Abstract
The 9 kDa calcium-binding protein, calbindin9kDa, was found to be soluble in 7% (v/v) perchloric acid. Calbindin9kDa was easily purified from rat duodenum in 1 day with perchloric acid precipitation followed by reverse-phase h.p.l.c. The yield was 21.4 +/- 2.3 nmol/g wet weight of tissue (mean +/- S.E.M.; n = 3) from normally fed 7-8-week-old rats (approx. 70% recovery). The purification was also effective with rabbit duodenum calbindin9kDa, but not with various other EF-hand calcium-binding proteins tested in the rat. Several criteria (h.p.l.c., u.v. spectrum, denaturing two-dimensional PAGE, N-terminal sequencing) indicated that the rat calbindin9kDa was purified to homogeneity and was not affected by proteolysis. High-affinity calcium-binding properties were retained and no evidence of isoforms or charge modification was observed. Residue 59, identified as Asn (not Asp as previously reported), was fully amidated. When adopted as a microassay with isocratic h.p.l.c., the perchloric acid procedure enabled rapid (less than 6 min) and direct (peptide bond absorbance) quantification of less than 1 pmol of calbindin9kDa. This new approach to purification and assay will be of particular utility for investigations of calbindin9kDa in previously intractable low-abundance sources (e.g. cultured cells).
Full text
PDF
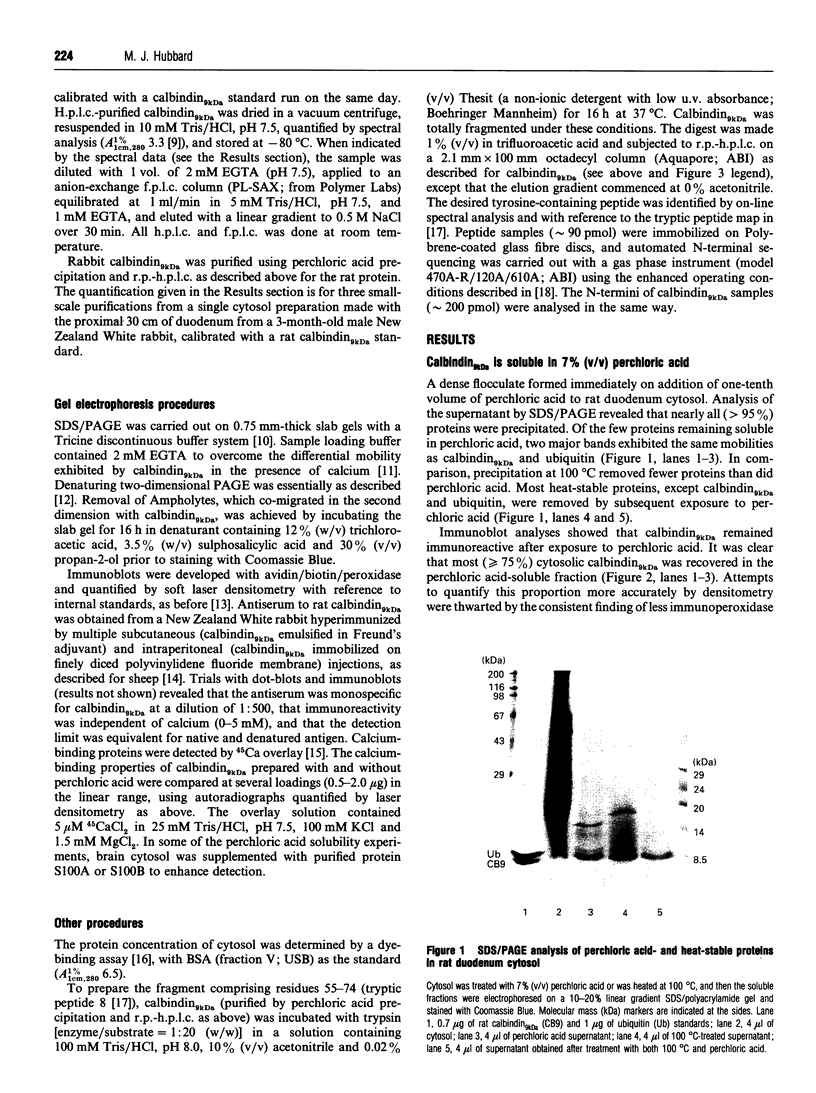


Images in this article
Selected References
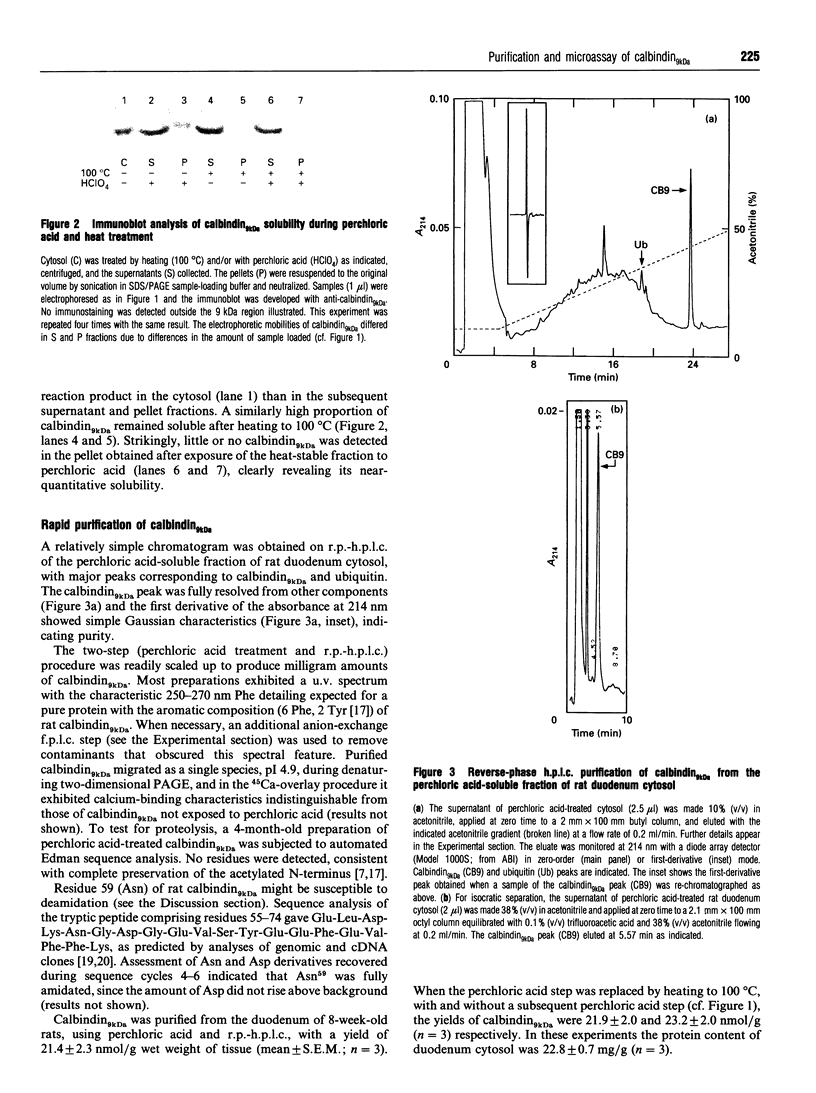
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akke M., Drakenberg T., Chazin W. J. Three-dimensional solution structure of Ca(2+)-loaded porcine calbindin D9k determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 4;31(4):1011–1020. doi: 10.1021/bi00119a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindels R. J., Timmermans J. A., Hartog A., Coers W., van Os C. H. Calbindin-D9k and parvalbumin are exclusively located along basolateral membranes in rat distal nephron. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1991 Dec;2(6):1122–1129. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V261122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns M. E., Fausto A., Avioli L. V. Placental calcium binding protein in rats. Apparent identity with vitamin D-dependent calcium binding protein from rat intestine. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3186–3190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chazin W. J., Kördel J., Thulin E., Hofmann T., Drakenberg T., Forsén S. Identification of an isoaspartyl linkage formed upon deamidation of bovine calbindin D9k and structural characterization by 2D 1H NMR. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8646–8653. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christakos S., Gabrielides C., Rhoten W. B. Vitamin D-dependent calcium binding proteins: chemistry, distribution, functional considerations, and molecular biology. Endocr Rev. 1989 Feb;10(1):3–26. doi: 10.1210/edrv-10-1-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgarno D. C., Levine B. A., Williams R. J., Fullmer C. S., Wasserman R. H. Proton-NMR studies of the solution conformations of vitamin-D-induced bovine intestinal calcium-binding protein. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Dec 15;137(3):523–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darwish H. M., Krisinger J., Strom M., DeLuca H. F. Molecular cloning of the cDNA and chromosomal gene for vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein of rat intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6108–6111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Chau V. Ubiquitination. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:25–69. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullmer C. S., Wasserman R. H. The amino acid sequence of bovine intestinal calcium-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5669–5674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleason W. A., Jr, Lankford G. L. Rat intestinal calcium-binding protein: rapid purification with AG MP-1 ion-exchange chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1981 Sep 15;116(2):256–263. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90353-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser D. F., Harrington M. G., Hochstrasser A. C., Miller M. J., Merril C. R. Methods for increasing the resolution of two-dimensional protein electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1988 Sep;173(2):424–435. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90209-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann T., Kawakami M., Hitchman A. J., Harrison J. E., Dorrington K. J. The amino acid sequence of porcine intestinal calcium-binding protein. Can J Biochem. 1979 Jun;57(6):737–748. doi: 10.1139/o79-092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard M. J., Cohen P. Targeting subunits for protein phosphatases. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:414–427. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard M. J., Klee C. B. Characterization of a high-affinity monoclonal antibody to calcineurin whose epitope defines a new structural domain of calcineurin A. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Nov 6;185(2):411–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. F., Yates J. R., 3rd, Shabanowitz J., Bruns M. E., Bruns D. E. Amino acid sequence analysis of two mouse calbindin-D9k isoforms by tandem mass spectrometry. Protein modification by internal insertion of a single amino acid. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6580–6586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Christakos S. Differential regulation by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 of calbindin-D9k and calbindin-D28k gene expression in mouse kidney. Endocrinology. 1991 Jun;128(6):2844–2852. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-6-2844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longbottom D., Sallenave J. M., van Heyningen V. Subunit structure of calgranulins A and B obtained from sputum, plasma, granulocytes and cultured epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 8;1120(2):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(92)90273-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacManus J. P., Watson D. C., Yaguchi M. The purification and complete amino acid sequence of the 9000-Mr Ca2+-binding protein from rat placenta. Identity with the vitamin D-dependent intestinal Ca2+-binding protein. