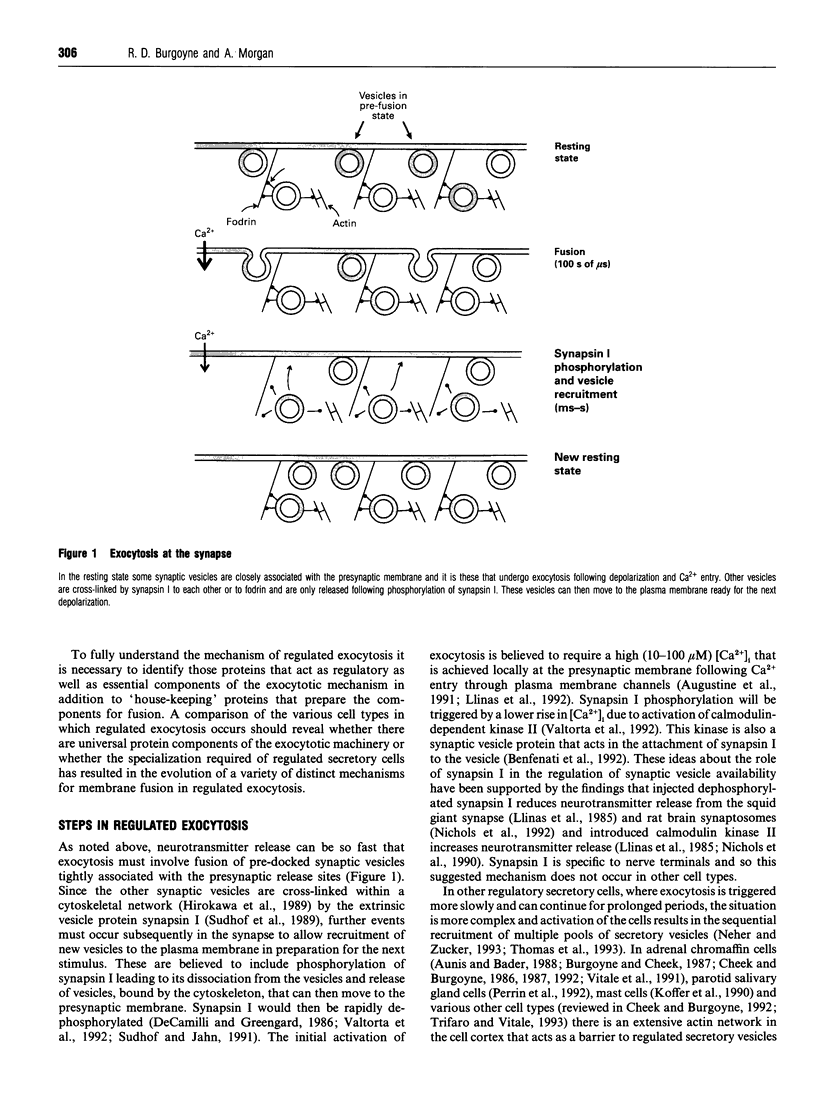
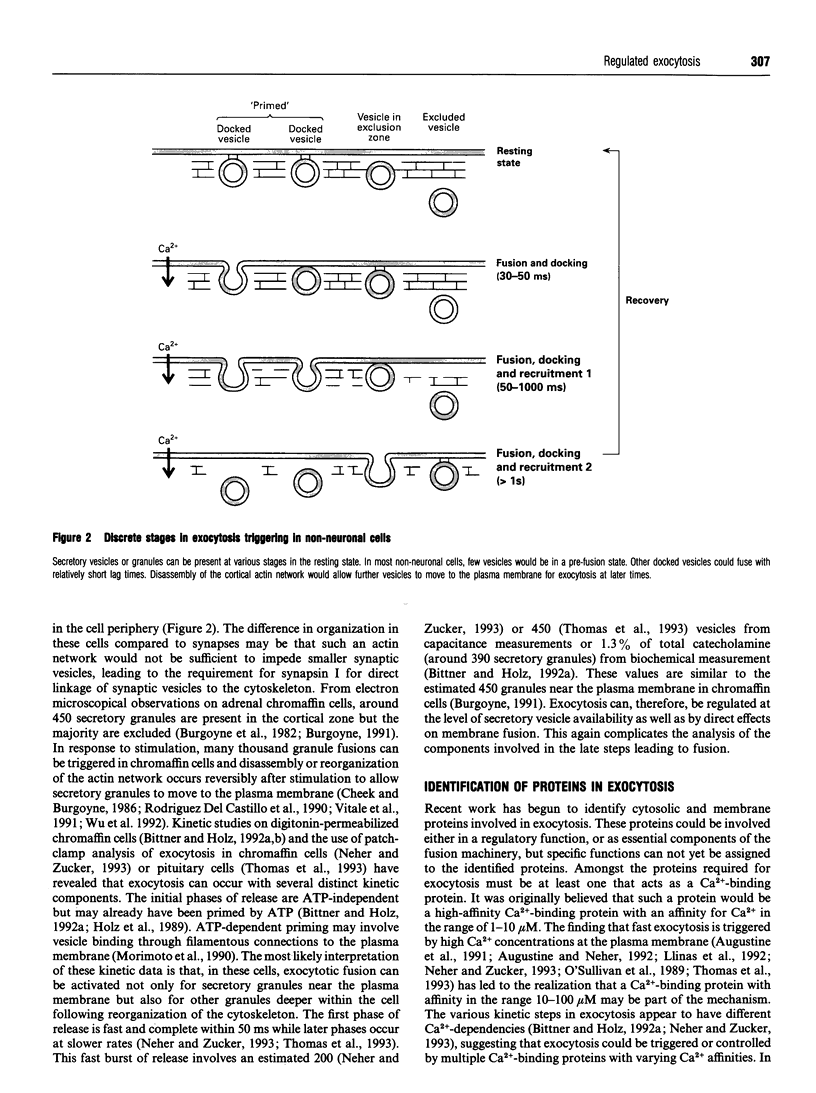
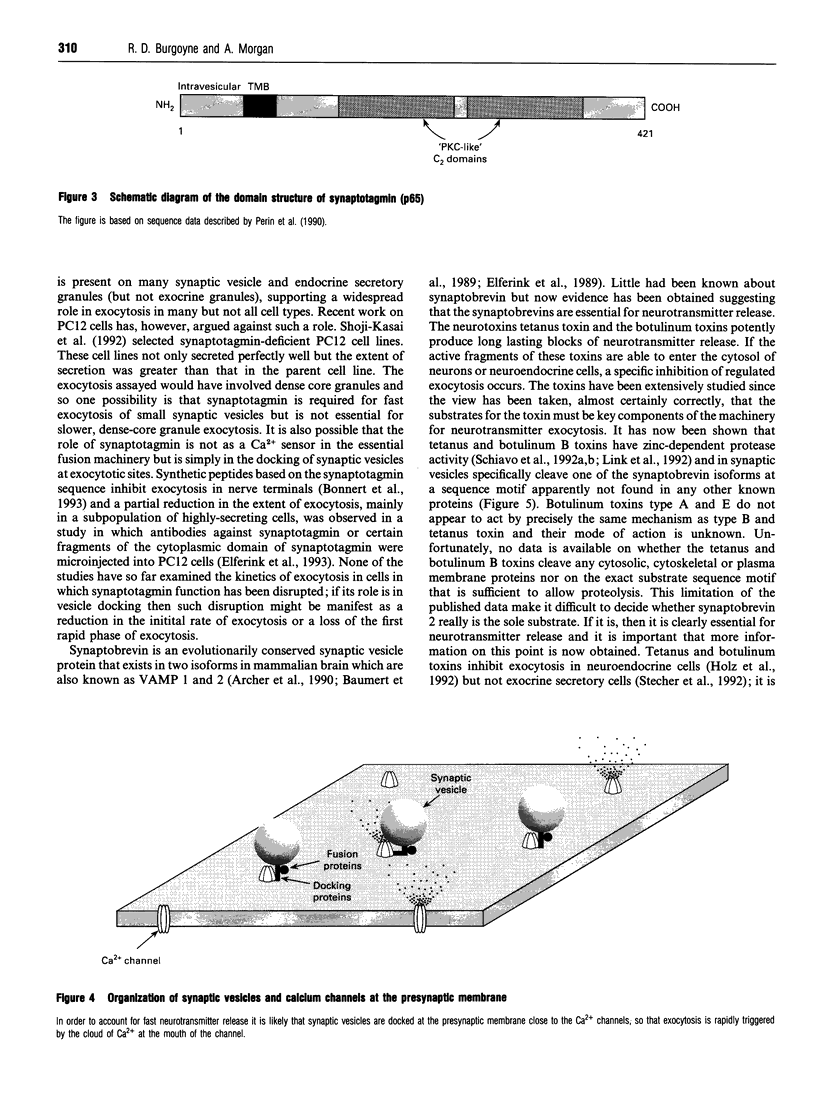
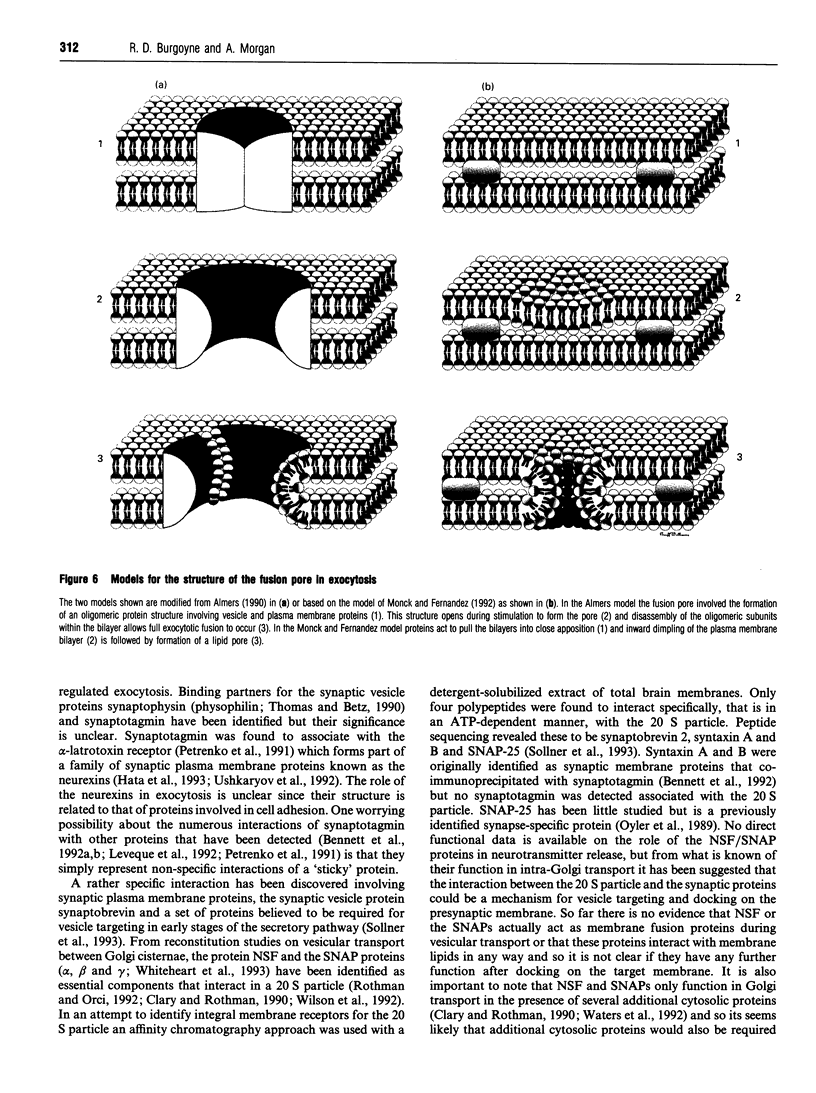
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahnert-Hilger G., Wegenhorst U., Stecher B., Spicher K., Rosenthal W., Gratz M. Exocytosis from permeabilized bovine adrenal chromaffin cells is differently modulated by guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate and guanosine 5'-[beta gamma-imido]triphosphate. Evidence for the involvement of various guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 1;284(Pt 2):321–326. doi: 10.1042/bj2840321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitken A., Amess B., Howell S., Jones D., Martin H., Patel Y., Robinson K., Toker A. The role of specific isoforms of 14-3-3 protein in regulating protein kinase activity in the brain. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 Aug;20(3):607–611. doi: 10.1042/bst0200607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitken A., Ellis C. A., Harris A., Sellers L. A., Toker A. Kinase and neurotransmitters. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):594–594. doi: 10.1038/344594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alder J., Lu B., Valtorta F., Greengard P., Poo M. M. Calcium-dependent transmitter secretion reconstituted in Xenopus oocytes: requirement for synaptophysin. Science. 1992 Jul 31;257(5070):657–661. doi: 10.1126/science.1353905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alder J., Xie Z. P., Valtorta F., Greengard P., Poo M. Antibodies to synaptophysin interfere with transmitter secretion at neuromuscular synapses. Neuron. 1992 Oct;9(4):759–768. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90038-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali S. M., Geisow M. J., Burgoyne R. D. A role for calpactin in calcium-dependent exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1989 Jul 27;340(6231):313–315. doi: 10.1038/340313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W. Exocytosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:607–624. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer B. T., 3rd, Ozçelik T., Jahn R., Francke U., Südhof T. C. Structures and chromosomal localizations of two human genes encoding synaptobrevins 1 and 2. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17267–17273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustine G. J., Adler E. M., Charlton M. P. The calcium signal for transmitter secretion from presynaptic nerve terminals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;635:365–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb36505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustine G. J., Neher E. Calcium requirements for secretion in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:247–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aunis D., Bader M. F. The cytoskeleton as a barrier to exocytosis in secretory cells. J Exp Biol. 1988 Sep;139:253–266. doi: 10.1242/jeb.139.1.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Knight D. E. Calcium-dependent exocytosis in bovine adrenal medullary cells with leaky plasma membranes. Nature. 1978 Dec 7;276(5688):620–622. doi: 10.1038/276620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Sagi D., Gomperts B. D. Stimulation of exocytotic degranulation by microinjection of the ras oncogene protein into rat mast cells. Oncogene. 1988 Oct;3(4):463–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr F. A., Leyte A., Huttner W. B. Trimeric G proteins and vesicle formation. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;2(4):91–94. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrowman M. M., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Two roles for guanine nucleotides in the stimulus-secretion sequence of neutrophils. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):504–507. doi: 10.1038/319504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumert M., Maycox P. R., Navone F., De Camilli P., Jahn R. Synaptobrevin: an integral membrane protein of 18,000 daltons present in small synaptic vesicles of rat brain. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):379–384. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Shlomo H., Sigmund O., Stabel S., Reiss N., Naor Z. Preferential release of catecholamine from permeabilized PC12 cells by alpha- and beta-type protein kinase C subspecies. Biochem J. 1991 Nov 15;280(Pt 1):65–69. doi: 10.1042/bj2800065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benfenati F., Valtorta F., Rubenstein J. L., Gorelick F. S., Greengard P., Czernik A. J. Synaptic vesicle-associated Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II is a binding protein for synapsin I. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):417–420. doi: 10.1038/359417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. P., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Rat mast cells permeabilized with ATP secrete histamine in response to calcium ions buffered in the micromolar range. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:335–345. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Calakos N., Kreiner T., Scheller R. H. Synaptic vesicle membrane proteins interact to form a multimeric complex. J Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;116(3):761–775. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.3.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Calakos N., Scheller R. H. Syntaxin: a synaptic protein implicated in docking of synaptic vesicles at presynaptic active zones. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):255–259. doi: 10.1126/science.1321498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Scheller R. H. The molecular machinery for secretion is conserved from yeast to neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2559–2563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner M. A., Holz R. W. A temperature-sensitive step in exocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16226–16229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner M. A., Holz R. W. Kinetic analysis of secretion from permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells reveals distinct components. