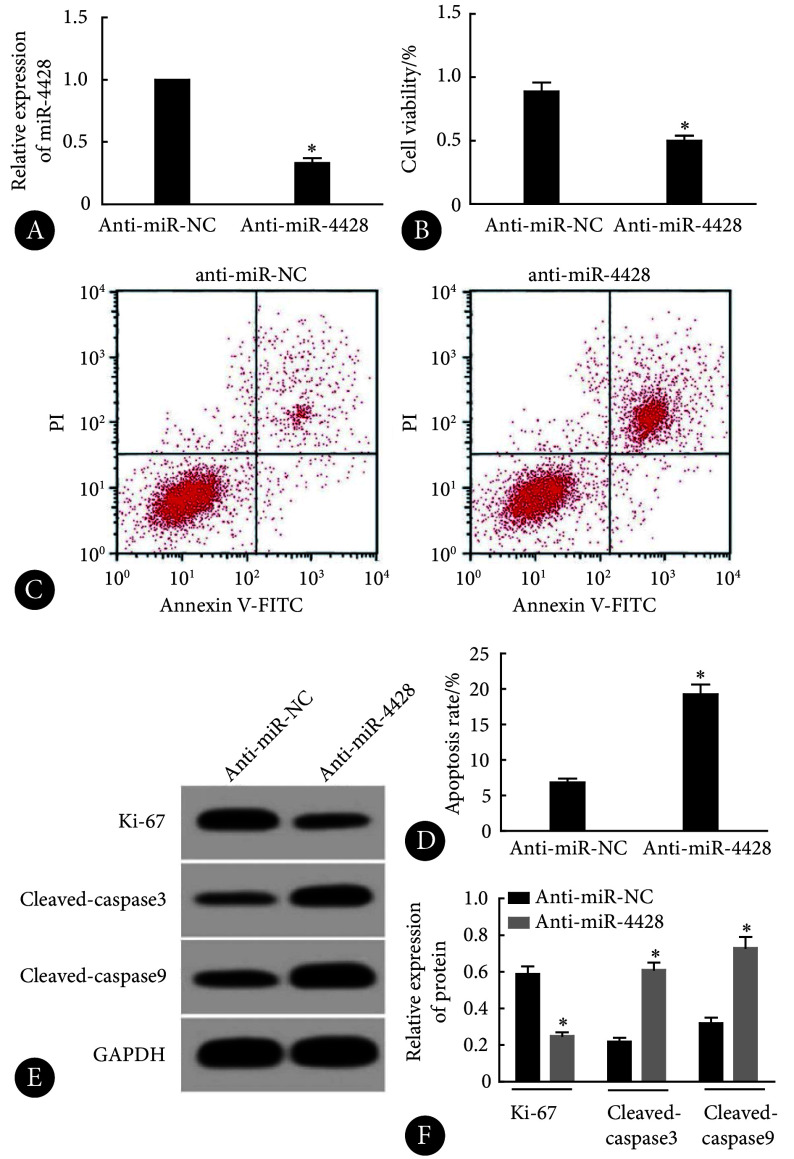
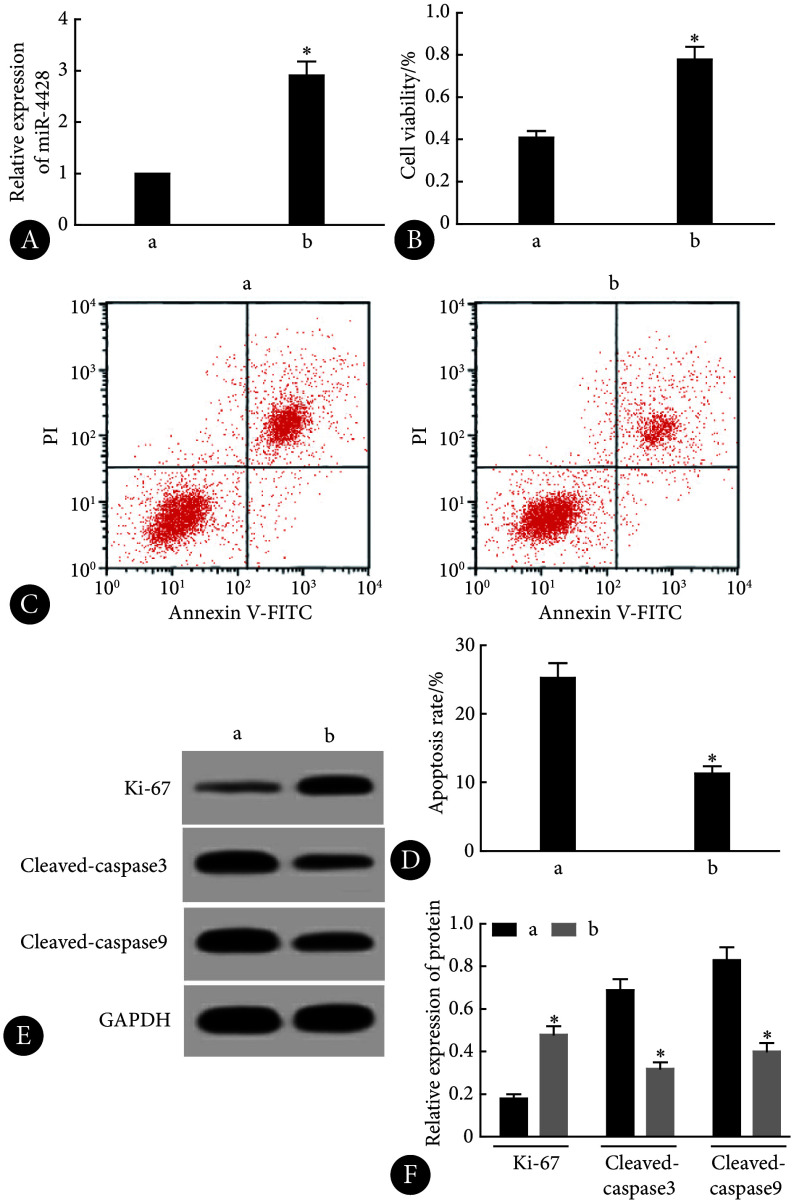
由图4可见,相对于anti-miR-NC组,anti-miR-4428组的miR-4428的表达减少,KOCL44细胞活力以及Ki-67蛋白水平降低,细胞凋亡率和cleaved caspase-3、cleaved caspase-9蛋白水平升高,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
图 4.
