Abstract
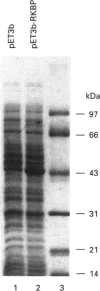
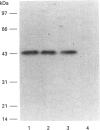
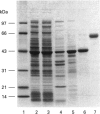
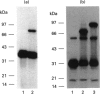
Rat kallikrein-binding protein is a novel serine-proteinase inhibitor that forms a covalent complex with tissue kallikrein. We have purified rat kallikrein-binding protein and cloned the cDNA and the gene encoding rat kallikrein-binding protein [Chao, Chai, Chen, Xiong, Chao, Woodley-Miller, Wang, Lu and Chao (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265, 16394-16401; Chai, Ma, Murray, Chao and Chao (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266, 16029-16036]. In the present study, we have expressed rat kallikrein-binding protein in Escherichia coli with a T7-polymerase/promoter expression system. A high level of expression was detected by an e.l.i.s.a. with an average of 24.2 mg of recombinant rat kallikrein-binding protein per 1 of culture. The recombinant protein appeared as a major protein in a crude extract of Escherichia coli on SDS/PAGE. It showed a molecular mass of 43 kDa and was recognized by polyclonal antibody to the native rat kallikrein-binding protein in Western-blot analysis. The recombinant rat kallikrein-binding protein has been purified to apparent homogeneity by DEAE-Sepharose CL-6B, hydroxyapatite Bio-Gel HPHT and Mono P 5/5 column chromatography. The purified recombinant rat kallikrein-binding protein showed immunological identity with the native rat kallikrein-binding protein purified from rat serum, in a specific e.l.i.s.a. To confirm the fidelity of the expression, the N-terminal ten amino acids of the recombinant rat kallikrein-binding protein were sequenced and were shown to match perfectly with those of the native rat kallikrein-binding protein. The purified recombinant rat kallikrein-binding protein formed SDS- and heat-stable complexes with rat tissue kallikrein (rK1) and T-kininogenase (rK10) in vitro, but not with other enzymes in the rat kallikrein gene family, such as tonin (rK2) and S3 protein (rK9), which indicates enzyme-specific binding. The properties of the recombinant rat kallikrein-binding protein including its size, charge, complex formation with target enzymes and immunological characteristics were compared with those of the native protein. This expression system provides a simple way to obtain a large amount of the biologically active recombinant protein, to study structure-function relationships of the rat kallikrein-binding protein and its interaction with its target enzymes.
Full text
PDF

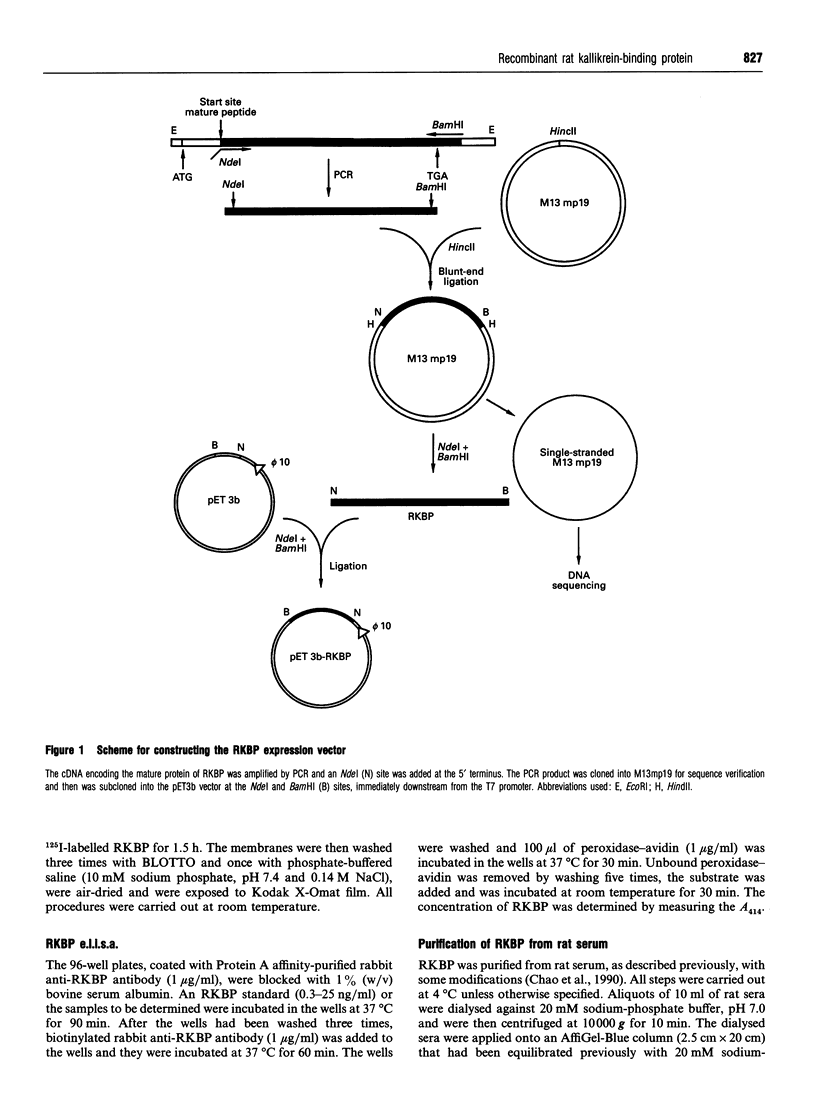

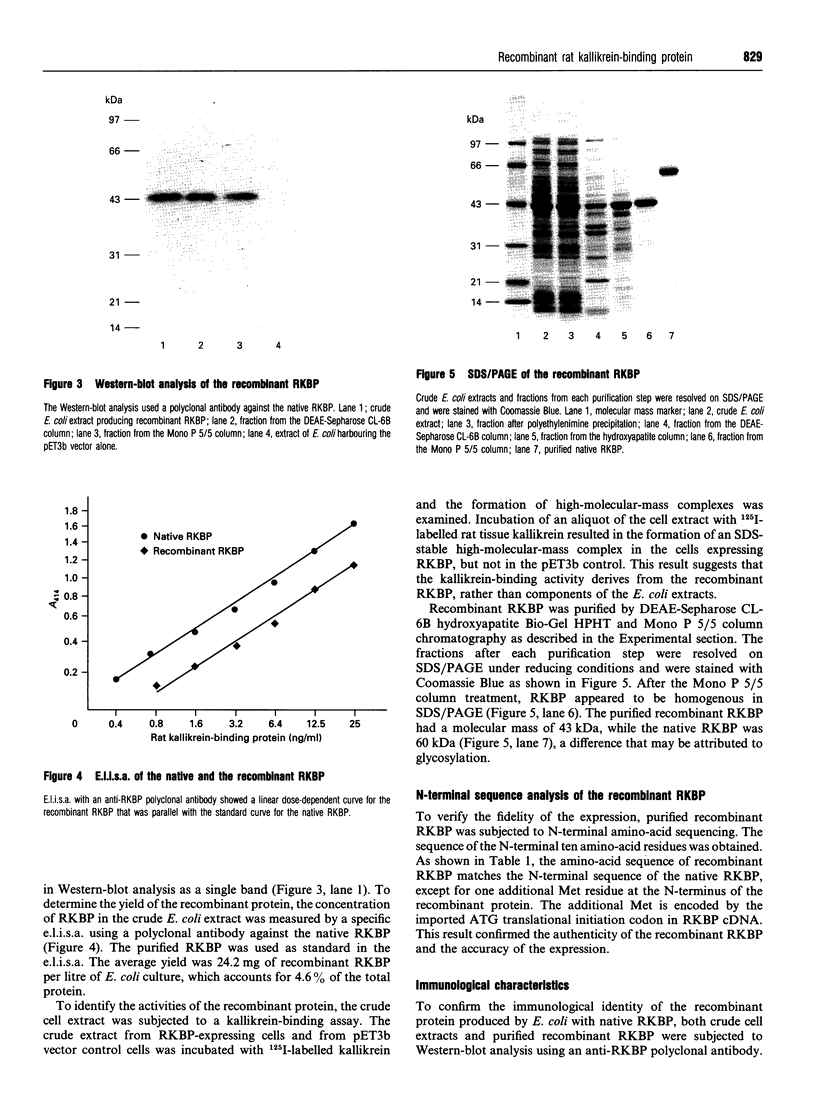



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashley P. L., MacDonald R. J. Tissue-specific expression of kallikrein-related genes in the rat. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 13;24(17):4520–4527. doi: 10.1021/bi00338a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlas A., Gao X. X., Greenbaum L. M. Isolation of a thiol-activated T-kininogenase from the rat submandibular gland. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 29;218(2):266–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg T., Bradshaw R. A., Carretero O. A., Chao J., Chao L., Clements J. A., Fahnestock M., Fritz H., Gauthier F., MacDonald R. J. A common nomenclature for members of the tissue (glandular) kallikrein gene families. Agents Actions Suppl. 1992;38(Pt 1):19–25. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7321-5_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry S. A., Seelig S. Substantial induction of a new serum protein by growth hormone: physiochemical and physiological characterization. Endocrinology. 1984 Sep;115(3):1164–1170. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-3-1164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Chen Z., Bartels K., Kutzbach C., Schmidt-Kastner G., Bartunik H. Refined 2 A X-ray crystal structure of porcine pancreatic kallikrein A, a specific trypsin-like serine proteinase. Crystallization, structure determination, crystallographic refinement, structure and its comparison with bovine trypsin. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 25;164(2):237–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chagas J. R., Hirata I. Y., Juliano M. A., Xiong W., Wang C., Chao J., Juliano L., Prado E. S. Substrate specificities of tissue kallikrein and T-kininogenase: their possible role in kininogen processing. Biochemistry. 1992 Jun 2;31(21):4969–4974. doi: 10.1021/bi00136a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chai K. X., Ma J. X., Murray S. R., Chao J., Chao L. Molecular cloning and analysis of the rat kallikrein-binding protein gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):16029–16036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao J., Chai K. X., Chen L. M., Xiong W., Chao S., Woodley-Miller C., Wang L. X., Lu H. S., Chao L. Tissue kallikrein-binding protein is a serpin. I. Purification, characterization, and distribution in normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16394–16401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao J., Chao L. A major difference of kallikrein-binding protein in spontaneously hypertensive versus normotensive rats. J Hypertens. 1988 Jul;6(7):551–557. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198807000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao J., Chao L., Tillman D. M., Woodley C. M., Margolius H. S. Characterization of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies to human tissue kallikrein. Hypertension. 1985 Nov-Dec;7(6 Pt 1):931–937. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.7.6.931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao J., Chen L. M., Chai K. X., Chao L. Expression of kallikrein-binding protein and alpha 1-antitrypsin genes in response to sex hormones, growth, inflammation and hypertension. Agents Actions Suppl. 1992;38(Pt 1):174–181. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7321-5_23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao J., Tillman D. M., Wang M. Y., Margolius H. S., Chao L. Identification of a new tissue-kallikrein-binding protein. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 15;239(2):325–331. doi: 10.1042/bj2390325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao S., Chao L., Chao J. Enhanced specificity in immunoscreening of expression cDNA clones using radiolabeled antigen overlay. Biotechniques. 1989 Jan;7(1):68–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. M., Chao L., Mayfield R. K., Chao J. Differential interactions of human kallikrein-binding protein and alpha 1-antitrypsin with human tissue kallikrein. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 1;267(1):79–84. doi: 10.1042/bj2670079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Margolius H. S. Kinins stimulate net chloride secretion by the rat colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Apr;75(4):587–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09178.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmoujahed A., Gutman N., Brillard M., Gauthier F. Substrate specificity of two kallikrein family gene products isolated from the rat submaxillary gland. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 4;265(1-2):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80903-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Enjyoji K., Miyata T., Hayashi I., Oh-ishi S., Iwanaga S. Demonstration of arginyl-bradykinin moiety in rat HMW kininogen: direct evidence for liberation of bradykinin by rat glandular kallikreins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 28;127(1):289–295. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80157-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam G., Le Cam A. Synthesis of the growth hormone-regulated rat liver anti-protease GHR-P63 is inhibited by acute inflammation. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 1;210(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81286-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H. S., Lin F. K., Chao L., Chao J. Human urinary kallikrein. Complete amino acid sequence and sites of glycosylation. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1989 Apr;33(4):237–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1989.tb01277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J. X., Chao J., Chao L. Molecular cloning and characterization of rKlk10, a cDNA encoding T-kininogenase from rat submandibular gland and kidney. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 10;31(44):10922–10928. doi: 10.1021/bi00159a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau T., Brillard-Bourdet M., Bouhnik J., Gauthier F. Protein products of the rat kallikrein gene family. Substrate specificities of kallikrein rK2 (tonin) and kallikrein rK9. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):10045–10051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray S. R., Chao J., Lin F. K., Chao L. Kallikrein multigene families and the regulation of their expression. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1990;15 (Suppl 6):S7–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pages G., Rouayrenc J. F., Le Cam G., Mariller M., Le Cam A. Molecular characterization of three rat liver serine-protease inhibitors affected by inflammation and hypophysectomy. Protein and mRNA analysis and cDNA cloning. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jun 20;190(2):385–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter M. Kallikreins (kininogenases)--a group of serine proteases with bioregulatory actions. Pharmacol Rev. 1979 Mar;31(1):1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzenberg S. J., Yoon J. B., Sharp H. L., Seelig S. Homologous rat hepatic protease inhibitor genes show divergent functional responses to inflammation. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 1):C413–C419. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.2.C413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamoto K., Chao J., Margolius H. S. The radioimmunoassay of human urinary kallikrein and comparisons with kallikrein activity measurements. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Oct;51(4):840–848. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-4-840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Tang C. Q., Zhou G. X., Chao L., Chao J. Biochemical characterization and substrate specificity of rat prostate kallikrein (S3): comparison with tissue kallikrein, tonin and T-kininogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jun 24;1121(3):309–316. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(92)90162-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wines D. R., Brady J. M., Southard E. M., MacDonald R. J. Evolution of the rat kallikrein gene family: gene conversion leads to functional diversity. J Mol Evol. 1991 Jun;32(6):476–492. doi: 10.1007/BF02102650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong W., Chen L. M., Chao J. Purification and characterization of a kallikrein-like T-kininogenase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2822–2827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J. B., Berry S. A., Seelig S., Towle H. C. An inducible nuclear factor binds to a growth hormone-regulated gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19947–19954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J. B., Towle H. C., Seelig S. Growth hormone induces two mRNA species of the serine protease inhibitor gene family in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4284–4289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou G. X., Chao L., Chao J. Kallistatin: a novel human tissue kallikrein inhibitor. Purification, characterization, and reactive center sequence. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25873–25880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]