Abstract
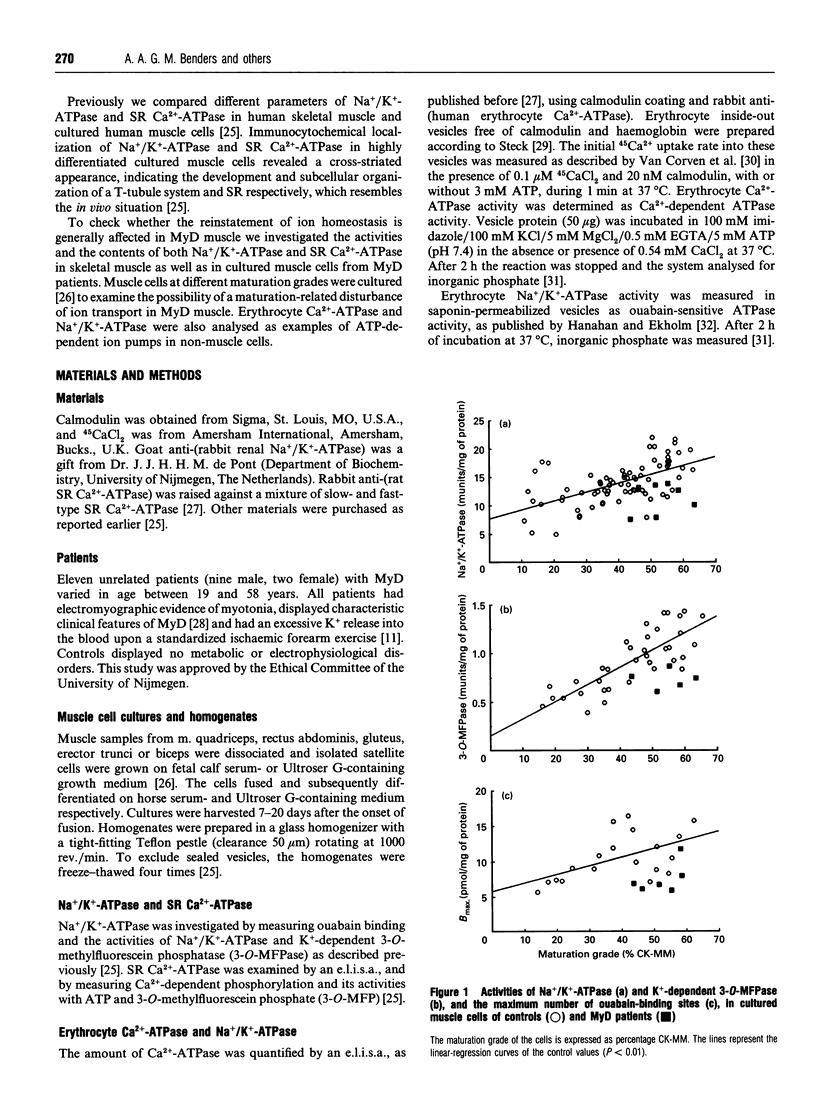
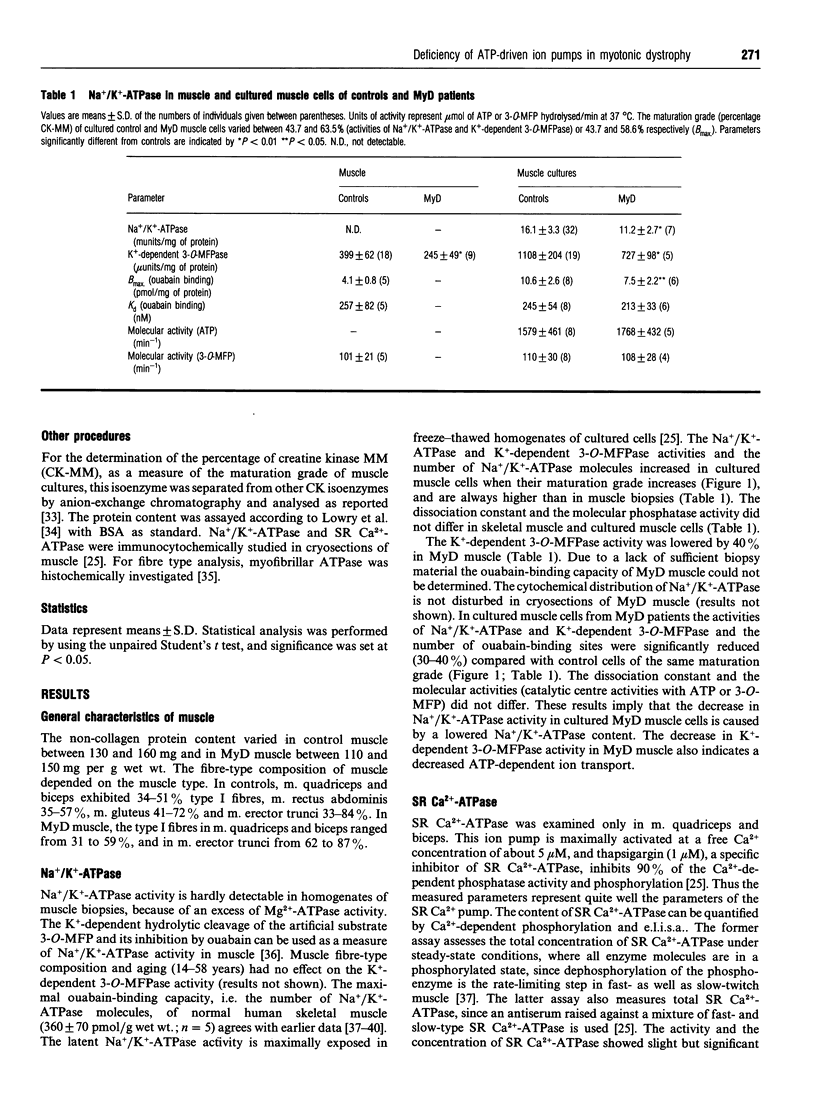
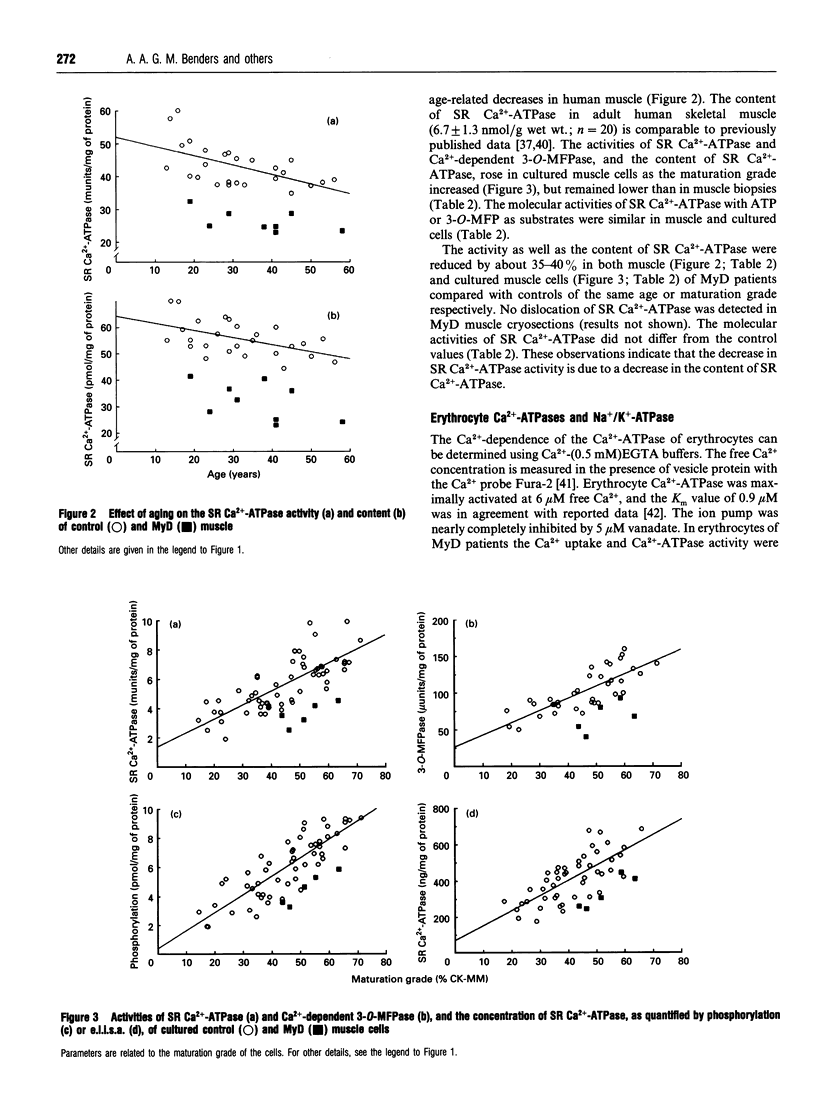
Since defective regulation of ion transport could initiate or contribute to the abnormal cellular function in myotonic dystrophy (MyD), Na+/K(+)-ATPase and sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca(2+)-ATPase were examined in skeletal muscle and cultured skeletal muscle cells of controls and MyD patients. Na+/K(+)-ATPase was investigated by measuring ouabain binding and the activities of Na+/K(+)-ATPase and K(+)-dependent 3-O-methylfluorescein phosphate (3-O-MFPase). SR Ca(2+)-ATPase was analysed by e.l.i.s.a., Ca(2+)-dependent phosphorylation and its activities with ATP and 3-O-methylfluorescein phosphatase (3-O-MFP). In MyD muscle the K(+)-dependent 3-O-MFPase activity and the activity and concentration of SR Ca(2+)-ATPase were decreased by 40%. In cultured muscle cells from MyD patients the activities as well as the concentration of both Na+/K(+)-ATPase and SR Ca(2+)-ATPase were reduced by about 30-40%. The ouabain-binding constant and the molecular activities, i.e. catalytic-centre activities with ATP or 3-O-MFP, of Na+/K(+)-ATPase and SR Ca(2+)-ATPase were similar in muscle as well as in cultured cells from both controls and MyD patients. Thus the decreased activity of both ATPases in MyD muscle is caused by a reduction in the number of their molecules. To check whether the deficiency of ATP-dependent ion pumps is a general feature of the pathology of MyD, we examined erythrocytes from the same patients. In these cells the Ca2+ uptake rate and the Ca(2+)-ATPase activity were lower than in controls, but the Ca(2+)-ATPase concentration was normal. Thus the reduced Ca(2+)-ATPase activity is caused by a decrease in the molecular activity of the ion pump. The Na+/K(+)-ATPase activity is also lower in erythrocytes of MyD patients. It is concluded that the observed alterations in ion pumps may contribute to the pathological phenomena in the muscle and other tissues in patients with MyD.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benders A. A., van Kuppevelt T. H., Oosterhof A., Veerkamp J. H. The biochemical and structural maturation of human skeletal muscle cells in culture: the effect of the serum substitute Ultroser G. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Aug;195(2):284–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90375-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benders A. G., van Kuppevelt T. H., Oosterhof A., Wevers R. A., Veerkamp J. H. Adenosine triphosphatases during maturation of cultured human skeletal muscle cells and in adult human muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Nov 23;1112(1):89–98. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90258-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borg J., Edström L., Butler-Browne G. S., Thornell L. E. Muscle fibre type composition, motoneuron firing properties, axonal conduction velocity and refractory period for foot extensor motor units in dystrophia myotonica. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987 Aug;50(8):1036–1044. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.50.8.1036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E. Calcium pump of the plasma membrane. Physiol Rev. 1991 Jan;71(1):129–153. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E. Intracellular calcium homeostasis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:395–433. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T. Regulation of active Na+-K+ transport in skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev. 1986 Jul;66(3):542–580. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1986.66.3.542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desnuelle C., Lombet A., Serratrice G., Lazdunski M. Sodium channel and sodium pump in normal and pathological muscles from patients with myotonic muscular dystrophy and lower motor neuron impairment. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):358–367. doi: 10.1172/JCI110459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durelli L., Mutani R., Fassio F., Delsedime M. The effects of the increase of arterial potassium upon the excitability of normal and dystrophic myotonic muscles in man. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Sep;55(3):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90123-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edström L., Wroblewski R. Intracellular elemental composition of single muscle fibres in muscular dystrophy and dystrophia myotonica. Acta Neurol Scand. 1989 Nov;80(5):419–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1989.tb03903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everts M. E., Andersen J. P., Clausen T., Hansen O. Quantitative determination of Ca2+-dependent Mg2+-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle biopsies. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 1;260(2):443–448. doi: 10.1042/bj2600443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everts M. E., Ording H., Hansen O., Nielsen P. A. Ca(2+)-ATPase and Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase content in skeletal muscle from malignant hyperthermia patients. Muscle Nerve. 1992 Feb;15(2):162–167. doi: 10.1002/mus.880150206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J., Garner S., McComas A. J. Abnormal M-wave responses during exercise in myotonic muscular dystrophy: a Na(+)--K+ pump defect? Muscle Nerve. 1991 Jan;14(1):79–84. doi: 10.1002/mus.880140113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer S., Inui M. Biochemistry and biophysics of excitation-contraction coupling. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:333–364. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke C., Hatt H., Iaizzo P. A., Lehmann-Horn F. Characteristics of Na+ channels and Cl- conductance in resealed muscle fibre segments from patients with myotonic dystrophy. J Physiol. 1990 Jun;425:391–405. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Pizzuti A., Fenwick R. G., Jr, King J., Rajnarayan S., Dunne P. W., Dubel J., Nasser G. A., Ashizawa T., de Jong P. An unstable triplet repeat in a gene related to myotonic muscular dystrophy. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1256–1258. doi: 10.1126/science.1546326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruener R., Stern L. Z., Markovitz D., Gerdes C. Electrophysiologic properties of intercostal muscle fibers in human neuromuscular diseases. Muscle Nerve. 