Effects of miR-4428 interference on KOCL44 cell proliferation and apoptosis
干扰miR-4428表达对KOCL44细胞增殖和凋亡的影响
A, qRT-PCR (n=9); B, CCK-8 (n=9); C, flow cytometry; D, apoptosis rate assessed by flow cytometry (n=9); E, Western blot (the relative molecular mass of Ki-67, cleaved caspase-3, cleaved caspase-9, and GAPDH proteins is 358×103, 17×103, 35×103, and 37×103, respectively); F, relative expression of proteins assessed by Western blot (n=3). * P<0.05, vs. anti-miR-NC.
2.5. 上调miR-4428表达对circVRK1过表达促进KOCL44细胞增殖和凋亡的逆转作用
由图5可见,与pcDNA-circVRK1+miR-NC组比较,pcDNA-circVRK1+miR-4428组KOCL44细胞活力以及Ki-67蛋白水平增加,细胞凋亡率和cleaved caspase-3、cleaved-caspase9蛋白水平降低,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
图 5.
Upregulation of miR-4428 reversed the effects of circVRK1 overexpression on KOCL44 cell proliferation and apoptosis
上调miR-4428表达逆转了circVRK1过表达对KOCL44细胞增殖和凋亡的作用
A, qRT-PCR (n=9); B, CCK-8 (n=9); C, flow cytometry; D, apoptosis rate assessed by flow cytometry (n=9); E, Western blot (the relative molecular mass of the proteins is as shown in Fig 4); F, relative expression of proteins assessed by Western blot (n=9); a, pcDNA-circVRK1+miR-NC; b, pcDNA-circVRK1+miR-4428. * P<0.05, vs. pcDNA-circVRK1+miR-NC.
3. 讨论
circRNA基因序列上富含miRNA的结合位点,并可通过吸附miRNA而负向调控miRNA的表达从而调控细胞增殖、凋亡等生物学过程[8-9]。circRNA中的miRNA结合位点(miRNA响应元件,MRE)能够与miRNA的互补序列结合,形成circRNA-miRNA复合物,ALL发生及发展也涉及此调控机制[10-12]。
敲低circVRK1可减轻氧糖剥夺对 人脑微血管内皮细胞的 迁移、血管生成、死亡、炎症反应和氧化应激的影响 [7]。在食管鳞状细胞癌组织和细胞中,circVRK1的表达水平通常较低。然而,当其表达上调时,食管鳞状细胞癌细胞的增殖和迁移能力受到抑制 [13]。但circVRK1在ALL进展中的角色还未见报道。本研究结果显示,circVRK1过表达可抑制ALL细胞增殖,同时降低Ki-67的表达水平,而Ki-67表达上调可促进细胞增殖[14],提示circVRK1过表达可减弱ALL细胞增殖能力。caspase9和caspase3被激活标志着细胞发生凋亡[15]。本研究通过分析细胞凋亡率和这两个蛋白的表达发现circVRK1促进ALL细胞凋亡。
干扰miR-4428表达可抑制肺腺癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭,促进细胞凋亡[16]。miR-4428在甲状腺癌中表达上调,并可能作为甲状腺诊断的潜在生物学标志物[17]。本研究证实circVRK1可靶向结合miR-4428,干扰miR-4428表达可抑制ALL细胞增殖及促进细胞凋亡,而miR-4428过表达可减弱circVRK1过表达造成的影响。提示circVRK1可通过靶向结合miR-4428对ALL细胞增殖和凋亡产生影响。
综上所述,circVRK1可通过下调miR-4428抑制ALL细胞增殖及促进细胞凋亡,该结果可能为ALL的治疗提供新的靶向方法。但本研究仅限于体外实验,其在体内的作用还有待研究。随后的研究将用动物模型验证本研究的结论,进一步分析miR-4428调控ALL细胞增殖及凋亡的机制。
* * *
作者贡献声明 张欢负责数据审编、正式分析、调查研究、研究方法、验证和初稿写作,吴斌负责论文构思、监督指导和审读与编辑写作,王月娇负责经费获取和提供资源。所有作者已经同意将文章提交给本刊,且对将要发表的版本进行最终定稿,并同意对工作的所有方面负责。
Author Contribution ZHANG Huan is responsible for data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, validation, and writing--original draft. WU Bin is responsible for conceptualization, supervision, and writing--review and editing. WANG Yuejiao is responsible for funding acquisition and resources. All authors consented to the submission of the article to the Journal. All authors approved the final version to be published and agreed to take responsibility for all aspects of the work.
