Abstract
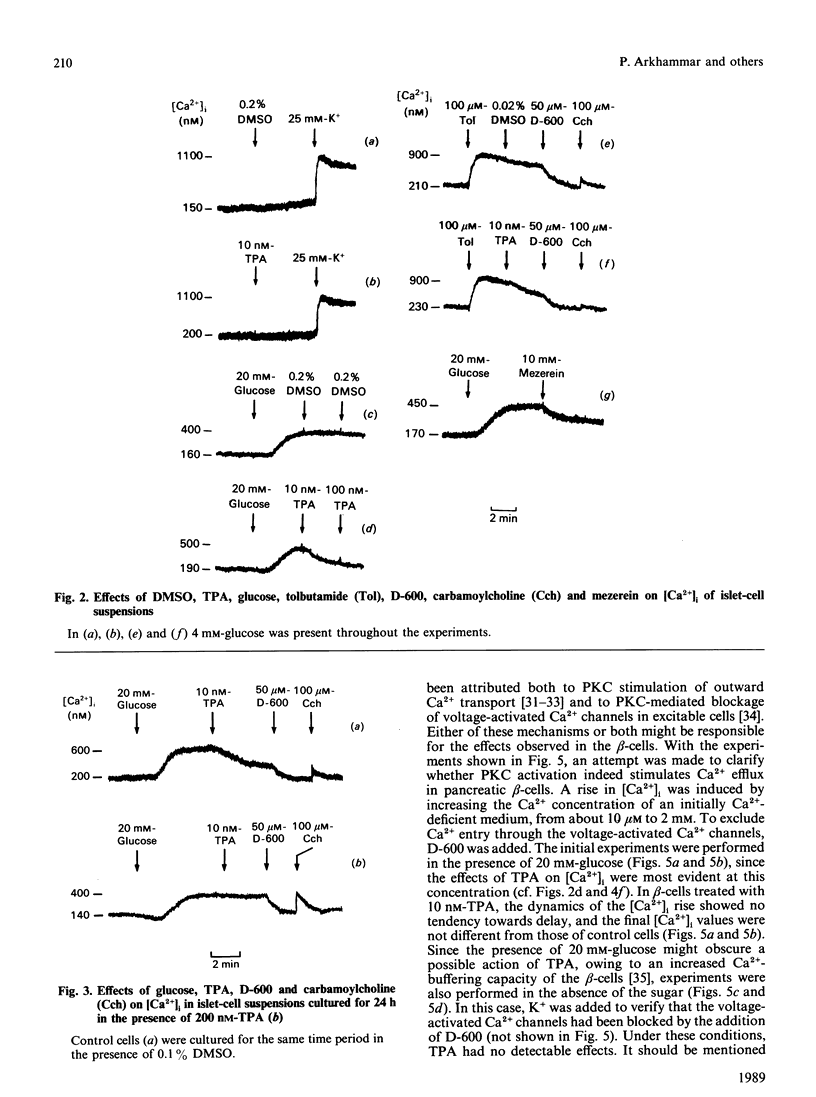
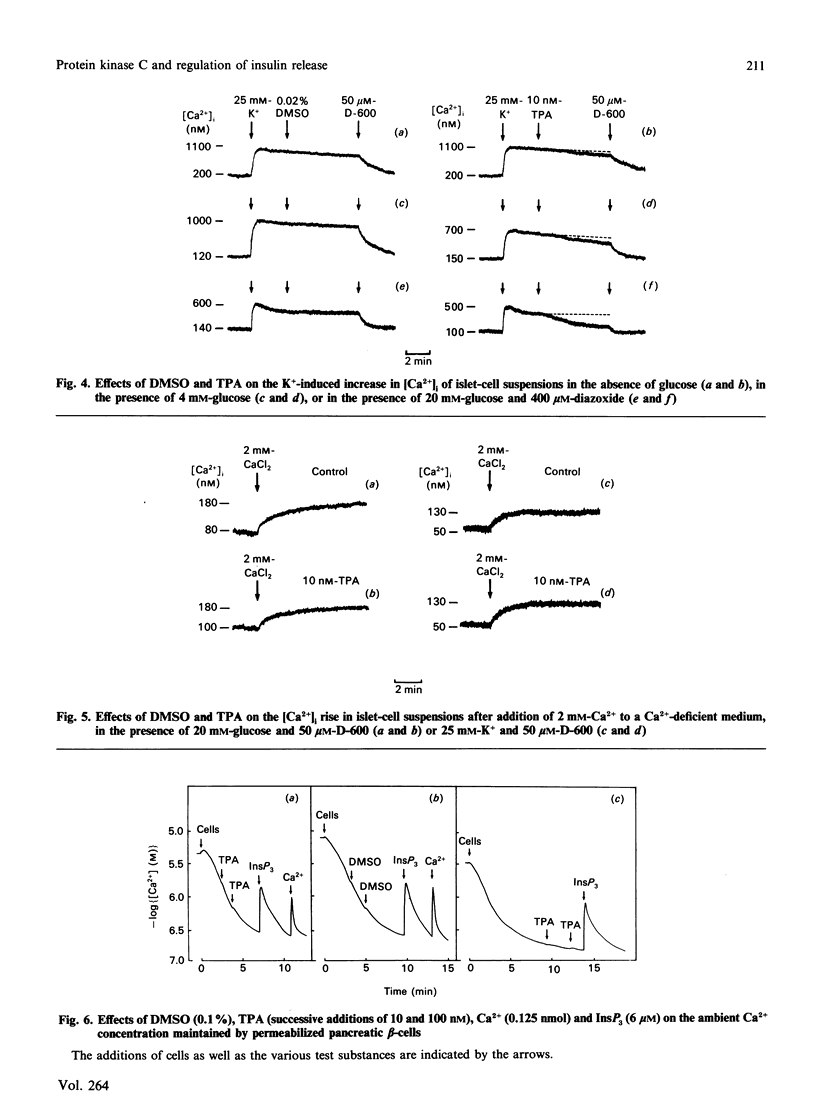
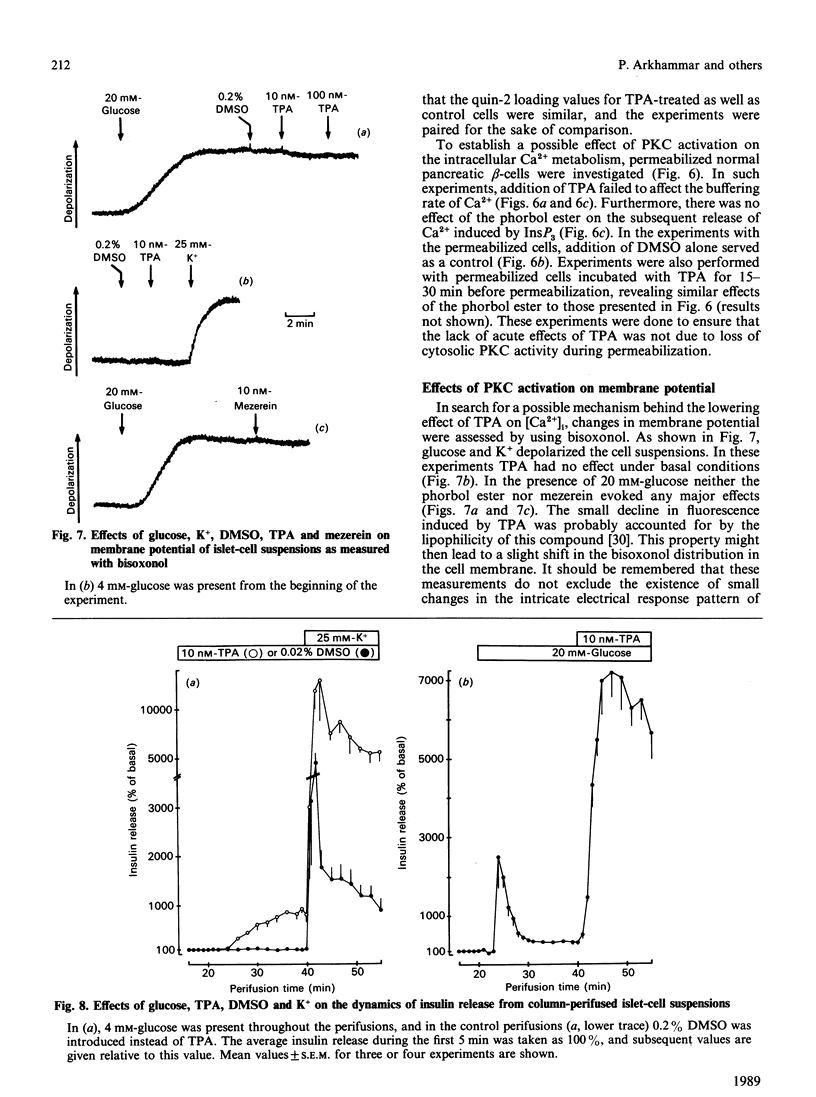
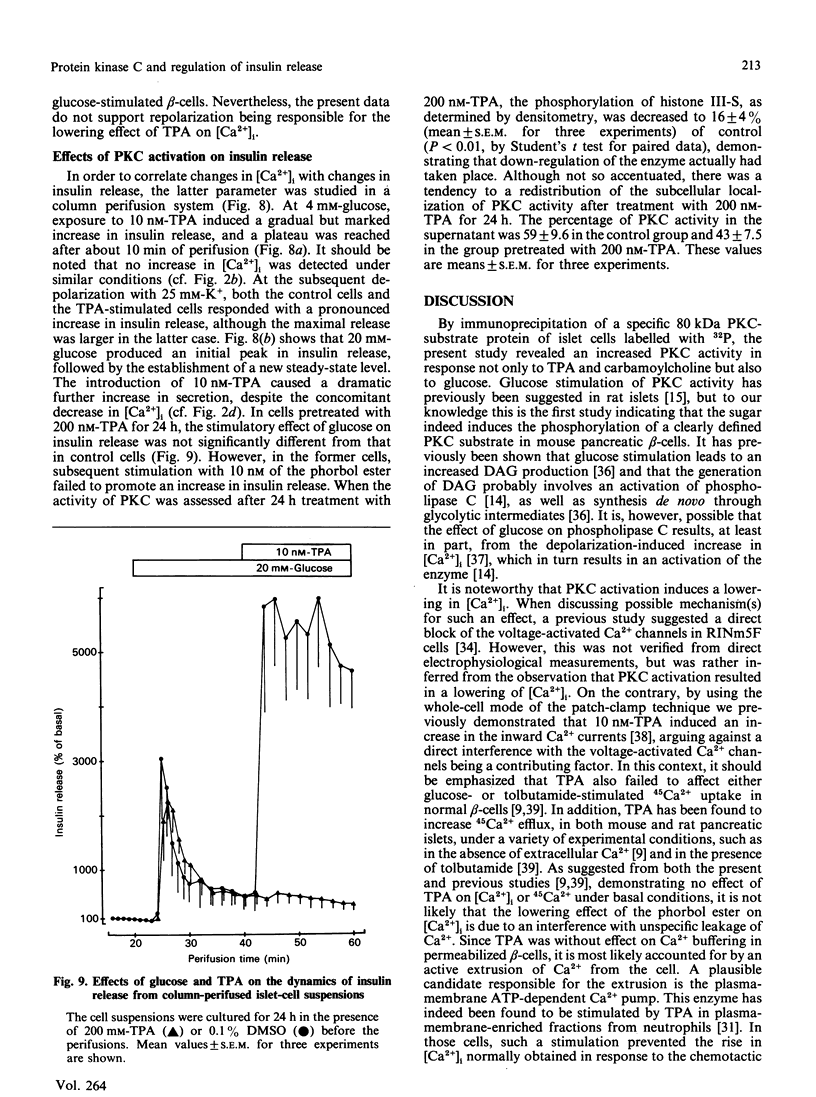
Effects of protein kinase C (PKC) activation on the insulin-secretory process were investigated, by using beta-cell-rich suspensions obtained from pancreatic islets of obese-hyperglycaemic mice. The phorbol ester 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA), which is known to activate PKC directly, the muscarinic-receptor agonist carbamoylcholine and high glucose concentration enhanced the phosphorylation of a specific 80 kDa PKC substrate in the beta-cells. At a non-stimulatory glucose concentration, 10 nM-TPA increased insulin release, although there were no changes in either the cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) or membrane potential, as measured with the fluorescent indicators quin-2 and bisoxonol respectively. At a stimulatory glucose concentration TPA caused a lowering in [Ca2+]i, whereas membrane potential was unaffected. Despite the decrease in [Ca2+]i, there was a large stimulation of insulin release. Addition of TPA lowered [Ca2+]i also in beta-cells stimulated by tolbutamide or high K+, although to a lesser extent than in those stimulated by glucose. There was no effect of TPA on either Ca2+ buffering or the ability of Ins(1,4,5)P3 to release Ca2+ in permeabilized beta-cells. However, the phorbol ester inhibited the rise in [Ca2+]i in response to carbamoylcholine, which stimulates the formation of InsP3, in intact beta-cells. Down-regulation of PKC influenced neither glucose-induced insulin release nor the increase in [Ca2+]i. Hence, although PKC activation is of no major importance in glucose-stimulated insulin release, this enzyme can serve as a modulator of the glucose-induced insulin-secretory response. Such a modulation involves mechanisms promoting both amplification of the secretory response and lowering of [Ca2+]i.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert K. A., Walaas S. I., Wang J. K., Greengard P. Widespread occurrence of "87 kDa," a major specific substrate for protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2822–2826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arkhammar P., Berggren P. O., Rorsman P. Direct evidence for opposite effects of D-glucose and D-glyceraldehyde on cytoplasmic pH of mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Biosci Rep. 1986 Apr;6(4):355–361. doi: 10.1007/BF01116422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arkhammar P., Nilsson T., Berggren P. O. Stimulation of insulin release by the phorbol ester 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate in the clonal cell line RINm5F despite a lowering of the free cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jul 11;887(2):236–241. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arkhammar P., Nilsson T., Rorsman P., Berggren P. O. Inhibition of ATP-regulated K+ channels precedes depolarization-induced increase in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration in pancreatic beta-cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5448–5454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrowman M. M., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Potentiation and inhibition of secretion from neutrophils by phorbol ester. FEBS Lett. 1986 May 26;201(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80586-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best L., Malaisse W. J. Phospholipids and islet function. Diabetologia. 1983 Oct;25(4):299–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00253189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biden T. J., Peter-Riesch B., Schlegel W., Wollheim C. B. Ca2+-mediated generation of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate and inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate in pancreatic islets. Studies with K+, glucose, and carbamylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3567–3571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biden T. J., Vallar L., Wollheim C. B. Regulation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate metabolism in insulin-secreting RINm5F cells. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 15;251(2):435–440. doi: 10.1042/bj2510435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocklehurst K. W., Hutton J. C. Involvement of protein kinase C in the phosphorylation of an insulin-granule membrane protein. Biochem J. 1984 May 15;220(1):283–290. doi: 10.1042/bj2200283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Virgilio F., Pozzan T., Wollheim C. B., Vicentini L. M., Meldolesi J. Tumor promoter phorbol myristate acetate inhibits Ca2+ influx through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in two secretory cell lines, PC12 and RINm5F. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):32–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond A. H. Bidirectional control of cytosolic free calcium by thyrotropin-releasing hormone in pituitary cells. 1985 Jun 27-Jul 3Nature. 315(6022):752–755. doi: 10.1038/315752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop M. E., Larkins R. G. Glucose-induced phospholipid-dependent protein phosphorylation in neonatal rat islets. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Aug 1;248(2):562–569. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90509-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison D. E., Ashcroft S. J., Christie M. R., Lord J. M. Protein phosphorylation in the pancreatic B-cell. Experientia. 1984 Oct 15;40(10):1075–1084. doi: 10.1007/BF01971454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B. Studies in obese-hyperglycemic mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Oct 8;131(1):541–558. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb34819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B. The significance of calcium for glucose stimulation of insulin release. Endocrinology. 