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16219–16225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel C. P., Wolfsberg T. G., Turck C. W., Myles D. G., Primakoff P., White J. M. A potential fusion peptide and an integrin ligand domain in a protein active in sperm-egg fusion. Nature. 1992 Mar 19;356(6366):248–252. doi: 10.1038/356248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bommert K., Charlton M. P., DeBello W. M., Chin G. J., Betz H., Augustine G. J. Inhibition of neurotransmitter release by C2-domain peptides implicates synaptotagmin in exocytosis. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):163–165. doi: 10.1038/363163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnemain H., Gulik-Krzywicki T., Grandchamp C., Cohen J. Interactions between genes involved in exocytotic membrane fusion in paramecium. Genetics. 1992 Mar;130(3):461–470. doi: 10.1093/genetics/130.3.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowser R., Müller H., Govindan B., Novick P. Sec8p and Sec15p are components of a plasma membrane-associated 19.5S particle that may function downstream of Sec4p to control exocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1041–1056. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge L. J., Almers W. Currents through the fusion pore that forms during exocytosis of a secretory vesicle. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):814–817. doi: 10.1038/328814a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brose N., Petrenko A. G., Südhof T. C., Jahn R. Synaptotagmin: a calcium sensor on the synaptic vesicle surface. Science. 1992 May 15;256(5059):1021–1025. doi: 10.1126/science.1589771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Cheek T. R. Reorganisation of peripheral actin filaments as a prelude to exocytosis. Biosci Rep. 1987 Apr;7(4):281–288. doi: 10.1007/BF01121449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D. Control of exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jul 22;1071(2):174–202. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90024-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Geisow M. J., Barron J. Dissection of stages in exocytosis in the adrenal chromaffin cell with use of trifluoperazine. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Aug 23;216(1202):111–115. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Geisow M. J. The annexin family of calcium-binding proteins. Review article. Cell Calcium. 1989 Jan;10(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(89)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Morgan A. Evidence for a role of calpactin in calcium-dependent exocytosis. Biochem Soc Trans. 1990 Dec;18(6):1101–1104. doi: 10.1042/bst0181101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Morgan A. Low molecular mass GTP-binding proteins of adrenal chromaffin cells are present on the secretory granule. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):122–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80204-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D. Secretory vesicle-associated proteins and their role in exocytosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:647–659. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain C. C., Trimble W. S., Lienhard G. E. Members of the VAMP family of synaptic vesicle proteins are components of glucose transporter-containing vesicles from rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11681–11684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler D. E., Heuser J. E. Arrest of membrane fusion events in mast cells by quick-freezing. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):666–674. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Parton R. G., Hauri H. P., Simons K., Zerial M. Localization of low molecular weight GTP binding proteins to exocytic and endocytic compartments. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):317–329. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90369-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek T. R., Burgoyne R. D. Cyclic AMP inhibits both nicotine-induced actin disassembly and catecholamine secretion from bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11663–11666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek T. R., Burgoyne R. D. Nicotine-evoked disassembly of cortical actin filaments in adrenal chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 20;207(1):110–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernomordik L. V., Vogel S. S., Sokoloff A., Onaran H. O., Leikina E. A., Zimmerberg J. Lysolipids reversibly inhibit Ca(2+)-, GTP- and pH-dependent fusion of biological membranes. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 22;318(1):71–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81330-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow R. H., von Rüden L., Neher E. Delay in vesicle fusion revealed by electrochemical monitoring of single secretory events in adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):60–63. doi: 10.1038/356060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clary D. O., Rothman J. E. Purification of three related peripheral membrane proteins needed for vesicular transport. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):10109–10117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutz C. E. The annexins and exocytosis. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):924–931. doi: 10.1126/science.1439804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler D. F., Cramer L. P. Sorting during transport to the surface of PC12 cells: divergence of synaptic vesicle and secretory granule proteins. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):721–730. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darchen F., Zahraoui A., Hammel F., Monteils M. P., Tavitian A., Scherman D. Association of the GTP-binding protein Rab3A with bovine adrenal chromaffin granules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5692–5696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J., van der Merwe P. A., Wakefield I., Millar R. P. Mechanisms of luteinizing hormone secretion: new insights from studies with permeabilized cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1991 Apr;76(1-3):C33–C38. