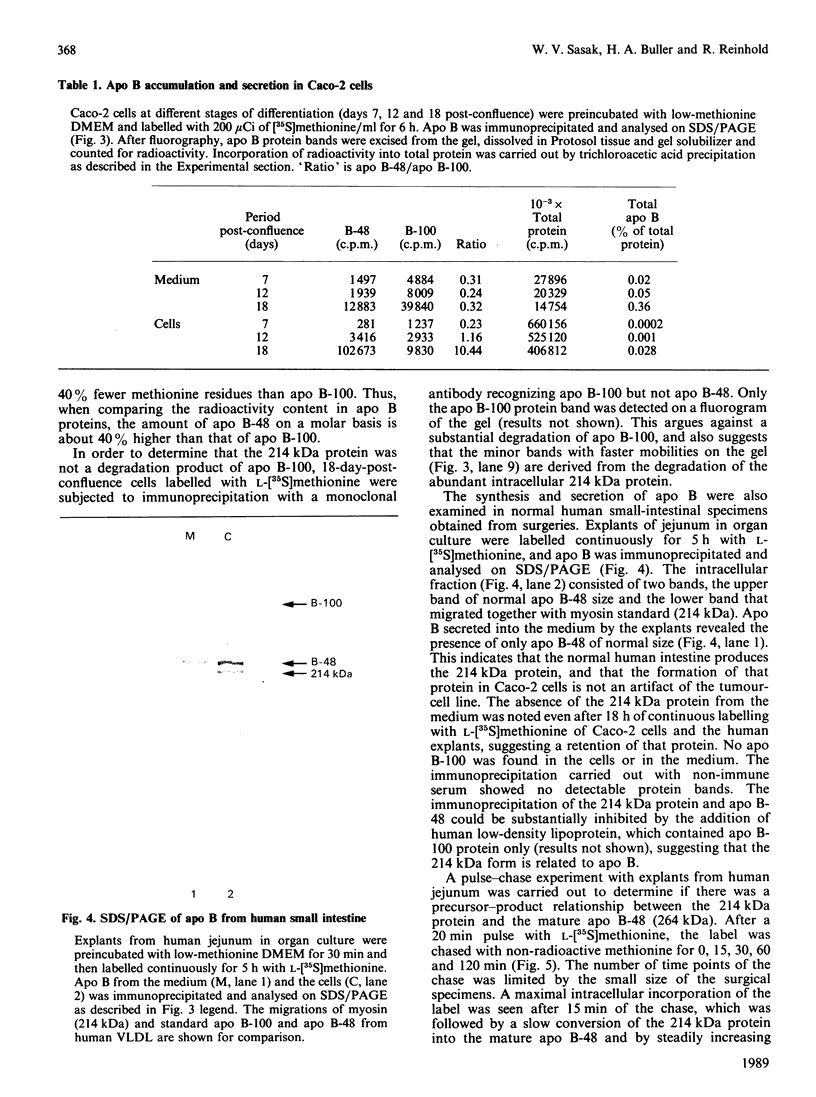
Abstract
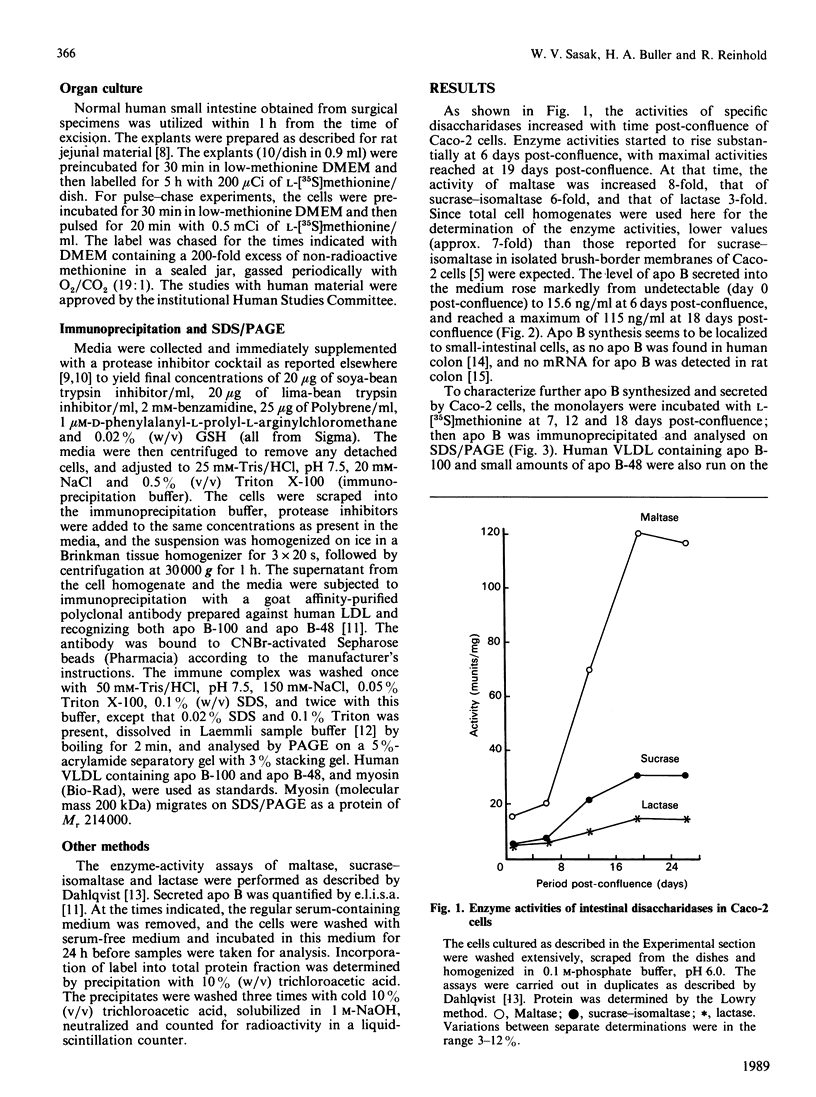
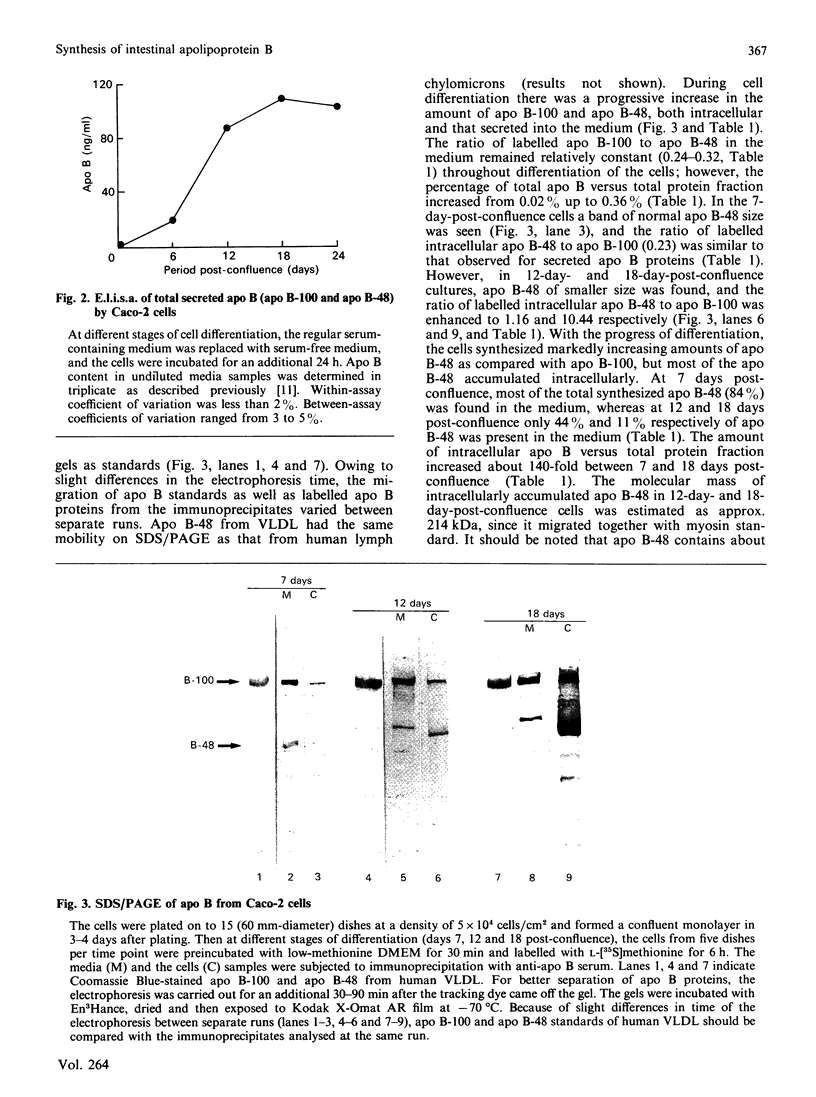
The synthesis and secretion of apolipoprotein B (apo B) was studied in a human colon carcinoma (Caco-2) cell line and in explants from normal human intestine. In Caco-2 cells, the specific activity of the intestinal disaccharidases maltase, sucrase-isomaltase and lactase was enhanced 8-, 6- and 3-fold respectively, at 19 days post-confluence as compared with 1-day-post-confluence cultures. The level of apo B secreted into the medium increased from undetectable in the cells just reaching confluency, to 115 ng/ml at 18 days post-confluence. The presence of apo B-100 and apo B-48 with mobilities on SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis corresponding to those of human very-low-density lipoproteins and lymph chylomicrons, respectively, was detected in the media from 7-, 12- and 18-days-post-confluence cells. These two apo B proteins were also found intracellularly in 7-day-post-confluence cultures. However, more differentiated cells (12 and 18 days post-confluence) accumulated large amount of a 214 kDa protein intracellularly. Apo B-related 214 kDa protein was also synthesized by normal human intestinal explants. A pulse-chase experiment with explants from normal human jejunum showed a slow intracellular conversion of the 214 kDa protein into the size of mature apo B-48 (264 kDa), concomitant with increasing amounts of mature apo B-48 in the medium, suggesting a precursor-product relationship. Despite large intracellular quantities, the 214 kDa protein from the normal human tissue and Caco-2 cells was absent from the medium. No apo B-100 synthesis was detected in the human explants. These findings may help in our understanding of cholesterol and lipid metabolism in health and in some disorders characterized by the inability to secrete apo B-containing lipoproteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouma M. E., Beucler I., Aggerbeck L. P., Infante R., Schmitz J. Hypobetalipoproteinemia with accumulation of an apoprotein B-like protein in intestinal cells. Immunoenzymatic and biochemical characterization of seven cases of Anderson's disease. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):398–410. doi: 10.1172/JCI112590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büller H. A., Montgomery R. K., Sasak W. V., Grand R. J. Biosynthesis, glycosylation, and intracellular transport of intestinal lactase-phlorizin hydrolase in rat. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17206–17211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardin A. D., Witt K. R., Chao J., Margolius H. S., Donaldson V. H., Jackson R. L. Degradation of apolipoprotein B-100 of human plasma low density lipoproteins by tissue and plasma kallikreins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8522–8528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. H., Habib G., Yang C. Y., Gu Z. W., Lee B. R., Weng S. A., Silberman S. R., Cai S. J., Deslypere J. P., Rosseneu M. Apolipoprotein B-48 is the product of a messenger RNA with an organ-specific in-frame stop codon. Science. 1987 Oct 16;238(4825):363–366. doi: 10.1126/science.3659919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demmer L. A., Levin M. S., Elovson J., Reuben M. A., Lusis A. J., Gordon J. I. Tissue-specific expression and developmental regulation of the rat apolipoprotein B gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8102–8106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field F. J., Albright E., Mathur S. N. Regulation of cholesterol esterification by micellar cholesterol in CaCo-2 cells. J Lipid Res. 1987 Sep;28(9):1057–1066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman R. M., Kilgore A., Khorana J. Chylomicron apoprotein localization within rat intestinal epithelium: studies of normal and impaired lipid absorption. J Lipid Res. 1978 Feb;19(2):260–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman R. M., Rogers M., Glickman J. N. Apolipoprotein B synthesis by human liver and intestine in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5296–5300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauri H. P., Sterchi E. E., Bienz D., Fransen J. A., Marxer A. Expression and intracellular transport of microvillus membrane hydrolases in human intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):838–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes T. E., Ordovas J. M., Schaefer E. J. Regulation of intestinal apolipoprotein B synthesis and secretion by Caco-2 cells. Lack of fatty acid effects and control by intracellular calcium ion. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3425–3431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes T. E., Sasak W. V., Ordovas J. M., Forte T. M., Lamon-Fava S., Schaefer E. J. A novel cell line (Caco-2) for the study of intestinal lipoprotein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3762–3767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P., Hardman D. A., Paulus H. E. Heterogeneity of apolipoprotein B: isolation of a new species from human chylomicrons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2465–2469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. W., Lackner