1975 Aug;97(2):392–398. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-2-392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Bozem M., Schmeer W., Nenquin M. Distinct mechanisms for two amplification systems of insulin release. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):393–399. doi: 10.1042/bj2460393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hii C. S., Jones P. M., Persaud S. J., Howell S. L. A re-assessment of the role of protein kinase C in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):489–493. doi: 10.1042/bj2460489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. J., Ashcroft S. J. Effects of a phorbol ester and clomiphene on protein phosphorylation and insulin secretion in rat pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 1;249(3):825–830. doi: 10.1042/bj2490825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. J., Christie M. R., Ashcroft S. J. Potentiators of insulin secretion modulate Ca2+ sensitivity in rat pancreatic islets. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 Apr;50(3):231–236. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C., Peshavaria M., Brocklehurst K. W. Phorbol ester stimulation of insulin release and secretory-granule protein phosphorylation in a transplantable rat insulinoma. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 1;224(2):483–490. doi: 10.1042/bj2240483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. M., Stutchfield J., Howell S. L. Effects of Ca2+ and a phorbol ester on insulin secretion from islets of Langerhans permeabilised by high-voltage discharge. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 21;191(1):102–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanatsuna T., Lernmark A., Rubenstein A. H., Steiner D. F. Block in insulin release from column-perifused pancreatic beta-cells induced by islet cell surface antibodies and complement. Diabetes. 1981 Mar;30(3):231–234. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.3.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Baker P. F. The phorbol ester TPA increases the affinity of exocytosis for calcium in 'leaky' adrenal medullary cells. FEBS Lett. 1983 Aug 22;160(1-2):98–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80944-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Sugden D., Baker P. F. Evidence implicating protein kinase C in exocytosis from electropermeabilized bovine chromaffin cells. J Membr Biol. 1988 Aug;104(1):21–34. doi: 10.1007/BF01871899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagast H., Pozzan T., Waldvogel F. A., Lew P. D. Phorbol myristate acetate stimulates ATP-dependent calcium transport by the plasma membrane of neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):878–883. doi: 10.1172/JCI111284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernmark A. The preparation of, and studies on, free cell suspensions from mouse pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 