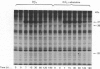
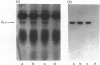
Abstract
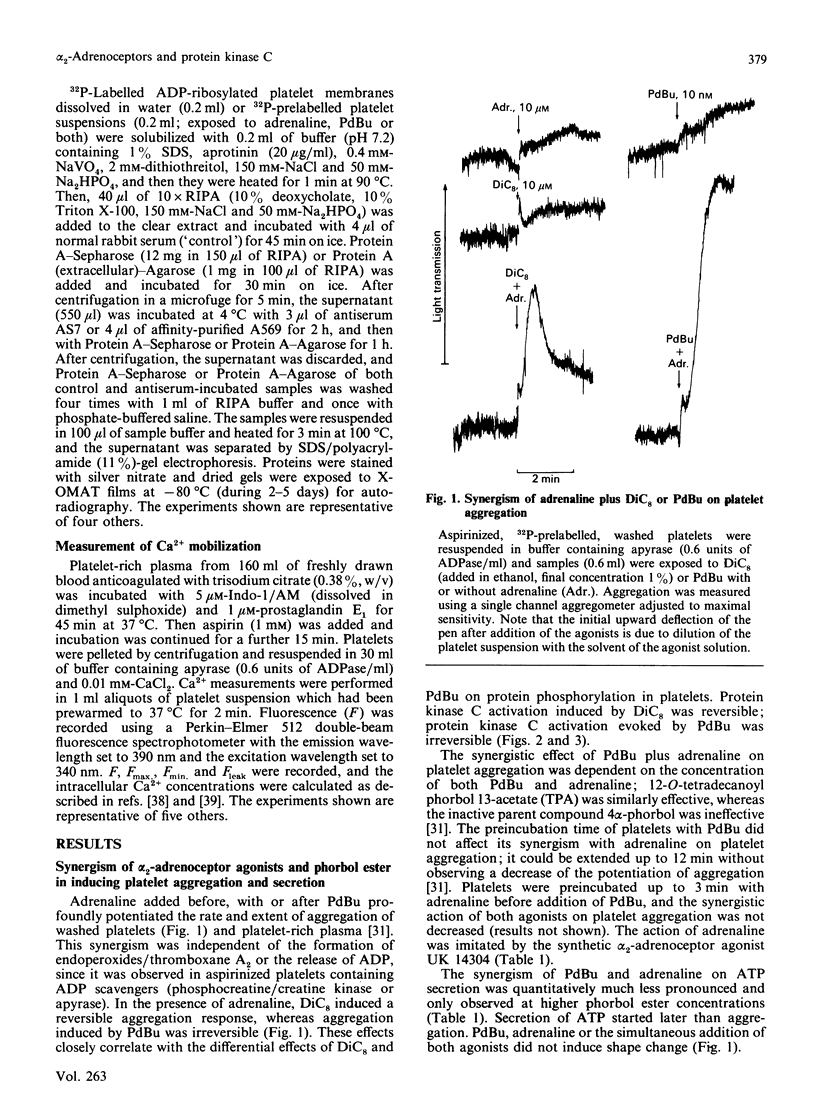
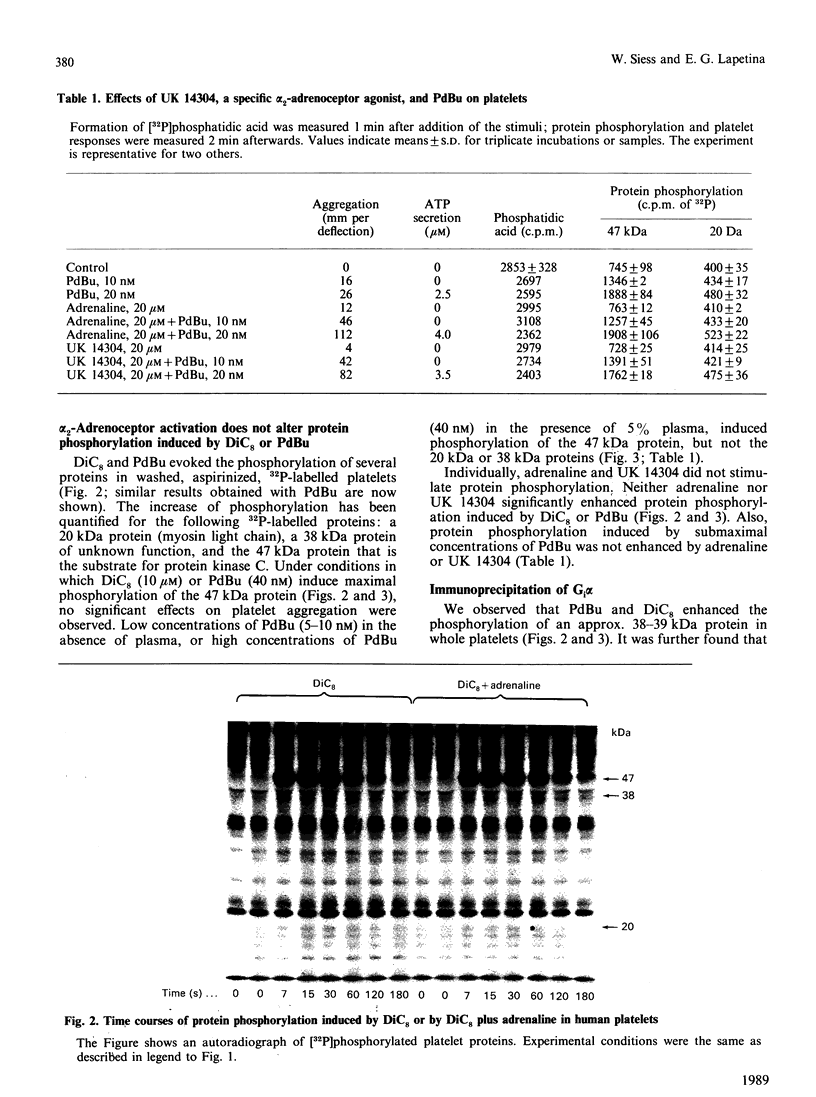
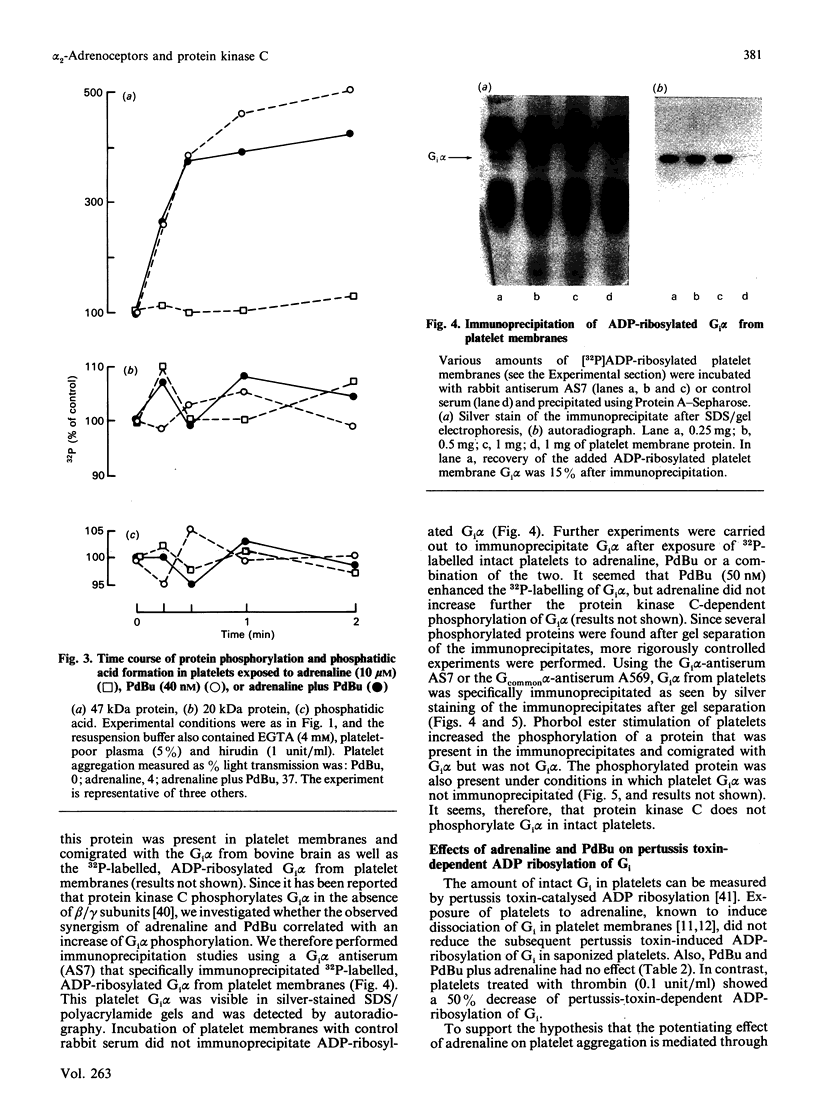
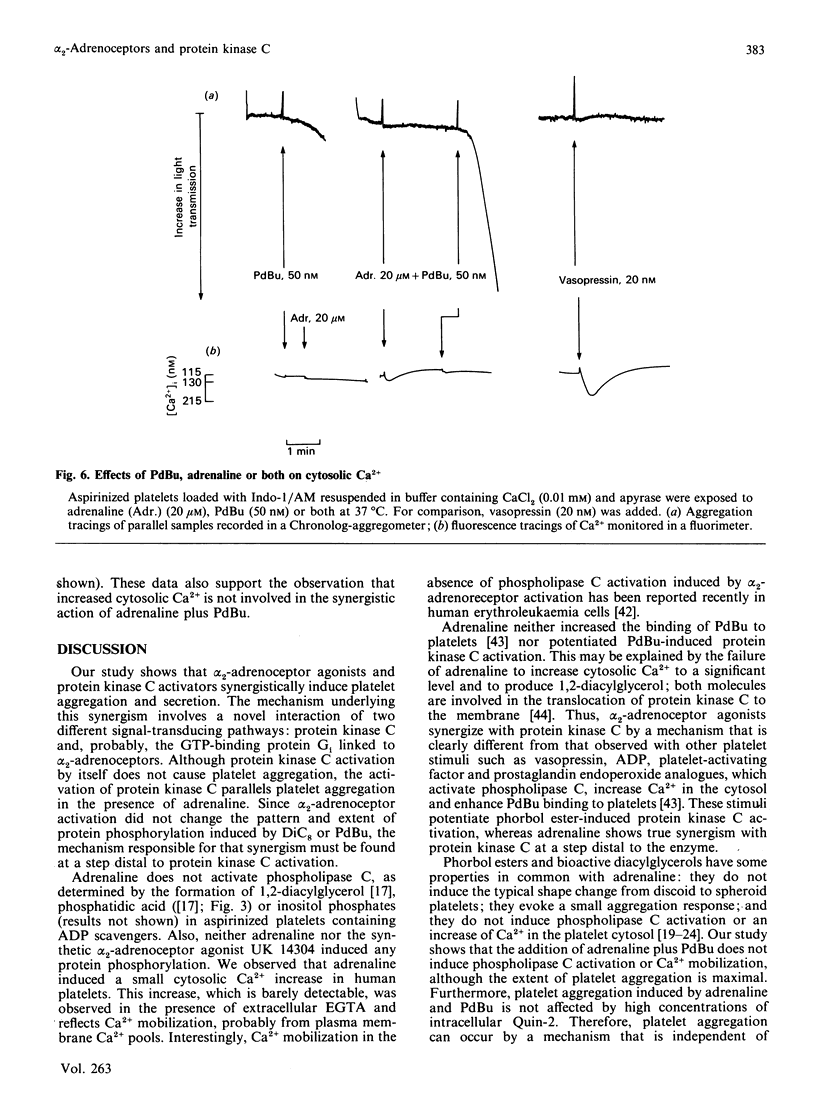
Adrenaline or UK 14304 (a specific alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist) and phorbol ester (phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate; PdBu) or bioactive diacylglycerols (sn-1,2-dioctanoylglycerol; DiC8) synergistically induced platelet aggregation and ATP secretion. The effect on aggregation was more pronounced than the effect on secretion, and it was observed in aspirinized, platelet-rich plasma or suspensions of washed aspirinized platelets containing ADP scavengers. No prior shape change was found. In the presence of adrenaline, DiC8 induced reversible aggregation and PdBu evoked irreversible aggregation that correlated with the different kinetics of DiC8- and PdBu-induced protein kinase C activation. Adrenaline and UK 14304 did not induce or enhance phosphorylation induced by DiC8 or PdBu of myosin light chain (20 kDa), the substrate of protein kinase C (47 kDa), or a 38 kDa protein. Immunoprecipitation studies using a Gcommon alpha antiserum or a Gi alpha antiserum showed that Gi alpha is not phosphorylated after exposure of platelets to PdBu or PdBu plus adrenaline. Adrenaline, PdBu or adrenaline plus PdBu did not cause stimulation of phospholipase C as reflected in production of [32P]phosphatidic acid. Adrenaline caused a small increase of Ca2+ in the platelet cytosol of platelets loaded with Indo-1; this effect was also observed in the absence of extracellular Ca2+. However, under conditions of maximal aggregation induced by adrenaline plus PdBu, no increase of cytosolic Ca2+ was observed. Platelet aggregation induced by PdBu plus adrenaline was not inhibited by a high intracellular concentration of the calcium chelator Quin-2. These experiments indicate that alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists, known to interact with Gi, and protein kinase C activators synergistically induced platelet aggregation through a novel mechanism. The synergism occurs distally to Gi protein activation and protein kinase C-dependent protein phosphorylation and does not involve phospholipase C activation or Ca2+ mobilization.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buss J. E., Mumby S. M., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G., Sefton B. M. Myristoylated alpha subunits of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7493–7497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerione R. A., Regan J. W., Nakata H., Codina J., Benovic J. L., Gierschik P., Somers R. L., Spiegel A. M., Birnbaumer L., Lefkowitz R. J. Functional reconstitution of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor with guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins in phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3901–3909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clare K. A., Scrutton M. C., Thompson N. T. Effects of alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists and of related compounds on aggregation of, and on adenylate cyclase activity in, human platelets. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Jun;82(2):467–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10782.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codina J., Yatani A., Grenet D., Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. The alpha subunit of the GTP binding protein Gk opens atrial potassium channels. Science. 1987 Apr 24;236(4800):442–445. doi: 10.1126/science.2436299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad G. W., Rink T. J. Platelet activating factor raises intracellular calcium ion concentration in macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;103(2):439–450. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glusa E., Markwardt F. Influence of clonidine-like hypotensive drugs on adrenergic platelet reactions. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Jun 1;30(11):1359–1360. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90321-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallam T. J., Sanchez A., Rink T. J. Stimulus-response coupling in human platelets. Changes evoked by platelet-activating factor in cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with the fluorescent calcium indicator quin2. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 15;218(3):819–827. doi: 10.1042/bj2180819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Davidson M. M., Desjardins J. V. Inhibition of adenylate cyclase by adenosine analogues in preparations of broken and intact human platelets. Evidence for the unidirectional control of platelet function by cyclic AMP. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 15;176(1):83–95. doi: 10.1042/bj1760083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Taylor A. Effects of catecholamines on the formation of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in human blood platelets. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):377–379. doi: 10.1042/bj1250377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobs K. H., Saur W., Schultz G. Reduction of adenylate cyclase activity in lysates of human platelets by the alpha-adrenergic component of epinephrine. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1976 Nov-Dec;2(6):381–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Sawamura M., Hoshijima M., Fujikura T., Nishizuka Y. Synergistic functions of protein phosphorylation and calcium mobilization in platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6701–6704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Gilman A. G., Watanabe Y., Bauer S., Jakobs K. H. Protein kinase C phosphorylates the inhibitory guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory component and apparently suppresses its function in hormonal inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):431–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara Y., Yamanishi J., Tsunemitsu M., Fukuzaki H. Protein phosphorylation and diglyceride production during serotonin release induced by epinephrine plus ADP in human platelets. Thromb Res. 1983 Jun 1;30(5):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90182-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanza F., Cazenave J. P. Studies of alpha 2-adrenergic receptors of intact and functional washed human platelets by binding of 3H-dihydroergocryptine and 3H-yohimbine--correlation of 3H-yohimbine binding with the potentiation by adrenaline of ADP-induced aggregation. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Aug 30;54(2):402–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G. Prostacyclin inhibition of phosphatidic acid synthesis in human platelets is not mediated by protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Apr 16;120(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91410-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Reep B., Chang K. J. Treatment of human platelets with trypsin, thrombin, or collagen inhibits the pertussis toxin-induced ADP-ribosylation of a 41-kDa protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5880–5883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Reep B., Ganong B. R., Bell R. M. Exogenous sn-1,2-diacylglycerols containing saturated fatty acids function as bioregulators of protein kinase C in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1358–1361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre D. E., McNicol A., Drummond A. H. Tumour-promoting phorbol esters inhibit agonist-induced phosphatidate formation and Ca2+ flux in human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 28;180(2):160–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane D. E., Mills D. C. The effects of ATP on platelets: evidence against the central role of released ADP in primary aggregation. Blood. 1975 Sep;46(3):309–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane D. E., Stump D. C. Parallel observation of the occupancy of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor in intact platelets and its ability to inhibit the adenylate cyclase. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;22(3):574–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Brass L. F., Williams A., Bokoch G. M., LaMorte V. J., Motulsky H. J. Alpha 2-adrenergic receptor stimulation mobilizes intracellular Ca2+ in human erythroleukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4986–4991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. C., Roberts G. C. Effects of adrenaline on human blood platelets. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):443–453. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubig R. R., Gantzos R. D., Brasier R. S. Agonist and antagonist binding to alpha 2-adrenergic receptors in purified membranes from human platelets. Implications of receptor-inhibitory nucleotide-binding protein stoichiometry. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Nov;28(5):475–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'BRIEN J. R. SOME EFFECTS OF ADRENALINE AND ANTI-ADRENALINE COMPOUNDS ON PLATELETS IN VITRO AND IN VIVO. Nature. 