1979 May-Jun;2(3):165–172. doi: 10.1002/mus.880020303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. J., Ekholm J. E. The expression of optimum ATPase activities in human erythrocytes. A comparison of different lytic procedures. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Apr 15;187(1):170–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson A. J., Huff M. W., Wright C. G., Silver M. M., Lo T. C., Banerjee D. The role of insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of myotonic muscular dystrophy. Brain. 1987 Apr;110(Pt 2):469–488. doi: 10.1093/brain/110.2.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs A. E., Benders A. A., Oosterhof A., Veerkamp J. H., van Mier P., Wevers R. A., Joosten E. M. The calcium homeostasis and the membrane potential of cultured muscle cells from patients with myotonic dystrophy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Nov 14;1096(1):14–19. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(90)90006-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen G., Mahadevan M., Amemiya C., Wormskamp N., Segers B., Hendriks W., O'Hoy K., Baird S., Sabourin L., Lennon G. Characterization of the myotonic dystrophy region predicts multiple protein isoform-encoding mRNAs. Nat Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):261–266. doi: 10.1038/ng0792-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennekens F. G., ten Kate L. P., de Visser M., Wintzen A. R. Diagnostic criteria for Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy and myotonic dystrophy. Neuromuscul Disord. 1991;1(6):389–391. doi: 10.1016/0960-8966(91)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakehi T., Kuzuya H., Kosaki A., Yamada K., Yoshimasa Y., Okamoto M., Nishimura H., Nishitani H., Saida K., Kuno S. Binding activity and autophosphorylation of the insulin receptor from patients with myotonic dystrophy. J Lab Clin Med. 1990 Jun;115(6):688–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsen K., Bjerregaard P., Richter E. A., Thomsen P. E., Nørgaard A. Na+,K+-ATPase concentration in rodent and human heart and skeletal muscle: apparent relation to muscle performance. Cardiovasc Res. 1988 Feb;22(2):95–100. doi: 10.1093/cvr/22.2.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsen K., Nørgaard A., Hau C. Human skeletal muscle Na, K-ATPase concentration quantified by 3H-ouabain binding to intact biopsies before and after moderate physical conditioning. Int J Sports Med. 1990 Aug;11(4):304–307. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1024812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klitgaard H., Ausoni S., Damiani E. Sarcoplasmic reticulum of human skeletal muscle: age-related changes and effect of training. Acta Physiol Scand. 1989 Sep;137(1):23–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1989.tb08717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klitgaard H., Clausen T. Increased total concentration of Na-K pumps in vastus lateralis muscle of old trained human subjects. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Dec;67(6):2491–2494. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.6.2491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi T., Askanas V., Saito K., Engel W. K., Ishikawa K. Abnormalities of aneural and innervated cultured muscle fibers from patients with myotonic atrophy (dystrophy). Arch Neurol. 1990 Aug;47(8):893–896. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1990.00530080077014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konagaya Y., Konagaya M., Mano Y., Takayanagi T., Tomita A. Evaluation of renal parathyroid hormone receptor function in myotonic dystrophy. J Neurol Sci. 1985 Oct;70(3):339–346. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(85)90175-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara T., Yuasa T., Ohno T., Yamamuro M., Miyatake T. Study on the erythrocytes from myotonic dystrophy with multi-nuclear NMR. Muscle Nerve. 1991 Jan;14(1):57–63. doi: 10.1002/mus.880140110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthra M. G., Stern L. Z., Kim H. D. (Ca++ + Mg++)-ATPase of red cells in Duchenne and myotonic dystrophy: effect of soluble cytoplasmic activator. Neurology. 1979 Jun;29(6):835–841. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.6.835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan M., Tsilfidis C., Sabourin L., Shutler G., Amemiya C., Jansen G., Neville C., Narang M., Barceló J., O'Hoy K. Myotonic dystrophy mutation: an unstable CTG repeat in the 3' untranslated region of the gene. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1253–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.1546325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechler F., Mastaglia F. L. Vascular adrenergic receptor responses in skeletal muscle in myotonic dystrophy. Ann Neurol. 1981 Feb;9(2):157–162. doi: 10.1002/ana.410090209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mege J. L., Pouget J., Capo C., Andre P., Benoliel A. M., Serratrice G., Bongrand P. Myotonic dystrophy: defective oxidative burst of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 Sep;44(3):180–186. doi: 10.1002/jlb.44.3.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merickel M., Gray R., Chauvin P., Appel S. Cultured muscle from myotonic muscular dystrophy patients: altered membrane electrical properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):648–652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishra S. K., Chetty S., Kataoka M. Abnormal insulin receptor binding in cultured monocytes in myotonic muscular dystrophy. Biochem Med Metab Biol. 1992 Apr;47(2):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0885-4505(92)90020-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nørgaard A., Kjeldsen K., Hansen O. (Na+ + K+)-ATPase activity of crude homogenates of rat skeletal muscle as estimated from their K+-dependent 3-O-methylfluorescein phosphatase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Mar 14;770(2):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90131-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono S., Kurisaki H., Inouye K., Mannen T. "Ragged-red" fibres in myotonic dystrophy. J Neurol Sci. 1986 Jul;74(2-3):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(86)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poggi P., Marchetti C., Scelsi R. Automatic morphometric analysis of skeletal muscle fibers in the aging man. Anat Rec. 1987 Jan;217(1):30–34. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092170106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raess B. U., Record D. M. Inhibition of erythrocyte Ca2(+)-pump by Ca2+ antagonists. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Dec 1;40(11):2549–2555. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90098-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud J. F., Desnuelle C., Schmid-Antomarchi H., Hugues M., Serratrice G., Lazdunski M. Expression of apamin receptor in muscles of patients with myotonic muscular dystrophy. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):678–680. doi: 10.1038/319678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüdel R., Lehmann-Horn F. Membrane changes in cells from myotonia patients. Physiol Rev. 1985 Apr;65(2):310–356. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1985.65.2.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüdel R., Ruppersberg J. P., Spittelmeister W. Abnormalities of the fast sodium current in myotonic dystrophy, recessive generalized myotonia, and adynamia episodica. Muscle Nerve. 1989 Apr;12(4):281–287. doi: 10.1002/mus.880120405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnat H. B., Silbert S. W. Maturational arrest of fetal muscle in neonatal myotonic dystrophy. A pathologic study of four cases. Arch Neurol. 1976 Jul;33(7):466–474. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1976.00500070008002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somer H., Mäki T., Härkönen M. Beta-adrenergic system in myotonic dystrophy. J Neurol Sci. 1992 Sep;111(2):214–217. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(92)90072-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans J. A., Kaune R., Bindels R. J., van Os C. H. Quantification of Ca(2+)-ATPases in porcine duodenum. Effects of 1,25(OH)2D3 deficiency. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 18;1065(2):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90228-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh F. S., Moore S. E., Dickson J. G. Expression of membrane antigens in myotonic dystrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 Jan;51(1):136–138. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.51.1.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wevers R. A., Joosten M. G., van de Biezenbos J. B., Theewes G. M., Veerkamp J. H. Excessive plasma K+ increase after ischemic exercise in myotonic muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve. 1990 Jan;13(1):27–32. doi: 10.1002/mus.880130107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Corven E. J., Roche C., van Os C. H. Distribution of Ca2+-ATPase, ATP-dependent Ca2+-transport, calmodulin and vitamin D-dependent Ca2+-binding protein along the villus-crypt axis in rat duodenum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Nov 7;820(2):274–282. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90121-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


