Abstract
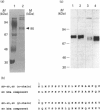
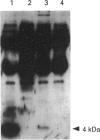
The amyloid fibrils deposited in Alzheimer's neuritic plaque cores and cerebral blood vessels are mainly composed of aggregated forms of a unique peptide, 39-42 amino acids long, named amyloid beta (A beta). A similar, although soluble, A beta ('sA beta') has been identified in cerebrospinal fluid, plasma and cell supernatants, indicating that it is normally produced by proteolytic processing of its precursor protein, amyloid precursor protein (APP). Using direct binding experiments we have isolated and characterized an 80 kDa circulating protein that specifically interacts with a synthetic peptide identical with A beta. The protein was unmistakably identified as SP-40,40 or ApoJ, a cytolytic inhibitor and lipid carrier, by means of amino acid sequence and immunoreactivity with specific antibodies. Immunoprecipitation with anti-SP-40,40 retrieved soluble A beta from cerebrospinal fluid, indicating that the interaction occurs in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham C. R., Selkoe D. J., Potter H. Immunochemical identification of the serine protease inhibitor alpha 1-antichymotrypsin in the brain amyloid deposits of Alzheimer's disease. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):487–501. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90462-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama H., Kawamata T., Dedhar S., McGeer P. L. Immunohistochemical localization of vitronectin, its receptor and beta-3 integrin in Alzheimer brain tissue. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Apr;32(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90067-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. P., Chen Y., Kim K. S., Robakis N. K. An alternative secretase cleavage produces soluble Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein containing a potentially amyloidogenic sequence. J Neurochem. 1992 Dec;59(6):2328–2331. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronow B. J., Lund S. D., Brown T. L., Harmony J. A., Witte D. P. Apolipoprotein J expression at fluid-tissue interfaces: potential role in barrier cytoprotection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):725–729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño E. M., Frangione B. Alzheimer's disease from the perspective of the systemic and localized forms of amyloidosis. Brain Pathol. 1991 Jul;1(4):263–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1991.tb00669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño E. M., Ghiso J., Prelli F., Gorevic P. D., Migheli A., Frangione B. In vitro formation of amyloid fibrils from two synthetic peptides of different lengths homologous to Alzheimer's disease beta-protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):782–789. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80241-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi-Miura N. H., Ihara Y., Fukuchi K., Takeda M., Nakano Y., Tobe T., Tomita M. SP-40,40 is a constituent of Alzheimer's amyloid. Acta Neuropathol. 1992;83(3):260–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00296787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi N. H., Mazda T., Tomita M. A serum protein SP40,40 modulates the formation of membrane attack complex of complement on erythrocytes. Mol Immunol. 1989 Sep;26(9):835–840. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90139-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi N. H., Tobe T., Hara K., Yoshida H., Tomita M. Sandwich ELISA assay for quantitative measurement of SP-40,40 in seminal plasma and serum. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Aug 7;131(2):159–163. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90186-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citron M., Oltersdorf T., Haass C., McConlogue L., Hung A. Y., Seubert P., Vigo-Pelfrey C., Lieberburg I., Selkoe D. J. Mutation of the beta-amyloid precursor protein in familial Alzheimer's disease increases beta-protein production. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):672–674. doi: 10.1038/360672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coria F., Castaño E., Prelli F., Larrondo-Lillo M., van Duinen S., Shelanski M. L., Frangione B. Isolation and characterization of amyloid P component from Alzheimer's disease and other types of cerebral amyloidosis. Lab Invest. 1988 Apr;58(4):454–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F. S., Keim P. S., Beattie E. C., Blacher R. W., Culwell A. R., Oltersdorf T., McClure D., Ward P. J. Cleavage of amyloid beta peptide during constitutive processing of its precursor. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1122–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.2111583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estus S., Golde T. E., Kunishita T., Blades D., Lowery D., Eisen M., Usiak M., Qu X. M., Tabira T., Greenberg B. D. Potentially amyloidogenic, carboxyl-terminal derivatives of the amyloid protein precursor. Science. 1992 Feb 7;255(5045):726–728. doi: 10.1126/science.1738846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser P. E., Nguyen J. T., Inouye H., Surewicz W. K., Selkoe D. J., Podlisny M. B., Kirschner D. A. Fibril formation by primate, rodent, and Dutch-hemorrhagic analogues of Alzheimer amyloid beta-protein. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 10;31(44):10716–10723. doi: 10.1021/bi00159a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandy S. E., Bhasin R., Ramabhadran T. V., Koo E. H., Price D. L., Goldgaber D., Greengard P. Alzheimer beta/A4-amyloid precursor protein: evidence for putative amyloidogenic fragment. J Neurochem. 1992 Jan;58(1):383–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09322.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiso J., Rostagno A., Gardella J. E., Liem L., Gorevic P. D., Frangione B. A 109-amino-acid C-terminal fragment of Alzheimer's-disease amyloid precursor protein contains a sequence, -RHDS-, that promotes cell adhesion. Biochem J. 1992 Dec 15;288(Pt 3):1053–1059. doi: 10.1042/bj2881053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golde T. E., Estus S., Younkin L. H., Selkoe D. J., Younkin S. G. Processing of the amyloid protein precursor to potentially amyloidogenic derivatives. Science. 1992 Feb 7;255(5045):728–730. doi: 10.1126/science.1738847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorevic P. D., Castano E. M., Sarma R., Frangione B. Ten to fourteen residue peptides of Alzheimer's disease protein are sufficient for amyloid fibril formation and its characteristic x-ray diffraction pattern. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 15;147(2):854–862. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griswold M. D., Roberts K., Bishop P. Purification and characterization of a sulfated glycoprotein secreted by Sertoli cells. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7265–7270. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haass C., Schlossmacher M. G., Hung A. Y., Vigo-Pelfrey C., Mellon A., Ostaszewski B. L., Lieberburg I., Koo E. H., Schenk D., Teplow D. B. Amyloid beta-peptide is produced by cultured cells during normal metabolism. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):322–325. doi: 10.1038/359322a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirszbaum L., Bozas S. E., Walker I. D. SP-40,40, a protein involved in the control of the complement pathway, possesses a unique array of disulphide bridges. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 3;297(1-2):70–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80330-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirszbaum L., Sharpe J. A., Murphy B., d'Apice A. J., Classon B., Hudson P., Walker I. D. Molecular cloning and characterization of the novel, human complement-associated protein, SP-40,40: a link between the complement and reproductive systems. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):711–718. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Stossel T. P., Orkin S. H., Mole J. E., Colten H. R., Yin H. L. Plasma and cytoplasmic gelsolins are encoded by a single gene and contain a duplicated actin-binding domain. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):455–458. doi: 10.1038/323455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Carman M. D., Fernandez-Madrid I. J., Power M. D., Lieberburg I., van Duinen S. G., Bots G. T., Luyendijk W., Frangione B. Mutation of the Alzheimer's disease amyloid gene in hereditary cerebral hemorrhage, Dutch type. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1124–1126. doi: 10.1126/science.2111584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto A., Fujiwara Y. Abnormal and deficient processing of beta-amyloid precursor protein in familial Alzheimer's disease lymphoblastoid cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 15;175(2):361–365. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91572-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., Kawamata T., Walker D. G. Distribution of clusterin in Alzheimer brain tissue. Brain Res. 1992 May 8;579(2):337–341. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90071-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullan M., Crawford F., Axelman K., Houlden H., Lilius L., Winblad B., Lannfelt L. A pathogenic mutation for probable Alzheimer's disease in the APP gene at the N-terminus of beta-amyloid. Nat Genet. 1992 Aug;1(5):345–347. doi: 10.1038/ng0892-345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. F., Kirszbaum L., Walker I. D., d'Apice A. J. SP-40,40, a newly identified normal human serum protein found in the SC5b-9 complex of complement and in the immune deposits in glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1858–1864. doi: 10.1172/JCI113531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. F., Saunders J. R., O'Bryan M. K., Kirszbaum L., Walker I. D., d'Apice A. J. SP-40,40 is an inhibitor of C5b-6-initiated haemolysis. Int Immunol. 1989;1(5):551–554. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.5.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordstedt C., Gandy S. E., Alafuzoff I., Caporaso G. L., Iverfeldt K., Grebb J. A., Winblad B., Greengard P. Alzheimer beta/A4 amyloid precursor protein in human brain: aging-associated increases in holoprotein and in a proteolytic fragment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8910–8914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Bryan M. K., Baker H. W., Saunders J. R., Kirszbaum L., Walker I. D., Hudson P., Liu D. Y., Glew M. D., d'Apice A. J., Murphy B. F. Human seminal clusterin (SP-40,40). Isolation and characterization. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1477–1486. doi: 10.1172/JCI114594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purrello M., Bettuzzi S., Di Pietro C., Mirabile E., Di Blasi M., Rimini R., Grzeschik K. H., Ingletti C., Corti A., Sichel G. The gene for SP-40,40, human homolog of rat sulfated glycoprotein 2, rat clusterin, and rat testosterone-repressed prostate message 2, maps to chromosome 8. Genomics. 1991 May;10(1):151–156. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90495-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramabhadran T. V., Gandy S. E., Ghiso J., Czernik A. J., Ferris D., Bhasin R., Goldgaber D., Frangione B., Greengard P. Proteolytic processing of human amyloid beta protein precursor in insect cells. Major carboxyl-terminal fragment is identical to its human counterpart. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):2009–2012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Cooper N. R., Webster S., Schultz J., McGeer P. L., Styren S. D., Civin W. H., Brachova L., Bradt B., Ward P. Complement activation by beta-amyloid in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10016–10020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seubert P., Oltersdorf T., Lee M. G., Barbour R., Blomquist C., Davis D. L., Bryant K., Fritz L. C., Galasko D., Thal L. J. Secretion of beta-amyloid precursor protein cleaved at the amino terminus of the beta-amyloid peptide. Nature. 1993 Jan 21;361(6409):260–263. doi: 10.1038/361260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seubert P., Vigo-Pelfrey C., Esch F., Lee M., Dovey H., Davis D., Sinha S., Schlossmacher M., Whaley J., Swindlehurst C. Isolation and quantification of soluble Alzheimer's beta-peptide from biological fluids. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):325–327. doi: 10.1038/359325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji M., Golde T. E., Ghiso J., Cheung T. T., Estus S., Shaffer L. M., Cai X. D., McKay D. M., Tintner R., Frangione B. Production of the Alzheimer amyloid beta protein by normal proteolytic processing. Science. 1992 Oct 2;258(5079):126–129. doi: 10.1126/science.1439760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisodia S. S., Koo E. H., Beyreuther K., Unterbeck A., Price D. L. Evidence that beta-amyloid protein in Alzheimer's disease is not derived by normal processing. Science. 1990 Apr 27;248(4954):492–495. doi: 10.1126/science.1691865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow A. D., Willmer J., Kisilevsky R. Sulfated glycosaminoglycans: a common constituent of all amyloids? Lab Invest. 1987 Jan;56(1):120–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Saunders A. M., Schmechel D., Pericak-Vance M., Enghild J., Salvesen G. S., Roses A. D. Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1977–1981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoka A., Kalaria R. N., Lieberburg I., Selkoe D. J. Identification of a stable fragment of the Alzheimer amyloid precursor containing the beta-protein in brain microvessels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1345–1349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobe T., Minoshima S., Yamase S., Choi N. H., Tomita M., Shimizu N. Assignment of a human serum glycoprotein SP-40,40 gene (CLI) to chromosome 8. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1991;57(4):193–195. doi: 10.1159/000133144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuruta J. K., Wong K., Fritz I. B., Griswold M. D. Structural analysis of sulphated glycoprotein 2 from amino acid sequence. Relationship to clusterin and serum protein 40,40. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 15;268(3):571–578. doi: 10.1042/bj2680571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R., Meschia J. F., Cotter R. J., Sisodia S. S. Secretion of the beta/A4 amyloid precursor protein. Identification of a cleavage site in cultured mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16960–16964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Frangione B. Apolipoprotein E: a pathological chaperone protein in patients with cerebral and systemic amyloid. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Feb 3;135(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90444-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Ghiso J., Frangione B. Peptides homologous to the amyloid protein of Alzheimer's disease containing a glutamine for glutamic acid substitution have accelerated amyloid fibril formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Sep 30;179(3):1247–1254. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91706-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Golabek A., Matsubara E., Ghiso J., Frangione B. Apolipoprotein E: binding to soluble Alzheimer's beta-amyloid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Apr 30;192(2):359–365. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Silva H. V., Harmony J. A., Stuart W. D., Gil C. M., Robbins J. Apolipoprotein J: structure and tissue distribution. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 5;29(22):5380–5389. doi: 10.1021/bi00474a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Silva H. V., Stuart W. D., Duvic C. R., Wetterau J. R., Ray M. J., Ferguson D. G., Albers H. W., Smith W. R., Harmony J. A. A 70-kDa apolipoprotein designated ApoJ is a marker for subclasses of human plasma high density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13240–13247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]