Abstract
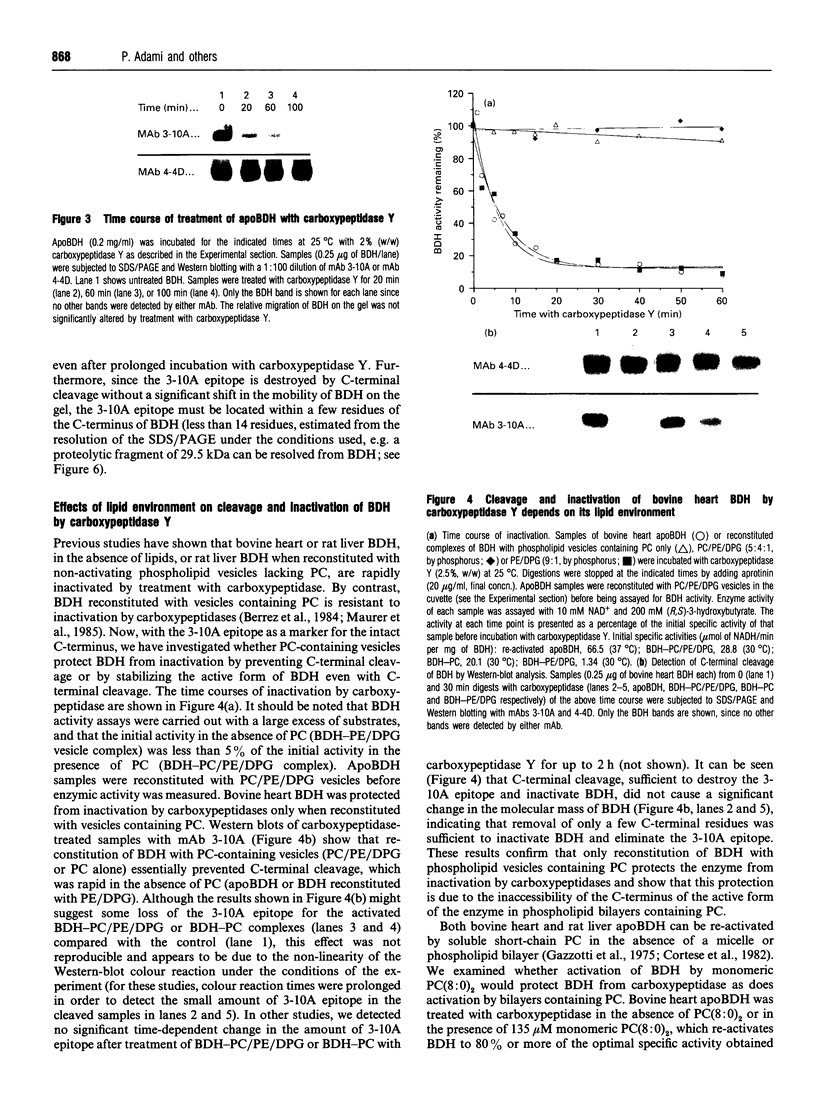
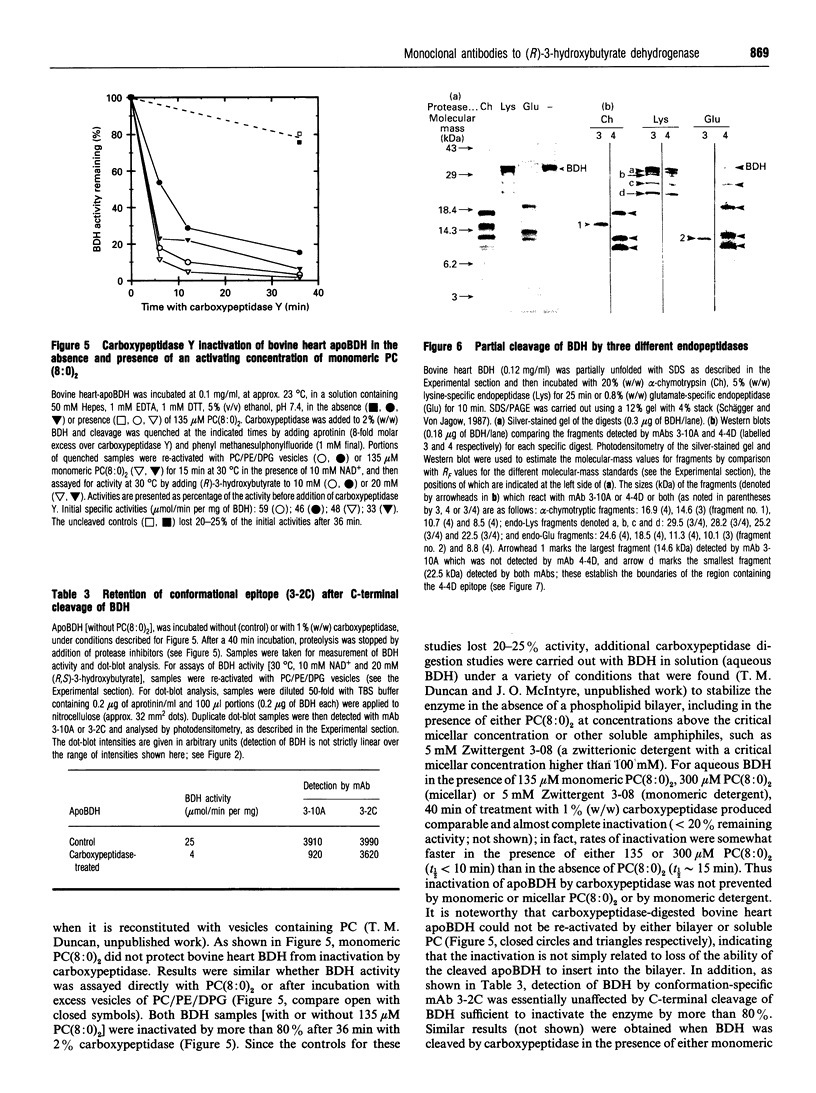
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have been used to study structure-function relationships of (R)-3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase (BDH) (EC 1.1.1.30), a lipid-requiring mitochondrial membrane enzyme with an absolute and specific requirement for phosphatidylcholine (PC) for enzymic activity. The purified enzyme (apoBDH, devoid of phospholipid and thereby inactive) can be re-activated with preformed phospholipid vesicles containing PC or by short-chain soluble PC. Five of six mAbs cross-react with BDH from bovine heart and rat liver, including two mAbs to conformational epitopes. One mAb was found to be specific for the C-terminal sequence of BDH and served to: (1) map endopeptidase cleavage and epitope sites on BDH; and (2) demonstrate that the C-terminus is essential for the activity of BDH. Carboxypeptidase cleavage of only a few (< or = 14) C-terminal amino acids from apoBDH (as detected by the loss of C-terminal epitope for mAb 3-10A) prevents activation by either bilayer or soluble PC. Further, for BDH in bilayers containing PC, the C-terminus is protected from carboxy-peptidase cleavage, whereas in bilayers devoid of PC the C-terminus is cleaved, and subsequent activation by PC is precluded. We conclude that: (1) the C-terminus of BDH is essential for enzymic activity, consistent with the prediction, from primary sequence analysis, that the PC-binding site is in the C-terminal domain of BDH; and (2) the allosteric activation of BDH by PC in bilayers protects the C-terminus from carboxypeptidase cleavage, indicative of a PC-induced conformational change in the enzyme.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berrez J. M., Latruffe N., Gaudemer Y. Limited proteolysis of D-beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase: relationships between phospholipid-protein interactions and catalytical activity. Biochem Int. 1984 May;8(5):697–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock H. O., Fleischer S. Purification of D-beta-hydroxybutyrate apodehydrogenase, a lecithin-requiring enzyme. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:374–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock H., Fleischer S. Preparation of a homogeneous soluble D-beta-hydroxybutyrate apodehydrogenase from mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):5774–5761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy K. G., Jr, LaTart D. B., Osterhoudt H. W. Modifications for SDS-PAGE of proteins. Biotechniques. 1989 Jul-Aug;7(7):692–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill P., Hempel J., Romovacek H., Zhang W. W., Brennan M., Churchill S. Primary structure of rat liver D-beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase from cDNA and protein analyses: a short-chain alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 21;31(15):3793–3799. doi: 10.1021/bi00130a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill P., McIntyre J. O., Eibl H., Fleischer S. Activation of D-beta-hydroxybutyrate apodehydrogenase using molecular species of mixed fatty acyl phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):208–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill P., McIntyre J. O., Vidal J. C., Fleischer S. Basis for decreased D-beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase activity in liver mitochondria from diabetic rats. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jul 15;224(2):659–670. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90253-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W. Peptide mapping in one dimension by limited proteolysis of sodium dodecyl sulfate-solubilized proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:222–229. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortese J. D., McIntyre J. O., Duncan T. M., Fleischer S. Cooperativity in lipid activation of 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase: role of lecithin as an essential allosteric activator. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):3000–3008. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortese J. D., Vidal J. C., Churchill P., McIntyre J. O., Fleischer S. Reactivation of D-beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase with short-chain lecithins: stoichiometry and kinetic mechanism. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 3;21(16):3899–3908. doi: 10.1021/bi00259a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. M. A single-step technique for selecting and cloning hybridomas for monoclonal antibody production. Methods Enzymol. 1986;121:307–322. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)21029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer S., Meissner G., Smigel M., Wood R. Preparation of submitochondrial vesicles using nitrogen decompression. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:292–299. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu C., Carter C. E. Detection of a circulating antigen in human schistosomiasis japonica using a monoclonal antibody. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1990 Apr;42(4):347–351. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1990.42.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzotti P., Bock H., Fleischer S. Interaction of D-beta-hydroxybutyrate apodehydrogenase with phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):5782–5790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabau C., Chang Y. Y., Cronan J. E., Jr Lipid binding by Escherichia coli pyruvate oxidase is disrupted by small alterations of the carboxyl-terminal region. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12510–12519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson Y. A., Deroo P. W., Rosenthal A. F., Bittman R., McIntyre J. O., Bock H. G., Gazzotti P., Fleischer S. The structural specificity of lecithin for activation of purified D-beta-hydroxybutyrate apodehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):117–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Active transport in Escherichia coli: passage to permease. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:279–319. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latruffe N., Berrez J. M., el Kebbaj M. S. Lipid-protein interactions in biomembranes studied through the phospholipid specificity of D-beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase. Biochimie. 1986 Mar;68(3):481–491. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)80015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie M. R., Warner N. L., Mitchell G. F. The binding of murine immunoglobulins to staphylococcal protein A. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1493–1496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks A. R., McIntyre J. O., Duncan T. M., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Fleischer S. Molecular cloning and characterization of (R)-3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase from human heart. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15459–15463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer A., McIntyre J. O., Churchill S., Fleischer S. Phospholipid protection against proteolysis of D-beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, a lecithin-requiring enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1661–1669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre J. O., Bock H. G., Fleischer S. The orientation of D-beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase in the mitochondrial inner membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 2;513(2):255–267. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre J. O., Churchill P., Maurer A., Berenski C. J., Jung C. Y., Fleischer S. Target size of D-beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase. Functional and structural molecular weight based on radiation inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):953–959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre J. O., Holladay L. A., Smigel M., Puett D., Fleischer S. Hydrodynamic properties of D-beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, a lipid-requiring enzyme. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 3;17(20):4169–4177. doi: 10.1021/bi00613a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre J. O., Latruffe N., Brenner S. C., Fleischer S. Comparison of 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase from bovine heart and rat liver mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Apr;262(1):85–98. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre J. O., Wang C. T., Fleischer S. The insertion of purified D-beta-hydroxybutyrate apodehydrogenase into membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5199–5207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Van Keuren M. L. Silver staining methods for polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:230–239. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moradi-Améli M., Godinot C. Availability to monoclonal antibodies of antigenic sites of the alpha and beta subunits in active, denatured or membrane-bound mitochondrial F1-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jan 16;890(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(87)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen N. C., Fleischer S. Mitochondrial D- -hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase. 3. Isolation and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2549–2555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen N. C., Zahler W. L., Fleischer S. Mitochondrial D- -hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase. IV. Kinetic analysis of reaction mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2556–2562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B., Dubois H., Mink R., Trommer W. E., McIntyre J. O., Fleischer S. Coenzyme binding by 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, a lipid-requiring enzyme: lecithin acts as an allosteric modulator to enhance the affinity for coenzyme. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 27;28(13):5354–5366. doi: 10.1021/bi00439a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandermann H., Jr, McIntyre J. O., Fleischer S. Site-site interaction in the phospholipid activation of D-beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6201–6208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanker L. H., Vanderlaan M., Juarez-Salinas H. One-step purification of mouse monoclonal antibodies from ascites fluid by hydroxylapatite chromatography. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Jan 21;76(1):157–169. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90488-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W. W., Churchill P. Purification of D-beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase from rat brain. Biochem Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;68(6):980–983. doi: 10.1139/o90-144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]