Abstract
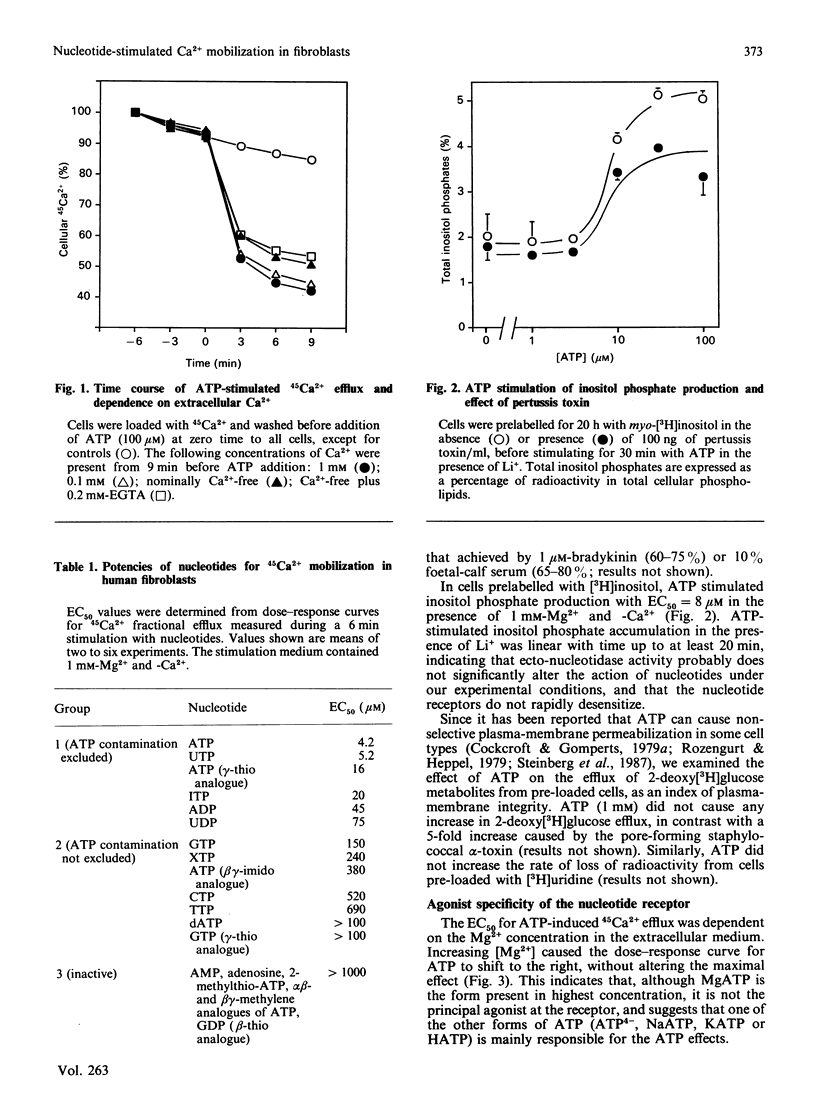
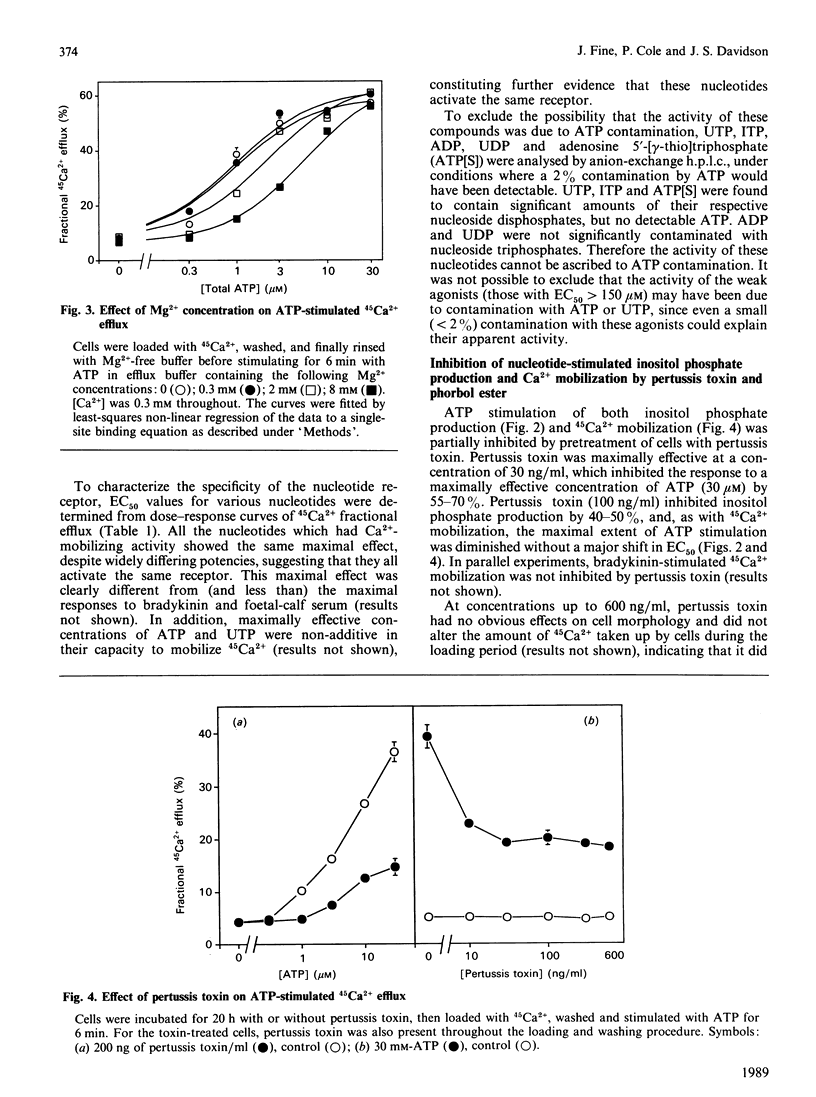
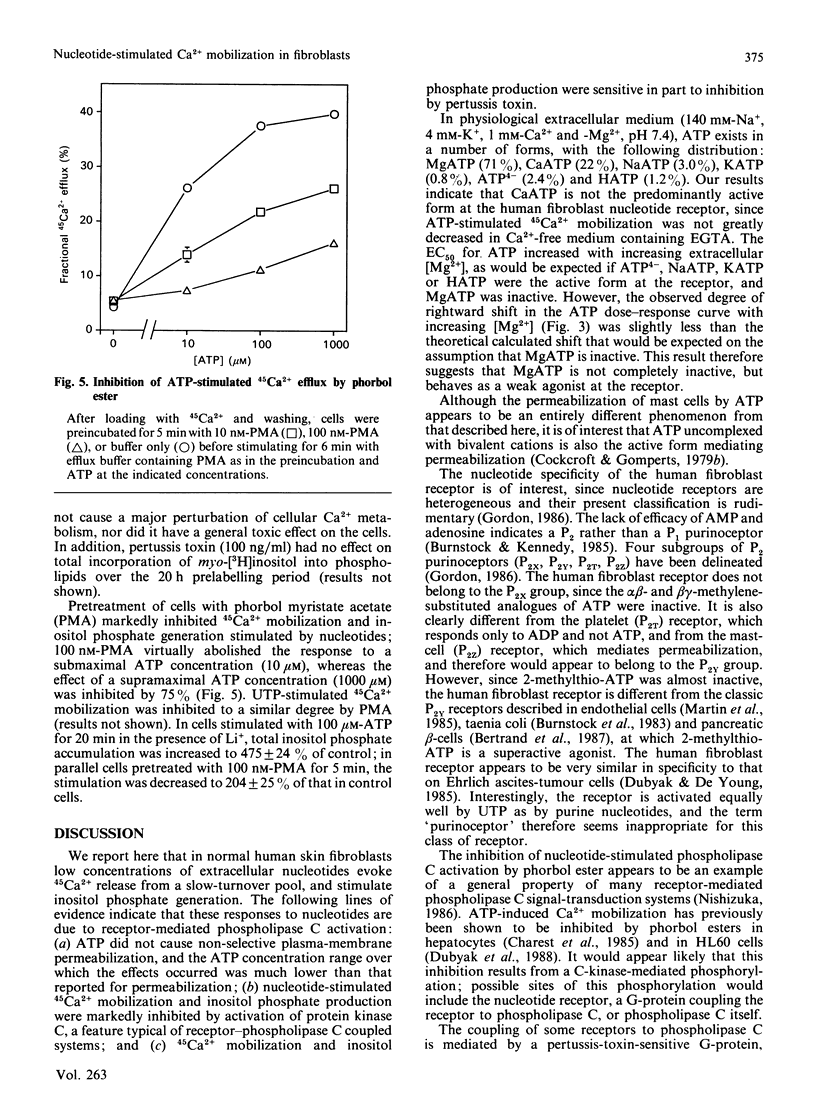
In human skin fibroblasts, low concentrations of extracellular ATP stimulated 45Ca2+ efflux from a slow-turnover intracellular pool, accompanied by inositol phosphate generation. These effects of ATP were not due to a generalized increase in plasma-membrane permeability. The EC50 (concn. giving 50% stimulation) for ATP was dependent on Ca2+ and Mg2+ concentrations in a manner which indicates that a form of ATP uncomplexed with bivalent cations is the active species. The rank order of potency of nucleotides was: ATP = UTP greater than adenosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate greater than ITP greater than ADP greater than UDP greater than other nucleoside triphosphates. Adenosine 5'-[alpha beta-methylene]triphosphate, adenosine 5'-[beta gamma-methylene]triphosphate and 2-methylthio-ATP were inactive. Thus the nucleotide specificity of this receptor is different from that of previously characterized P2 purinoceptors. Nucleotide-stimulated 45Ca2+ mobilization and inositol phosphate production were markedly inhibited by phorbol ester, and partially inhibited by pertussis-toxin pretreatment. These findings suggest that the coupling of nucleotide receptor to phospholipase C is mediated both by a pertussis-toxin-sensitive G-protein and by a pertussis-toxin-insensitive mechanism.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand G., Chapal J., Loubatières-Mariani M. M., Roye M. Evidence for two different P2-purinoceptors on beta cell and pancreatic vascular bed. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Aug;91(4):783–787. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeynaems J. M., Galand N. Stimulation of vascular prostacyclin synthesis by extracellular ADP and ATP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Apr 15;112(1):290–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91829-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Cusack N. J., Hills J. M., MacKenzie I., Meghji P. Studies on the stereoselectivity of the P2-purinoceptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Aug;79(4):907–913. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10535.