1963 Nov 23;200:763–764. doi: 10.1038/200763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. J., Martin J. M., Hunter D. D., Nathanson N. M., Hille B. GTP-binding proteins couple cardiac muscarinic receptors to a K channel. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):536–538. doi: 10.1038/317536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao G. H., White J. G. Epinephrine potentiation of arachidonate-induced aggregation of cyclooxygenase-deficient platelets. Am J Hematol. 1981 Dec;11(4):355–366. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830110404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro-Neto F. A., Mattera R., Hildebrandt J. D., Codina J., Field J. B., Birnbaumer L., Sekura R. D. ADP-ribosylation of membrane components by pertussis and cholera toxin. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:566–572. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09115-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Sanchez A., Hallam T. J. Diacylglycerol and phorbol ester stimulate secretion without raising cytoplasmic free calcium in human platelets. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):317–319. doi: 10.1038/305317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse S. E., Sasson J. P. Mass changes in myoinositol trisphosphate in human platelets stimulated by thrombin. Inhibitory effects of phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8657–8660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Beemon K., Hunter T. Comparison of the expression of the src gene of Rous sarcoma virus in vitro and in vivo. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):957–971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.957-971.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W. Evidence for the formation of inositol 4-monophosphate in stimulated human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 3;185(1):151–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80760-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Lapetina E. G. Ca2+ mobilization primes protein kinase C in human platelets. Ca2+ and phorbol esters stimulate platelet aggregation and secretion synergistically through protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):309–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Lapetina E. G. Phorbol esters sensitize platelets to activation by physiological agonists. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1373–1381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Lapetina E. G. Prostacyclin inhibits platelet aggregation induced by phorbol ester or Ca2+ ionophore at steps distal to activation of protein kinase C and Ca2+-dependent protein kinases. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 15;258(1):57–65. doi: 10.1042/bj2580057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Roth P., Weber P. C. Stimulated platelet aggregation, thromboxane B2 formation and platelet sensitivity to prostacyclin - a critical evaluation. Thromb Haemost. 