Abstract
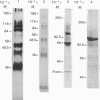
1. A monoclonal antibody (1G4) was raised against the red-cell Ca2+ pump, and it reacted with the pump, as verified by Western blot analysis and by the e.l.i.s.a. method. 2. At 1 mM-ATP and 10 microM-Ca2+, 1G4 inhibited the activity of the purified Ca2+ pump by 40%. 3. Ca2+ pump inhibition by the antibody was non-competitive with regard to Ca2+, calmodulin and the high-affinity portion of the ATP curve. Thus its mechanism was quite different from that of the antibody previously reported [Verbist, Wuytack, Raemaekers, VanLeuven, Cassiman & Casteels (1986) Biochem. J. 240, 633-640], which partially caused inhibition by competition at the ATP site. 4. Antibody 1G4 reduced the steady-state level of phosphorylated intermediate and increased by 50% the calmodulin-activated p-nitrophenyl phosphatase activity of the pump. 5. The experimental results are consistent with the hypothesis that 1G4 inhibits the Ca2+ pump by decreasing the rate of the transition from the E2 form to the E1 form, causing a higher concentration of E2. 6. Analysis by Western blot of the pattern of cross-reaction of 1G4 after tryptic digestion of the pump showed that this antibody reacts with bands of Mr 90,000, 85,000, 50,000 and 33,000. After chymotryptic digestion, the antibody reacts almost exclusively with a fragment of Mr 105,000 that is fully active but is not responsive to calmodulin. Altogether, the results indicate that 1G4 binds to an epitope involved in the functional properties of the enzyme but which is not related to the calmodulin-binding domain.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball W. J., Jr Uncoupling of ATP binding to Na+,K+-ATPase from its stimulation of ouabain binding: studies of the inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase by a monoclonal antibody. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):7155–7162. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borke J. L., Minami J., Verma A., Penniston J. T., Kumar R. Monoclonal antibodies to human erythrocyte membrane Ca++-Mg++ adenosine triphosphatase pump recognize an epitope in the basolateral membrane of human kidney distal tubule cells. J Clin Invest. 1987 Nov;80(5):1225–1231. doi: 10.1172/JCI113196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Jr, Josephson L., Warner R., Yanagisawa M., Lechene C., Guidotti G. Vanadate is a potent (Na,K)-ATPase inhibitor found in ATP derived from muscle. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7421–7423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caride A. J., Gorski J. P., Penniston J. T. Topology of the erythrocyte Ca2+ pump. A monoclonal antibody against the almost inaccessible extracellular face. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 15;255(2):663–670. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caride A. J., Rega A. F., Garrahan P. J. The role of the sites for ATP of the Ca2+ -ATPase from human red cell membranes during Ca2+ -phosphatase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 12;689(3):421–428. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90298-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douillard J. Y., Hoffman T. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for screening monoclonal antibody production using enzyme-labeled second antibody. Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:168–174. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enyedi A., Minami J., Caride A. J., Penniston J. T. Characteristics of the Ca2+ pump and Ca2+-ATPase in the plasma membrane of rat myometrium. Biochem J. 1988 May 15;252(1):215–220. doi: 10.1042/bj2520215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filoteo A. G., Gorski J. P., Penniston J. T. The ATP-binding site of the erythrocyte membrane Ca2+ pump. Amino acid sequence of the fluorescein isothiocyanate-reactive region. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6526–6530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf E., Verma A. K., Gorski J. P., Lopaschuk G., Niggli V., Zurini M., Carafoli E., Penniston J. T. Molecular properties of calcium-pumping ATPase from human erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 31;21(18):4511–4516. doi: 10.1021/bi00261a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James P., Maeda M., Fischer R., Verma A. K., Krebs J., Penniston J. T., Carafoli E. Identification and primary structure of a calmodulin binding domain of the Ca2+ pump of human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2905–2910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James P., Zvaritch E. I., Shakhparonov M. I., Penniston J. T., Carafoli E. The amino acid sequence of the phosphorylation domain of the erythrocyte Ca2+ ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 30;149(1):7–12. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91597-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitsky D. O., Syrbu S. I., Cherepakhin V. V., Rokhlin O. V. Monoclonal antibodies to dog heart sarcoplasmic reticulum. Antibodies that inhibit Ca2+-pump systems of cardiac and skeletal muscles. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Apr 15;164(2):477–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11081.