K. J., Hospattankar A. V., Anchors J. M., Sakaguchi A. Y., Naylor S. L., Brewer H. B., Jr Human apolipoprotein B-100: cloning, analysis of liver mRNA, and assignment of the gene to chromosome 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8340–8344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Marcel Y., Deckelbaum R. J., Milne R., Lepage G., Seidman E., Bendayan M., Roy C. C. Intestinal apoB synthesis, lipids, and lipoproteins in chylomicron retention disease. J Lipid Res. 1987 Nov;28(11):1263–1274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naim H. Y., Sterchi E. E., Lentze M. J. Structure, biosynthesis, and glycosylation of human small intestinal maltase-glucoamylase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19709–19717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogier-Denis E., Codogno P., Chantret I., Trugnan G. The processing of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides in HT-29 cells is a function of their state of enterocytic differentiation. An accumulation of Man9,8-GlcNAc2-Asn species is indicative of an impaired N-glycan trimming in undifferentiated cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6031–6037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordovas J. M., Peterson J. P., Santaniello P., Cohn J. S., Wilson P. W., Schaefer E. J. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for human plasma apolipoprotein B. J Lipid Res. 1987 Oct;28(10):1216–1224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell L. M., Wallis S. C., Pease R. J., Edwards Y. H., Knott T. J., Scott J. A novel form of tissue-specific RNA processing produces apolipoprotein-B48 in intestine. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90510-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber M. G., Kayden H. J., Rindler M. J. Polarized secretion of newly synthesized lipoproteins by the Caco-2 human intestinal cell line. J Lipid Res. 1987 Nov;28(11):1350–1363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trugnan G., Rousset M., Chantret I., Barbat A., Zweibaum A. The posttranslational processing of sucrase-isomaltase in HT-29 cells is a function of their state of enterocytic differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1987 May;104(5):1199–1205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. G., Bertics S. J., Curtiss L. K., Witztum J. L. Characterization of an abnormal species of apolipoprotein B, apolipoprotein B-37, associated with familial hypobetalipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1831–1841. doi: 10.1172/JCI113025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]