Abstract
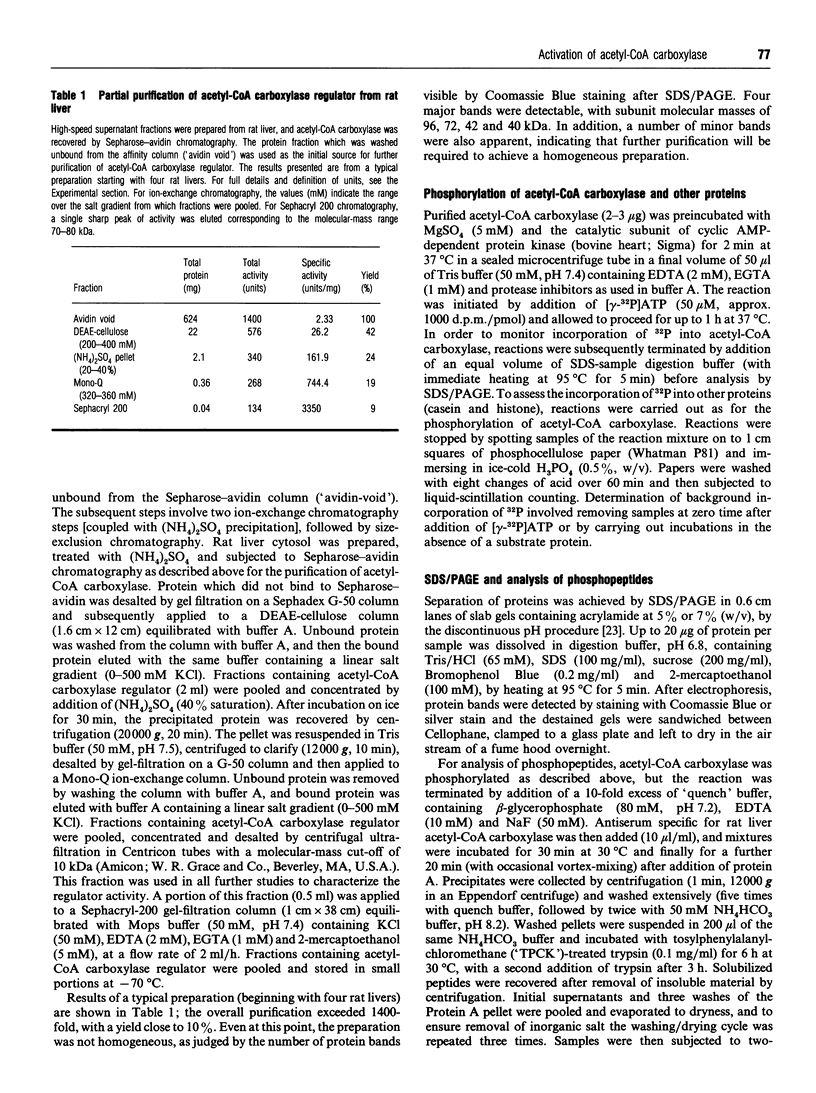
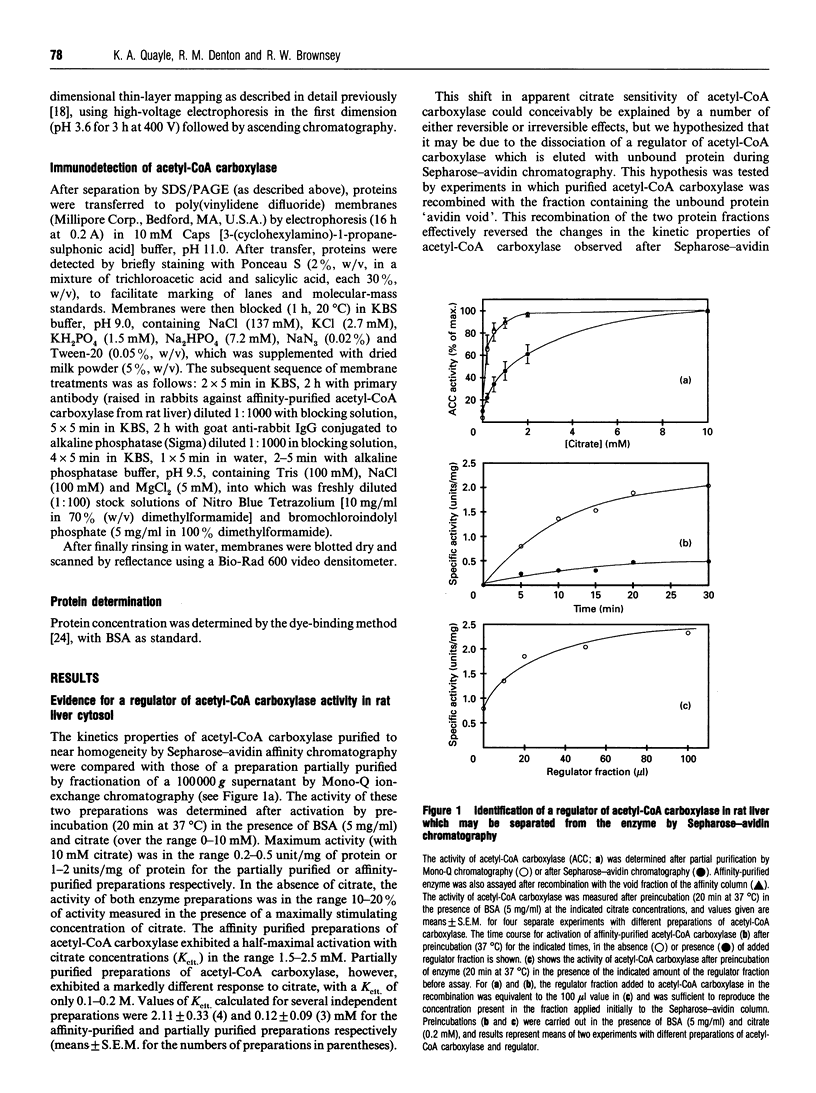
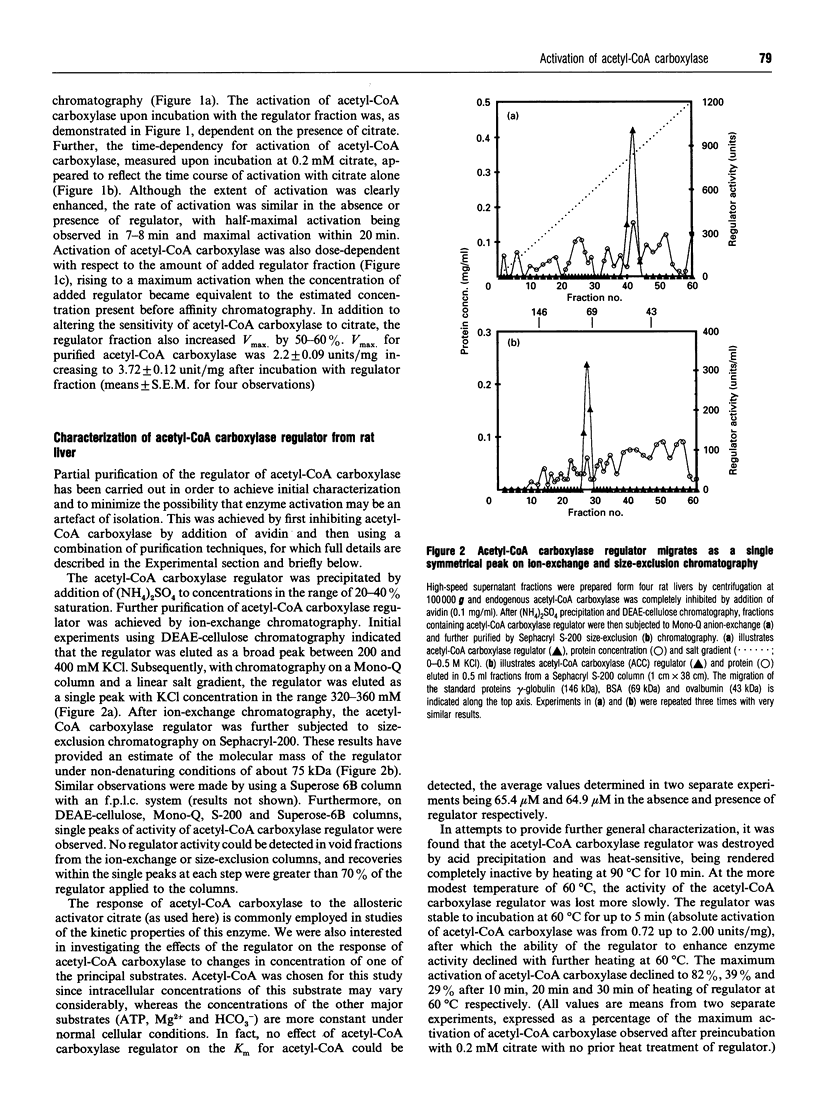
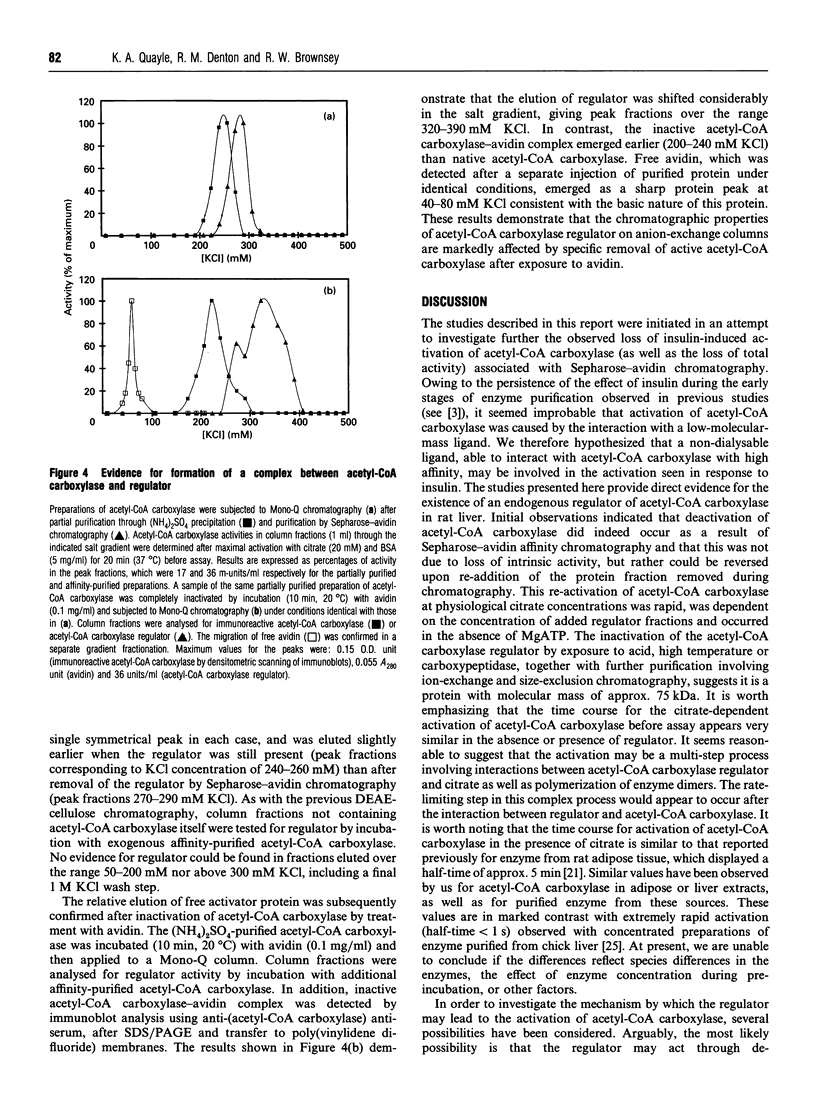
1. A regulator of acetyl-CoA carboxylase has been identified in high-speed supernatant fractions from rat liver. The regulator was found to activate highly purified acetyl-CoA carboxylase 2-3-fold at physiological citrate concentrations (0.1-0.5 mM). The effects of the regulator on acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity were dose-dependent, and half-maximal activation occurred in 7-8 min at 30 degrees C. 2. The acetyl-CoA carboxylase regulator was non-dialysable and was inactivated by heating or by exposure to carboxypeptidase. The regulator was enriched from rat liver cytosol by first removing the endogenous acetyl-CoA carboxylase and then using a combination of purification steps, including (NH4)2SO4 precipitation, ion-exchange chromatography and size-exclusion chromatography. The regulator activity appeared to be a protein with a molecular mass of approx. 75 kDa, which could be eluted from mono-Q with approx. 0.35 M KCl as a single peak of activity. 3. Studies of the effects of the regulator on phosphorylation or subunit size of acetyl-CoA carboxylase indicated that the changes in enzyme activity are most unlikely to be explained by dephosphorylation or by proteolytic cleavage. 4. The regulator co-migrates with acetyl-CoA carboxylase through several purification steps, including ion-exchange chromatography and precipitation with (NH4)2SO4; however, the proteins may be separated by Sepharose-avidin chromatography, and the association between the proteins is also disrupted by addition of avidin in solution. Furthermore, the binding of the regulator itself to DEAE-cellulose is altered by the presence of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Taken together, these observations suggest that the effects of the regulator on acetyl-CoA carboxylase may be explained by direct protein-protein interaction in vitro.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Halim M. N., Porter J. W. A new mechanism of regulation of rat liver acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):441–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaty N. B., Lane M. D. Kinetics of activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase by citrate. Relationship to the rate of polymerization of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):13043–13050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blyatt H. J., Kim K. H. Phosphoinositide inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase from rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Feb;213(2):523–529. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90579-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borthwick A. C., Edgell N. J., Denton R. M. Protein-serine kinase from rat epididymal adipose tissue which phosphorylates and activates acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Possible role in insulin action. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 15;270(3):795–801. doi: 10.1042/bj2700795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownsey R. W., Denton R. M. Evidence that insulin activates fat-cell acetyl-CoA carboxylase by increased phosphorylation at a specific site. Biochem J. 1982 Jan 15;202(1):77–86. doi: 10.1042/bj2020077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownsey R. W., Hughes W. A., Denton R. M. Adrenaline and the regulation of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase in rat epididymal adipose tissue. Inactivation of the enzyme is associated with phosphorylation and can be reversed on dephosphorylation. Biochem J. 1979 Oct 15;184(1):23–32. doi: 10.1042/bj1840023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buechler K. F., Gibson D. M. Guanosine triphosphate and colchicine affect the activity and the polymeric state of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Sep;233(2):698–707. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90496-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy P. S., Hardie D. G. Regulation of mammalian acetyl-CoA carboxylase: limited proteolysis mimics dephosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 1981 Sep 14;132(1):67–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80428-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halestrap A. P., Denton R. M. Insulin and the regulation of adipose tissue acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;132(3):509–517. doi: 10.1042/bj1320509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie D. G., Cohen P. Dephosphorylation and activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase from lactating rabbit mammary gland. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jul 15;103(2):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81356-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie D. G. Regulation of fatty acid synthesis via phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Prog Lipid Res. 1989;28(2):117–146. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(89)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haystead T. A., Campbell D. G., Hardie D. G. Analysis of sites phosphorylated on acetyl-CoA carboxylase in response to insulin in isolated adipocytes. Comparison with sites phosphorylated by casein kinase-2 and the calmodulin-dependent multiprotein kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 1;175(2):347–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haystead T. A., Hardie D. G. Evidence that activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase by insulin in adipocytes is mediated by a low-Mr effector and not by increased phosphorylation. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):99–106. doi: 10.1042/bj2400099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haystead T. A., Moore F., Cohen P., Hardie D. G. Roles of the AMP-activated and cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinases in the adrenaline-induced inactivation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase in rat adipocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jan 12;187(1):199–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. H., López-Casillas F., Bai D. H., Luo X., Pape M. E. Role of reversible phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase in long-chain fatty acid synthesis. FASEB J. 1989 Sep;3(11):2250–2256. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.11.2570725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakower G. R., Kim K. H. Dephosphorylation and activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase by phosphorylase phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):389–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90345-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Casillas F., Bai D. H., Luo X. C., Kong I. S., Hermodson M. A., Kim K. H. Structure of the coding sequence and primary amino acid sequence of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5784–5788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moule S. K., Edgell N. J., Borthwick A. C., Denton R. M. Coenzyme A is a potent inhibitor of acetyl-CoA carboxylase from rat epididymal fat-pads. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 1;283(Pt 1):35–38. doi: 10.1042/bj2830035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S., Paddon H. B., Quayle K. A., Brownsey R. W. Identification of a major maturation-activated acetyl-CoA carboxylase kinase in sea star oocytes as p44mpk. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 15;274(Pt 3):759–767. doi: 10.1042/bj2740759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Doble A., Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Putative mediators of insulin action regulate hepatic acetyl CoA carboxylase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Feb 10;110(3):789–795. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song C. S., Kim K. H. Reevaluation of properties of acetyl-CoA carboxylase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7786–7788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thampy K. G., Wakil S. J. Activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Purification and properties of a Mn2+-dependent phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6318–6323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada K., Tanabe T. Dephosphorylation and activation of chicken liver acetyl-coenzyme-A carboxylase. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Sep 1;135(1):17–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07612.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A., Friedman S. A., Tipper J. P., Bacon G. W. Regulation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase by guanine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8573–8578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A., Tipper J. P., Bacon G. W. Stimulation of site-specific phosphorylation of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase by insulin and epinephrine. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5643–5648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh L. A., Kim K. H. Regulation of acetyl-coA carboxylase: properties of coA activation of acetyl-coA carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3351–3355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh L. A., Song C. S., Kim K. H. Coenzyme A activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2289–2296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]