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 15;235(2):585–595. doi: 10.1042/bj2350585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mach H., Middaugh C. R., Lewis R. V. Statistical determination of the average values of the extinction coefficients of tryptophan and tyrosine in native proteins. Anal Biochem. 1992 Jan;200(1):74–80. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90279-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Mikawa T., Ebashi S. Detection of calcium binding proteins by 45Ca autoradiography on nitrocellulose membrane after sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis. J Biochem. 1984 Feb;95(2):511–519. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathieu C. L., Mills S. E., Burnett S. H., Cloney D. L., Bruns D. E., Bruns M. E. The presence and estrogen control of immunoreactive calbindin-D9k in the fallopian tube of the rat. Endocrinology. 1989 Nov;125(5):2745–2750. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-5-2745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perret C., Lomri N., Gouhier N., Auffray C., Thomasset M. The rat vitamin-D-dependent calcium-binding protein (9-kDa CaBP) gene. Complete nucleotide sequence and structural organization. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Feb 15;172(1):43–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13853.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche C., Bellaton C., Pansu D., Miller A., 3rd, Bronner F. Localization of vitamin D-dependent active Ca2+ transport in rat duodenum and relation to CaBP. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 1):G314–G320. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.3.G314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempst P., Riviere L. Examination of automated polypeptide sequencing using standard phenyl isothiocyanate reagent and subpicomole high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis. Anal Biochem. 1989 Dec;183(2):290–300. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90482-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomasset M., Parkes C. O., Cuisinier-Gleizes P. Rat calcium-binding proteins: distribution, development, and vitamin D dependence. Am J Physiol. 1982 Dec;243(6):E483–E488. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.243.6.E483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendt B., Hofmann T., Martin S. R., Bayley P., Brodin P., Grundström T., Thulin E., Linse S., Forsén S. Effect of amino acid substitutions and deletions on the thermal stability, the pH stability and unfolding by urea of bovine calbindin D9k. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;175(3):439–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson K. D., Cox M. J., O'Connor L. B., Shapira R. Structure and activities of a variant ubiquitin sequence from bakers' yeast. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):4999–5004. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]