Abstract
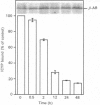
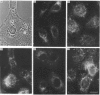
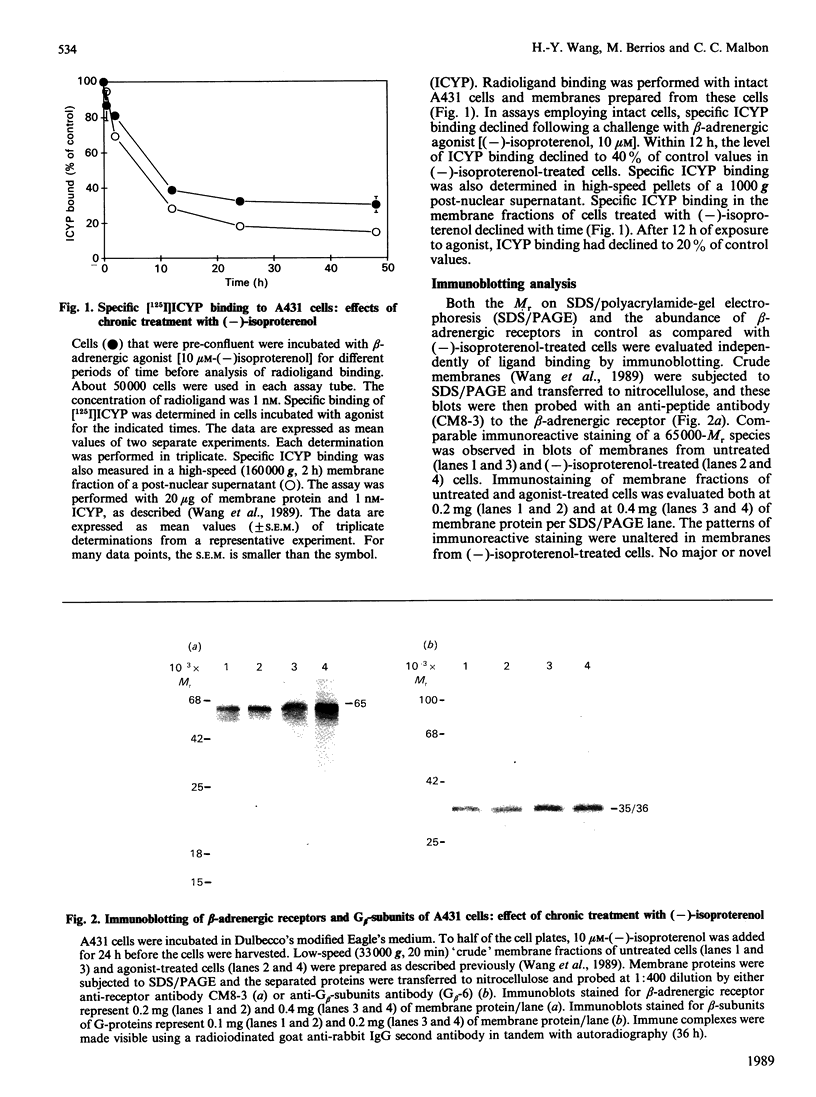
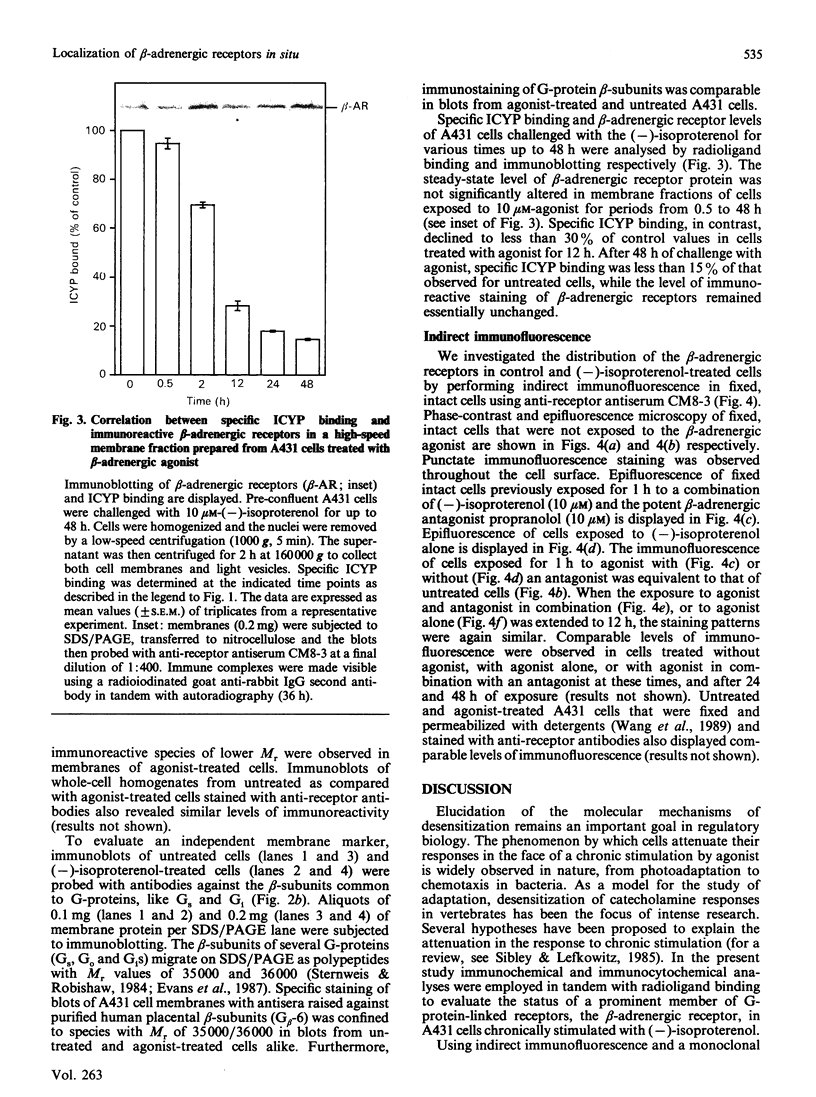
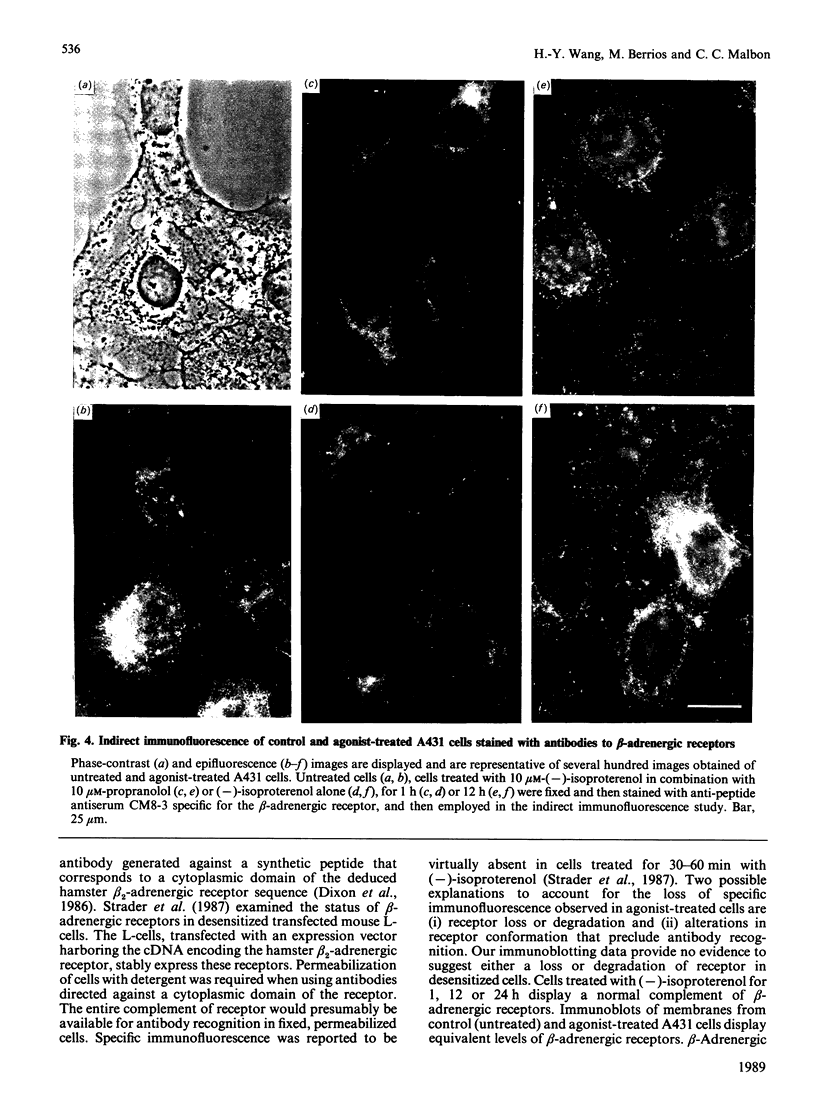
The status of beta-adrenergic receptors was investigated in A431 cells exposed to chronic stimulation by the beta-adrenergic agonist, (-)-isoproterenol. Specific binding of beta-adrenergic antagonist (-)-[125I]iodocyanopindolol declined to 60-80% below control values within 12 h of agonist treatment. This decline in ligand binding was also observed in high-speed membrane fractions prepared from agonist-treated cells. Immunoblots probed with anti-receptor antibodies revealed both that beta-adrenergic receptors from untreated and treated cells migrated as 65,000-Mr peptides and that the cellular complement of receptor was unchanged. Indirect immunofluorescence localization of beta-adrenergic receptors was comparable in control (untreated) cells and cells challenged with (-)-isoproterenol for 1, 12, or 24 h. Thus receptor complement, migration on SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis, and localization in situ are largely unaffected by agonist stimulation. Receptor binding of antagonist radioligands, in contrast, is markedly down-regulated in cells stimulated chronically with beta-adrenergic agonists. These data argue in favour of agonist-induced alteration(s) in the conformation of the receptor that preclude radioligand binding rather than agonist-induced receptor sequestration and/or degradation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alho H., Dillion-Carter O., Moxham C. P., Malbon C. C., Chuang D. M. Changes in immunohistochemical properties of beta-adrenergic receptors in frog erythrocytes by isoproterenol-induced desensitization. Life Sci. 1988;42(3):321–328. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90641-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang D. M., Costa E. Evidence for internalization of the recognition site of beta-adrenergic receptors during receptor subsensitivity induced by (-)-isoproterenol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):3024–3028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.3024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook N., Nahorski S. R., Barnett D. B. Human platelet beta 2-adrenoceptors: agonist-induced internalisation and down-regulation in intact cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;92(3):587–596. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11360.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowlen M. S., Toews M. L. Effects of agonist and phorbol ester on adrenergic receptors of DDT1 MF-2 cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Nov;243(2):527–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Kobilka B. K., Strader D. J., Benovic J. L., Dohlman H. G., Frielle T., Bolanowski M. A., Bennett C. D., Rands E., Diehl R. E. Cloning of the gene and cDNA for mammalian beta-adrenergic receptor and homology with rhodopsin. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):75–79. doi: 10.1038/321075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doss R. C., Perkins J. P., Harden T. K. Recovery of beta-adrenergic receptors following long term exposure of astrocytoma cells to catecholamine. Role of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12281–12286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Fawzi A., Fraser E. D., Brown M. L., Northup J. K. Purification of a beta 35 form of the beta gamma complex common to G-proteins from human placental membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):176–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbrother B. J., Boyle P. F., Slater D. N., George J., Nolan M. S., Fox M. The effect of ischemia on the duct-ligated pancreatic transplant in the rat. Transplant Proc. 1980 Dec;12(4 Suppl 2):172–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George S. T., Berrios M., Hadcock J. R., Wang H. Y., Malbon C. C. Receptor density and cAMP accumulation: analysis in CHO cells exhibiting stable expression of a cDNA that encodes the beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 29;150(2):665–672. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillet J. G., Kaveri S. V., Durieu O., Delavier C., Hoebeke J., Strosberg A. D. beta-Adrenergic agonist activity of a monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1781–1784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Malbon C. C. Down-regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors: agonist-induced reduction in receptor mRNA levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5021–5025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Malbon C. C. Regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors by "permissive" hormones: glucocorticoids increase steady-state levels of receptor mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8415–8419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden T. K. Agonist-induced desensitization of the beta-adrenergic receptor-linked adenylate cyclase. Pharmacol Rev. 1983 Mar;35(1):5–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden T. K., Cotton C. U., Waldo G. L., Lutton J. K., Perkins J. P. Catecholamine-induced alteration in sedimentation behavior of membrane bound beta-adrenergic receptors. Science. 1980 Oct;210(4468):441–443. doi: 10.1126/science.6254143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertel C., Coulter S. J., Perkins J. P. A comparison of catecholamine-induced internalization of beta-adrenergic receptors and receptor-mediated endocytosis of epidermal growth factor in human astrocytoma cells. Inhibition by phenylarsine oxide. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12547–12553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertel C., Perkins J. P. Receptor-specific mechanisms of desensitization of beta-adrenergic receptor function. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1984 Oct;37(3):245–256. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(84)90094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertel C., Staehelin M. Reappearance of beta-adrenergic receptors after isoproterenol treatment in intact C6-cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1538–1543. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashles O., Levitzki A. Characterization of the beta 2-adrenoceptor-dependent adenylate cyclase of A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 May 1;36(9):1531–1538. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassis S., Fishman P. H. Functional alteration of the beta-adrenergic receptor during desensitization of mammalian adenylate cyclase by beta-agonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6686–6690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassis S., Olasmaa M., Sullivan M., Fishman P. H. Desensitization of the beta-adrenergic receptor-coupled adenylate cyclase in cultured mammalian cells. Receptor sequestration versus receptor function. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12233–12237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassis S., Zaremba T., Patel J., Fishman P. H. Phorbol esters and beta-adrenergic agonists mediate desensitization of adenylate cyclase in rat glioma C6 cells by distinct mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8911–8917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limas C. J., Limas C. Rapid recovery of cardiac beta-adrenergic receptors after isoproterenol-induced "down"-regulation. Circ Res. 1984 Oct;55(4):524–531. doi: 10.1161/01.res.55.4.524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahan L. C., Koachman A. M., Insel P. A. Genetic analysis of beta-adrenergic receptor internalization and down-regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):129–133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahan L. C., Motulsky H. J., Insel P. A. Do agonists promote rapid internalization of beta-adrenergic receptors? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6566–6570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham C. P., George S. T., Graziano M. P., Brandwein H. J., Malbon C. C. Mammalian beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors. Immunological and structural comparisons. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14562–14570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham C. P., Ross E. M., George S. T., Malbon C. C. Beta-adrenergic receptors display intramolecular disulfide bridges in situ: analysis by immunoblotting and functional reconstitution. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 May;33(5):486–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross A., Rapuano M., Prives J. Induction of phosphorylation and cell surface redistribution of acetylcholine receptors by phorbol ester and carbamylcholine in cultured chick muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1139–1145. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shear M., Insel P. A., Melmon K. L., Coffino P. Agonist-specific refractoriness induced by isoproterenol. Studies with mutant cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7572–7576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Regulation of transmembrane signaling by receptor phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):913–922. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90700-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Lefkowitz R. J. Molecular mechanisms of receptor desensitization using the beta-adrenergic receptor-coupled adenylate cyclase system as a model. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):124–129. doi: 10.1038/317124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles G. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptors: biochemical mechanisms of physiological regulation. Physiol Rev. 1984 Apr;64(2):661–743. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.2.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Sibley D. R., Lefkowitz R. J. Association of sequestered beta-adrenergic receptors with the plasma membrane: a novel mechanism for receptor down regulation. Life Sci. 1984 Oct 8;35(15):1601–1610. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90359-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Sigal I. S., Blake A. D., Cheung A. H., Register R. B., Rands E., Zemcik B. A., Candelore M. R., Dixon R. A. The carboxyl terminus of the hamster beta-adrenergic receptor expressed in mouse L cells is not required for receptor sequestration. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):855–863. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90623-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su Y. F., Harden T. K., Perkins J. P. Catecholamine-specific desensitization of adenylate cyclase. Evidence for a multistep process. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7410–7419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. Y., Berrios M., Malbon C. C. Indirect immunofluorescence localization of beta-adrenergic receptors and G-proteins in human A431 cells. Biochem J. 1989 Oct 15;263(2):519–532. doi: 10.1042/bj2630519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemcik B. A., Strader C. D. Fluorescent localization of the beta-adrenergic receptor on DDT-1 cells. Down-regulation by adrenergic agonists. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 15;251(2):333–339. doi: 10.1042/bj2510333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]