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(91)90278-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Greengard P. Synapsin I: a synaptic vesicle-associated neuronal phosphoprotein. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Dec 15;35(24):4349–4357. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90747-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Matteis M. A., Di Tullio G., Buccione R., Luini A. Characterization of calcium-triggered secretion in permeabilized rat basophilic leukemia cells. Possible role of vectorially acting G proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10452–10460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekker L. V., De Graan P. N., Oestreicher A. B., Versteeg D. H., Gispen W. H. Inhibition of noradrenaline release by antibodies to B-50 (GAP-43). Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):74–76. doi: 10.1038/342074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drust D. S., Creutz C. E. Aggregation of chromaffin granules by calpactin at micromolar levels of calcium. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):88–91. doi: 10.1038/331088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn L. A., Holz R. W. Catecholamine secretion from digitonin-treated adrenal medullary chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4989–4993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwardson J. M., Daniels-Holgate P. U. Reconstitution in vitro of a membrane-fusion event involved in constitutive exocytosis. A role for cytosolic proteins and a GTP-binding protein, but not for Ca2+. Biochem J. 1992 Jul 15;285(Pt 2):383–385. doi: 10.1042/bj2850383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink L. A., Peterson M. R., Scheller R. H. A role for synaptotagmin (p65) in regulated exocytosis. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90059-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink L. A., Trimble W. S., Scheller R. H. Two vesicle-associated membrane protein genes are differentially expressed in the rat central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11061–11064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emans N., Gorvel J. P., Walter C., Gerke V., Kellner R., Griffiths G., Gruenberg J. Annexin II is a major component of fusogenic endosomal vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(6):1357–1369. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.6.1357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez J. M., Neher E., Gomperts B. D. Capacitance measurements reveal stepwise fusion events in degranulating mast cells. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):453–455. doi: 10.1038/312453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer von Mollard G., Mignery G. A., Baumert M., Perin M. S., Hanson T. J., Burger P. M., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. rab3 is a small GTP-binding protein exclusively localized to synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1988–1992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer von Mollard G., Südhof T. C., Jahn R. A small GTP-binding protein dissociates from synaptic vesicles during exocytosis. Nature. 1991 Jan 3;349(6304):79–81. doi: 10.1038/349079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilligan D. M., Satir B. H. Protein phosphorylation/dephosphorylation and stimulus-secretion coupling in wild type and mutant Paramecium. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13903–13906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomperts B. D. GE: a GTP-binding protein mediating exocytosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:591–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata Y., Davletov B., Petrenko A. G., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Interaction of synaptotagmin with the cytoplasmic domains of neurexins. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):307–315. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90320-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J. C., Martin T. F. Resolution of regulated secretion into sequential MgATP-dependent and calcium-dependent stages mediated by distinct cytosolic proteins. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(1):139–151. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms J. B., Karrenbauer A., Wirtz K. W., Rothman J. E., Wieland F. T. Reconstitution of steps in the constitutive secretory pathway in permeabilized cells. Secretion of glycosylated tripeptide and truncated sphingomyelin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):20027–20032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess S. D., Doroshenko P. A., Augustine G. J. A functional role for GTP-binding proteins in synaptic vesicle cycling. Science. 1993 Feb 19;259(5098):1169–1172. doi: 10.1126/science.8438167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N., Sobue K., Kanda K., Harada A., Yorifuji H. The cytoskeletal architecture of the presynaptic terminal and molecular structure of synapsin 1. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;108(1):111–126. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz R. W., Bittner M. A., Peppers S. C., Senter R. A., Eberhard D. A. MgATP-independent and MgATP-dependent exocytosis. Evidence that MgATP primes adrenal chromaffin cells to undergo exocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5412–5419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell T. W., Gomperts B. D. Rat mast cells permeabilised with streptolysin O secrete histamine in response to Ca2+ at concentrations buffered in the micromolar range. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Feb 18;927(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90132-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höhne-Zell B., Knoll G., Riedel-Gras U., Hofer W., Plattner H. A cortical phosphoprotein ('PP63') sensitive to exocytosis triggering in Paramecium cells. Immunolocalization and quenched-flow correlation of time course of dephosphorylation with membrane fusion. Biochem J. 1992 Sep 15;286(Pt 3):843–849. doi: 10.1042/bj2860843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isobe T., Hiyane Y., Ichimura T., Okuyama T., Takahashi N., Nakajo S., Nakaya K. Activation of protein kinase C by the 14-3-3 proteins homologous with Exo1 protein that stimulates calcium-dependent exocytosis. FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 17;308(2):121–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81257-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivins K. J., Neve K. A., Feller D. J., Fidel S. A., Neve R. L. Antisense GAP-43 inhibits the evoked release of dopamine from PC12 cells. J Neurochem. 1993 Feb;60(2):626–633. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kish P. E., Ueda T. Calcium-dependent release of accumulated glutamate from synaptic vesicles within permeabilized nerve terminals. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Jan 28;122(2):179–182. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90852-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Baker P. F. Calcium-dependence of catecholamine release from bovine adrenal medullary cells after exposure to intense electric fields. J Membr Biol. 1982;68(2):107–140. doi: 10.1007/BF01872259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Baker P. F. Guanine nucleotides and Ca-dependent exocytosis. Studies on two adrenal cell preparations. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 23;189(2):345–349. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Baker P. F. The phorbol ester TPA increases the affinity of exocytosis for calcium in 'leaky' adrenal medullary cells. FEBS Lett. 1983 Aug 22;160(1-2):98–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80944-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll G., Braun C., Plattner H. Quenched flow analysis of exocytosis in Paramecium cells: time course, changes in membrane structure, and calcium requirements revealed after rapid mixing and rapid freezing of intact cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(6):1295–1304. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.6.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffer A., Gomperts B. D. Soluble proteins as modulators of the exocytotic reaction of permeabilised rat mast cells. J Cell Sci. 1989 Nov;94(Pt 3):585–591. doi: 10.1242/jcs.94.3.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffer A., Tatham P. E., Gomperts B. D. Changes in the state of actin during the exocytotic reaction of permeabilized rat mast cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):919–927. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leveque C., Hoshino T., David P., Shoji-Kasai Y., Leys K., Omori A., Lang B., el Far O., Sato K., Martin-Moutot N. The synaptic vesicle protein synaptotagmin associates with calcium channels and is a putative Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3625–3629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. C., Südhof T. C., Anderson R. G. Annexin VI is required for budding of clathrin-coated pits. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90102-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindau M., Gomperts B. D. Techniques and concepts in exocytosis: focus on mast cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 12;1071(4):429–471. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90006-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link E., Edelmann L., Chou J. H., Binz T., Yamasaki S., Eisel U., Baumert M., Südhof T. C., Niemann H., Jahn R. Tetanus toxin action: inhibition of neurotransmitter release linked to synaptobrevin proteolysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Dec 15;189(2):1017–1023. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92305-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linstedt A. D., Kelly R. B. Synaptophysin is sorted from endocytotic markers in neuroendocrine PC12 cells but not transfected fibroblasts. Neuron. 1991 Aug;7(2):309–317. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90269-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., McGuinness T. L., Leonard C. S., Sugimori M., Greengard P. Intraterminal injection of synapsin I or calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alters neurotransmitter release at the squid giant synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3035–3039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Silver R. B. Microdomains of high calcium concentration in a presynaptic terminal. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):677–679. doi: 10.1126/science.1350109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomneth R., Martin T. F., DasGupta B. R. Botulinum neurotoxin light chain inhibits norepinephrine secretion in PC12 cells at an intracellular membranous or cytoskeletal site. J Neurochem. 1991 Oct;57(4):1413–1421. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martens G. J., Piosik P. A., Danen E. H. Evolutionary conservation of the 14-3-3 protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 15;184(3):1456–1459. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F., Walent J. H. A new method for cell permeabilization reveals a cytosolic protein requirement for Ca2+ -activated secretion in GH3 pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):10299–10308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew W. D., Tsavaler L., Reichardt L. F. Identification of a synaptic vesicle-specific membrane protein with a wide distribution in neuronal and neurosecretory tissue. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):257–269. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. G., Moore H. P. Reconstitution of constitutive secretion using semi-intact cells: regulation by GTP but not calcium. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(1):39–54. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochly-Rosen D., Khaner H., Lopez J. Identification of intracellular receptor proteins for activated protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3997–4000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochly-Rosen D., Miller K. G., Scheller R. H., Khaner H., Lopez J., Smith B. L. p65 fragments, homologous to the C2 region of protein kinase C, bind to the intracellular receptors for protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 8;31(35):8120–8124. doi: 10.1021/bi00150a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momayezi M., Lumpert C. J., Kersken H., Gras U., Plattner H., Krinks M. H., Klee C. B. Exocytosis induction in Paramecium tetraurelia cells by exogenous phosphoprotein phosphatase in vivo and in vitro: possible involvement of calcineurin in exocytotic membrane fusion. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):181–189. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monck J. R., Alvarez de Toledo G., Fernandez J. M. Tension in secretory granule membranes causes extensive membrane transfer through the exocytotic fusion pore. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7804–7808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monck J. R., Fernandez J. M. The exocytotic fusion pore. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1395–1404. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Burgoyne R. D. Exo1 and Exo2 proteins stimulate calcium-dependent exocytosis in permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1992 Feb 27;355(6363):833–836. doi: 10.1038/355833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Burgoyne R. D. Interaction between protein kinase C and Exo1 (14-3-3 protein) and its relevance to exocytosis in permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochem J. 1992 Sep 15;286(Pt 3):807–811. doi: 10.1042/bj2860807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Burgoyne R. D. Relationship between arachidonic acid release and Ca2(+)-dependent exocytosis in digitonin-permeabilized bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochem J. 1990 Nov 1;271(3):571–574. doi: 10.1042/bj2710571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Roth D., Martin H., Aitken A., Burgoyne R. D. Identification of cytosolic protein regulators of exocytosis. Biochem Soc Trans. 1993 May;21(2):401–405. doi: 10.1042/bst0210401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto T., Ogihara S., Takisawa H. Anchorage of secretion-competent dense granules on the plasma membrane of bovine platelets in the absence of secretory stimulation. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;111(1):79–86. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata T., Sobue K., Hirokawa N. Conformational change and localization of calpactin I complex involved in exocytosis as revealed by quick-freeze, deep-etch electron microscopy and immunocytochemistry. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;110(1):13–25. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanavati C., Markin V. S., Oberhauser A. F., Fernandez J. M. The exocytotic fusion pore modeled as a lipidic pore. Biophys J. 1992 Oct;63(4):1118–1132. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81679-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naor Z., Dan-Cohen H., Hermon J., Limor R. Induction of exocytosis in permeabilized pituitary cells by alpha- and beta-type protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4501–4504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navone F., Jahn R., Di Gioia G., Stukenbrok H., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Protein p38: an integral membrane protein specific for small vesicles of neurons and neuroendocrine cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2511–2527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Marty A. Discrete changes of cell membrane capacitance observed under conditions of enhanced secretion in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6712–6716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Zucker R. S. Multiple calcium-dependent processes related to secretion in bovine chromaffin cells. Neuron. 1993 Jan;10(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90238-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols R. A., Chilcote T. J., Czernik A. J., Greengard P. Synapsin I regulates glutamate release from rat brain synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1992 Feb;58(2):783–785. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols R. A., Sihra T. S., Czernik A. J., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II increases glutamate and noradrenaline release from synaptosomes. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):647–651. doi: 10.1038/343647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizaki T., Walent J. H., Kowalchyk J. A., Martin T. F. A key role for a 145-kDa cytosolic protein in the stimulation of Ca(2+)-dependent secretion by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23972–23981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Ferro S., Schekman R. Order of events in the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan A. J., Cheek T. R., Moreton R. B., Berridge M. J., Burgoyne R. D. Localization and heterogeneity of agonist-induced changes in cytosolic calcium concentration in single bovine adrenal chromaffin cells from video imaging of fura-2. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):401–411. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03391.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhauser A. F., Monck J. R., Balch W. E., Fernandez J. M. Exocytotic fusion is activated by Rab3a peptides. Nature. 1992 Nov 19;360(6401):270–273. doi: 10.1038/360270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhauser A. F., Monck J. R., Fernandez J. M. Events leading to the opening and closing of the exocytotic fusion pore have markedly different temperature dependencies. Kinetic analysis of single fusion events in patch-clamped mouse mast cells. Biophys J. 1992 Mar;61(3):800–809. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81884-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara-Imaizumi M., Kameyama K., Kawae N., Takeda K., Muramatsu S., Kumakura K. Regulatory role of the GTP-binding protein, G(o), in the mechanism of exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1992 Jun;58(6):2275–2284. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10974.