Abstract
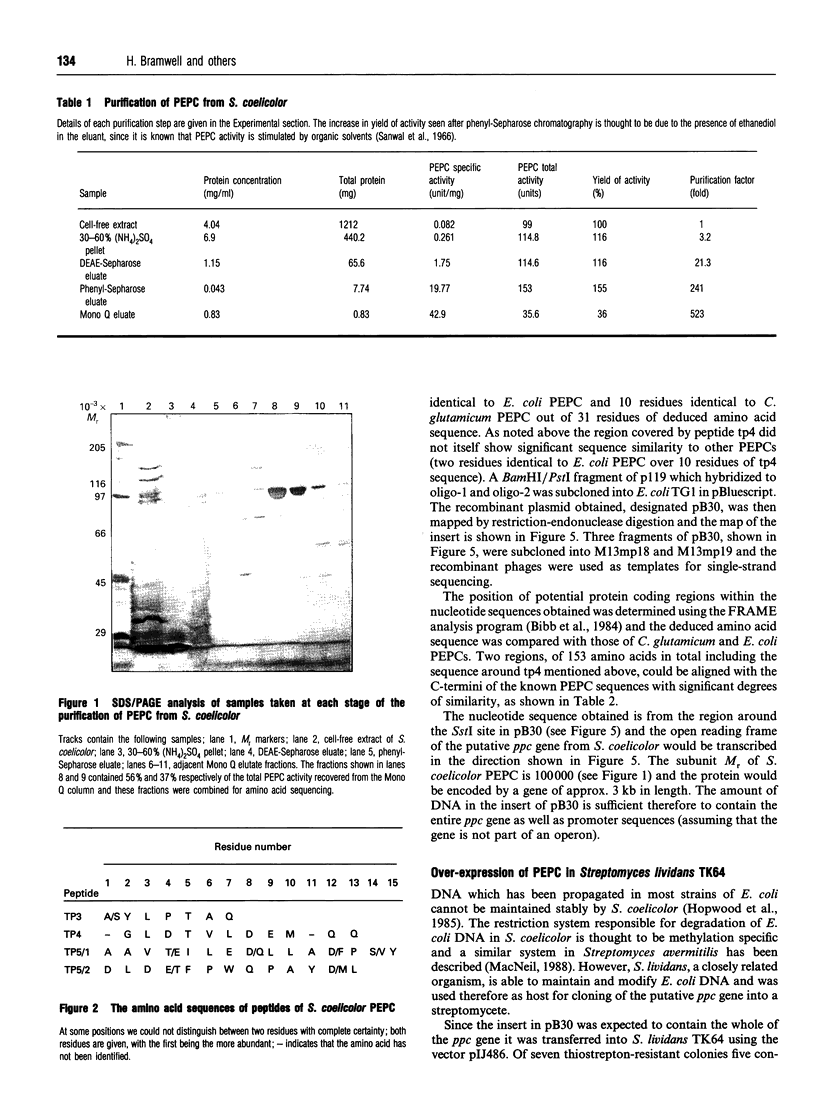
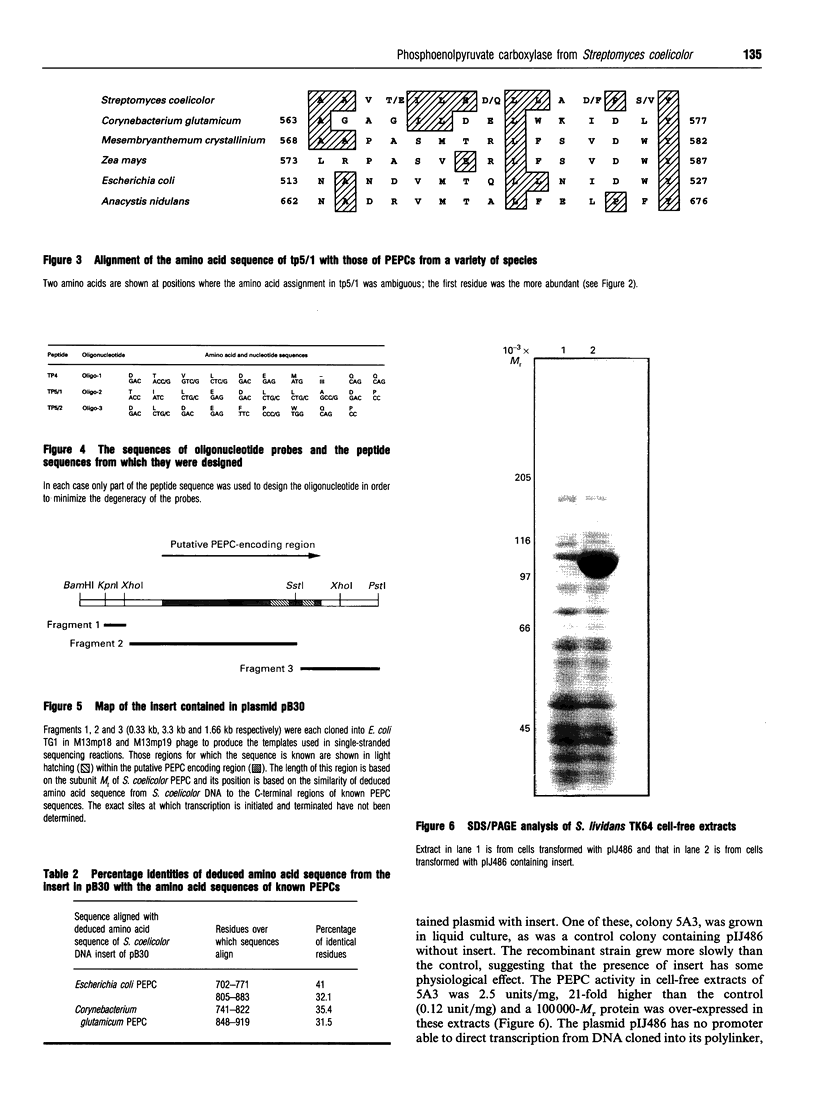
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase [PEPC; orthophosphate:oxaloacetate carboxy-lyase (phosphorylating); EC 4.1.1.31] is a major anaplerotic enzyme in the polyketide producer Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). PEPC was purified from S. coelicolor and the amino-acid sequences of four tryptic peptides were determined. Synthetic oligonucleotides based on the sequences of two of the peptides hybridized to the same bands in various restriction-enzyme digests of S. coelicolor genomic DNA. This hybridization allowed molecular cloning of an 8 kb BamHI fragment of genomic DNA. Partial DNA sequencing of this fragment showed that it could encode amino acid sequences similar to those of PEPC from other microorganisms. A BamHI/PstI fragment was subcloned into the streptomycete high-copy-number plasmid vector pIJ486 and transferred into Streptomyces lividans. The resulting strain over-expressed PEPC activity 21-fold and also over-expressed a protein with a subunit of 100,000 M(r), the same as that of purified S. coelicolor PEPC.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bibb M. J., Findlay P. R., Johnson M. W. The relationship between base composition and codon usage in bacterial genes and its use for the simple and reliable identification of protein-coding sequences. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch A. J. Biosynthesis of polyketides and related compounds. Science. 1967 Apr 14;156(3772):202–206. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3772.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANNATA J. J., STOPPANI A. O. Phosphopyruvate carboxylase from baker's yeast. I. Isolation, purification, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1963 Apr;238:1196–1207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekleva M. L., Strohl W. R. Activity of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase of an anthracycline-producing streptomycete. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Nov;34(11):1241–1246. doi: 10.1139/m88-218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita N., Miwa T., Ishijima S., Izui K., Katsuki H. The primary structure of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase of Escherichia coli. Nucleotide sequence of the ppc gene and deduced amino acid sequence. J Biochem. 1984 Apr;95(4):909–916. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieser H. M., Kieser T., Hopwood D. A. A combined genetic and physical map of the Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(17):5496–5507. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.17.5496-5507.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakey J. H., Lea E. J., Rudd B. A., Wright H. M., Hopwood D. A. A new channel-forming antibiotic from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) which requires calcium for its activity. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Dec;129(12):3565–3573. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-12-3565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNeil D. J. Characterization of a unique methyl-specific restriction system in Streptomyces avermitilis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5607–5612. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5607-5612.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R., Lardy H. A., Kneifel H. P. Rat liver pyruvate carboxylase. I. Preparation, properties, and cation specificity. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3569–3578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori M., Shiio I. Purification and some properties of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from Brevibacterium flavum and its aspartate-overproducing mutant. J Biochem. 1985 Apr;97(4):1119–1128. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Regan M., Thierbach G., Bachmann B., Villeval D., Lepage P., Viret J. F., Lemoine Y. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase-coding gene of Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC13032. Gene. 1989 Apr 30;77(2):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omura S. The expanded horizon for microbial metabolites--a review. Gene. 1992 Jun 15;115(1-2):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90552-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porro M., Viti S., Antoni G., Saletti M. Ultrasensitive silver-stain method for the detection of proteins in polyacrylamide gels and immunoprecipitates on agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Dec;127(2):316–321. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90179-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanwal B. D., Maeba P., Cook R. A. Interaction of macroions and dioxane with the allosteric phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Nov 25;241(22):5177–5182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch E., Takano E., Baylis H. A., Bibb M. J. The stringent response in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):289–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivekananda J., Oliver D. J. Isolation and partial characterization of the glutamate/aspartate transporter from pea leaf mitochondria using a specific monoclonal antibody. Plant Physiol. 1989 Sep;91(1):272–277. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.1.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang I. K., Vining L. C., Walter J. A., McInnes A. G. Use of carbon-13 in biosynthetic studies: origin of the malonyl coenzyme A incorporated into tetracycline by Streptomyces aureofaciens. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1986 Sep;39(9):1281–1287. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.39.1281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. M., Janssen G. R., Kieser T., Bibb M. J., Buttner M. J., Bibb M. J. Construction and characterisation of a series of multi-copy promoter-probe plasmid vectors for Streptomyces using the aminoglycoside phosphotransferase gene from Tn5 as indicator. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jun;203(3):468–478. doi: 10.1007/BF00422072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga T., Izui K., Katsuki H. Purification and molecular properties of allosteric phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1970 Nov;68(5):747–750. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]