Abstract
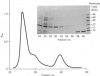
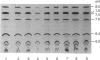
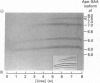
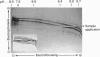
Human serum amyloid A protein (apo-SAA) can be prepared by gel filtration of delipidated acute-phase high-density lipoprotein in the presence of urea. The resultant apo-SAA is soluble (greater than 90% solubility) in a wide range of buffer solutions, with all of the six major isoforms of apo-SAA being equally soluble. In urea-containing solutions the isoforms behave qualitatively differently in various urea concentrations, probably reflecting subtle primary-structure variations. The higher-pI isoforms are only completely unfolded at greater than 7 M-urea. By immunizing with apo-SAA adsorbed to acid-treated bacteria (Salmonella minnesota R595), high-titre antibodies can easily be elicited in rabbits.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bausserman L. L., Herbert P. N., Forte T., Klausner R. D., McAdam K. P., Osborne J. C., Jr, Rosseneu M. Interaction of the serum amyloid A proteins with phospholipid. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10681–10688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bausserman L. L., Herbert P. N., McAdam K. P. Heterogeneity of human serum amyloid A proteins. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):641–656. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellstedt D. U., Human P. A., Rowland G. F., Van der Merwe K. J. Acid-treated, naked bacteria as immune carriers for protein antigens. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Apr 16;98(2):249–255. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coetzee G. A., Strachan A. F., van der Westhuyzen D. R., Hoppe H. C., Jeenah M. S., de Beer F. C. Serum amyloid A-containing human high density lipoprotein 3. Density, size, and apolipoprotein composition. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9644–9651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton T. E. Electrophoretic analysis of the unfolding of proteins by urea. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 5;129(2):235–264. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90279-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton T. E. Kinetic study of protein unfolding and refolding using urea gradient electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 15;137(1):61–80. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90157-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein C., Lim C. T., Scanu A. M. On the subunit structure of the protein of human serum high density lipoprotein. I. A study of its major polypeptide component (Sephadex, fraction 3). J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 25;247(18):5842–5849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godenir N. L., Jeenah M. S., Coetzee G. A., Van der Westhuyzen D. R., Strachan A. F., De Beer F. C. Standardisation of the quantitation of serum amyloid A protein (SAA) in human serum. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Nov 7;83(2):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90243-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubb A., Löfberg H., Thysell H., Ljunggren L., Olsson T., Skinner M., Shirahama T., Cohen A. S. Production of an amino acid sequence-specific antiserum against human amyloid A (AA) and serum amyloid A (SAA) protein. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1987 Oct;47(6):619–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. S., Benditt E. P. Plasma clearance kinetics of the amyloid-related high density lipoprotein apoprotein, serum amyloid protein (apoSAA), in the mouse. Evidence for rapid apoSAA clearance. J Clin Invest. 1983 Apr;71(4):926–934. doi: 10.1172/JCI110847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. S., Benditt E. P. Secretion of serum amyloid protein and assembly of serum amyloid protein-rich high density lipoprotein in primary mouse hepatocyte culture. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10518–10522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. S., Ericsson L. H., Eriksen N., Walsh K. A., Benditt E. P. Murine tissue amyloid protein AA. NH2-terminal sequence identity with only one of two serum amyloid protein (ApoSAA) gene products. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):641–646. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluve-Beckerman B., Dwulet F. E., Benson M. D. Human serum amyloid A. Three hepatic mRNAs and the corresponding proteins in one person. J Clin Invest. 1988 Nov;82(5):1670–1675. doi: 10.1172/JCI113779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavie G., Zucker-Franklin D., Franklin E. C. Degradation of serum amyloid A protein by surface-associated enzymes of human blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1020–1031. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek R. L., Hoffman J. S., Benditt E. P. Amyloidogenesis. One serum amyloid A isotype is selectively removed from the circulation. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):499–510. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B. Measurement of serum amyloid A protein concentrations as test of renal allograft rejection. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Mar 17;288(6420):859–860. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6420.859-d. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal C. J., Franklin E. C., Frangione B., Greenspan J. Isolation and partial characterization of SAA-an amyloid-related protein from human serum. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1415–1418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. M., Lim C. T., Edelstein C. On the subunit structure of the protein of human serum high density lipoprotein. II. A study of Sephadex fraction IV. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 25;247(18):5850–5855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlecht S., Ring K., Kutscher J., Eschweiler W. Ein neuer Laboratoriumsfermenter zur Züchtung von Mikroorganismen im turbidostatischen, chemostatischen und "batch"-Verfahren. I. Techniche Beschreibung des Fermenters. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1968 Mar;206(2):246–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan A. F., de Beer F. C., van der Westhuyzen D. R., Coetzee G. A. Identification of three isoform patterns of human serum amyloid A protein. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 15;250(1):203–207. doi: 10.1042/bj2500203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. B., Spector M. S. The self-association of human apolipoprotein A-IV. Evidence for an in vivo circulating dimeric form. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14279–14286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]