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornberg R. L., Reese T. S. Beginning of exocytosis captured by rapid-freezing of Limulus amebocytes. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;90(1):40–54. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyler G. A., Higgins G. A., Hart R. A., Battenberg E., Billingsley M., Bloom F. E., Wilson M. C. The identification of a novel synaptosomal-associated protein, SNAP-25, differentially expressed by neuronal subpopulations. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):3039–3052. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padfield P. J., Balch W. E., Jamieson J. D. A synthetic peptide of the rab3a effector domain stimulates amylase release from permeabilized pancreatic acini. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1656–1660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perin M. S., Brose N., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Domain structure of synaptotagmin (p65) J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):623–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perin M. S., Fried V. A., Mignery G. A., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Phospholipid binding by a synaptic vesicle protein homologous to the regulatory region of protein kinase C. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):260–263. doi: 10.1038/345260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin D., Möller K., Hanke K., Söling H. D. cAMP and Ca(2+)-mediated secretion in parotid acinar cells is associated with reversible changes in the organization of the cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):127–134. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrenko A. G., Perin M. S., Davletov B. A., Ushkaryov Y. A., Geppert M., Südhof T. C. Binding of synaptotagmin to the alpha-latrotoxin receptor implicates both in synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):65–68. doi: 10.1038/353065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer S. R. GTP-binding proteins in intracellular transport. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;2(2):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90161-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plutner H., Schwaninger R., Pind S., Balch W. E. Synthetic peptides of the Rab effector domain inhibit vesicular transport through the secretory pathway. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2375–2383. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07412.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocotte S. L., Frye R. A., Senter R. A., TerBush D. R., Lee S. A., Holz R. W. Effects of phorbol ester on catecholamine secretion and protein phosphorylation in adrenal medullary cell cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):930–934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H. B., Guy H. R., Arispe N., de la Fuente M., Lee G., Rojas E. M., Pollard J. R., Srivastava M., Zhang-Keck Z. Y., Merezhinskaya N. Calcium channel and membrane fusion activity of synexin and other members of the Annexin gene family. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;62(1):15–18. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81764-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H. B., Rojas E., Pastor R. W., Rojas E. M., Guy H. R., Burns A. L. Synexin: molecular mechanism of calcium-dependent membrane fusion and voltage-dependent calcium-channel activity. Evidence in support of the "hydrophobic bridge hypothesis" for exocytotic membrane fusion. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;635:328–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb36503.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryer N. K., Wuestehube L. J., Schekman R. Vesicle-mediated protein sorting. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:471–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehm H., Wiedenmann B., Betz H. Molecular characterization of synaptophysin, a major calcium-binding protein of the synaptic vesicle membrane. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):535–541. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04243.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez Del Castillo A., Lemaire S., Tchakarov L., Jeyapragasan M., Doucet J. P., Vitale M. L., Trifaró J. M. Chromaffin cell scinderin, a novel calcium-dependent actin filament-severing protein. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):43–52. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08078.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D., Morgan A., Burgoyne R. D. Identification of a key domain in annexin and 14-3-3 proteins that stimulate calcium-dependent exocytosis in permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1993 Apr 12;320(3):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80587-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Orci L. Molecular dissection of the secretory pathway. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):409–415. doi: 10.1038/355409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Régnier-Vigouroux A., Tooze S. A., Huttner W. B. Newly synthesized synaptophysin is transported to synaptic-like microvesicles via constitutive secretory vesicles and the plasma membrane. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3589–3601. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04925.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salminen A., Novick P. J. A ras-like protein is required for a post-Golgi event in yeast secretion. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):527–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90455-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarafian T., Aunis D., Bader M. F. Loss of proteins from digitonin-permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells essential for exocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16671–16676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarafian T., Pradel L. A., Henry J. P., Aunis D., Bader M. F. The participation of annexin II (calpactin I) in calcium-evoked exocytosis requires protein kinase C. J Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;114(6):1135–1147. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.6.1135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste J., Kuismanen E. Pre- and post-Golgi vacuoles operate in the transport of Semliki Forest virus membrane glycoproteins to the cell surface. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):535–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90508-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satir B. H., Hamasaki T., Reichman M., Murtaugh T. J. Species distribution of a phosphoprotein (parafusin) involved in exocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):930–932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheuner D., Logsdon C. D., Holz R. W. Bovine chromaffin granule membranes undergo Ca(2+)-regulated exocytosis in frog oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):359–365. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo G., Benfenati F., Poulain B., Rossetto O., Polverino de Laureto P., DasGupta B. R., Montecucco C. Tetanus and botulinum-B neurotoxins block neurotransmitter release by proteolytic cleavage of synaptobrevin. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):832–835. doi: 10.1038/359832a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo G., Poulain B., Rossetto O., Benfenati F., Tauc L., Montecucco C. Tetanus toxin is a zinc protein and its inhibition of neurotransmitter release and protease activity depend on zinc. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3577–3583. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05441.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer F. E., Schäfer T., Tapparelli C., Grob M., Karli U. O., Heumann R., Thoenen H., Bookman R. J., Burger M. M. Inhibition of exocytosis by intracellularly applied antibodies against a chromaffin granule-binding protein. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):709–712. doi: 10.1038/339709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senyshyn J., Balch W. E., Holz R. W. Synthetic peptides of the effector-binding domain of rab enhance secretion from digitonin-permeabilized chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 31;309(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80735-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. E., Stoehr S. J., Kuczynski B., Koh E. K., Omann G. M. Dual effects of guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate on secretion by electroporated human neutrophils. Biochem J. 1991 Nov 1;279(Pt 3):657–664. doi: 10.1042/bj2790657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stecher B., Ahnert-Hilger G., Weller U., Kemmer T. P., Gratzl M. Amylase release from streptolysin O-permeabilized pancreatic acinar cells. Effects of Ca2+, guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate, cyclic AMP, tetanus toxin and botulinum A toxin. Biochem J. 1992 May 1;283(Pt 3):899–904. doi: 10.1042/bj2830899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stecher B., Höhne B., Gras U., Momayezi M., Glas-Albrecht R., Plattner H. Involvement of a 65 kDa phosphoprotein in the regulation of membrane fusion during exocytosis in Paramecium cells. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 19;223(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80503-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztul E., Colombo M., Stahl P., Samanta R. Control of protein traffic between distinct plasma membrane domains. Requirement for a novel 108,000 protein in the fusion of transcytotic vesicles with the apical plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1876–1885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söllner T., Whiteheart S. W., Brunner M., Erdjument-Bromage H., Geromanos S., Tempst P., Rothman J. E. SNAP receptors implicated in vesicle targeting and fusion. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):318–324. doi: 10.1038/362318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Czernik A. J., Kao H. T., Takei K., Johnston P. A., Horiuchi A., Kanazir S. D., Wagner M. A., Perin M. S., De Camilli P. Synapsins: mosaics of shared and individual domains in a family of synaptic vesicle phosphoproteins. Science. 1989 Sep 29;245(4925):1474–1480. doi: 10.1126/science.2506642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Jahn R. Proteins of synaptic vesicles involved in exocytosis and membrane recycling. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):665–677. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90165-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Lottspeich F., Greengard P., Mehl E., Jahn R. A synaptic vesicle protein with a novel cytoplasmic domain and four transmembrane regions. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1142–1144. doi: 10.1126/science.3120313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor T. C., Kahn R. A., Melançon P. Two distinct members of the ADP-ribosylation factor family of GTP-binding proteins regulate cell-free intra-Golgi transport. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):69–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90534-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tester M., Zorec R. Cytoplasmic calcium stimulates exocytosis in a plant secretory cell. Biophys J. 1992 Sep;63(3):864–867. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81662-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L., Betz H. Synaptophysin binds to physophilin, a putative synaptic plasma membrane protein. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):2041–2052. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.2041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L., Hartung K., Langosch D., Rehm H., Bamberg E., Franke W. W., Betz H. Identification of synaptophysin as a hexameric channel protein of the synaptic vesicle membrane. Science. 1988 Nov 18;242(4881):1050–1053. doi: 10.1126/science.2461586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P., Wong J. G., Almers W. Millisecond studies of secretion in single rat pituitary cells stimulated by flash photolysis of caged Ca2+. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):303–306. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05657.