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton D. B., Robertson S. M., Olson M. S. Stimulation of glycogenolysis by adenine nucleotides in the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 1;237(3):773–780. doi: 10.1042/bj2370773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charest R., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Characterization of responses of isolated rat hepatocytes to ATP and ADP. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15789–15794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. ATP induces nucleotide permeability in rat mast cells. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):541–542. doi: 10.1038/279541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Activation and inhibition of calcium-dependent histamine secretion by ATP ions applied to rat mast cells. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:229–243. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Stutchfield J. G-proteins, the inositol lipid signalling pathway, and secretion. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 26;320(1199):247–265. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlquist R., Diamant B. Interaction of ATP and calcium on the rat mast cell: effect on histamine release. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1974 May;34(5):368–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1974.tb03533.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delahunty T. M., Cronin M. J., Linden J. Regulation of GH3-cell function via adenosine A1 receptors. Inhibition of prolactin release, cyclic AMP production and inositol phosphate generation. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):69–77. doi: 10.1042/bj2550069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubyak G. R., Cowen D. S., Meuller L. M. Activation of inositol phospholipid breakdown in HL60 cells by P2-purinergic receptors for extracellular ATP. Evidence for mediation by both pertussis toxin-sensitive and pertussis toxin-insensitive mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18108–18117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubyak G. R., De Young M. B. Intracellular Ca2+ mobilization activated by extracellular ATP in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10653–10661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Myoplasmic free calcium concentration reached during the twitch of an intact isolated cardiac cell and during calcium-induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of a skinned cardiac cell from the adult rat or rabbit ventricle. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Nov;78(5):457–497. doi: 10.1085/jgp.78.5.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S., Di Virgilio F., Steinberg T. H., Silverstein S. C. Extracellular nucleotides mediate Ca2+ fluxes in J774 macrophages by two distinct mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10337–10343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory S., Kern M. Adenosine and adenine nucleotides are mitogenic for mouse thymocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 14;83(3):1111–1116. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91510-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallam T. J., Pearson J. D. Exogenous ATP raises cytoplasmic free calcium in fura-2 loaded piglet aortic endothelial cells. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 20;207(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikehara S., Pahwa R. N., Lunzer D. G., Good R. A., Modak M. J. Adenosine-5'-triphosphate-(ATP) mediated stimulation and suppression of DNA synthesis in lymphoid cells. I. Characterization of ATP responsive cells in mouse lymphoid organs. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1834–1838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loubatieres-Mariani M. M., Chapal J., Lignon F., Valette G. Structural specificity of nucleotides for insulin secretory action from the isolated perfused rat pancreas. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Nov 16;59(3-4):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90291-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F. Measurement of phospholipid turnover in cultured hormone responsive pituitary cells. Methods Enzymol. 1986;124:424–442. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)24033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Cusack N. J., Carleton J. S., Gordon J. L. Specificity of P2-purinoceptor that mediates endothelium-dependent relaxation of the pig aorta. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 5;108(3):295–299. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90452-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Minkes M. S., Douglas J. R., Jr Stimulation of prostaglandin biosynthesis by adenine nucleotides. Profile of prostaglandin release by perfused organs. Circ Res. 1974 Apr;34(4):455–460. doi: 10.1161/01.res.34.4.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. D. Purine nucleotides as regulators of vessel tone. Biochem Soc Trans. 