Abstract
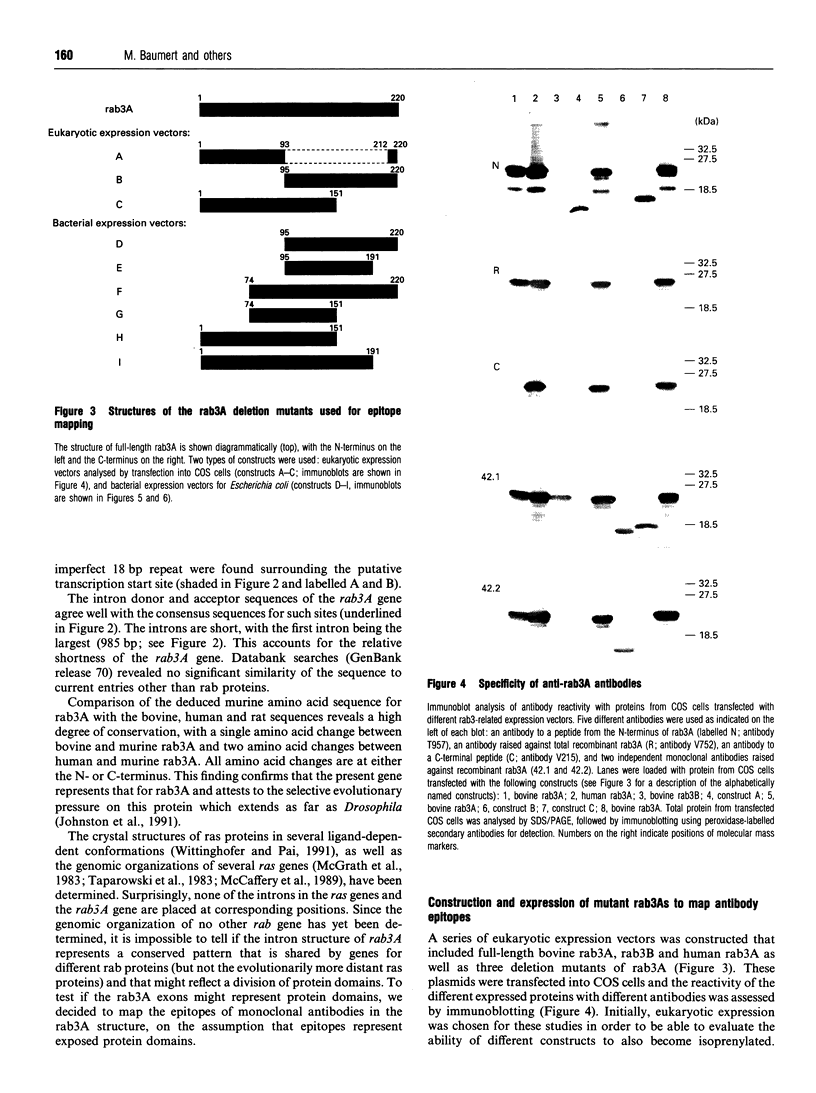
Rab3A is a neuronal low-molecular-mass GTP-binding protein that is modified post-translationally by two geranylgeranyl groups and specifically targeted to synaptic vesicles. We have now cloned and characterized the murine gene coding for rab3A. With a size of less than 8 kb including the promoter, the rab3A gene is relatively small. It contains five exons, the first of which is non-coding. The organization of the rab3A coding sequence into exons in the gene is different from that of ras proteins, the only other low-molecular-mass GTP-binding proteins with currently characterized gene structures. Nevertheless, the intron placement in the primary structure of rab3A may be indicative of a domain division of the protein, since each coding exon contains one of the four major conserved rab protein sequence motifs. The epitopes of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies to rab3A were mapped with the hypothesis that antibody epitopes might represent distinct exposed protein domains and correlate with exon structures. Two monoclonal antibodies, named 42.1 and 42.2, were found to recognize epitopes with a different degree of conservation between different rab3 isoforms. These epitopes were mapped to relatively short amino acid sequences corresponding to exons 4 and 5 respectively, whereas a polyclonal antibody recognized a complex epitope that required the presence of intact rab3A. Comparison of the sequence of rab3A with that of ras, whose crystal structure has been determined, revealed that the epitopes for the monoclonal antibodies correspond to regions in ras that are highly exposed. Taken together, these results suggest that exons 4 and 5 at least represent distinct exposed protein domains that also form major natural epitopes in rab3A.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E. Small GTP-binding proteins in vesicular transport. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Dec;15(12):473–477. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90301-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldini G., Hohl T., Lin H. Y., Lodish H. F. Cloning of a Rab3 isotype predominantly expressed in adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5049–5052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R. Do GTPases direct membrane traffic in secretion? Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):669–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90081-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Vingron M., Sander C., Simons K., Zerial M. Molecular cloning of YPT1/SEC4-related cDNAs from an epithelial cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6578–6585. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnsworth C. C., Kawata M., Yoshida Y., Takai Y., Gelb M. H., Glomset J. A. C terminus of the small GTP-binding protein smg p25A contains two geranylgeranylated cysteine residues and a methyl ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6196–6200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer von Mollard G., Mignery G. A., Baumert M., Perin M. S., Hanson T. J., Burger P. M., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. rab3 is a small GTP-binding protein exclusively localized to synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1988–1992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer von Mollard G., Mignery G. A., Baumert M., Perin M. S., Hanson T. J., Burger P. M., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. rab3 is a small GTP-binding protein exclusively localized to synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1988–1992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer von Mollard G., Südhof T. C., Jahn R. A small GTP-binding protein dissociates from synaptic vesicles during exocytosis. Nature. 1991 Jan 3;349(6304):79–81. doi: 10.1038/349079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. The cellular functions of small GTP-binding proteins. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):635–640. doi: 10.1126/science.2116664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn R., Schiebler W., Ouimet C., Greengard P. A 38,000-dalton membrane protein (p38) present in synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4137–4141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. A., Archer B. T., 3rd, Robinson K., Mignery G. A., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. rab3A attachment to the synaptic vesicle membrane mediated by a conserved polyisoprenylated carboxy-terminal sequence. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90078-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khosravi-Far R., Lutz R. J., Cox A. D., Conroy L., Bourne J. R., Sinensky M., Balch W. E., Buss J. E., Der C. J. Isoprenoid modification of rab proteins terminating in CC or CXC motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6264–6268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda K., Sakamoto C., Nakano O., Konda Y., Matozaki T., Wada K., Kasuga M., Mizoguchi A., Kikuchi A., Takai Y. Distribution of smg p25A and smg p21s, ras p21-like guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, in the rat stomach. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jan;262(1 Pt 1):G69–G73. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.1.G69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui Y., Kikuchi A., Kondo J., Hishida T., Teranishi Y., Takai Y. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of a GTP-binding protein family with molecular weights of 25,000 from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11071–11074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteoli M., Takei K., Cameron R., Hurlbut P., Johnston P. A., Südhof T. C., Jahn R., De Camilli P. Association of Rab3A with synaptic vesicles at late stages of the secretory pathway. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):625–633. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffery R. E., Coggins L. W., Doherty I., Kennedy I., O'Prey M., McColl L., Campo M. S. Multiple Harvey-ras genes in the bovine genome. Oncogene. 1989 Dec;4(12):1441–1448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Capon D. J., Smith D. H., Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H., Goeddel D. V., Levinson A. D. Structure and organization of the human Ki-ras proto-oncogene and a related processed pseudogene. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):501–506. doi: 10.1038/304501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignery G. A., Newton C. L., Archer B. T., 3rd, Südhof T. C. Structure and expression of the rat inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12679–12685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizoguchi A., Kim S., Ueda T., Takai Y. Tissue distribution of smg p25A, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein, studied by use of a specific monoclonal antibody. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):1438–1445. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90835-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson B., Chardin P., Touchot N., Zahraoui A., Tavitian A. Expression of the ras-related ralA, rho12 and rab genes in adult mouse tissues. Oncogene. 1988 Aug;3(2):231–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer S. R. GTP-binding proteins in intracellular transport. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;2(2):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90161-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Kikuchi A., Matsui Y., Teranishi Y., Takai Y. Tissue-specific expression of a novel GTP-binding protein (smg p25A) mRNA and its increase by nerve growth factor and cyclic AMP in rat pheochromocytoma PC-12 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 31;158(2):377–385. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Kikuchi A., Araki S., Hata Y., Isomura M., Kuroda S., Takai Y. Purification and characterization from bovine brain cytosol of a protein that inhibits the dissociation of GDP from and the subsequent binding of GTP to smg p25A, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2333–2337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Schmidt M. C., Berk A. J., Baltimore D. Transcriptional activation by Sp1 as directed through TATA or initiator: specific requirement for mammalian transcription factor IID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4509–4513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Russell D. W. The LDL receptor gene: a mosaic of exons shared with different proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):815–822. doi: 10.1126/science.2988123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Jahn R. Proteins of synaptic vesicles involved in exocytosis and membrane recycling. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):665–677. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90165-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taparowsky E., Shimizu K., Goldfarb M., Wigler M. Structure and activation of the human N-ras gene. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):581–586. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90390-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touchot N., Chardin P., Tavitian A. Four additional members of the ras gene superfamily isolated by an oligonucleotide strategy: molecular cloning of YPT-related cDNAs from a rat brain library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8210–8214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittinghofer A., Pai E. F. The structure of Ras protein: a model for a universal molecular switch. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Oct;16(10):382–387. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90156-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahraoui A., Touchot N., Chardin P., Tavitian A. The human Rab genes encode a family of GTP-binding proteins related to yeast YPT1 and SEC4 products involved in secretion. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12394–12401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]