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toutant M., Aunis D., Bockaert J., Homburger V., Rouot B. Presence of three pertussis toxin substrates and Go alpha immunoreactivity in both plasma and granule membranes of chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 11;215(2):339–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifaró J. M., Fournier S., Novas M. L. The p65 protein is a calmodulin-binding protein present in several types of secretory vesicles. Neuroscience. 1989;29(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90327-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tugal H. B., van Leeuwen F., Apps D. K., Haywood J., Phillips J. H. Glycosylation and transmembrane topography of bovine chromaffin granule p65. Biochem J. 1991 Nov 1;279(Pt 3):699–703. doi: 10.1042/bj2790699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turkewitz A. P., Madeddu L., Kelly R. B. Maturation of dense core granules in wild type and mutant Tetrahymena thermophila. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):1979–1987. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07727.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M. D., Rennison M. E., Handel S. E., Wilde C. J., Burgoyne R. D. Proteins are secreted by both constitutive and regulated secretory pathways in lactating mouse mammary epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(2):269–278. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M. D., Wilde C. J., Burgoyne R. D. Exocytosis from permeabilized lactating mouse mammary epithelial cells. Stimulation by Ca2+ and phorbol ester, but inhibition of regulated exocytosis by guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate. Biochem J. 1992 Aug 15;286(Pt 1):13–15. doi: 10.1042/bj2860013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushkaryov Y. A., Petrenko A. G., Geppert M., Südhof T. C. Neurexins: synaptic cell surface proteins related to the alpha-latrotoxin receptor and laminin. Science. 1992 Jul 3;257(5066):50–56. doi: 10.1126/science.1621094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtorta F., Benfenati F., Greengard P. Structure and function of the synapsins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7195–7198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitale M. L., Rodríguez Del Castillo A., Tchakarov L., Trifaró J. M. Cortical filamentous actin disassembly and scinderin redistribution during chromaffin cell stimulation precede exocytosis, a phenomenon not exhibited by gelsolin. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):1057–1067. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walent J. H., Porter B. W., Martin T. F. A novel 145 kd brain cytosolic protein reconstitutes Ca(2+)-regulated secretion in permeable neuroendocrine cells. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):765–775. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90310-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. G., Clary D. O., Rothman J. E. A novel 115-kD peripheral membrane protein is required for intercisternal transport in the Golgi stack. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1015–1026. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M. Membrane fusion. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):917–924. doi: 10.1126/science.1439803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteheart S. W., Griff I. C., Brunner M., Clary D. O., Mayer T., Buhrow S. A., Rothman J. E. SNAP family of NSF attachment proteins includes a brain-specific isoform. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):353–355. doi: 10.1038/362353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. W., Whiteheart S. W., Wiedmann M., Brunner M., Rothman J. E. A multisubunit particle implicated in membrane fusion. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(3):531–538. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.3.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. P., Kirshner N. Calcium-evoked secretion from digitonin-permeabilized adrenal medullary chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4994–5000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y. N., Vu N. D., Wagner P. D. Anti-(14-3-3 protein) antibody inhibits stimulation of noradrenaline (norepinephrine) secretion by chromaffin-cell cytosolic proteins. Biochem J. 1992 Aug 1;285(Pt 3):697–700. doi: 10.1042/bj2850697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y. N., Wagner P. D. Calpactin-depleted cytosolic proteins restore Ca(2+)-dependent secretion to digitonin-permeabilized bovine chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 22;282(1):197–199. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80476-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaks W. J., Creutz C. E. Ca(2+)-dependent annexin self-association on membrane surfaces. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 8;30(40):9607–9615. doi: 10.1021/bi00104a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieseniss E., Plattner H. Synchronous exocytosis in Paramecium cells involves very rapid (less than or equal to 1 s), reversible dephosphorylation of a 65-kD phosphoprotein in exocytosis-competent strains. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2028–2035. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerberg J., Curran M., Cohen F. S. A lipid/protein complex hypothesis for exocytotic fusion pore formation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;635:307–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb36501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerberg J., Curran M., Cohen F. S., Brodwick M. Simultaneous electrical and optical measurements show that membrane fusion precedes secretory granule swelling during exocytosis of beige mouse mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1585–1589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zupan L. A., Steffens D. L., Berry C. A., Landt M., Gross R. W. Cloning and expression of a human 14-3-3 protein mediating phospholipolysis. Identification of an arachidonoyl-enzyme intermediate during catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):8707–8710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]