1988 Aug;16(4):480–482. doi: 10.1042/bst0160480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. D., Slakey L. L., Gordon J. L. Stimulation of prostaglandin production through purinoceptors on cultured porcine endothelial cells. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 15;214(1):273–276. doi: 10.1042/bj2140273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phaneuf S., Berta P., Casanova J., Cavadore J. C. ATP stimulates inositol phosphates accumulation and calcium mobilization in a primary culture of rat aortic myocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 13;143(2):454–460. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91375-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirotton S., Raspe E., Demolle D., Erneux C., Boeynaems J. M. Involvement of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and calcium in the action of adenine nucleotides on aortic endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17461–17466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice W. R., Singleton F. M. P2Y-purinoceptor regulation of surfactant secretion from rat isolated alveolar type II cells is associated with mobilization of intracellular calcium. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Aug;91(4):833–838. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Heppel L. A. Reciprocal control of membrane permeability of transformed cultures of mouse cell lines by external and internal ATP. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):708–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg T. H., Newman A. S., Swanson J. A., Silverstein S. C. ATP4- permeabilizes the plasma membrane of mouse macrophages to fluorescent dyes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8884–8888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wreggett K. A., Irvine R. F. A rapid separation method for inositol phosphates and their isomers. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):655–660. doi: 10.1042/bj2450655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Merwe P. A., Wakefield I. K., Fine J., Millar R. P., Davidson J. S. Extracellular adenosine triphosphate activates phospholipase C and mobilizes intracellular calcium in primary cultures of sheep anterior pituitary cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 30;243(2):333–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