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthra M. G. Trifluoperazine inhibition of calmodulin-sensitive Ca2+ -ATPase and calmodulin insensitive (Na+ +K+)- and Mg2+ -ATPase activities of human and rat red blood cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 8;692(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90531-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall T., Williams K. M. Artifacts associated with 2-mercaptoethanol upon high resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jun;139(2):502–505. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Dunau M. L., Goldman D. A rapid sensitive silver stain for polypeptides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 1;110(1):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90136-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli V., Adunyah E. S., Penniston J. T., Carafoli E. Purified (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase of the erythrocyte membrane. Reconstitution and effect of calmodulin and phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):395–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli V., Penniston J. T., Carafoli E. Purification of the (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase from human erythrocyte membranes using a calmodulin affinity column. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):9955–9958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rega A. F., Richards D. E., Garrahan P. J. Calcium ion-dependent p-nitrophenyl phosphate phosphatase activity and calcium ion-dependent adenosine triphosphatase activity from human erythrocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;136(1):185–194. doi: 10.1042/bj1360185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards D. E., Rega A. F., Garrahan P. J. Two classes of site for ATP in the Ca2+-ATPase from human red cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 4;511(2):194–201. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90313-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi J. P., Garrahan P. J., Rega A. F. The activation of phosphatase activity of the Ca2+-ATPase from human red cell membranes by calmodulin, ATP and partial proteolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 13;858(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90287-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkadi B., Enyedi A., Földes-Papp Z., Gárdos G. Molecular characterization of the in situ red cell membrane calcium pump by limited proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9552–9557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkadi B., Szász I., Gárdos G. Characteristics and regulation of active calcium transport in inside-out red cell membrane vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 23;598(2):326–338. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzmann H. J., Tschabold M. The lanthanides Ho3+ and Pr3+ as inhibitors of calcium transport in human red cells. Experientia. 1971 Jan 15;27(1):59–61. doi: 10.1007/BF02137741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Greeb J. Molecular cloning of two isoforms of the plasma membrane Ca2+-transporting ATPase from rat brain. Structural and functional domains exhibit similarity to Na+,K+- and other cation transport ATPases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8646–8657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieger J., Luterbacher S. Some properties of the purified (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase from human red cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 20;641(1):270–275. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90591-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasheva B., Dessev G. Artifacts in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis due to 2-mercaptoethanol. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;129(1):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbist J., Wuytack F., Raeymaekers L., Van Leuven F., Cassiman J. J., Casteels R. A monoclonal antibody to the calmodulin-binding (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-dependent ATPase from pig stomach smooth muscle inhibits plasmalemmal (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-dependent ATPase activity. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):633–640. doi: 10.1042/bj2400633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma A. K., Filoteo A. G., Stanford D. R., Wieben E. D., Penniston J. T., Strehler E. E., Fischer R., Heim R., Vogel G., Mathews S. Complete primary structure of a human plasma membrane Ca2+ pump. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14152–14159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma A. K., Gorski J. P., Penniston J. T. Antibodies directed toward human erythrocyte Ca2+-ATPase: effect on enzyme function and immunoreactivity of Ca2+-ATPases from other sources. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 May;215(2):345–354. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90095-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma A. K., Penniston J. T. Two Ca2+-requiring p-nitrophenylphosphatase activities of the highly purified Ca2+-pumping adenosinetriphosphatase of human erythrocyte membranes, one requiring calmodulin and the other ATP. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5010–5015. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]