1981 Jun 30;45(3):204–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Siegel F. L., Lapetina E. G. Arachidonic acid stimulates the formation of 1,2-diacylglycerol and phosphatidic acid in human platelets. Degree of phospholipase C activation correlates with protein phosphorylation, platelet shape change, serotonin release, and aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11236–11242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Weber P. C., Lapetina E. G. Activation of phospholipase C is dissociated from arachidonate metabolism during platelet shape change induced by thrombin or platelet-activating factor. Epinephrine does not induce phospholipase C activation or platelet shape change. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8286–8292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A., North R. A. Mechanism of synaptic inhibition by noradrenaline acting at alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jun 22;234(1274):85–114. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. T., Scrutton M. C. Intracellular calcium fluxes in human platelets. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 1;147(2):421–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargaftig B. B., Fouque F., Benveniste J., Odiot J. Adrenaline and PAF-acether synergize to trigger cyclooxygenase-independent activation of plasma-free human platelets. Thromb Res. 1982 Nov 15;28(4):557–573. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90171-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J. A., Johnson P. C., Smith M., Salzman E. W. Effect of common agonists on cytoplasmic ionized calcium concentration in platelets. Measurement with 2-methyl-6-methoxy 8-nitroquinoline (quin2) and aequorin. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):878–886. doi: 10.1172/JCI112385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Lapetina E. G. 1,2-Diacylglycerol and phorbol ester inhibit agonist-induced formation of inositol phosphates in human platelets: possible implications for negative feedback regulation of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2623–2626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. A., Murphy W., Haslam R. J. Effects of activation of protein kinase C on the agonist-induced stimulation and inhibition of cyclic AMP formation in intact human platelets. Biochem J. 1987 May 1;243(3):667–678. doi: 10.1042/bj2430667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M., LeVine H., 3rd, May W. S., Jr, Cuatrecasas P., Sahyoun N. A model for intracellular translocation of protein kinase C involving synergism between Ca2+ and phorbol esters. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):546–549. doi: 10.1038/317546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavoico G. B., Halenda S. P., Sha'afi R. I., Feinstein M. B. Phorbol myristate acetate inhibits thrombin-stimulated Ca2+ mobilization and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis in human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3859–3862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Troll W., Belman S. The tumor-promoter phorbol ester (12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate), a potent aggregating agent for blood platelets. J Cell Biol. 1974 Feb;60(2):325–336. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]