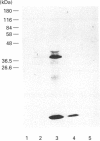
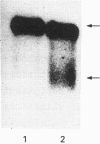
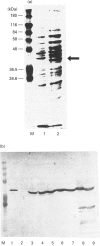
Abstract
Horse blood leucocytes contain an elastase inhibitor (HLEI) belonging to the serpin family. Poly(A)+RNA isolated from these cells was used to construct a cDNA library in lambda gt10, which was first screened with a synthetic degenerate oligonucleotide probe corresponding to the amino acid sequence of the reactive centre of the inhibitor. Three clones were obtained covering the entire coding region of the protein. Sequencing of these clones showed identity with the amino acid sequence obtained from Edman degradation of the elastase inhibitor. The coding sequence of the HLEI cDNA was cloned into the bacterial expression vector pKK233-2 and expressed in Escherichia coli cells. Transformed bacteria expressed significant amounts of the protein, which was immunoprecipitated with a specific anti-HLEI antiserum. Furthermore, HLEI expressed in bacteria inhibited the activity of elastase but not trypsin.
Full text
PDF



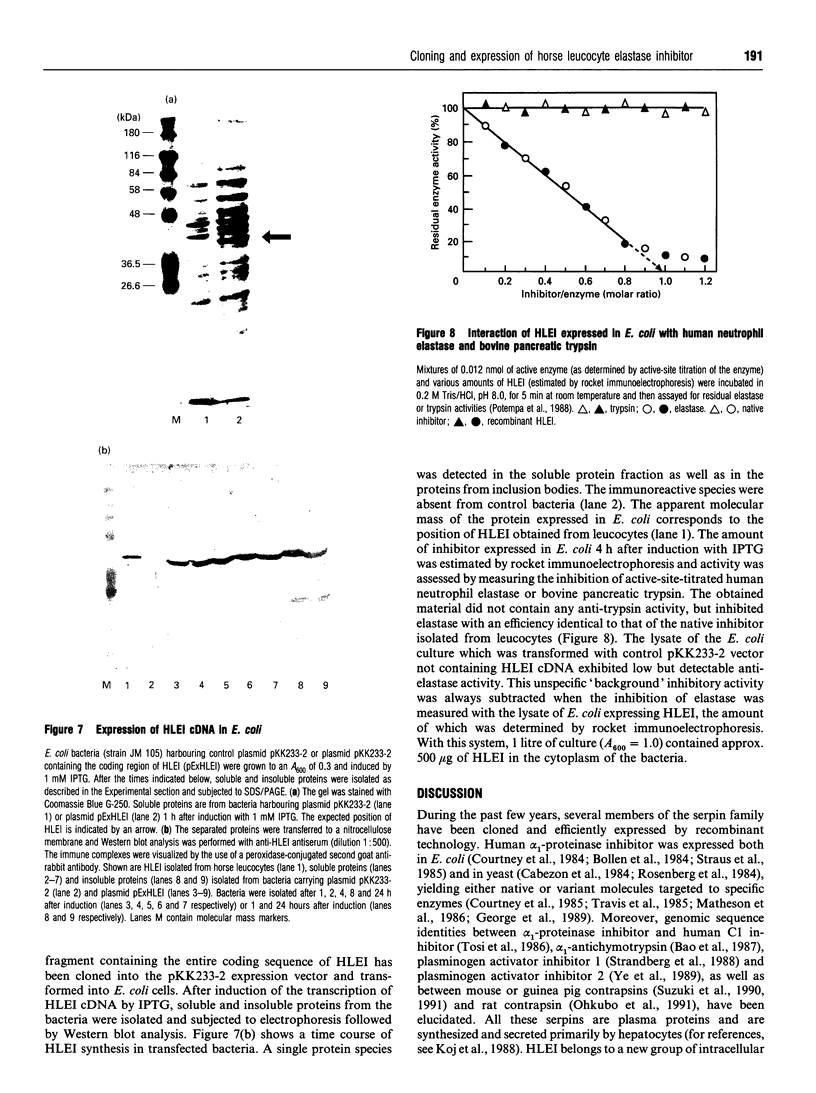


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bao J. J., Sifers R. N., Kidd V. J., Ledley F. D., Woo S. L. Molecular evolution of serpins: homologous structure of the human alpha 1-antichymotrypsin and alpha 1-antitrypsin genes. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7755–7759. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollen A., Loriau R., Herzog A., Hérion P. Expression of human alpha 1-antitrypsin in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 23;166(1):67–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabezón T., De Wilde M., Herion P., Loriau R., Bollen A. Expression of human alpha 1-antitrypsin cDNA in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6594–6598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney M., Buchwalder A., Tessier L. H., Jaye M., Benavente A., Balland A., Kohli V., Lathe R., Tolstoshev P., Lecocq J. P. High-level production of biologically active human alpha 1-antitrypsin in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):669–673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney M., Jallat S., Tessier L. H., Benavente A., Crystal R. G., Lecocq J. P. Synthesis in E. coli of alpha 1-antitrypsin variants of therapeutic potential for emphysema and thrombosis. Nature. 1985 Jan 10;313(5998):149–151. doi: 10.1038/313149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin A. A polyvalent proteinase inhibitor from horse-blood-leucocyte cytosol. Isolation, purification and some molecular parameters. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Mar 1;73(2):429–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin A., Hauck M. The interaction between chymotrypsin and horse leucocyte neutral proteinases inhibitor. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1981 Oct;362(10):1345–1349. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1981.362.2.1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin A., Koj A., Chudzik J. Isolation and some molecular parameters of elastase-like normal proteinases from horse blood leucocytes. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):389–396. doi: 10.1042/bj1530389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin A., Koj A. Proteinase inhibitors from horse plasma and leucocytes: properties and biological functions. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1986;45(11-12):1391–1396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin A., Potempa J., Kurdowska A., Pajdak W., Koj A. Comparison of antiproteolytic activities of alpha-1-proteinase inhibitors from the plasma of some mammalian species. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1986;83(2):375–380. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(86)90383-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin A., Potempa J., Silberring J. Alpha 2-macroglobulin from horse plasma. Purification, properties and interaction with certain serine proteinases. Biochem Int. 1984 Apr;8(4):589–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin A., Potempa J., Silberring J. Horse leucocyte proteinase-inhibitor system. Kinetic parameters of the inhibition reaction. Int J Biochem. 1985;17(4):509–513. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(85)90147-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin A., Travis J., Enghild J. J., Potempa J. Equine leukocyte elastase inhibitor. Primary structure and identification as a thymosin-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6576–6583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger T., Andus T., Bauer J., Northoff H., Ganter U., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Heinrich P. C. Cell-free-synthesized interleukin-6 (BSF-2/IFN-beta 2) exhibits hepatocyte-stimulating activity. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jul 15;175(1):181–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George P. M., Pemberton P., Bathurst I. C., Carrell R. W., Gibson H. L., Rosenberg S., Hallewell R. A., Barr P. J. Characterization of antithrombins produced by active site mutagenesis of human alpha 1-antitrypsin expressed in yeast. Blood. 1989 Feb;73(2):490–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerger H. Chronic pulmonary disease in the horse. Equine Vet J. 1973 Jan;5(1):26–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff A. Elastases and emphysema. Current assessment of the protease-antiprotease hypothesis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Aug;132(2):417–433. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.2.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koj A., Chudzik J., Dubin A. Substrate specificity and modifications of the active centre of elastase-like neutral proteinases from horse blood leucocytes. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):397–402. doi: 10.1042/bj1530397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koj A., Kurdowska A. Interaction of horse plasma antithrombin III and alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor with some serine proteinases. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1981;40(10-11):1561–1570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koj A., Magielska-Zero D., Kurdowska A., Bereta J. Proteinase inhibitors as acute phase reactants: regulation of synthesis and turnover. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1988;240:171–181. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-1057-0_21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüttgen A., Rose-John S., Möller C., Wroblowski B., Wollmer A., Müllberg J., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Heinrich P. C. Structure-function analysis of human interleukin-6. Evidence for the involvement of the carboxy-terminus in function. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 26;262(2):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheson N. R., Gibson H. L., Hallewell R. A., Barr P. J., Travis J. Recombinant DNA-derived forms of human alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. Studies on the alanine 358 and cysteine 358 substituted mutants. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10404–10409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkubo K., Ogata S., Misumi Y., Takami N., Ikehara Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of rat contrapsin-like protease inhibitor and related proteins. J Biochem. 1991 Feb;109(2):243–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potempa J. Cibacron Blue-induced modification of neutral proteinase from horse blood leukocytes. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1982;41(1):47–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potempa J., Dubin A., Watorek W., Travis J. An elastase inhibitor from equine leukocyte cytosol belongs to the serpin superfamily. Further characterization and amino acid sequence of the reactive center. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7364–7369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potempa J., Korzus E., Dubin A., Silberring J. Elastinolytic activity of horse leukocyte proteinases. Comparison with elastases from human leukocytes and porcine pancreas. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 1986;24(2):149–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potempa J., Wunderlich J. K., Travis J. Comparative properties of three functionally different but structurally related serpin variants from horse plasma. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 1;274(Pt 2):465–471. doi: 10.1042/bj2740465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold-O'Donnell E., Chin J., Alberts M. Sequence and molecular characterization of human monocyte/neutrophil elastase inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5635–5639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose-John S., Dietrich A., Marks F. Molecular cloning of mouse protein kinase C (PKC) cDNA from Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):465–471. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S., Barr P. J., Najarian R. C., Hallewell R. A. Synthesis in yeast of a functional oxidation-resistant mutant of human alpha-antitrypsin. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):77–80. doi: 10.1038/312077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. A., Siegfried W., Yoshimura K., Yoneyama K., Fukayama M., Stier L. E., Päkkö P. K., Gilardi P., Stratford-Perricaudet L. D., Perricaudet M. Adenovirus-mediated transfer of a recombinant alpha 1-antitrypsin gene to the lung epithelium in vivo. Science. 1991 Apr 19;252(5004):431–434. doi: 10.1126/science.2017680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiel X., Rose-John S., Dufhues G., Schooltink H., Gross V., Heinrich P. C. Microheterogeneity of human interleukin 6 synthesized by transfected NIH/3T3 cells: comparison with human monocytes, fibroblasts and endothelial cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Apr;20(4):883–887. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandberg L., Lawrence D., Ny T. The organization of the human-plasminogen-activator-inhibitor-1 gene. Implications on the evolution of the serine-protease inhibitor family. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 1;176(3):609–616. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus S. D., Fells G. A., Wewers M. D., Courtney M., Tessier L. H., Tolstoshev P., Lecocq J. P., Crystal R. G. Evaluation of recombinant DNA-directed E.coli produced alpha 1-antitrypsin as an anti-neutrophil elastase for potential use as replacement therapy of alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 15;130(3):1177–1184. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91739-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Yamamoto K., Sinohara H. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of full-length cDNA coding for mouse contrapsin. J Biochem. 1990 Sep;108(3):344–346. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Yoshida K., Honda E., Sinohara H. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of cDNAs coding for guinea pig alpha 1-antiproteinases S and F and contrapsin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):928–932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi M., Duponchel C., Bourgarel P., Colomb M., Meo T. Molecular cloning of human C1 inhibitor: sequence homologies with alpha 1-antitrypsin and other members of the serpins superfamily. Gene. 1986;42(3):265–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90230-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J., Owen M., George P., Carrell R., Rosenberg S., Hallewell R. A., Barr P. J. Isolation and properties of recombinant DNA produced variants of human alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4384–4389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Shine J., Chirgwin J., Pictet R., Tischer E., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Rat insulin genes: construction of plasmids containing the coding sequences. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1313–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.325648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye R. D., Ahern S. M., Le Beau M. M., Lebo R. V., Sadler J. E. Structure of the gene for human plasminogen activator inhibitor-2. The nearest mammalian homologue of chicken ovalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5495–5502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Fellenberg R., Kohler L., Grünig G., Pellegrini A. Comparison of neutrophil elastases and of neutrophil protease inhibitors in the horse and man. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Dec;46(12):2480–2484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]