Abstract
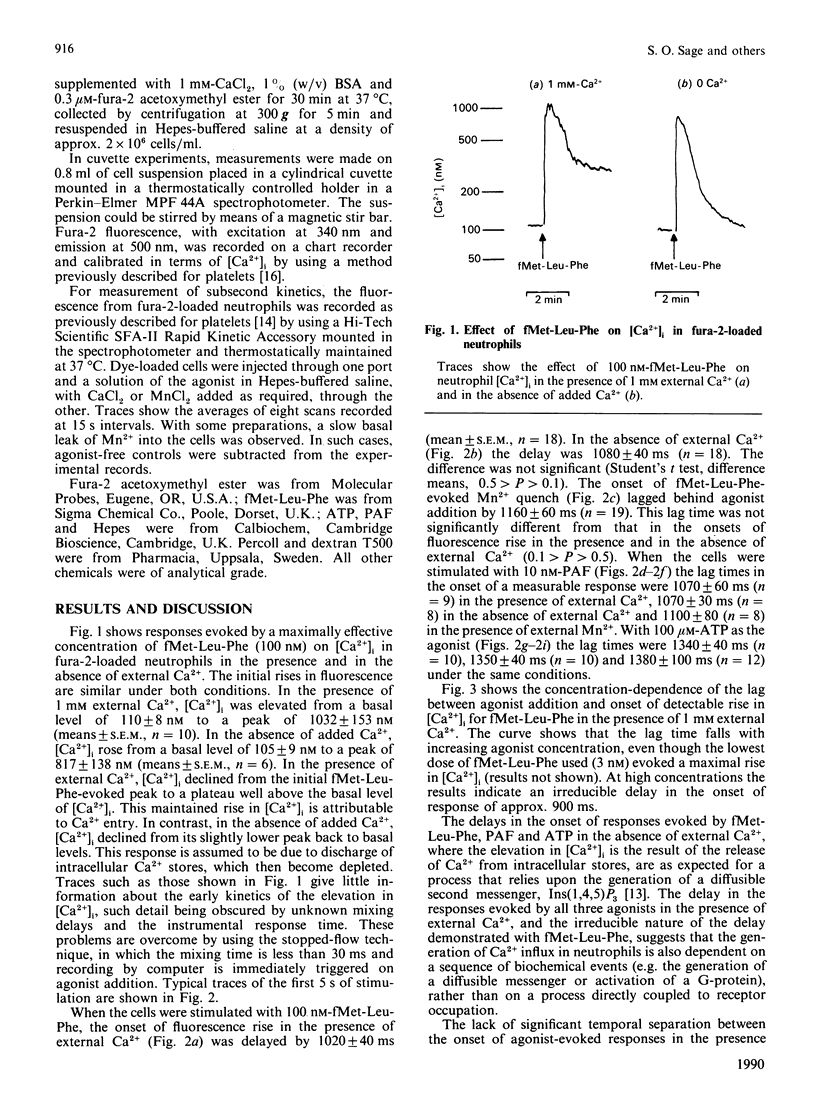
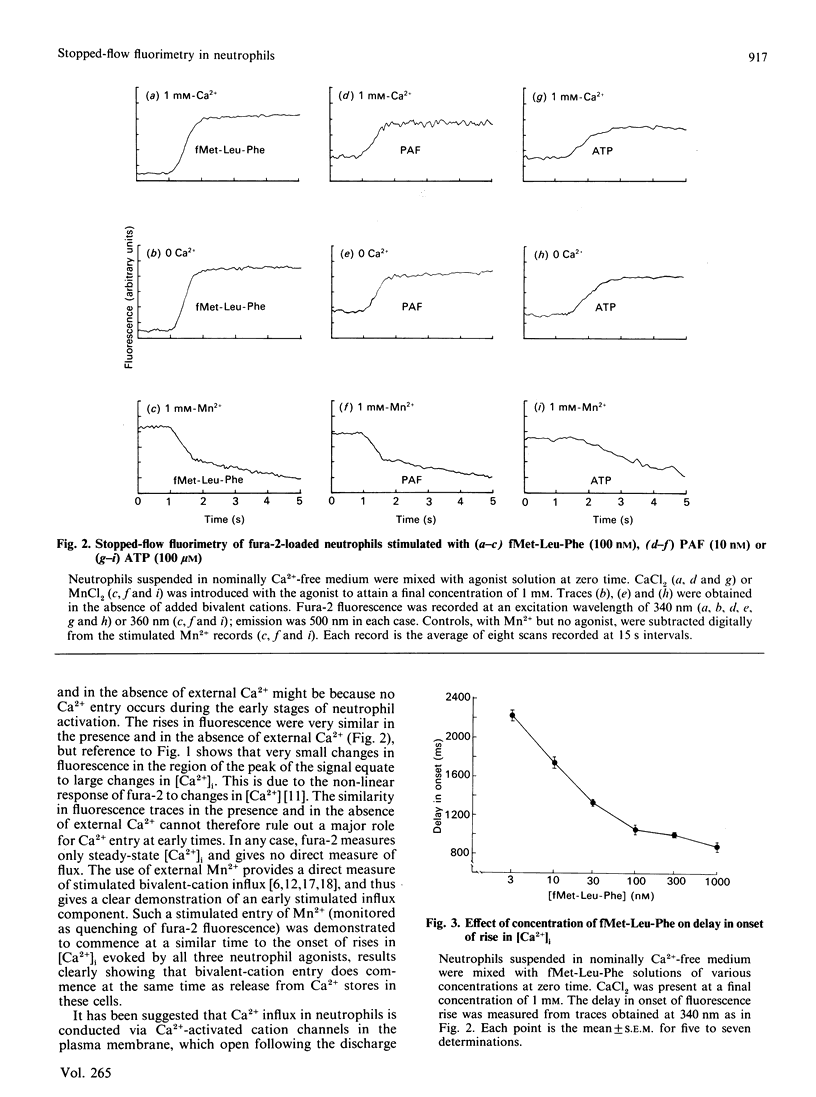
The initial kinetics of agonist-evoked rises in the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration [Ca2+]i were investigated in fura-2-loaded human neutrophils by stopped-flow fluorimetry. The rises in [Ca2+]i evoked by chemotactic peptide (fMet-Leu-Phe), platelet-activating factor and ADP all lagged behind agonist addition by 1-1.3 s. Lag times were not significantly different in the presence and in the absence of external Ca2+. Stimulation of the cells in the presence of extracellular Mn2+ resulted in a quench of fluorescence with a similar lag time to [Ca2+]i rise. The delay in onset of the rise in [Ca2+]i evoked by fMet-Leu-Phe was dependent on concentration, becoming longer at lower concentrations of agonist. These results indicate that both the agonist-evoked discharge of the intracellular Ca2+ stores and the generation of bivalent-cation influx lag behind agonist-receptor binding in neutrophils. Both pathways thus appear to be mediated by indirect mechanisms, rather than by a directly coupled process such as a receptor-operated channel. The temporal coincidence of the onset of store discharge with the commencement of bivalent-cation influx suggests that the two events may be causally linked.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson T., Dahlgren C., Pozzan T., Stendahl O., Lew P. D. Characterization of fMet-Leu-Phe receptor-mediated Ca2+ influx across the plasma membrane of human neutrophils. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;30(5):437–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallam T. J., Jacob R., Merritt J. E. Influx of bivalent cations can be independent of receptor stimulation in human endothelial cells. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 1;259(1):125–129. doi: 10.1042/bj2590125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korchak H. M., Rutherford L. E., Weissmann G. Stimulus response coupling in the human neutrophil. I. Kinetic analysis of changes in calcium permeability. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4070–4075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew P. D., Monod A., Waldvogel F. A., Pozzan T. Role of cytosolic free calcium and phospholipase C in leukotriene-B4-stimulated secretion in human neutrophils. Comparison with the chemotactic peptide formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jan 2;162(1):161–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10556.