利益冲突 所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突
Declaration of Conflicting Interests All authors declare no competing interests.
Funding Statement
国家自然科学基金(No. 82101898)和辽宁省民生科技计划联合计划项目(No. 2021JH2/10300092)资助
Contributor Information
欢 张 (Huan ZHANG), Email: 18940253567@163.com.
斌 吴 (Bin WU), Email: wub1sj@163.com.
References
- 1.BURATIN A, PAGANIN M, GAFFO E, et al Large-scale circular RNA deregulation in T-ALL: unlocking unique ectopic expression of molecular subtypes. Blood Adv. 2020;4(23):5902–5914. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020002337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.GHETTI M, VANNINI I, STORLAZZI C T, et al Linear and circular PVT1 in hematological malignancies and immune response: two faces of the same coin. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):69–79. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01187-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.LI Q, REN X, WANG Y, et al CircRNA: a rising star in leukemia. PeerJ. 2023;11:e15577. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.PANDA A C Circular RNAs Act as miRNA Sponges. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1087:67–79. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-1426-1_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.张蕾, 查显丰, 温旺荣 环状RNA在急性髓系白血病中的研究进展. 分子诊断与治疗杂志. 2020;12(2):123–126. [Google Scholar]; ZHANG L, ZHA X F, WEN W R Research progress of circular RNA in acute myeloid leukemia. J Mol Diagn Ther. 2020;12(2):123–126. [Google Scholar]
- 6.DENG F, ZHANG C, LU T, et al Roles of circRNAs in hematological malignancies. Biomark Res. 2022;10(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s40364-022-00392-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.TAN L, WANG L, LIU J, et al Circvrk1 downregulation attenuates brain microvascular endothelial cell damage induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation through modulating the miR-150-5p/MLLT1 axis. Exp Brain Res. 2023;241(3):781–791. doi: 10.1007/s00221-023-06555-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.CHENG Y, SU Y, WANG S, et al Identification of circRNA-lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA competitive endogenous rna network as novel prognostic markers for acute myeloid leukemia. Genes (Basel) 2020;11(8):868. doi: 10.3390/genes11080868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.HOU Y, SUN J, HUANG J, et al Circular RNA circRNA_0000094 sponges microRNA-223-3p and up-regulate F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7 to restrain T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia progression. Hum Cell. 2021;34(3):977–989. doi: 10.1007/s13577-021-00504-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.HU J, HAN Q, GU Y, et al Circular RNA PVT1 expression and its roles in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Epigenomics. 2018;10(6):723–732. doi: 10.2217/epi-2017-0142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.LIU X, ZHOU C, LI Y, et al Upregulation of circ-0000745 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia enhanced cell proliferation by activating ERK pathway. Gene. 2020;751(1):144726–144736. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.GAFFO E, BOLDRIN E, DAL MOLIN A, et al Circular RNA differential expression in blood cell populations and exploration of circRNA deregulation in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):14670–14680. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50864-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.HE Y, MINGYAN E, WANG C, et al CircVRK1 regulates tumor progression and radioresistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating miR-624-3p/PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;125(1):116–123. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.CARLOS J A E G, LIMA K, COSTA-LOTUFO L V, et al AD80, a multikinase inhibitor, exhibits antineoplastic effects in acute leukemia cellular models targeting the PI3K/STMN1 axis. Invest New Drugs. 2021;39(4):1139–1149. doi: 10.1007/s10637-021-01066-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.LIN X L, LI K, YANG Z, et al Dulcitol suppresses proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating SIRT1/p53 pathway. Phytomedicine. 2020;66(1):153112–153122. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.153112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.YING K, WANG L, LONG G, et al ACTA2-AS1 suppresses lung adenocarcinoma progression via sequestering miR-378a-3p and miR-4428 to elevate SOX7 expression. Cell Biol Int. 2020;44(12):2438–2449. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.WU S, ZHU J, JIANG T, et al Long non-coding RNA ACTA2-AS1 suppresses metastasis of papillary thyroid cancer via regulation of miR-4428/KLF9 axis. Clin Epigenetics. 2024;16(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13148-023-01622-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]