1974 Oct;10(5):431–438. doi: 10.1007/BF01221634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. M., Ashcroft S. J. Identification and characterization of Ca2+-phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in rat islets and hamster beta-cells. Biochem J. 1984 Apr 15;219(2):547–551. doi: 10.1042/bj2190547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre D. E., McNicol A., Drummond A. H. Tumour-promoting phorbol esters inhibit agonist-induced phosphatidate formation and Ca2+ flux in human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 28;180(2):160–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Sener A., Herchuelz A., Carpinelli A. R., Poloczek P., Winand J., Castagna M. Insulinotropic effect of the tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate in rat pancreatic islets. Cancer Res. 1980 Oct;40(10):3827–3831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A. Perspectives in diabetes. Is protein kinase C required for physiologic insulin release? Diabetes. 1988 Jan;37(1):3–7. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.1.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake R., Tanaka Y., Tsuda T., Kaibuchi K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Activation of protein kinase C by non-phorbol tumor promoter, mezerein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jun 15;121(2):649–656. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Arkhammar P., Hallberg A., Hellman B., Berggren P. O. Characterization of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release in pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 1;248(2):329–336. doi: 10.1042/bj2480329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orellana S. A., Solski P. A., Brown J. H. Phorbol ester inhibits phosphoinositide hydrolysis and calcium mobilization in cultured astrocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5236–5239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdew G. H., Schaup H. W., Selivonchick D. P. The use of a zwitterionic detergent in two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of trout liver microsomes. Anal Biochem. 1983 Dec;135(2):453–455. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90711-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter-Riesch B., Fathi M., Schlegel W., Wollheim C. B. Glucose and carbachol generate 1,2-diacylglycerols by different mechanisms in pancreatic islets. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1154–1161. doi: 10.1172/JCI113430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickard J. E., Sheterline P. Evidence that phorbol ester interferes with stimulated Ca2+ redistribution by activating Ca2+ efflux in neutrophil leucocytes. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 1;231(3):623–628. doi: 10.1042/bj2310623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Montecucco C., Hesketh T. R., Tsien R. Y. Lymphocyte membrane potential assessed with fluorescent probes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980;595(1):15–30. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Sanchez A., Hallam T. J. Diacylglycerol and phorbol ester stimulate secretion without raising cytoplasmic free calcium in human platelets. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):317–319. doi: 10.1038/305317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Abrahamsson H., Gylfe E., Hellman B. Dual effects of glucose on the cytosolic Ca2+ activity of mouse pancreatic beta-cells. FEBS Lett. 1984 May 7;170(1):196–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81398-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Arkhammar P., Berggren P. O. Voltage-activated Na+ currents and their suppression by phorbol ester in clonal insulin-producing RINm5F cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Dec;251(6 Pt 1):C912–C919. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.6.C912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):67–69. doi: 10.1038/306067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamagawa T., Niki H., Niki A. Insulin release independent of a rise in cytosolic free Ca2+ by forskolin and phorbol ester. FEBS Lett. 1985 Apr 22;183(2):430–432. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80825-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanigawa K., Kuzuya H., Imura H., Taniguchi H., Baba S., Takai Y., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in rat pancreas islets of langerhans. Its possible role in glucose-induced insulin release. FEBS Lett. 1982 Feb 22;138(2):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80436-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thams P., Capito K., Hedeskov C. J. Endogenous substrate proteins for Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent, Ca2+-phospholipid-dependent and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases in mouse pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 1;221(1):247–253. doi: 10.1042/bj2210247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M. A., Steffes M. W., Estensen R. D. Phorbol myristate acetate: effect of a tumor promoter on insulin release from isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Endocrinology. 1978 Mar;102(3):706–711. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-3-706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Dunne M. J., Peter-Riesch B., Bruzzone R., Pozzan T., Petersen O. H. Activators of protein kinase C depolarize insulin-secreting cells by closing K+ channels. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2443–2449. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03090.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawalich W., Brown C., Rasmussen H. Insulin secretion: combined effects of phorbol ester and A23187. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 16;117(2):448–455. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91221-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