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Jacob R., Hallam T. J. Use of manganese to discriminate between calcium influx and mobilization from internal stores in stimulated human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1522–1527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Rink T. J. Rapid increases in cytosolic free calcium in response to muscarinic stimulation of rat parotid acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):4958–4960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmith P. E., Grinstein S. Are Ca2+ channels in neutrophils activated by a rise in cytosolic free Ca2+? FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 31;221(1):95–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80359-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock W. K., Rink T. J., Irvine R. F. Liberation of [3H]arachidonic acid and changes in cytosolic free calcium in fura-2-loaded human platelets stimulated by ionomycin and collagen. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):869–877. doi: 10.1042/bj2350869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzan T., Lew D. P., Wollheim C. B., Tsien R. Y. Is cytosolic ionized calcium regulating neutrophil activation? Science. 1983 Sep 30;221(4618):1413–1415. doi: 10.1126/science.6310757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Wollheim C. B., Lew P. D. Ca2+ homeostasis in permeabilized human neutrophils. Characterization of Ca2+-sequestering pools and the action of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13777–13782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage S. O., Merritt J. E., Hallam T. J., Rink T. J. Receptor-mediated calcium entry in fura-2-loaded human platelets stimulated with ADP and thrombin. Dual-wavelengths studies with Mn2+. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 15;258(3):923–926. doi: 10.1042/bj2580923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage S. O., Reast R., Rink T. J. ADP evokes biphasic Ca2+ influx in fura-2-loaded human platelets. Evidence for Ca2+ entry regulated by the intracellular Ca2+ store. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 1;265(3):675–680. doi: 10.1042/bj2650675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage S. O., Rink T. J. The kinetics of changes in intracellular calcium concentration in fura-2-loaded human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16364–16369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Tscharner V., Deranleau D. A., Baggiolini M. Calcium fluxes and calcium buffering in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10163–10168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Tscharner V., Prod'hom B., Baggiolini M., Reuter H. Ion channels in human neutrophils activated by a rise in free cytosolic calcium concentration. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):369–372. doi: 10.1038/324369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


