Abstract
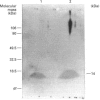
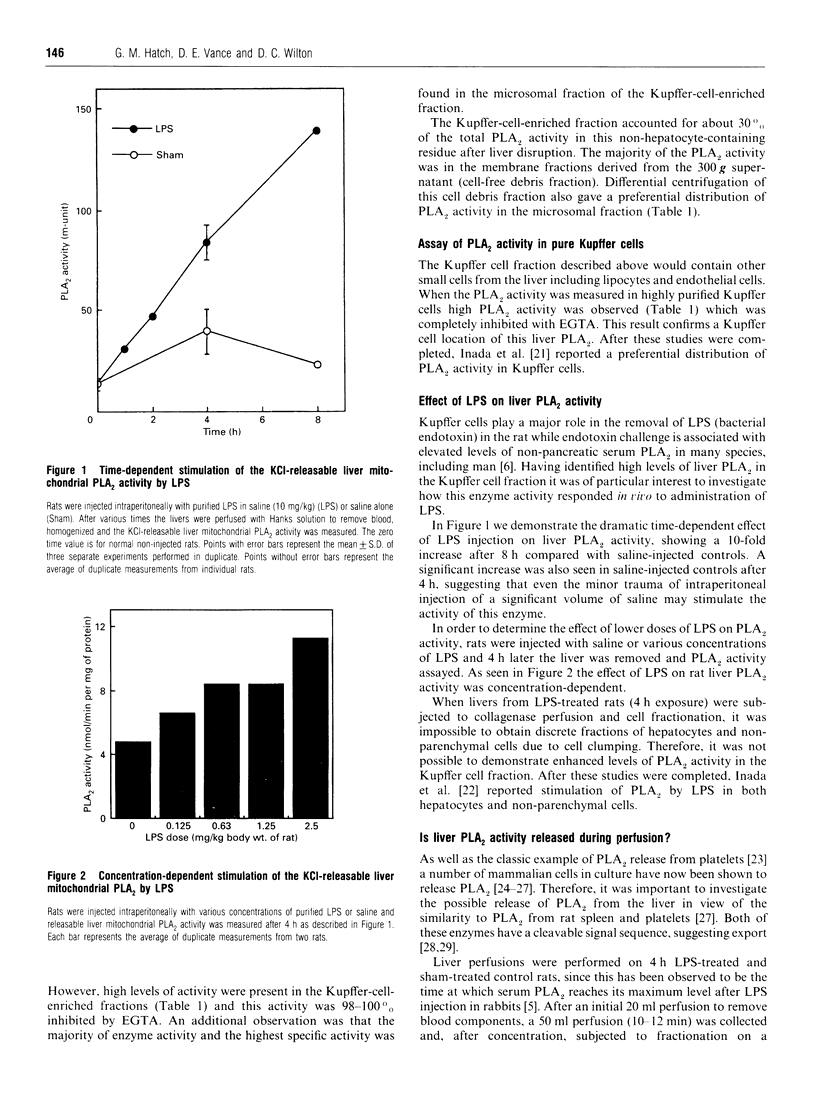
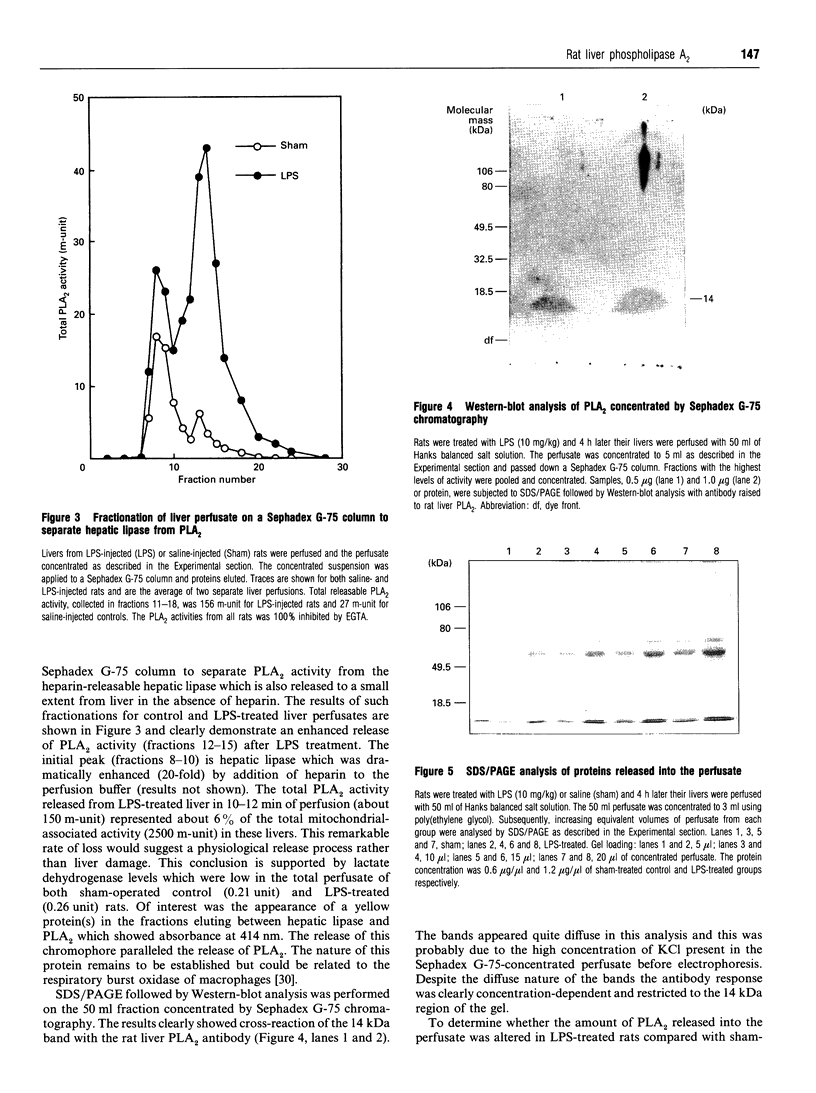
A novel fluorescence assay for phospholipase A2 [Wilton (1990) Biochem. J. 266, 435-439] has been used to study the Group-II rat liver mitochondrial enzyme, and a number of novel properties of this enzyme were identified. (1) The enzyme activity was located in the liver macrophages (Kupffer cells) while negligible activity was associated with hepatocytes. (2) Although subcellular fractionation of whole liver confirmed the predominantly mitochondrial location of this enzyme activity, the analysis of the hepatocyte-free Kupffer-cell-enriched fraction revealed a different enzyme distribution, with the majority of activity being associated with the microsomal membrane fraction. (3) Bacterial endotoxin has been previously shown to be scavenged by Kupffer cells in rats. Treatment of rats with bacterial lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin) resulted in a dramatic time- and dose-dependent increase in liver phospholipase A2 activity. (4) It is known that injection of endotoxin into rodents results in elevated serum phospholipase A2 activity, while a similar phenomenon is seen in the condition of septic shock in man. The source of this serum enzyme was unknown. In this study perfusion of livers from rats pretreated with lipopolysaccharide with physiological saline demonstrated a 6-fold increase in phospholipase A2 activity in the perfusate compared with sham-treated controls, with only minor release of hepatic lipase. (5) Western-blot analysis confirmed an increased release of this Group-II phospholipase A2 into the perfusate of lipopolysaccharide-treated rats compared with sham-treated controls. These results suggest that liver Kupffer cells are a major source of the endotoxin-induced serum Group-II phospholipase A2 activity associated with bacterial infection and trauma.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aarsman A. J., de Jong J. G., Arnoldussen E., Neys F. W., van Wassenaar P. D., Van den Bosch H. Immunoaffinity purification, partial sequence, and subcellular localization of rat liver phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):10008–10014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur M. J., Friedman S. L., Roll F. J., Bissell D. M. Lipocytes from normal rat liver release a neutral metalloproteinase that degrades basement membrane (type IV) collagen. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1076–1085. doi: 10.1172/JCI114270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belcher J. D., Sisson P. J., Waite M. Degradation of mono-oleoylglycerol, trioleoylglycerol and phosphatidylcholine in emulsions and lipoproteins by rat hepatic acylglycerol lipase. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):343–351. doi: 10.1042/bj2290343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. D., Lin L. L., Kriz R. W., Ramesha C. S., Sultzman L. A., Lin A. Y., Milona N., Knopf J. L. A novel arachidonic acid-selective cytosolic PLA2 contains a Ca(2+)-dependent translocation domain with homology to PKC and GAP. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90556-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowl R. M., Stoller T. J., Conroy R. R., Stoner C. R. Induction of phospholipase A2 gene expression in human hepatoma cells by mediators of the acute phase response. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2647–2651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. A., Engelhorn S. C., Pangburn S. H., Weinstein D. B., Steinberg D. Very low density lipoprotein synthesis and secretion by cultured rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):2010–2016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis E. A., Rhee S. G., Billah M. M., Hannun Y. A. Role of phospholipase in generating lipid second messengers in signal transduction. FASEB J. 1991 Apr;5(7):2068–2077. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.7.1901288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser K. B., Asmis R., Dennis E. A. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide priming of P388D1 macrophage-like cells for enhanced arachidonic acid metabolism. Platelet-activating factor receptor activation and regulation of phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8658–8664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampton R. Y., Golenbock D. T., Penman M., Krieger M., Raetz C. R. Recognition and plasma clearance of endotoxin by scavenger receptors. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):342–344. doi: 10.1038/352342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara S., Kudo I., Inoue K. Augmentation of prostaglandin E2 production by mammalian phospholipase A2 added exogenously. J Biochem. 1991 Aug;110(2):163–165. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horigome K., Hayakawa M., Inoue K., Nojima S. Selective release of phospholipase A2 and lysophosphatidylserine-specific lysophospholipase from rat platelets. J Biochem. 1987 Jan;101(1):53–61. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inada M., Tojo H., Kawata S., Tarui S., Okamoto M. Induction of group II-like phospholipase A2 by lipopolysaccharide in the liver of BCG-primed rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 14;174(3):1077–1083. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91530-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inada M., Tojo H., Kawata S., Tarui S., Okamoto M. Preferential distribution of group-II-like phospholipase A2 in mononuclear phagocytic cells in rat spleen and liver. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Apr 23;197(2):323–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaki J., Ohara O., Nakamura E., Tamaki M., Ono T., Kanda A., Yoshida N., Teraoka H., Tojo H., Okamoto M. cDNA cloning and sequence determination of rat membrane-associated phospholipase A2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):1030–1036. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90777-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinkaid A. R., Wilton D. C. A study of the 14 kDa phospholipase A2 from rat liver using a continuous fluorescent displacement assay for the enzyme. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 Aug;20(3):287S–287S. doi: 10.1042/bst020287s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinkaid A., Wilton D. C. Comparison of the catalytic properties of phospholipase A2 from pancreas and venom using a continuous fluorescence displacement assay. Biochem J. 1991 Sep 15;278(Pt 3):843–848. doi: 10.1042/bj2780843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komada M., Kudo I., Mizushima H., Kitamura N., Inoue K. Structure of cDNA coding for rat platelet phospholipase A2. J Biochem. 1989 Oct;106(4):545–547. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Kudo I., Inoue K. Eicosanoid generation from antigen-primed mast cells by extracellular mammalian 14-kDa group II phospholipase A2. FEBS Lett. 1991 Dec 9;294(3):247–251. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81440-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Arita H. Enhanced expression of group II phospholipase A2 gene in the tissues of endotoxin shock rats and its suppression by glucocorticoid. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 29;273(1-2):23–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81042-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka S., Arita H. Inflammatory factors stimulate expression of group II phospholipase A2 in rat cultured astrocytes. Two distinct pathways of the gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9956–9960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono T., Tojo H., Kuramitsu S., Kagamiyama H., Okamoto M. Purification and characterization of a membrane-associated phospholipase A2 from rat spleen. Its comparison with a cytosolic phospholipase A2 S-1. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5732–5738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzanski W., Vadas P. Soluble phospholipase A2 in human pathology: clinical-laboratory interface. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1990;279:239–251. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-0651-1_17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez F., Jain M. K. Phospholipase A2 at the bilayer interface. Proteins. 1991;9(4):229–239. doi: 10.1002/prot.340090402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggerson E. D., Greenbaum A. L. The effect of dietary and hormonal conditions on the activities of glycolytic enzymes in rat epididymal adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(3):405–417. doi: 10.1042/bj1150405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samborski R. W., Ridgway N. D., Vance D. E. Evidence that only newly made phosphatidylethanolamine is methylated to phosphatidylcholine and that phosphatidylethanolamine is not significantly deacylated-reacylated in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18322–18329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalkwijk C., Pfeilschifter J., Märki F., van den Bosch H. Interleukin-1 beta- and forskolin-induced synthesis and secretion of group II phospholipase A2 and prostaglandin E2 in rat mesangial cells is prevented by transforming growth factor-beta 2. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):8846–8851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp J. D., White D. L., Chiou X. G., Goodson T., Gamboa G. C., McClure D., Burgett S., Hoskins J., Skatrud P. L., Sportsman J. R. Molecular cloning and expression of human Ca(2+)-sensitive cytosolic phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):14850–14853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Pruzanski W. Role of secretory phospholipases A2 in the pathobiology of disease. Lab Invest. 1986 Oct;55(4):391–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Pruzanski W., Stefanski E. Extracellular phospholipase A2: causative agent in circulatory collapse of septic shock? Agents Actions. 1988 Jul;24(3-4):320–325. doi: 10.1007/BF02028289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verger R., Ferrato F., Mansbach C. M., Pieroni G. Novel intestinal phospholipase A2: purification and some molecular characteristics. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6883–6889. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilton D. C. A continuous fluorescence displacement assay for the measurement of phospholipase A2 and other lipases that release long-chain fatty acids. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 1;266(2):435–439. doi: 10.1042/bj2660435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilton D. C. A continuous fluorescence-displacement assay for triacylglycerol lipase and phospholipase C that also allows the measurement of acylglycerols. Biochem J. 1991 May 15;276(Pt 1):129–133. doi: 10.1042/bj2760129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worrall A. F., Evans C., Wilton D. C. Synthesis of a gene for rat liver fatty-acid-binding protein and its expression in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1991 Sep 1;278(Pt 2):365–368. doi: 10.1042/bj2780365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright G. C., Weiss J., Kim K. S., Verheij H., Elsbach P. Bacterial phospholipid hydrolysis enhances the destruction of Escherichia coli ingested by rabbit neutrophils. Role of cellular and extracellular phospholipases. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1925–1935. doi: 10.1172/JCI114655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright G. W., Ooi C. E., Weiss J., Elsbach P. Purification of a cellular (granulocyte) and an extracellular (serum) phospholipase A2 that participate in the destruction of Escherichia coli in a rabbit inflammatory exudate. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6675–6681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]