Abstract
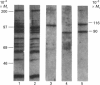
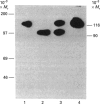
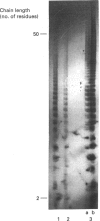
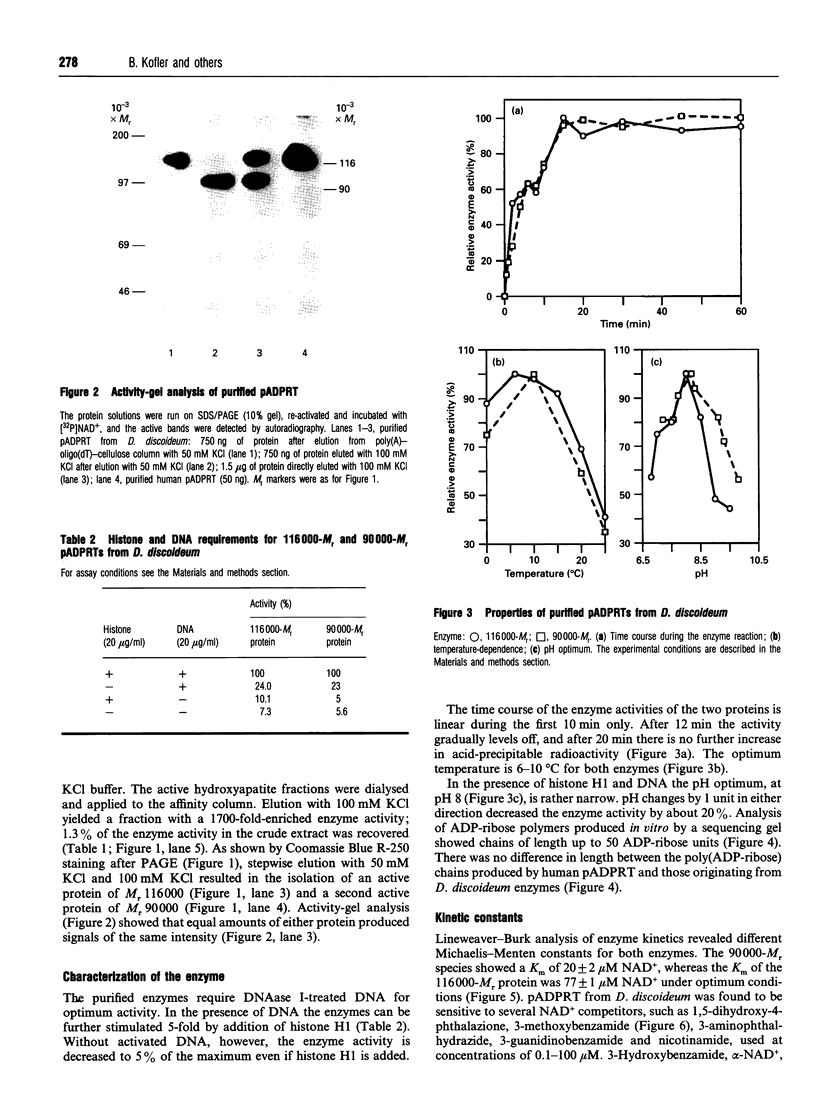
A novel affinity-purification scheme based on the tight binding of NAD+:ADP-ribosyltransferase (polymerizing) [pADPRT; poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase; EC 2.4.2.30] to single-strand nicks in DNA, single-stranded patches and DNA ends has been developed to facilitate the purification of this enzyme from the lower eukaryote Dictyostelium discoideum. Two homogeneous forms of the enzyme, with M(r) values of 116,000 and 90,000, were prepared from D. discoideum by using poly(A) hybridized to oligo(dT)-cellulose as affinity material. The Km is 20 microM NAD+ for the 90,000-M(r) protein and 77 microM NAD+ for the 116,000-M(r) protein. The optimum conditions for the enzyme activity in vitro are 6-10 degrees C and pH 8. The time course is linear during the first 10 min of the reaction only. As in enzymes of higher eukaryotes, the activity is dependent on DNA and histone H1 and is inhibited by 3-methoxybenzamide, nicotinamide, theophylline, caffeine and thymidine.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benjamin R. C., Gill D. M. Poly(ADP-ribose) synthesis in vitro programmed by damaged DNA. A comparison of DNA molecules containing different types of strand breaks. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10502–10508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtscher H. J., Auer B., Klocker H., Schweiger M., Hirsch-Kauffmann M. Isolation of ADP-ribosyltransferase by affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90410-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtscher H. J., Klocker H., Schneider R., Auer B., Hirsch-Kauffmann M., Schweiger M. ADP-ribosyltransferase from Helix pomatia. Purification and characterization. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 15;248(3):859–864. doi: 10.1042/bj2480859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtscher H. J., Schneider R., Klocker H., Auer B., Hirsch-Kauffmann M., Schweiger M. ADP-ribosyltransferase is highly conserved: purification and characterization of ADP-ribosyltransferase from a fish and its comparison with the human enzyme. J Comp Physiol B. 1987;157(5):567–572. doi: 10.1007/BF00700976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter S. G., Berger N. A. Purification and characterization of human lymphoid poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose) polymerase. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5475–5481. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesarone C. F., Scarabelli L., Scovassi A. I., Izzo R., Menegazzi M., Carcereri De Prati A., Orunesu M., Bertazzoni U. Changes in activity and mRNA levels of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase during rat liver regeneration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Oct 23;1087(2):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90211-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colon-Otero G., Sando J. J., Sims J. L., McGrath E., Jensen D. E., Quesenberry P. J. Inhibition of hemopoietic growth factor-induced proliferation by adenosine diphosphate-ribosylation inhibitors. Blood. 1987 Sep;70(3):686–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exley R., Gordon J., Clemens M. J. Induction of B-cell differentiation antigens in interferon- or phorbol ester-treated Daudi cells is impaired by inhibitors of ADP-ribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6467–6470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golderer G., Schneider R., Auer B., Loidl P., Gröbner P. ADP-ribosylation in isolated nuclei of Physarum polycephalum. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):859–867. doi: 10.1042/bj2530859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gradwohl G., Ménissier de Murcia J. M., Molinete M., Simonin F., Koken M., Hoeijmakers J. H., de Murcia G. The second zinc-finger domain of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase determines specificity for single-stranded breaks in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2990–2994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Shizuta Y., Hayaishi O. Purification and characterization of poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3647–3651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J., Patel B. N., Skidmore C. J. Benzamides can stimulate as well as inhibit the activity of nuclear ADP-ribosyltransferase. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Nov;9(11):2023–2026. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.11.2023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser P., Auer B., Schweiger M. Inhibition of cell proliferation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by expression of human NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase requires the DNA binding domain ("zinc fingers"). Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Mar;232(2):231–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00280001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameshita I., Matsuda M., Nishikimi M., Ushiro H., Shizuta Y. Reconstitution and poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of proteolytically fragmented poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3863–3868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosaki T., Ushiro H., Mitsuuchi Y., Suzuki S., Matsuda M., Matsuda Y., Katunuma N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Hirose T. Primary structure of human poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase as deduced from cDNA sequence. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):15990–15997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küpper J. H., de Murcia G., Bürkle A. Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation by overexpressing the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase DNA-binding domain in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18721–18724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb L. A. Purification and properties of deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from nuclei of sea urchin embryos. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 10;244(7):1672–1681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNerney R., Tavasolli M., Shall S., Brazinski A., Johnstone A. Changes in mRNA levels of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase during activation of human lymphocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Nov 2;1009(2):185–187. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panzeter P. L., Althaus F. R. High resolution size analysis of ADP-ribose polymers using modified DNA sequencing gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2194–2194. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickwood D., Osman M. S. Characterisation of poly(ADP-Rib) polymerase activity in nuclei from the slime mould Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;27(2):79–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00218351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh M. S., Lindahl T. Role of poly(ADP-ribose) formation in DNA repair. Nature. 1992 Mar 26;356(6367):356–358. doi: 10.1038/356356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R., Auer B., Kühne C., Herzog H., Klocker H., Burtscher H. J., Hirsch-Kauffmann M., Wintersberger U., Schweiger M. Isolation of a cDNA clone for human NAD+: protein ADP-ribosyltransferase. Eur J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;44(2):302–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweiger M., Auer B., Burtscher H. J., Hirsch-Kauffmann M., Klocker H., Schneider R. The Fritz-Lipmann lecture. DNA repair in human cells. Biochemistry of the hereditary diseases Fanconi's anaemia and Cockayne syndrome. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jun 1;165(2):235–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11433.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scovassi A. I., Izzo R., Franchi E., Bertazzoni U. Structural analysis of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase in higher and lower eukaryotes. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Aug 15;159(1):77–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09835.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scovassi A. I., Stefanini M., Bertazzoni U. Catalytic activities of human poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase from normal and mutagenized cells detected after sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10973–10977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonin F., Briand J. P., Muller S., de Murcia G. Detection of poly(ADP ribose) polymerase in crude extracts by activity-blot. Anal Biochem. 1991 Jun;195(2):226–231. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90321-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surowy C. S., Berger N. A. Diadenosine 5', 5"'-P1,P4-tetraphosphate stimulates processing of adp-ribosylated poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):579–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surowy C. S., Berger N. A. Proteolysis of poly(ADPribose) polymerase by a pyrophosphate- and nucleotide-stimulated system dependent on two different classes of proteinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Nov 8;832(1):33–45. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90171-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiro H., Yokoyama Y., Shizuta Y. Purification and characterization of poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase from human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2352–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts D. J., Ashworth J. M. Growth of myxameobae of the cellular slime mould Dictyostelium discoideum in axenic culture. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(2):171–174. doi: 10.1042/bj1190171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Murcia G., Huletsky A., Poirier G. G. Modulation of chromatin structure by poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation. Biochem Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;66(6):626–635. doi: 10.1139/o88-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]