Abstract
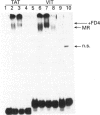
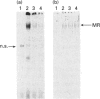
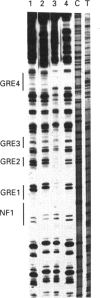
Although the mineralocorticosteroid receptor (MR) belongs to the superfamily of hormone-dependent transcription factors, the molecular mechanism by which it regulates gene expression is poorly understood. Binding of the MR to target gene promoters has never been characterized, and specific mineralocorticosteroid response elements (MREs) remain to be identified. The human MR (hMR) was overexpressed in Sf21 insect cells using the baculovirus system. The high degree of similarity between the glucocorticosteroid receptor (GR) and the MR prompted us to examine the DNA-binding properties of the recombinant MR with glucocorticosteroid-regulated genes. Gel shift mobility assays demonstrated that the recombinant receptor interacted with oligonucleotides containing perfect and imperfect palindromic sequences of GRE. A monoclonal anti-hMR antibody (FD4) induced a supershift of protein-DNA complexes and identified the MR in Western blot analysis. In vitro DNAse I protection assays with the hormone-regulated murine mammary tumour virus promoter showed that recombinant hMR generated four footprints whose limits encompassed the GRE motifs. By means of these two complementary approaches, no difference between the interaction of free, agonist- or antagonist-bound MR and DNA was detected. We provide evidence that hMR functions as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alnemri E. S., Maksymowych A. B., Robertson N. M., Litwack G. Overexpression and characterization of the human mineralocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18072–18081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arriza J. L., Simerly R. B., Swanson L. W., Evans R. M. The neuronal mineralocorticoid receptor as a mediator of glucocorticoid response. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):887–900. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90136-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arriza J. L., Weinberger C., Cerelli G., Glaser T. M., Handelin B. L., Housman D. E., Evans R. M. Cloning of human mineralocorticoid receptor complementary DNA: structural and functional kinship with the glucocorticoid receptor. Science. 1987 Jul 17;237(4812):268–275. doi: 10.1126/science.3037703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly A., Le Page C., Rauch M., Milgrom E. Sequence-specific DNA binding of the progesterone receptor to the uteroglobin gene: effects of hormone, antihormone and receptor phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3235–3241. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04634.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. DNA binding specificity of steroid receptors. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1065–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binart N., Lombes M., Rafestin-Oblin M. E., Baulieu E. E. Characterization of human mineralocorticosteroid receptor expressed in the baculovirus system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10681–10685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Sharp P. A. Human estrogen receptor forms multiple protein-DNA complexes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11238–11243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemeier U., Rogge L., Winnacker E. L., Beato M. Nuclear factor I acts as a transcription factor on the MMTV promoter but competes with steroid hormone receptors for DNA binding. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2233–2239. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07393.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairns C., Gustafsson J. A., Carlstedt-Duke J. Identification of protein contact sites within the glucocorticoid/progestin response element. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Apr;5(4):598–604. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-4-598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato A. C., Weinmann J. Mineralocorticoid regulation of transcription of transfected mouse mammary tumor virus DNA in cultured kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):2119–2125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.2119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalepakis G., Arnemann J., Slater E., Brüller H. J., Gross B., Beato M. Differential gene activation by glucocorticoids and progestins through the hormone regulatory element of mouse mammary tumor virus. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):371–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Wang C., DeLuca H. F., Ross T. K., Shih C. C. Characterization of human androgen receptor overexpressed in the baculovirus system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5946–5950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen K., Estes P. A., Oñate S. A., Beck C. A., DeMarzo A., Altmann M., Lieberman B. A., St John J., Nordeen S. K., Edwards D. P. Characterization and functional properties of the A and B forms of human progesterone receptors synthesized in a baculovirus system. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Nov;5(11):1755–1770. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-11-1755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couette B., Lombes M., Baulieu E. E., Rafestin-Oblin M. E. Aldosterone antagonists destabilize the mineralocorticosteroid receptor. Biochem J. 1992 Mar 15;282(Pt 3):697–702. doi: 10.1042/bj2820697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis S. W., Korach K. S. Uterine estrogen receptor-DNA complexes: effects of different ERE sequences, ligands, and receptor forms. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jul;5(7):959–966. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-7-959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlman-Wright K., Wright A., Gustafsson J. A., Carlstedt-Duke J. Interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain with DNA as a dimer is mediated by a short segment of five amino acids. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3107–3112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen L. P., Harmon J. M. Activation of the rat kidney mineralocorticoid receptor. Endocrinology. 1986 Oct;119(4):1419–1426. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-4-1419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawell S. E., White R., Hoare S., Sydenham M., Page M., Parker M. G. Inhibition of estrogen receptor-DNA binding by the "pure" antiestrogen ICI 164,384 appears to be mediated by impaired receptor dimerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6883–6887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouilleux F., Sola B., Couette B., Richard-Foy H. Cooperation between structural elements in hormono-regulated transcription from the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1563–1569. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Krummel B., Saiki R. K. A general method of in vitro preparation and specific mutagenesis of DNA fragments: study of protein and DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7351–7367. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Giguere V., Segui P., Evans R. M. Colocalization of DNA-binding and transcriptional activation functions in the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90753-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Aldosterone regulation of gene transcription leading to control of ion transport. Hypertension. 1992 Mar;19(3):221–227. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.19.3.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N., van Ooyen A. J., Kennedy N., Herrlich P., Ponta H., Groner B. Subfragments of the large terminal repeat cause glucocorticoid-responsive expression of mouse mammary tumor virus and of an adjacent gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3637–3641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Strähle U., Gloss B., Stewart F., Schmid W., Boshart M., Miksicek R., Schütz G. Cooperativity of glucocorticoid response elements located far upstream of the tyrosine aminotransferase gene. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90752-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Chambon P. The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudet V., Hänni C., Coll J., Catzeflis F., Stéhelin D. Evolution of the nuclear receptor gene superfamily. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1003–1013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05139.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luisi B. F., Xu W. X., Otwinowski Z., Freedman L. P., Yamamoto K. R., Sigler P. B. Crystallographic analysis of the interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor with DNA. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):497–505. doi: 10.1038/352497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald P. N., Haussler C. A., Terpening C. M., Galligan M. A., Reeder M. C., Whitfield G. K., Haussler M. R. Baculovirus-mediated expression of the human vitamin D receptor. Functional characterization, vitamin D response element interactions, and evidence for a receptor auxiliary factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18808–18813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J., Varmus H. E. A small region of the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat confers glucocorticoid hormone regulation on a linked heterologous gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5866–5870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., Wahli W. Cooperative binding of estrogen receptor to imperfect estrogen-responsive DNA elements correlates with their synergistic hormone-dependent enhancer activity. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3781–3791. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08555.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P. D., Sherman T. G., Goldman D. J., Watson S. J. Molecular cloning of a mineralocorticoid (type I) receptor complementary DNA from rat hippocampus. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1877–1885. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-11-1877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., DeFranco D., Firestone G. L., Edgar B., Wrange O., Okret S., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Sequence-specific binding of glucocorticoid receptor to MTV DNA at sites within and upstream of the transcribed region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann T., Eriksson P., Wrange O. Quantitative analysis of the glucocorticoid receptor-DNA interaction at the mouse mammary tumor virus glucocorticoid response element. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17222–17229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pham T. A., Elliston J. F., Nawaz Z., McDonnell D. P., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Antiestrogen can establish nonproductive receptor complexes and alter chromatin structure at target enhancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3125–3129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafestin-Oblin M. E., Couette B., Radanyi C., Lombes M., Baulieu E. E. Mineralocorticosteroid receptor of the chick intestine. Oligomeric structure and transformation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9304–9309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafestin-Oblin M. E., Lombes M., Couette B., Baulieu E. E. Differences between aldosterone and its antagonists in binding kinetics and ligand-induced hsp90 release from mineralocorticosteroid receptor. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1992 Mar;41(3-8):815–821. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(92)90430-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabbah M., Gouilleux F., Sola B., Redeuilh G., Baulieu E. E. Structural differences between the hormone and antihormone estrogen receptor complexes bound to the hormone response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):390–394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer M., Chalepakis G., Willmann T., Beato M. Binding of hormone accelerates the kinetics of glucocorticoid and progesterone receptor binding to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1123–1127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Geisse S., Westphal H. M., Beato M. The glucocorticoid receptor binds to defined nucleotide sequences near the promoter of mouse mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):749–752. doi: 10.1038/304749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman G., Miller-Diener A., Litwack G., Bastl C. P. Characterization of the rat colonic aldosterone receptor and its activation process. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12102–12108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan G., Thompson E. B. Overexpression of full-length human glucocorticoid receptor in Spodoptera frugiperda cells using the baculovirus expression vector system. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Feb;4(2):209–216. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-2-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka H., Dong Y., Li Q., Okret S., Gustafsson J. A. Identification and characterization of a cis-acting element that interferes with glucocorticoid-inducible activation of the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5393–5397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truss M., Chalepakis G., Beato M. Contacts between steroid hormone receptors and thymines in DNA: an interference method. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7180–7184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willmann T., Beato M. Steroid-free glucocorticoid receptor binds specifically to mouse mammary tumour virus DNA. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):688–691. doi: 10.1038/324688a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R. Steroid receptor regulated transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:209–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]