Abstract
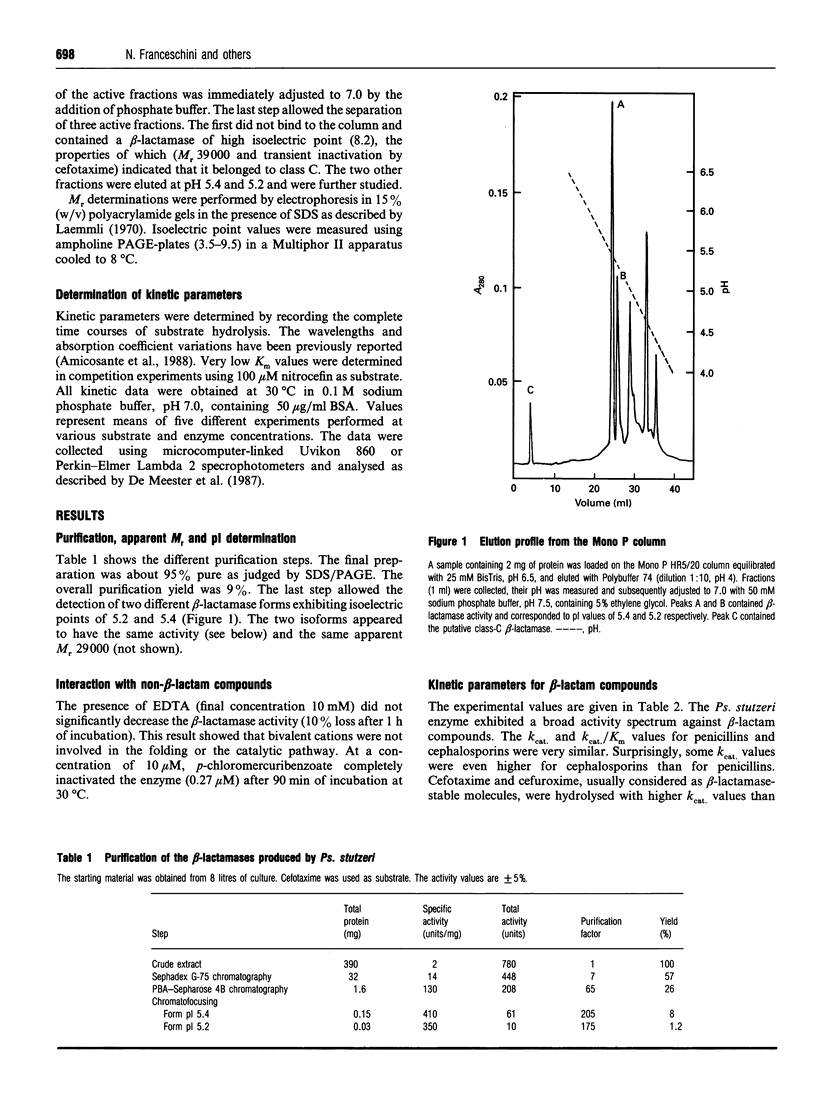
A beta-lactamase produced by Pseudomonas stutzeri was purified to protein homogeneity, and its physicochemical and catalytic properties were determined. Its profile was unusual since, in addition to penicillins, the enzyme hydrolysed second- and third-generation 'beta-lactamase-stable' cephalosporins and monobactams with similar efficiencies. On the basis of the characteristics of the interaction with beta-iodopenicillanic acid, the enzyme could be classified as a class-A beta-lactamase. However, when compared with most class-A beta-lactamases, it exhibited significantly lower kcat./Km values for the compounds usually considered to be the best substrates of these enzymes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P., Coulson A. F., Frère J. M., Ghuysen J. M., Joris B., Forsman M., Levesque R. C., Tiraby G., Waley S. G. A standard numbering scheme for the class A beta-lactamases. Biochem J. 1991 May 15;276(Pt 1):269–270. doi: 10.1042/bj2760269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P. The structure of beta-lactamases. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 May 16;289(1036):321–331. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1980.0049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amicosante G., Franceschini N., Segatore B., Oratore A., Fattorini L., Orefici G., Van Beeumen J., Frere J. M. Characterization of a beta-lactamase produced in Mycobacterium fortuitum D316. Biochem J. 1990 Nov 1;271(3):729–734. doi: 10.1042/bj2710729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amicosante G., Oratore A., Franceschini N., Maccarrone M., Strom R., Galleni M., Frère J. M. Citrobacter diversus ULA-27 beta-lactamases. Improved purification and general properties. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 15;254(3):885–890. doi: 10.1042/bj2540885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boissinot M., Levesque R. C. Nucleotide sequence of the PSE-4 carbenicillinase gene and correlations with the Staphylococcus aureus PC1 beta-lactamase crystal structure. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):1225–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K. Characterization of beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Mar;33(3):259–263. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.3.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K., Freudenberger J. S., Sykes R. B. Interaction of azthreonam and related monobactams with beta-lactamases from gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Sep;22(3):414–420. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright S. J., Waley S. G. Purification of beta-lactamases by affinity chromatography on phenylboronic acid-agarose. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 15;221(2):505–512. doi: 10.1042/bj2210505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Meester F., Joris B., Reckinger G., Bellefroid-Bourguignon C., Frère J. M., Waley S. G. Automated analysis of enzyme inactivation phenomena. Application to beta-lactamases and DD-peptidases. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Jul 15;36(14):2393–2403. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90609-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franceschini N., Amicosante G., Perilli M., Maccarrone M., Oratore A., van Beeumen J., Frère J. M. Proteolytic interconversion and N-terminal sequences of the Citrobacter diversus major beta-lactamases. Biochem J. 1991 May 1;275(Pt 3):629–633. doi: 10.1042/bj2750629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris B., Ledent P., Dideberg O., Fonzé E., Lamotte-Brasseur J., Kelly J. A., Ghuysen J. M., Frère J. M. Comparison of the sequences of class A beta-lactamases and of the secondary structure elements of penicillin-recognizing proteins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Nov;35(11):2294–2301. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.11.2294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Guionie M., Barthélémy M. Properties of three carbenicillin-hydrolysing beta-lactamases (CARB) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: identification of a new enzyme. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Jan;7(1):49–56. doi: 10.1093/jac/7.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matagne A., Joris B., Van Beeumen J., Frère J. M. Ragged N-termini and other variants of class A beta-lactamases analysed by chromatofocusing. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 1;273(Pt 3):503–510. doi: 10.1042/bj2730503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matagne A., Misselyn-Bauduin A. M., Joris B., Erpicum T., Granier B., Frère J. M. The diversity of the catalytic properties of class A beta-lactamases. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 1;265(1):131–146. doi: 10.1042/bj2650131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M., Stanier R. Y., Solánes R. E., Mandel M. Taxonomy of the aerobic pseudomonads: the properties of the Pseudomonas stutzeri group. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Feb;60(2):215–231. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-2-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perilli M., Franceschini N., Segatore B., Amicosante G., Oratore A., Duez C., Joris B., Frère J. M. Cloning and nucleotide sequencing of the gene encoding the beta-lactamase from Citrobacter diversus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Sep 15;67(1):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90448-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sougakoff W., Goussard S., Gerbaud G., Courvalin P. Plasmid-mediated resistance to third-generation cephalosporins caused by point mutations in TEM-type penicillinase genes. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):879–884. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowek J. A., Singer S. B., Ohringer S., Malley M. F., Dougherty T. J., Gougoutas J. Z., Bush K. Substitution of lysine at position 104 or 240 of TEM-1pTZ18R beta-lactamase enhances the effect of serine-164 substitution on hydrolysis or affinity for cephalosporins and the monobactam aztreonam. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 2;30(13):3179–3188. doi: 10.1021/bi00227a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


